Physics Fundamentals: Units, Vectors, Motion, and Newton's Laws
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What are the three fundamental physical quantities?
Mass, length, and time.
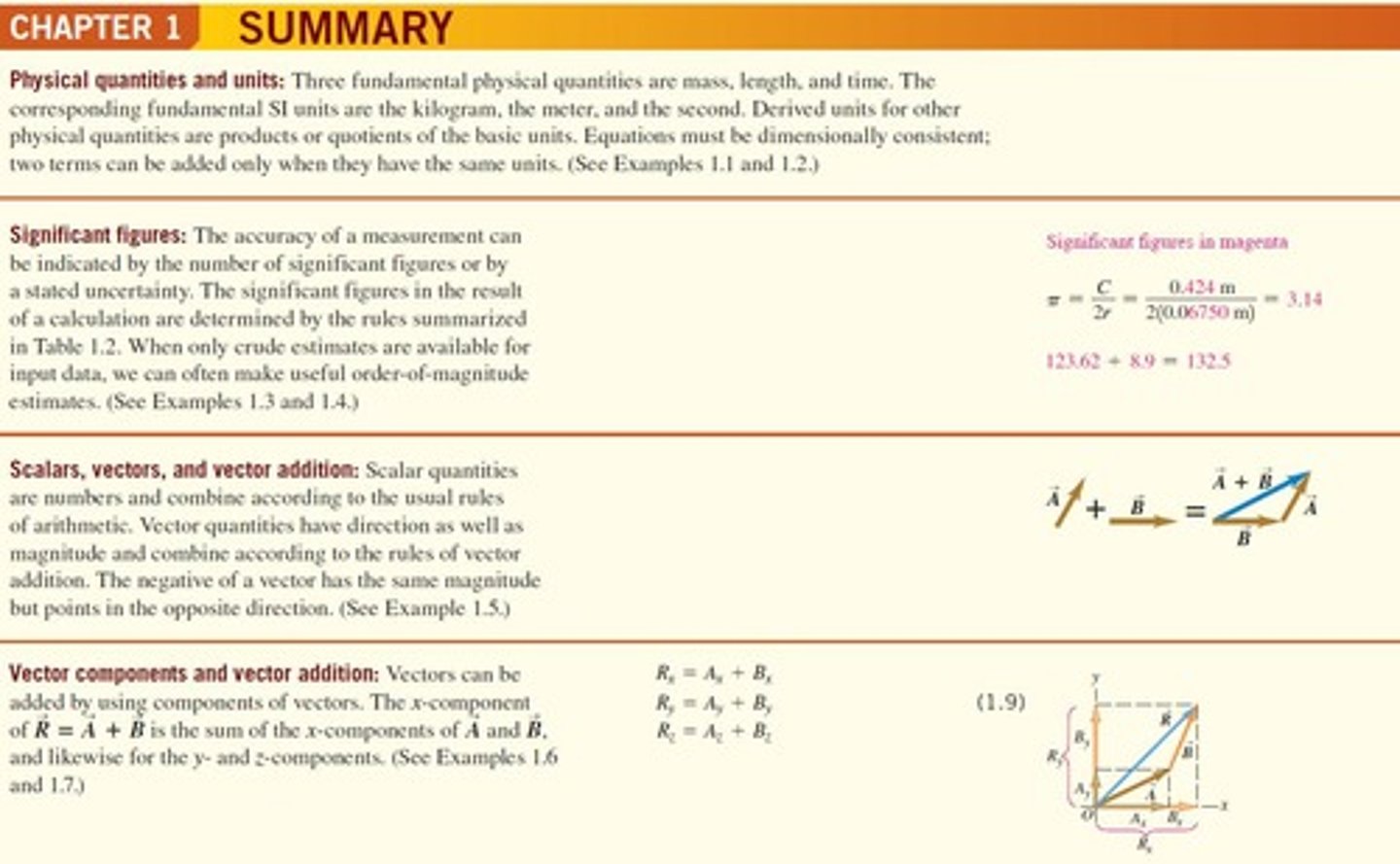
What are the SI units for mass, length, and time?
Kilogram (kg), meter (m), and second (s) respectively.
What is the significance of significant figures in measurements?
They indicate the accuracy of a measurement.
How are significant figures determined in calculations?
By following specific rules that consider the precision of input data.
What is the difference between scalar and vector quantities?
Scalars have magnitude only, while vectors have both magnitude and direction.
How are vector quantities combined?
According to the rules of vector addition.

What is a unit vector?
A vector with a magnitude of 1, used to describe directions in space.
