Module 8: Oral Manifestations of HIV/AIDS
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
candidiasis pathophysiology
*Opportunistic fungal infection
*C. Albicans (67%) or otherwise C. Dubliniensis (oropharyngeal)
candidiasis epidemiology
*Most common intra-oral manifestation of HIV/AIDS
-often presenting sx that leads to diagnosis
*Predictive of increased immunosuppression and progression to AIDS
candidiasis oral manifestations- pseudomembranous candidiasis
- white removeable plaques
- most common form in HIV + with initial progressive immune suppression (CD4 <400 cells/mm3)
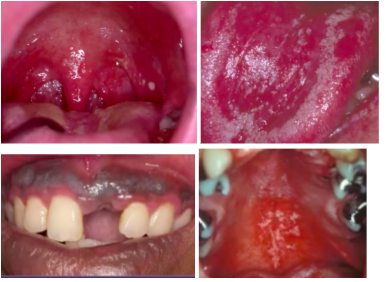
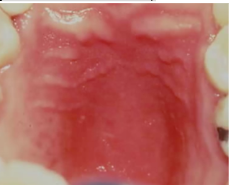
candidiasis oral manifestations- erythematous or atrophic candidiasis
- most commonly seen during early stages of HIV (in combination with pseudomembranous form)
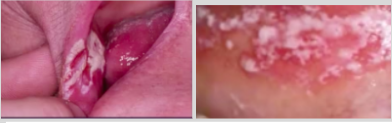
candidiasis oral manifestations- hyperplastic candidiasis
- most often associated with severe immune suppression: long standing HIV disease
- can NOT be entirely wiped off
+/- sx such as burning, sensitivity to certain foods/beverages, altered taste
candidiasis diagnosis
*Clinical (plaques are removable/non-removeable)
*Smear
*PAS stain show fungal hyphae
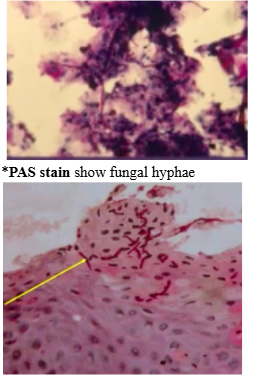
candidiasis treatment
*Nystatin oral suspension
*Clotrimazole (Mycelex) torches
Fluconazole (Difulcan) tablets (recommended)- contraindicated in liver disease
*Mycolog or Lotrisone cream
histoplasmosis epidemiology
*Most common endemic respiratory fungal infection in US
-subclinical and self-limiting in healthy pts
-most common disseminated fungal disease in pts with AIDS
histoplasmosis manifestations
Systemic
-Flu-like sx
Oral
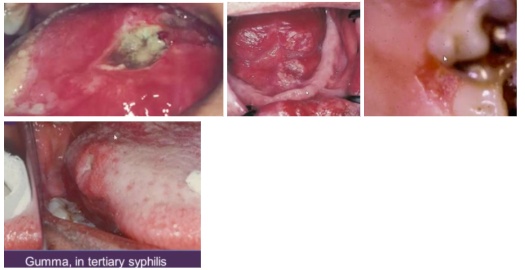
-Deep fungal ulcers
-Can look like gumma in tertiary syphilis
oral hairy leukoplakia pathophysiology
*EBV-related white mucosal patch that doesn’t rub off (leukoplakia)
oral hairy leukoplakia oral manifestations
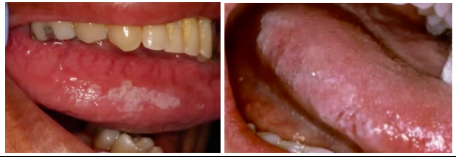
*White leukoplakia, non-removable patch (differential dx: EBV, OHL, dysplasia)
-Lateral tongue
oral hairy leukoplakia diagnosis
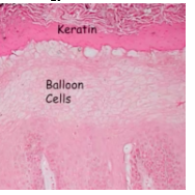
*Histology shows balloon cells
*Test balloon cells – EBER (in-situ hybridization for EBV)
