PSYCH Final Exam
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
The most common treatment for ADHD is a central nervous system stimulant, such as methylphenidate (Ritalin) or Adderall.
o The actions of these drugs are not fully understood, but they may affect multiple neurotransmitters, particularly (BLANK)
dopamine
Nearly constant anxiety not associated with a particular object or situation
o People with this disorder are constantly anxious and worry incessantly about even minor matters
o NOT just a general feeling of anxiety
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
There are five major DSM-5 symptoms for (BLANK):
1. Delusions
2. Hallucinations
3. Disorganized speech
4. Disorganized behavior
5. Negative symptoms
schizophrenia
As of 2018, (BLANK) is the second leading cause of death among Americans 10–34 years old
• Deaths by BLANK have been increasing for emerging adults over the past 20 years
• U.S. men were four times more likely to die by BLANK than women were
• “People desire death when two fundamental needs are frustrated” (Thomas Joiner, 2005, p.47)
o The need to belong, to feel connected with others
o The need for competence
suicide
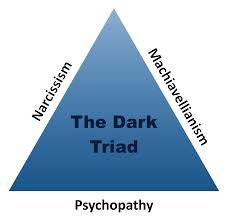
Psychopathy can be considered a personality trait. It revolves around a general lack of caring for the welfare of others, and, along with narcissism and Machiavellianism, it is part of the BLANK
dark triad
BLANK is a physical stress response. A consistent pattern of physical responses to stress that consists of three stages:
o Alarm
o Resistance
o Exhaustion
General adaptation syndrome
BLANK:
We experience pain when pain receptors are activated and a neural “gate” in the spinal cord allows the signals through to the brain (Melzack & Wall, 1982).
• These ideas were radical in that they depict pain as a perceptual experience within the brain rather than simply a response to nerve stimulation.
Gate control theory

The founders of BLANK psychology postulated a series of laws to explain how our brains group the perceived features of a visual scene into organized wholes.
Gestalt
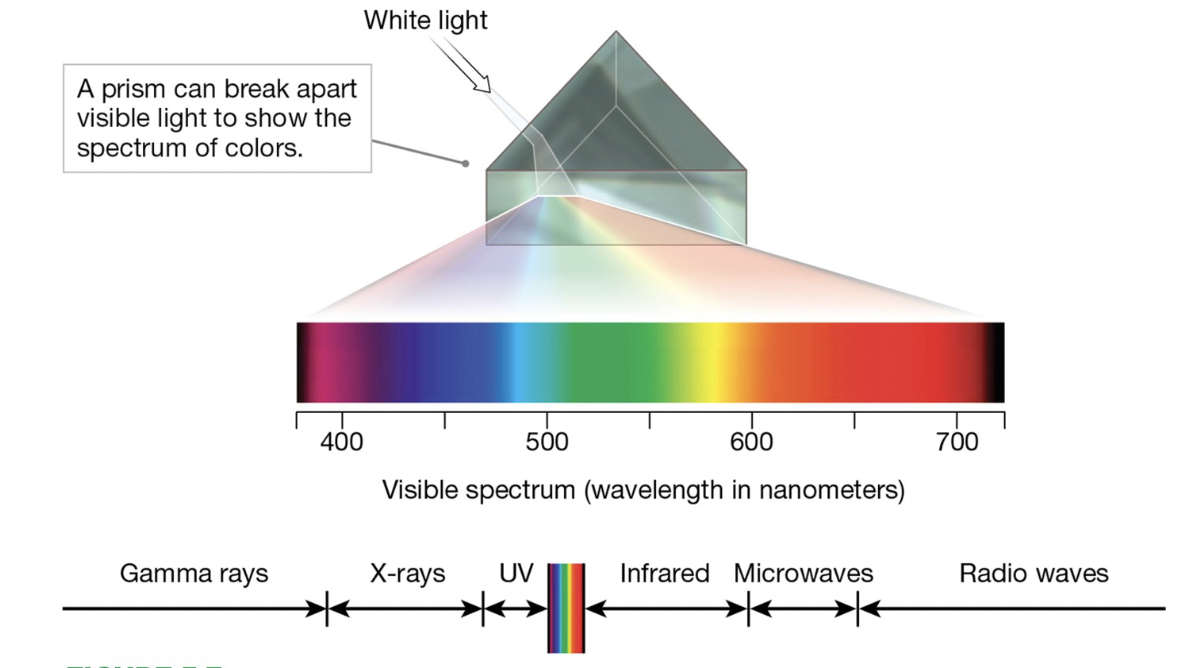
For humans, visible light consists of BLANK waves ranging in length from about 400 to 700 nanometers.
o The amplitude is the height of the light wave from base to peak; people experience this quality as brightness.
o The wavelength of the light wave is the distance from peak to peak. This distance determines your perception of hue.
electromagnetic
The process of BLANK begins when sound waves arrive at the shell-shaped structure of your outer ear.
o The shell shape of the outer ear increases the ear’s ability to capture sound waves and then funnel the waves down the auditory canal.
hearing
BLANK thinking (novel and creative)
o The ability to generate multiple ideas or
solutions to a problem
o Example: the invention of smart watches
Divergent
BLANK thinking (conventional)
o The ability to generate the single best or most correct solution to a problem or question
o Example: watches are useful for telling time
Convergent
A decrease in sensitivity to a constant level of stimulation
sensory adaptation
The sense of BLANK, which is also called gustation.