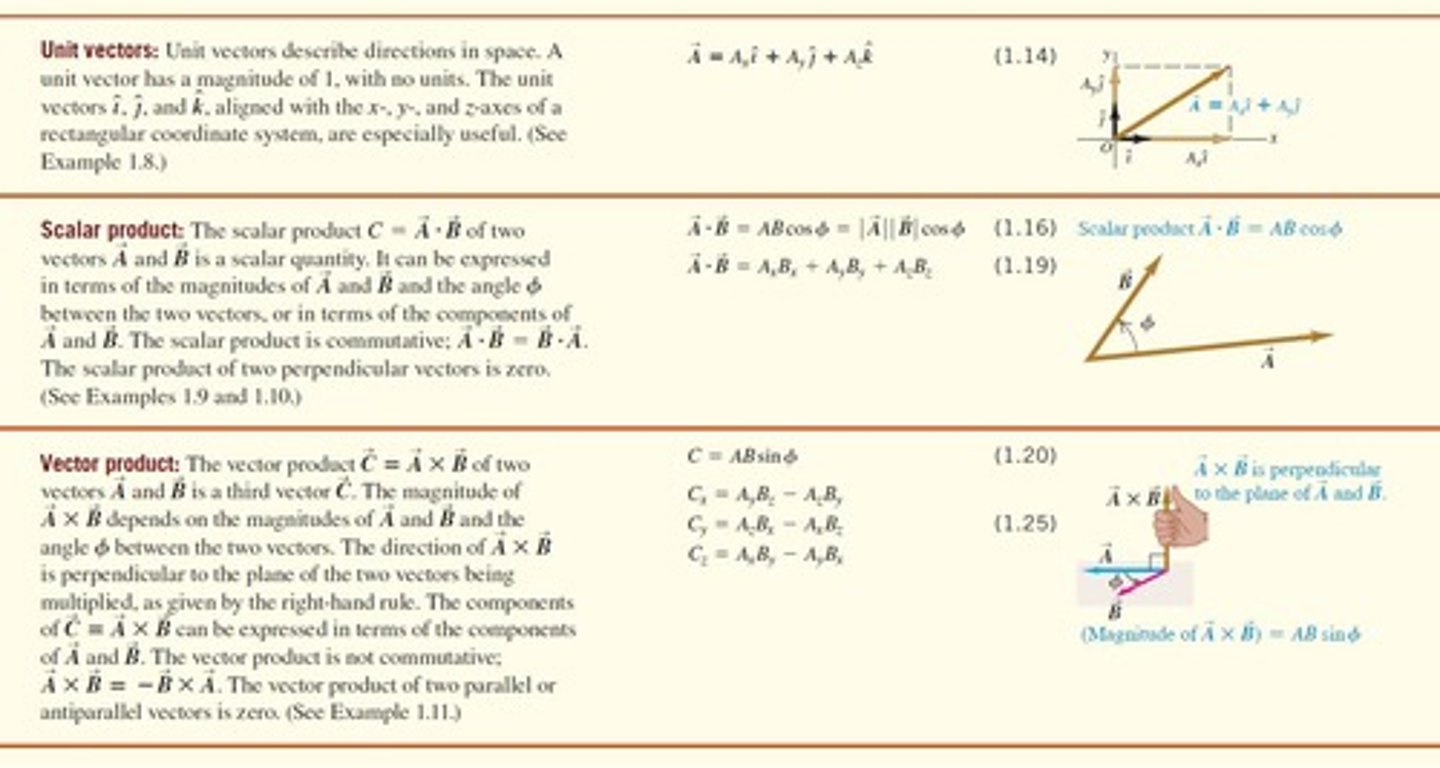
What is the scalar product of two vectors?
A scalar quantity calculated as the product of their magnitudes and the cosine of the angle between them.
What is the vector product of two vectors?
A vector that is perpendicular to the plane formed by the two vectors, calculated using the right-hand rule.
What is the average x-velocity during a time interval?
It is equal to the displacement divided by the time interval.

How is instantaneous x-velocity defined?
As the derivative of the position function with respect to time.
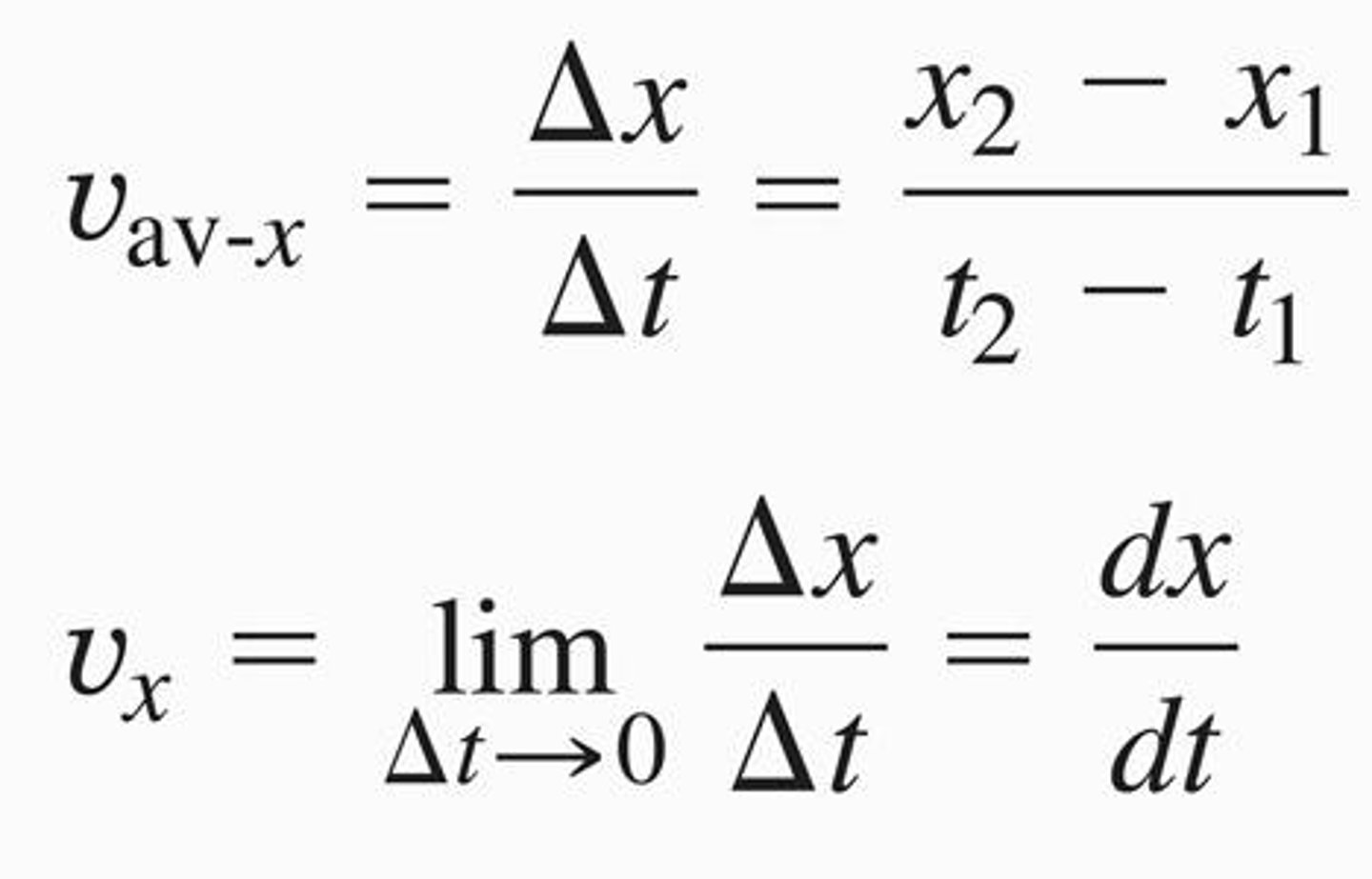
What is the average x-acceleration during a time interval?