oral hairy leukoplakia treatment
*If in non-immunocompromised patients, mandates a thorough PE to r/o immunocompromised status
*If in immunocompromised patients, indicates severe immune suppression and advanced disease
*None other than referral to MD
*Surgical excision for aesthetic concerns
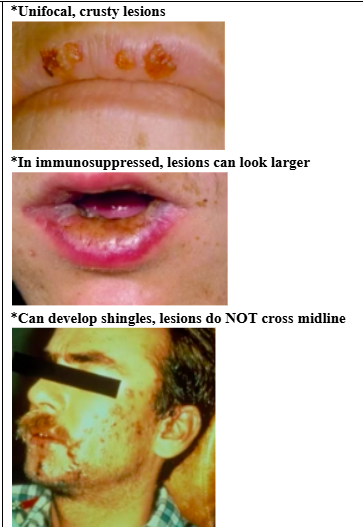
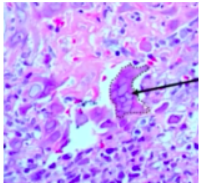
HSV oral manifestations
HSV diagnosis
*Cytology/biopsy needs to be done early in disease (1-3 days) – this is when we can visualize herpetic infected cells
*3 Ms: Multinucleation, molding, margination (chromatin at periphery)
HPV pathophysiology
*dsDNA virus that infects epithelial cells of skin and mucosa
*Oral papillomas, verruca vulgaris, condyloma accuminatum
HPV epidemiology
*Oral warts are becoming more common in HIV+ in era of HAART
-possibly due to immune reconstitution the form of increased numbers of APCs in the oral mucosa may trigger greater recognition of HPV
-present a significant challenge
*Leading cause of oropharyngeal cancer
*A very small number of oral cavity cancer also occur form HPV
*Of ~20 strains of HPV only 9 are associated with cancer
-of the 9 that are high risk only HPV16 and HPV18 are strongly associated with oropharyngeal cancer
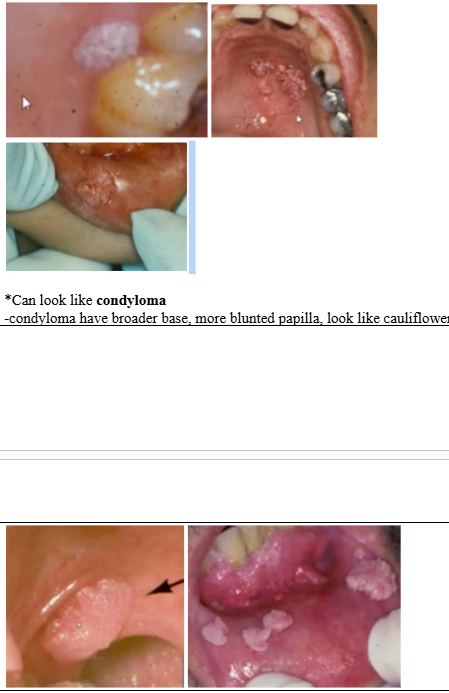
HPV oral manifestations
*Can look like condyloma
-condyloma have broader base, more blunted papilla, look like cauliflower
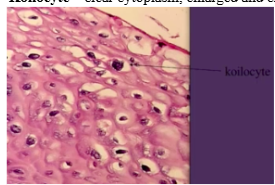
HPV diagnosis
*Koilocyte – clear cytoplasm, enlarged and crinkled nucleus
HPV treatment
*Excision
*Trichloroacetic acid- caustic in mouth
HIV-associated periodontal disease types
*Linear Gingival Erythema
*Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
*Necrotizing ulcerative periodontitis
HIV-associated periodontal disease oral manifestations
*Linear Gingival Erythema
-Etiology = candida
-Can be confused with marginal gingivitis
*Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
-Punched out gingival papillae
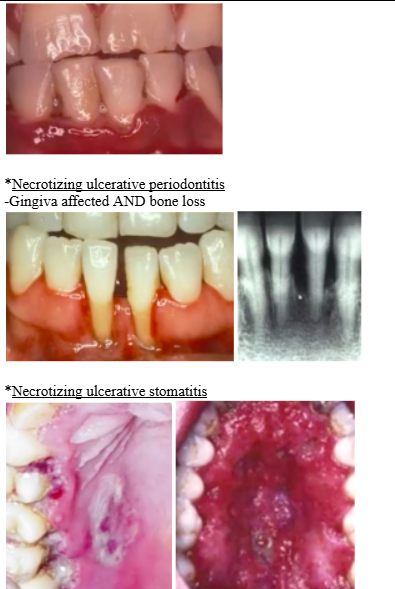
*Necrotizing ulcerative periodontitis
-Gingiva affected AND bone loss
*Necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis
HIV-associated periodontal disease treatment
*Linear gingival erythema: antifungal
