Lecture 3 (1) From crops to the jungle
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Definition of tree
A woody plant with usually a single stem growing to a height of at least 2m
Or if multi-stemmed, then at least one vertical stem 5 cm in diameter at breast height
Definition of forest
A large area covered chiefly with trees and undergrowth
Land spanning more than 0.5 hectares with trees higher than 5 meters, and a canopy cover of more than 10%
Include land that’s predominantly under agricultural or urban land use
Primary or natural forest
Naturally regenerated forest of native species, where there are no clearly visible indications of human activities and the ecological processes are not significantly disturbed
Forest estate
All the land containing a forest endowment
Forest stand
A continuous piece of land covered by a relatively homogeneous forest type
Forest plot
A polygon, usually circular and small (e.g. 300 m^2) where all trees are measured to estimate stand- or estate-level forest metrics
Afforestation
Establishment of forest through planting and/or deliberate seeding on land that, until then, was not classified as forest
Reforestation
Re-establishment of forest through planting and/or deliberate seeding on land classified as forest
Deforestation
The conversion of forests to another land use, or the permanent reduction of tree canopy cover below the 10% threshold (degradation)
Variables affecting climate and microclimate
(deal spats)
Distance to water bodies
Elevation
Atmospheric pressure
Latitude
Surface albedo
Precipitation magnitude & type
Air temperature
Topography
Solar radiation
What summarizes everything (variables affecting climate cand microclimate)
Air temp.: Avg. amd variation
Precipitation: Sum and variation
World biomes
The type of vegetation present in an area depends on climate, which is summarized by temperature and precipitation (averages and seasonal variation)
Biome
Very large areas of the Earth’s surface that have similar climates and vegetation
Formation
Community with a specific vegetation structure (e.x. Cold desert or temperate deciduous forest), also used as a subdivision of biome
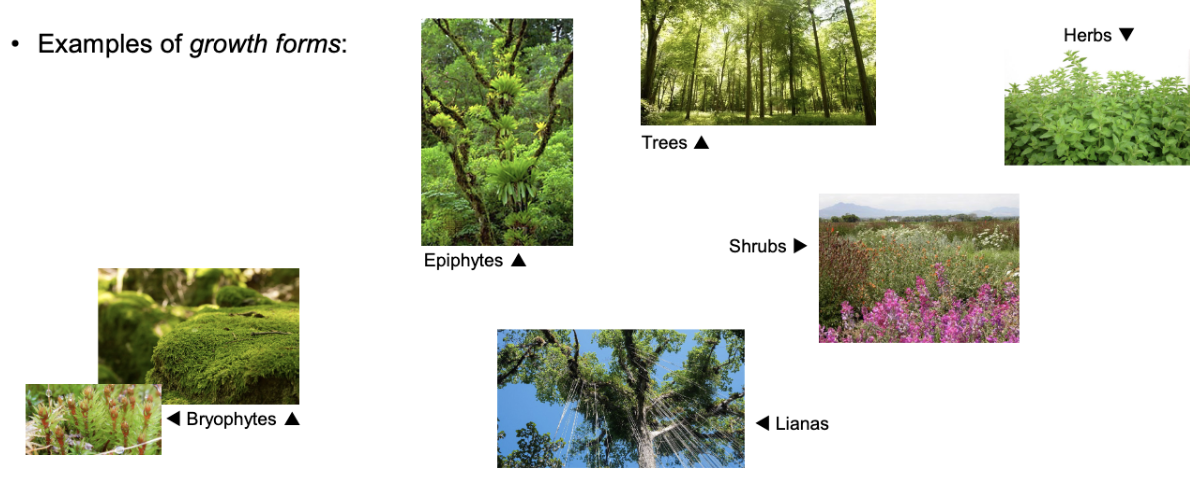
Growth form
Types of plant such as trees, shrubs, herbs, epiphytes (non-parasitical upon another plant), lianas (woody vines), and bryophytes (mosses & lichens)

Factors that affect forests: Human
Degradation
Defaunation
Fragmentation
Illegal logging
Invasive species
Deforestation
Agricultural conversion
Urbanization
Mining
Factors that affect forests: Natural
Abiotic
Fire: Superficial, Canopy
Water: Flooding, drought
Temperature: Heat, frost
Snow/Ice: Avalanches, physical damage
Wind
Geomorphic: Landslides, volcanic eruptions
Earthquakes
Biotic
Insects: Defoliators, Wood borers & bark beetles
Pathogens: Virus, bacteria, fungi
Tree fall
Vertebrates
Forests in BC
BC has Boreal, Coastal, Columbia, Montane, and Subalpine
Biogeoclimatic zone
A geographic area having similar patterns of energy flow, vegetation, and soils as a result of a broadly homogeneous microclimate”
Developed by Vladimir Krajina from UBC in the 1960s and 1970s
Each zone has subzones related to precipitation and temperature: IDFdk means INterior Douglas fir day (d) and cool (k)
According to FAO, a fast-growing industrial ___
IS a forest
The industrial plantation is the best type of forest to use TRIAD
Planted forests by objective
Timber production: Ex. Pinus radiata plantations in New Zealand
Non-timber products and services: Ex. Maple syrup plantations in Vermont
Protection and restoration: Soil erosion control in South Korea
Planted forests by timber product
Pulp: Ex. Eucalyptus
Fiber and particle boards: Ex. Pinus patula plantation
Solid lumber (wood): Ex. Teak plantation
Veneer: Black walnut plantation
Specialty plantation
Bamboo plantation
Not forestry
Fruits
Palm oil
Cork
Additional ___ million ha of plantations are required to supply 100% of global timber (It’s ___ million ha now)
371, 204
Wood supply from plantations is expected to reach __% of total by 2050 (It’s __% now)
60, 35
Classification criteria (Characteristic: Predominance in natural vs. planted forests)
Regeneration type: Natural vs. planted
Age: Multi-age vs. contemporary
Tree species: Multiple vs. single
Harvesting age: Undefined, long s. defined, short
Management intensity: Low vs. high
Harvesting method: Selective vs. clearcutting
Biodiversity: High vs. low
Species origin: Native vs. exotic
Tree density (Nha)
Trees/ha
Number of trees in a hectare (typically extrapolated)
An area-level metric
Synonym is stocking density
Diameter at Breast height (DBH)
A linear measurement (cm or in), representing the diameter of the tree at 1.3 meters above the ground
Height (H)
Tree height from the ground to highest top
Basal area
Cross-sectional area of a tree trunk at breast height (typically 1.3 meters or 4.5 feet above the ground) (m²/ha)
At the plot or stand level, G can be expressed as basal area per hectare (Gha) (m²/ha) sum of the basal area of all trees in a hectare (typically extrapolated)
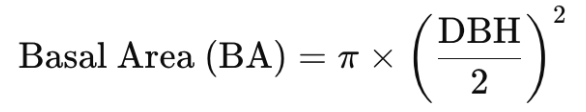
Volume (V)
m³ Timber ___ from ground to tip
Volume per hectare (Vha)
(m^3/ha): Sum of timber volume of all trees, extrapolated to ha
Total volume (Vt)
(m^3): Total timber volume in a given stand (m^3/ha x ha)
Merchantable volume
Volume excluding stump (e.g. 30cm height) and treetop (ex. Less than 10 cm in diameter)
Individual tree (direct) multiscale
Species
DBH
Height
Notable defects
→ Individual tree (processed)
Basal area
Volume
Plot multiscale
Stocking density
Basal area
Forest cover (%)
Dominant height
Volume (m^3/ha)
Stand and land totals
Area (ha)
Volume (m^3)
Commercial value ($)