The change in velocity divided by the time interval.
What is free fall?
Vertical motion without air resistance, influenced only by gravity.
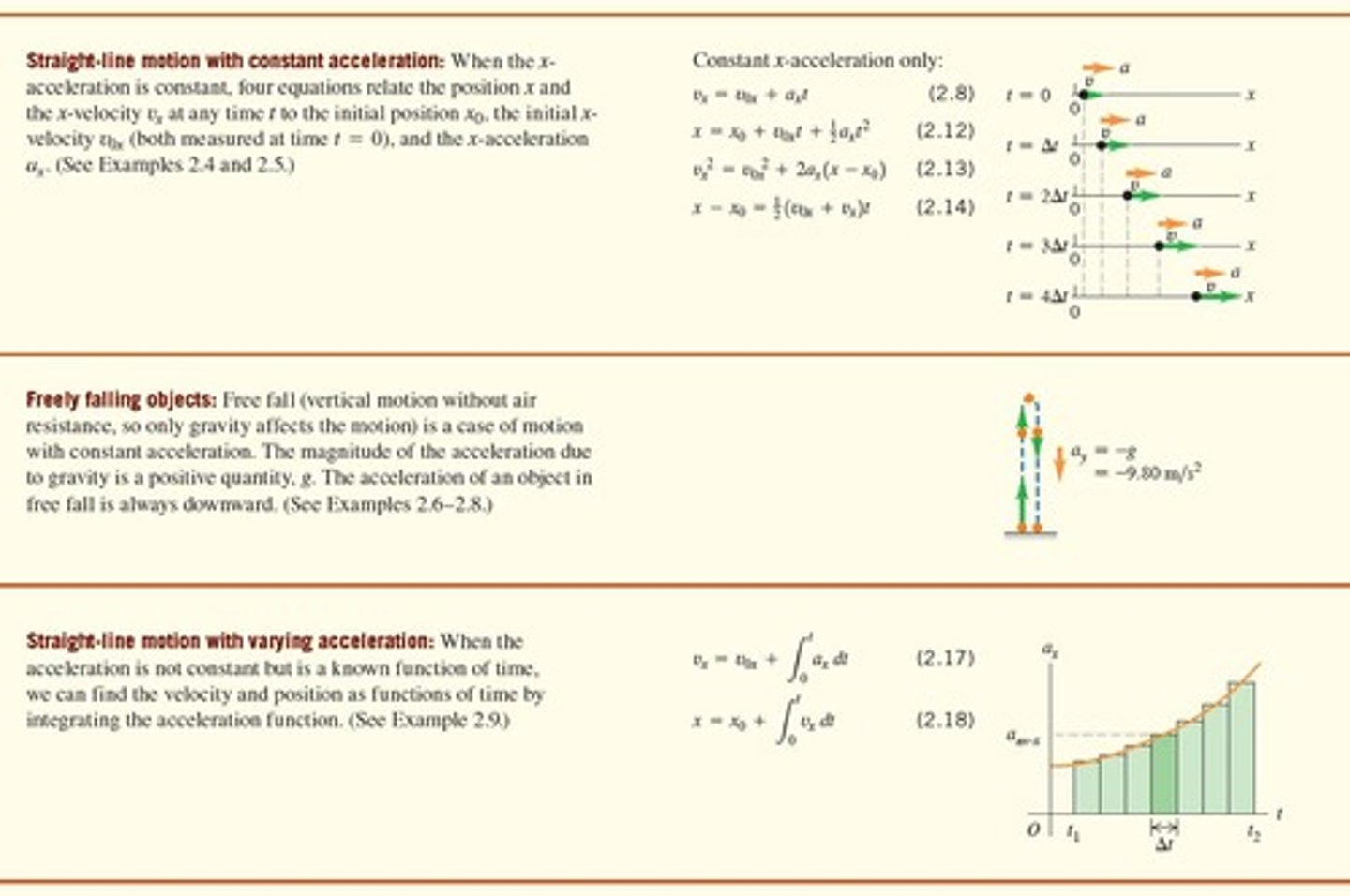
What is the acceleration due to gravity?
Approximately 9.80 m/s² downward.
What equations relate position, velocity, and acceleration in straight-line motion with constant acceleration?
Equations that connect initial position, initial velocity, acceleration, and time.