*NUG and NUP: debridement, antimicrobial therapy, follow up and long term maintenance
aphthous ulcers pathophysiology
*Aka canker sores
*Exact cause not completely understood, but involves a T-cell mediated immune response triggered by a variety of factors
*Very common, affecting about 20% of general population
*Not contagious
*Appear on NON-keratinized mucosa (i.e. anywhere except attached gingiva, hard palate, dorsum of tongue)- can be on keratinizing surfaces in more severe forms
*Ulcers occur periodically and typically heal in 7-10 days in healthy patients
aphthous ulcer types
*Minor aphthous
-most common
-lesions are 2-3 mm in diameter and affect non-keratinized mucosal surfaces
-1 to several can appear at the same time
-heal in 7-10 days without scarring
*Major aphthous
-10% of cases
->10 mm in diameter
-healing takes longer and can leave scar
*Herpetiform
-lesions resemble HSV infection, however they are not caused by HSV
-<1mm in diameter, up to 100 at a time
-adjacent ulcers merge to form larger areas of ulceration
-healing occurs within 15 days without scarring
-can affect keratinized mucosa
*RAS type ulceration or aphthous like ulcers
-recurrent oral ulcerations associated with systemic conditions
aphthous ulcer oral manifestations
*Ulcers with peripheral erythema
*In immunosuppressed – looks larger
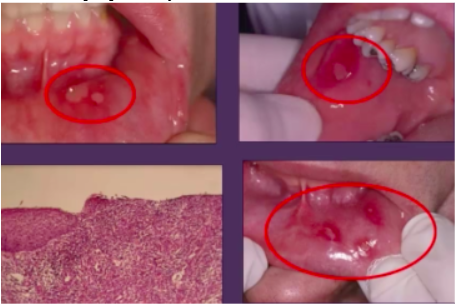
aphthous ulcers treatment
*No cure
*Treatments aim to manage pain, reduce healing time, reduce frequency of episodes of ulceration
mollusum contagiosum pathophysiology
*Infection of skin caused by Poxvirus
-self-limiting in healthy pts (trunk and genital regions)
-pts with AIDS 100’s may be present (face common)
*Immunosuppressed patients can develop lesions that spread, last a long time, very difficult to treat
*Molluscum itself not serious
mollusum contagiosum epidemiology
*20% of people with AIDS will develop molluscum
mollusum contagiosum oral manifestations
*Most are <1/2 inch in diameter with a, center has indentation
-same color as normal skin but appear waxy
-usually asx
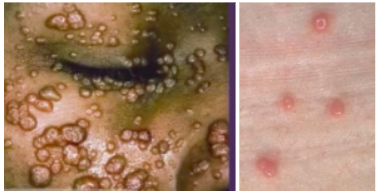
mollusum contagiosum diagnosis
*Millions of virions proliferate in cytoplasm of affected epithelial cells resulting in characteristic intracytoplasmic bodies