• Taste buds: Structures, located in papillae on the tongue, that contain the sensory receptors.
• Papillae: Structures on the tongue that contain groupings of taste buds.
o The BLANK information is sent to other brain regions through a set of nerves, primarily the facial nerve.
o After processing by the thalamus, the information is further processed in the primary gustatory cortex.
taste
Five main BLANK
• Sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami (Japanese for “savory” or “yummy”) are the five basic taste qualities.
o As of 2007, umami is the most recently recognized taste sensation.
• Supertasters are highly aware of flavors and textures and are more likely than others to feel pain when eating very spicy foods.
o Supertasters have nearly six times as many taste buds as normal tasters.
tastes

Self-concept
How you feel about your sense of self
• Many theories propose that BLANK is based on how we believe others perceive us, this view is known as reflected appraisal
• Self-compassion refers to treating oneself with care, acceptance, and kindness during difficult times; it was found was a good predictor of better mental health during the first year of college (Kroshus et al., 2021)
self-esteem
The BLANK states that most psychological disorders are influenced by biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors
Although people are anxious about different things, the etiology of various types of anxiety is best explained using a BLANK
OCD is another example of how the BLANK explains the causes of some mental disorders
biopsychosocial approach
A field that integrates research on health and on psychology; it involves the application of psychological principles in promoting health and well-being.
Health psychology
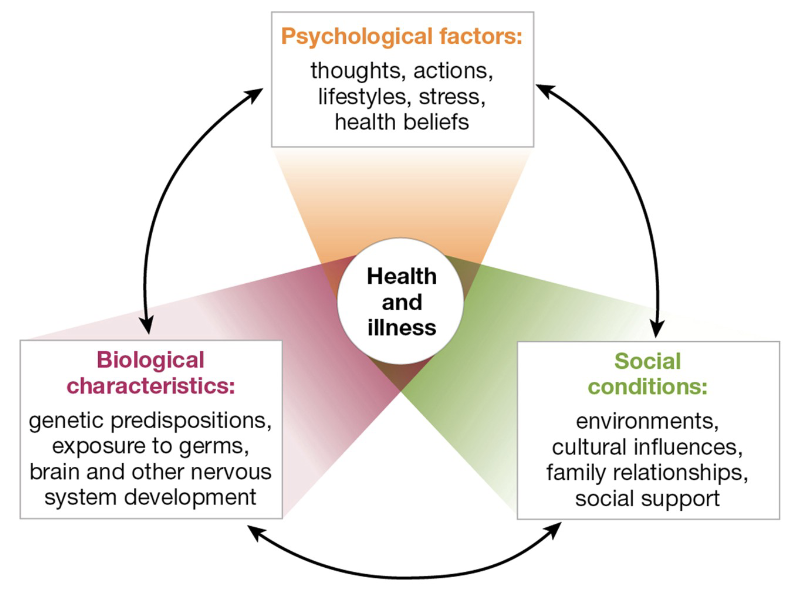
The Biopsychosocial model is central to understanding the difference between the traditional medical model and the approach taken by BLANK.
health psychologists
• Drugs that affect mental processes and that can be used to treat psychological disorders
o BLANK act by changing brain neurochemistry
Psychotropic medications

Type of drug:
Anti-anxiety drugs
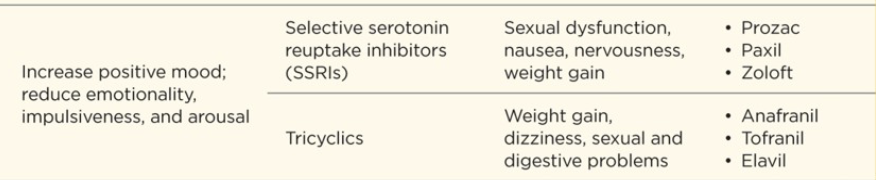
Type of drug:
Antidepressant drugs

Type of drug:
Mood stabilizer drugs
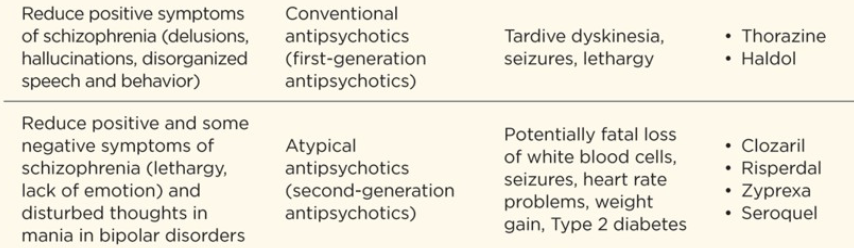
Type of drug:
Antipsychotic drugs

Type of drug:
Stimulants
Mood disorder characterized by extremely elevated moods (mania).