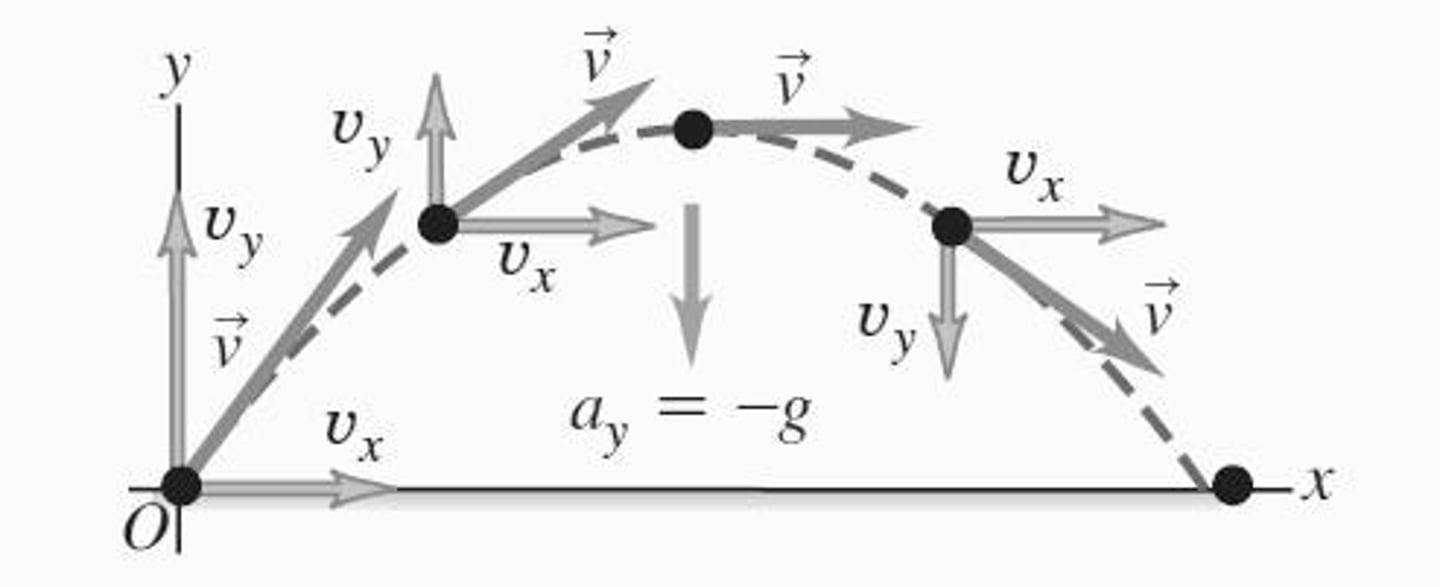
What is projectile motion?
Motion of an object thrown into the air, where only gravity acts on it, resulting in a parabolic path.
What characterizes uniform circular motion?
Constant speed with acceleration directed towards the center of the circle.

What is the relationship between speed, radius, and period in circular motion?
Speed is equal to the circumference divided by the period (v = 2πR/T).
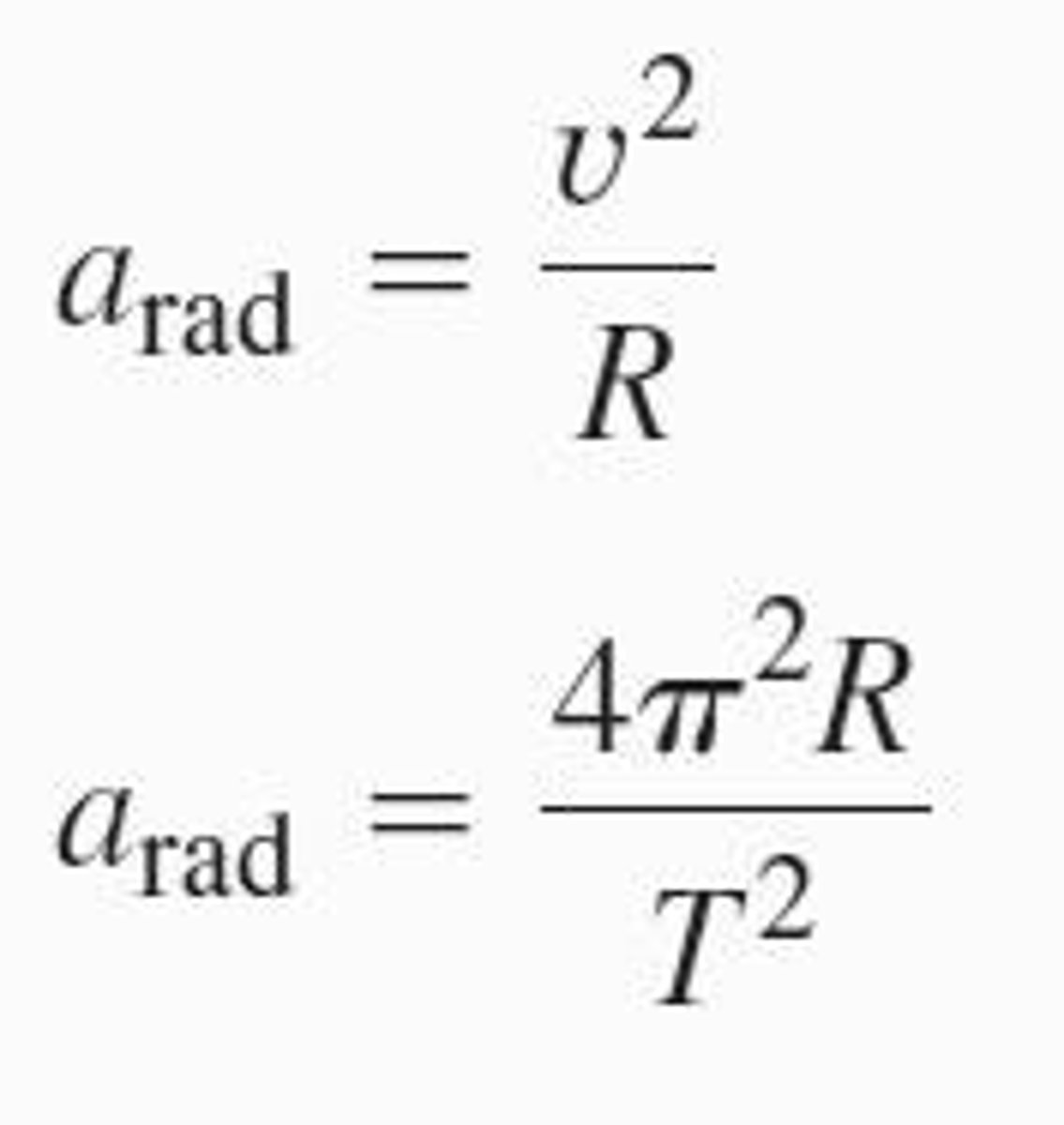
What happens to the acceleration in nonuniform circular motion?
