Prep and characteristics of Blood components
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
platelet poor plasma
8-24 hours labeled PF24 plasma
<8 hours labeled FFP
FFP
Stored frozen colder than -18 C —> (thawed at 30-37C) —> FFP thawed (can give to patient)
OR store at 4C @ >24 hour labeled as thawed plasma (can give it patient) 5day after thawing
homologous donations
CPD - store of 21 days, No. of viable cells 80
CP2D
Autologous donations
CPDA-1
Whole blood store for 35 days, No. of viable cells 79
Red blood cells store for 35 days, No. of viable cells 71
Adheresis
A powerful methodology where the donor/patient’s blood stream is connected to a centrifuge system to remove selected blood elements.
Hyperventilation
Common in young donors; shortness of breath, facial twitching
Paper bag rebreathing trick
Vado-vagal
Hypotension and slowed heart rate
Elevate feet; cold compress on neck
Hypotensive shock
Hypotension and accelerated heart rate
Give volume infusion
Citrate effect
Tingling around mouth; rarely tetany and cardiac arrhythmias
Slow re-infusion of donor’s blood; give calcium
Whole Blood
4C for 35 days
RBC
4C for 42 days can be frozen 10 years
Need for increased O2 carrying capacity
Each unit will increase Hgb ~1 g/dL
Platelets
5 days at 20-24, gentle agitation
Thrombocytopenia
Platelets <10,000/microL
Bleeding/invasive procedures
Platelets <50,000/microL
Plasma
12 months at -18C
Dosage 20 mL/kg to raise coagulation factors 20%
Cyroprecipitate
1 year at < -18C
Dosage ~1 unit/5-10 kg recipient body weight
Leukoreduction (LR )
Prevent FNHTR*, CMV transmission, HLA alloimmunization
Gamma-irradiation (Irr)
Prevent TA-GvHD
Washing
Prevent repetitive/severe allergic/hyper- sensitivity reactions
CMV seronegative
Prevent CMV transmission
HLA-matched platelets
Treat platelet refractoriness
Cross-matched platelets
Treat platelet refractoriness
Leukoreduction
FDA mandated cut off
< 5 x 106 WBCs/blood unit
Equivalent to removal of 99.9–99.99% of WBCs
>85% original RBC retained
Febrile nonhemolytic transfusion reactions (FNHTR)
Common: 0.5 - 2% of transfusions
Transfusion-transmitted CMV infection (TT-CMV)
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is an opportunistic virus
Can be lethal in immunocompromised recipients
CMV can be transmitted by blood products
Primarily found in WBCs (monocytes)
HLA alloimmunization
Anti-HLA antibodies bind to transfused platelets and eliminate them
Gamma-irradiation
Viable WBCs in blood transfusions can attack the recipient if they are immunocompromised
Leads to TA-GvHD
~95% lethal!
Completely preventable by 25 Gy irradiation before transfusion
Irradiation = TA-GvHD
Accepted for gamma-irradiation
Hodgkin diease
Immunocompromised
Donations from relatives, HLA- matched donors
Intrauterine transfusions
Neonatal exchange transfusion ECMP
Congenital cell mediated immunodeficiencies
Washed platelets
pRBCs and platelets can be washed with saline to remove > 98% of plasma proteins
However....
Washed RBCs must be used within 24 hrs
Washed platelets must be used within 4 hrs
RBC/platelet dose decreased 20% or more
C/T ratio
Only the units transfused would be cross matched ideally C/T ratio = 1
The goal (and regulatory standard) is a C/T of < 1.5
Elevated C/T is problematic
Removes RBCs from inventory that then have to be returned
Wastes resources (time, effort, reagents)
Can complicate inventory management
Emergency transfusion
O Rh (D) negative blood give to women of child bearing age in male wont make a difference
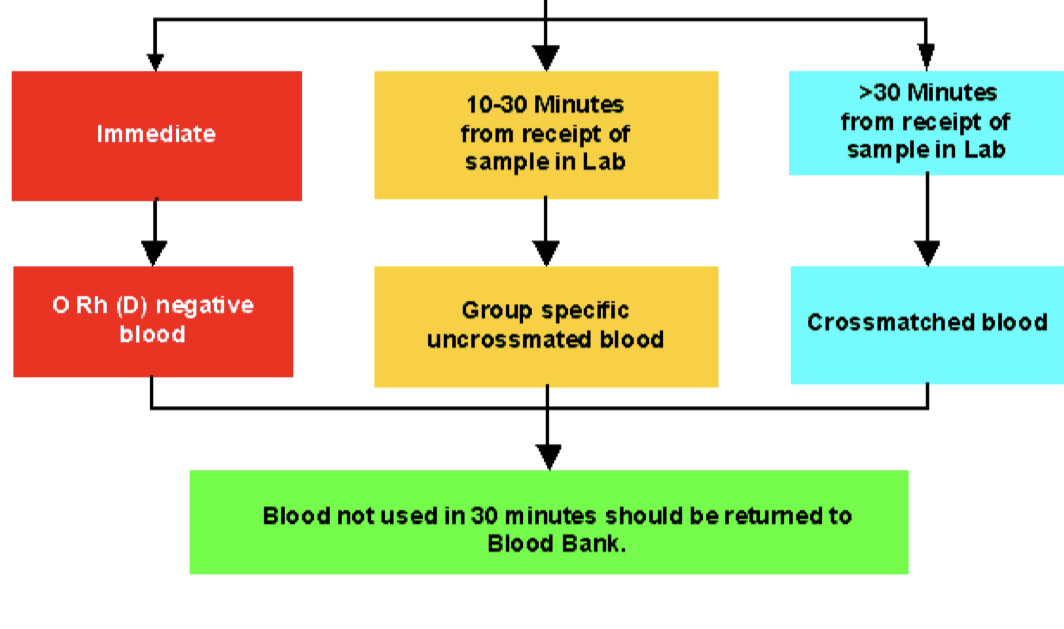
blood administration
Monitor patient closely for first 15 minutes
This is the time period during which most of the most significant adverse events occur
Regularly monitor thereafter
Complete transfusions within 4 hours
Coagulation factors factor VIII
Hemophilia A
Coagulation factors factor IX
Hemophilia B
Coagulation factors Factor VIIa (Novoseven)
Various bleeding situations
albumin
Volume expanders, typically for plasma exchange
Therapeutic apheresis
Therapeutic apheresis is the removal of a single blood component to treat an underlying disease
Blood flow rates up to 120 mL/min.
Either peripheral or central lines can be
used for access to the patient’s circulation
Citrate used for anticoagulation