Bipolar I disorder
Mood disorder characterized by alternating periods of extremely depressed and mildly elevated moods (hypomania).
Bipolar II disorder
Our BLANK sense allows us to maintain balance.
Uses information from receptors in structures of the inner ear called the semicircular canals.
vestibular
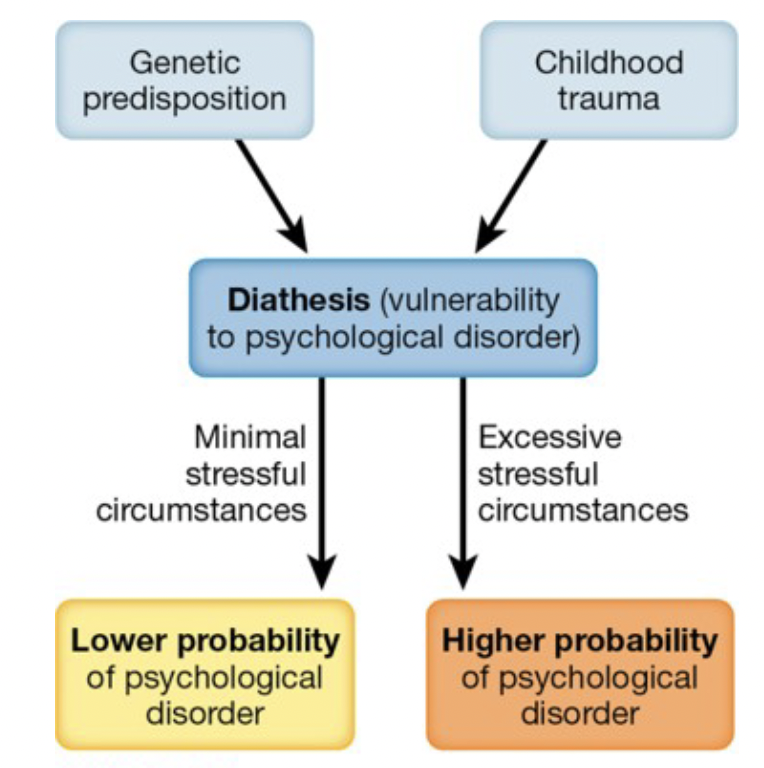
The BLANK
• Proposes that a disorder may develop when an underlying vulnerability is coupled with a precipitating event
o According to this model, the onset of mental disorders occurs due to both vulnerability for the disorder and the presence of stressful events
Diathesis-stress model
The Miller Analogy Test predicts not only graduate students’ academic BLANK but also individuals’ productivity, creativity, and job performance in the workplace
performance
BLANK: a psychometric test that is designed to test a person’s ability to learn—that is, the person’s future performance
Aptitude test
David Wechsler developed the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale in 1939. The first test for use with adults, it measured two factors of intelligence
Verbal and Performance
An assessment of a child’s intellectual standing compared with that of same-age peers; determined by comparing the child’s test score with the average score for children of each chronological age
• IQ scores forms a bell curve, known as normal distribution
Mental age
Rotter proposed that personalities are based on BLANK
o BLANK refers to people’s perception of whether they control the rewards and punishments they experience (internal locus of control) or not (external locus of control)
locus of control
BLANK: relying on the standardized and objective procedures of the scientific method to collect empirical evidence and to test whether hypotheses are valid
Formal reasoning
A mathematical measure of intelligence (originally computed by dividing a child’s estimated mental age by the child’s chronological age and then multiplying this number by 100)
Intelligence quotient (IQ)
Charles Spearman
o BLANK: The idea that one general factor underlies intelligence
Influences important life outcomes
There is now substantial evidence that a single factor of BLANK is universal for humans across cultures
General intelligence
Raymond Cattell
o BLANK: Intelligence that reflects the ability to process information, particularly in novel or complex circumstances
Fluid intelligence
Raymond Cattell
BLANK: Intelligence that reflects both the knowledge a person acquires through experience and the ability to use that knowledge
Crystallized intelligence
BLANK by Howard Gardner
• The idea that people have many different types of intelligence that are independent of one another
o Bodily-kinesthetic
o Linguistic
o Mathematical/logical
o Spatial
o Musical
o Intrapersonal and interpersonal
Multiple intelligences
BLANK intelligence (EI)
• Four abilities
o Managing our own emotions
o Using our emotions to guide our thoughts and actions
o Recognizing other people’s emotions
o Understanding emotional language
Emotional
Sensory receptors in the skin, muscles, organs, and membranes around both bones and joints; these myelinated fibers quickly convey intense sensory input to the brain, where it is perceived as sharp, immediate pain.