There is both a radial component and a tangential component affecting speed.
What is the instantaneous speed?
The magnitude of the instantaneous velocity vector.
How is the average acceleration vector calculated?
By dividing the change in velocity vector by the time interval.
What does the position vector represent?
The vector from the origin to a point in space, defined by its components x, y, and z.

What is the significance of the right-hand rule in vector products?
It determines the direction of the resulting vector from the vector product.
What is the formula for the scalar product of two vectors in component form?
A · B = AxBx + AyBy + AzBz.
What does the negative of a vector signify?
It has the same magnitude but points in the opposite direction.
What is the limit of average acceleration as time approaches zero?
It becomes the instantaneous acceleration.
What does the term 'displacement' refer to?
The change in position of an object.
What is relative velocity?
Relative velocity is the velocity of an object P as observed from another object B, which itself is moving relative to a reference frame A.
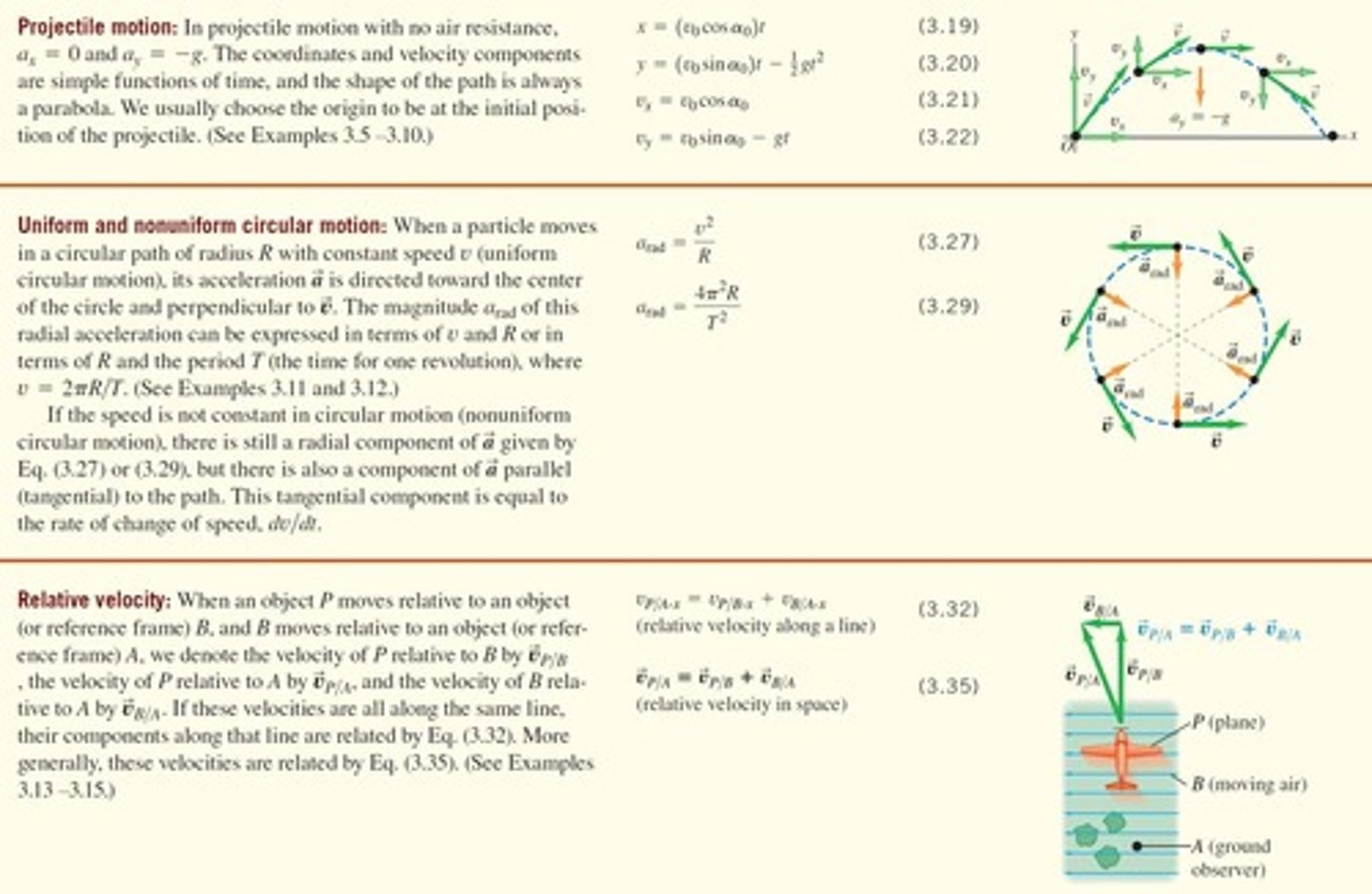
How is the velocity of P relative to B denoted?
It is denoted as UP/B.
What does Newton's first law state?
Newton's first law states that if the net external force on an object is zero, the object is in equilibrium and has zero acceleration.