-these viral inclusions are the largest in all of the human body
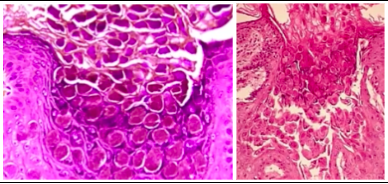
mollusum contagiosum treatment
*Treated the same as cutaneous warts – frozen with liquid nitrogen, laser ablated, chemically treated with caustic agents i.e. TCA, podophyllin or podofilox, surgically excised, application of antiviral meds directly onto lesions
*Resolution with HAART documented
cancer epidemiology
*Significant cause of morbidity and mortality in HIV patients
-30-40% will develop malignancy during lifetime
-Majority of cancer affects HIV+ patients are those established as AIDS defining: Kaposi’s sarcoma, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, invasive cervical ca
cancer oral manifestations- Kaposi’s sarcoma
-multifocal endothelial cell neoplasm of skin or oral mucosa (HHV-8)
-skin: trunk, arms, H and N
-oral cavity: hard palate, gingiva, tongue
-lesions: brown/red/purple flat patch -> plaques -> nodules
-pain, bleeding, necrosis necessitates tx
-microscopically looks like proliferation of spindle cells
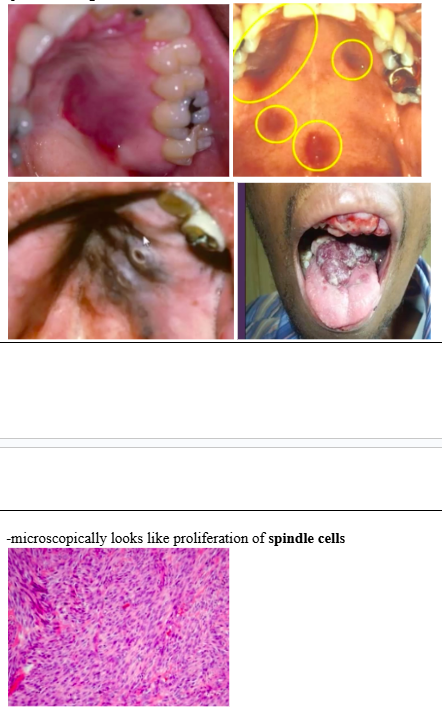
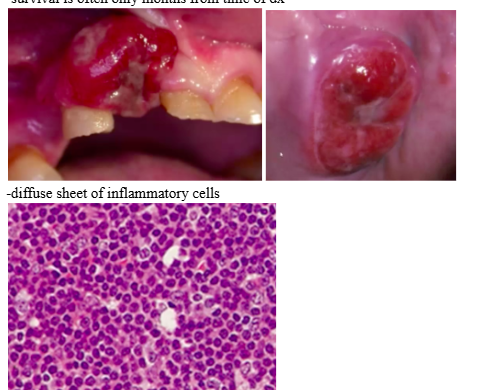
cancer oral manifestations- NHL
-2nd most common malignancy in HIV+
-in AIDS, it is high grade and aggressive (EBV and HHV-8 detected, usually in extra-nodal sites such as CNS and oral cavity)
-gingiva, palate, tongue, tonsils most frequent sites
-survival is often only months from time of dx
-diffuse sheet of inflammatory cells
cancer oral manifestations- plasmablastic lymphoma
-B cell lymphoma with plasmablastic morphology predominantly associated with HIV infection
-arises in 2 settings: most cases involve oral cavity or jaw, some cases associated with multi-centric Castleman disease
-nearly all cases in HIV+ patients
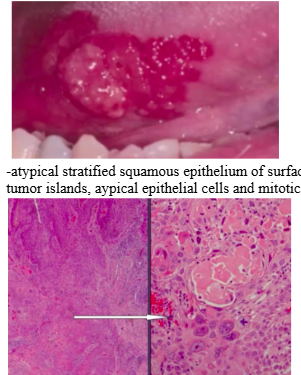
cancer oral manifestations- squamous cell carcinoma
-same risk factors as general population
-red patch with exophytic nodule, feels firm on palpation
-atypical stratified squamous epithelium of surface that invades into connective tissue -> tumor islands, atypical epithelial cells and mitotic figures
Karposi’s and NHL treatment
*Karposi: no specific treatment, use HAART therapy to get AIDS under control
*NHL: HAART has only reduced some cases