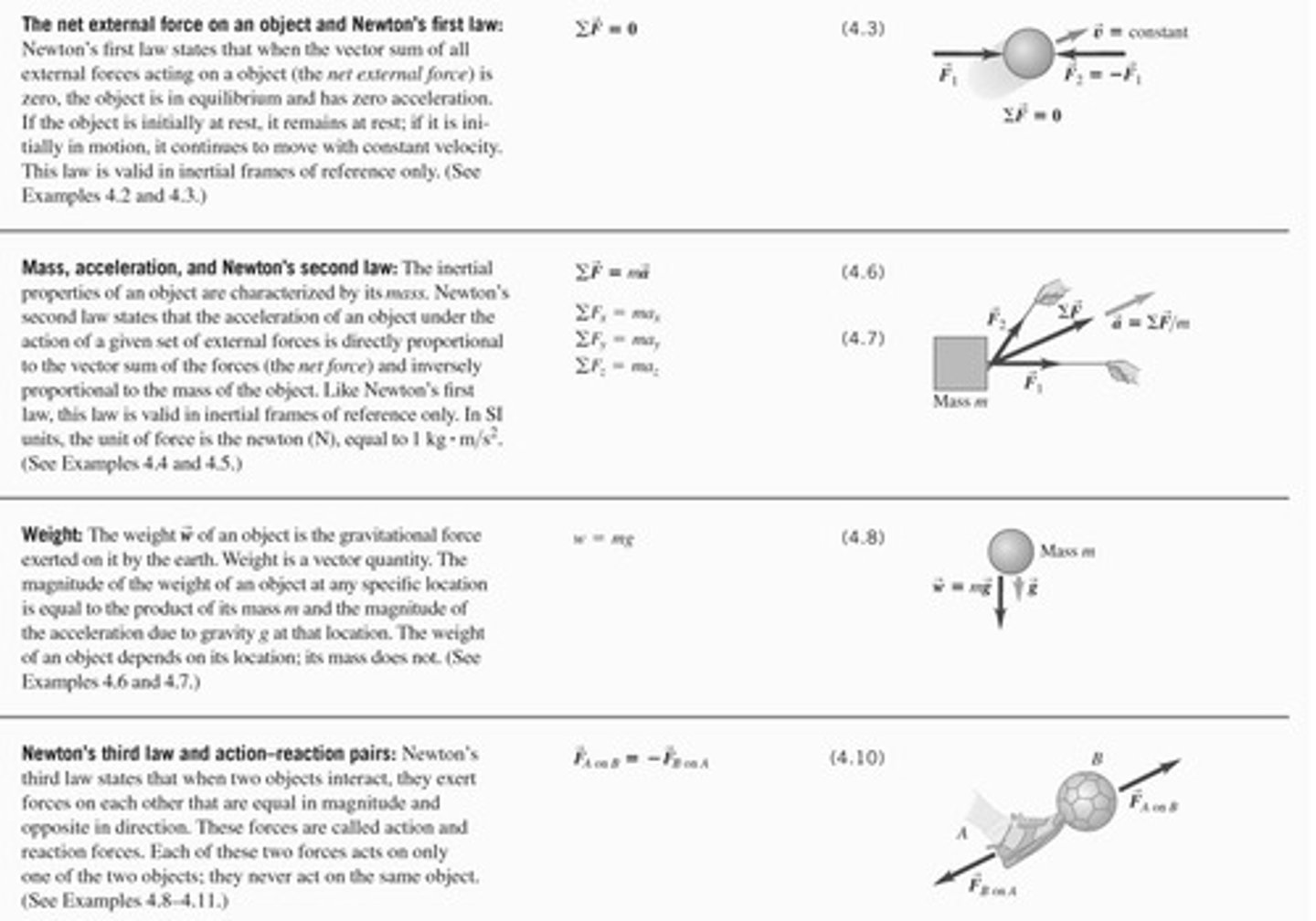
What is the unit of force in SI units?
The unit of force is the newton (N), which is equal to 1 kg·m/s².
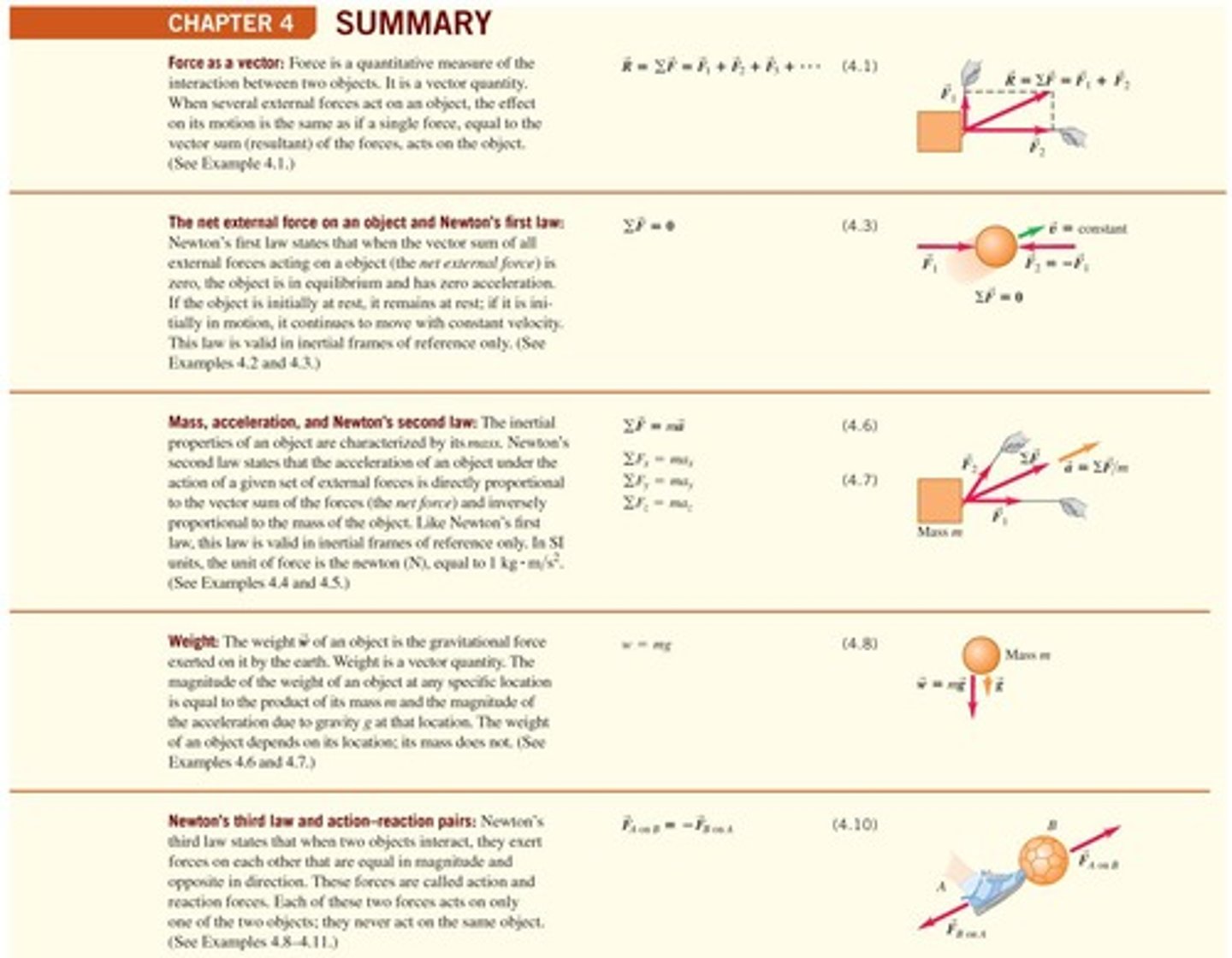
What does Newton's second law describe?
Newton's second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass.
What is weight in physics?
Weight is the gravitational force exerted on an object by the Earth, calculated as the product of its mass and the acceleration due to gravity.
What does Newton's third law state?
Newton's third law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction, meaning forces between two objects are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
What is the equation for the net external force?
The net external force is represented as ΣF = F₁ + F₂ + ... + Fₙ.
How do you calculate the acceleration of an object?
Acceleration can be calculated using the formula a = ΣF/m, where ΣF is the net force and m is the mass of the object.
What is the relationship between mass and weight?
Weight (w) is equal to mass (m) multiplied by the acceleration due to gravity (g), expressed as w = mg.
What are action-reaction pairs?
Action-reaction pairs are forces that two objects exert on each other, which are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
How is the vector product defined?
The vector product C = A × B results in a third vector that is perpendicular to the plane formed by A and B, with a magnitude depending on the magnitudes of A and B and the sine of the angle between them.
What is the equation for horizontal motion in projectile motion?
The horizontal position is given by x = (v₀ cos α)t, where v₀ is the initial velocity and α is the launch angle.
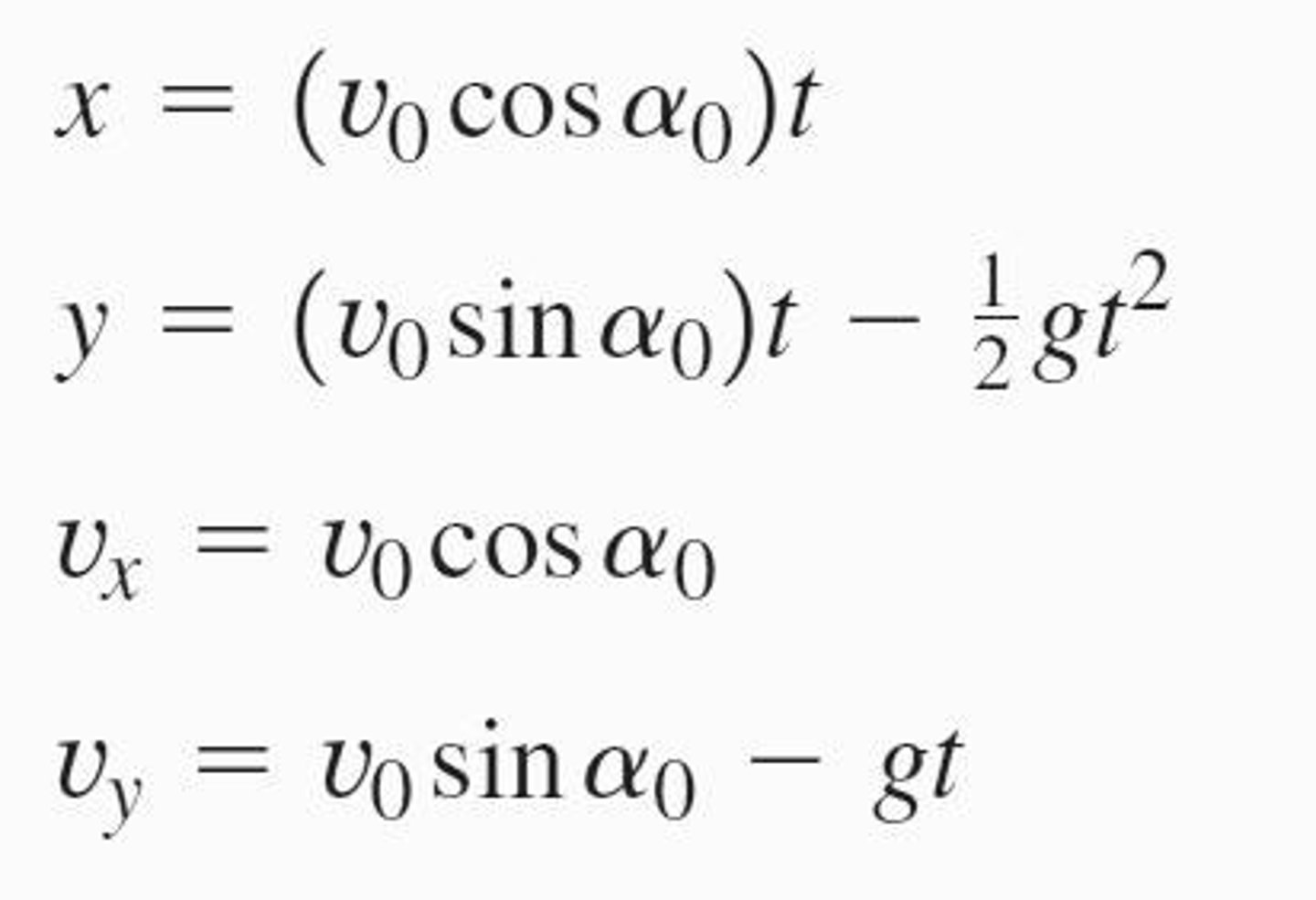
What is the equation for vertical motion in projectile motion?
The vertical position is given by y = (v₀ sin α)t - (1/2)gt², where g is the acceleration due to gravity.
What is uniform circular motion?
Uniform circular motion occurs when an object moves in a circular path with constant speed, with acceleration directed towards the center of the circle.
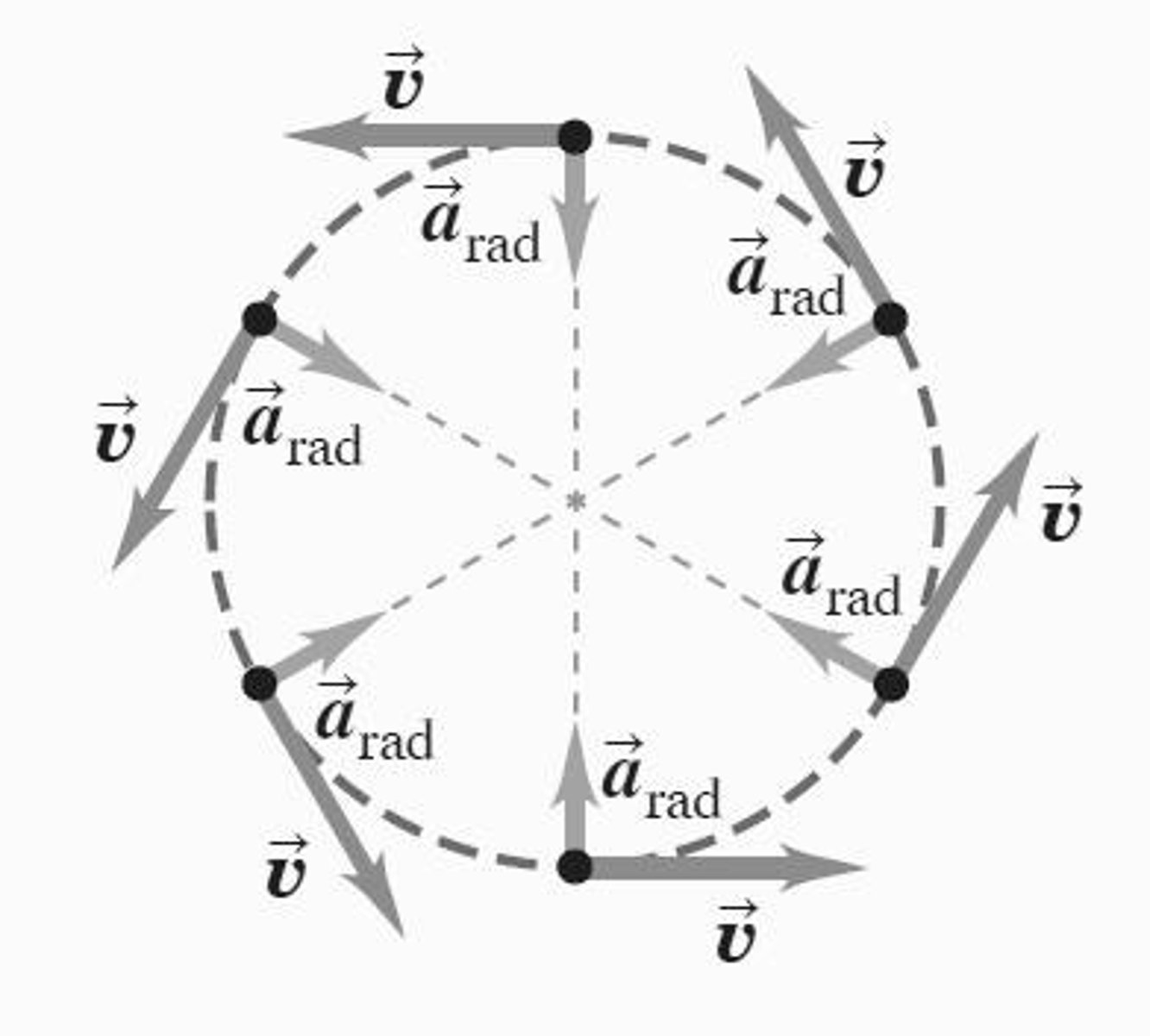
How is radial acceleration expressed?
Radial acceleration can be expressed as a_rad = v²/R, where v is the speed and R is the radius of the circular path.
What does the equation Ux = Vox + axt represent?
This equation relates the final x-velocity (Ux) to the initial x-velocity (Vox), acceleration (a), and time (t).

What is the significance of the equation v² = v₀² + 2a(x - x₀)?
This equation relates the final velocity squared to the initial velocity squared, acceleration, and displacement.
What is the relationship between vector components and vector addition?
Vectors can be added by summing their respective components along each axis.
What is the equation for the components of the resultant vector R?
The components of the resultant vector R are given by Rx = Ax + Bx, Ry = Ay + By, and Rz = Az + Bz.