Fast fibers
Sensory receptors in the skin, muscles, organs, and membranes around both bones and joints; these unmyelinated fibers slowly convey intense sensory input to the brain, where it is perceived as chronic, dull, steady pain.
slow fibers
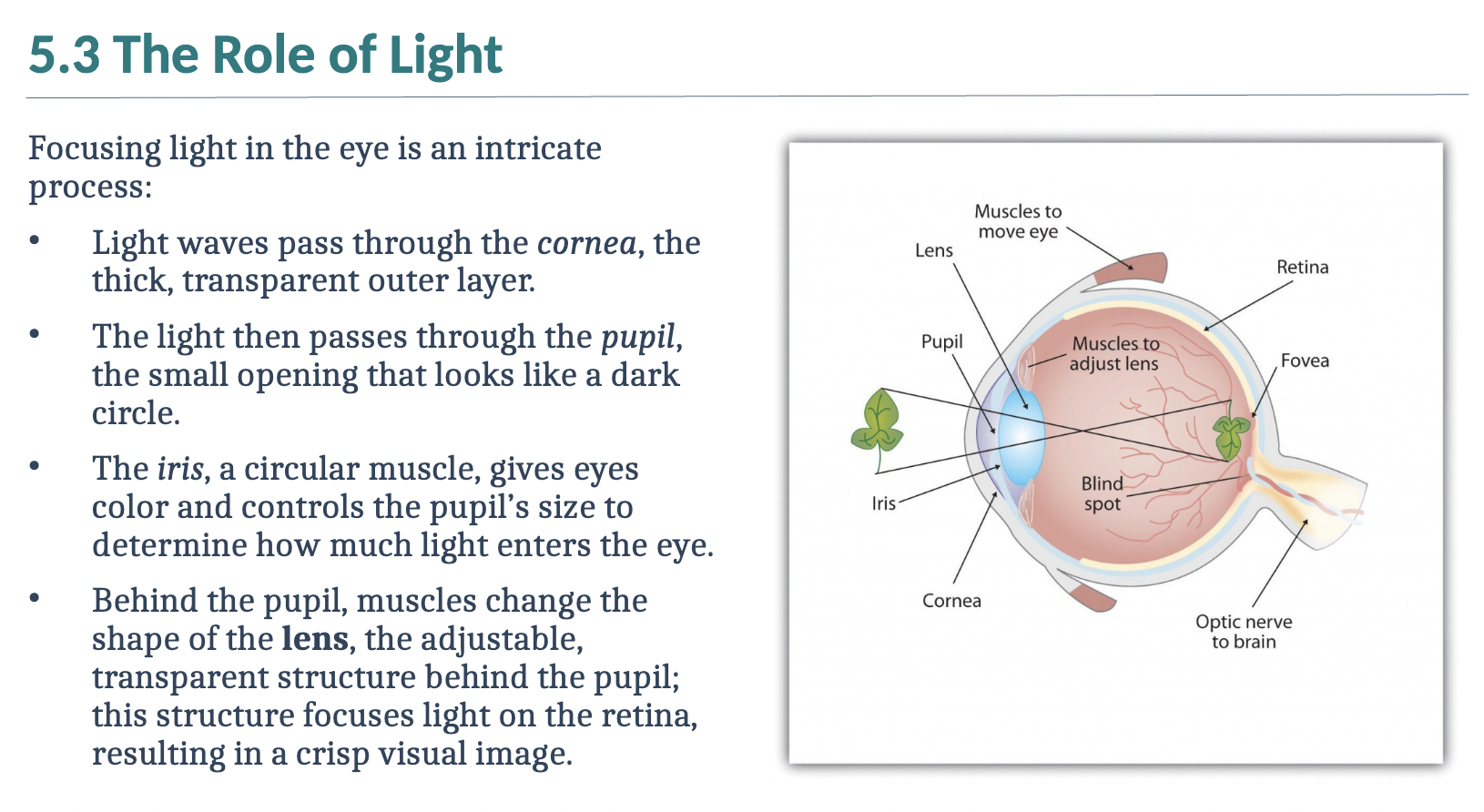
Review the role of light
I’ve reviewed the role of light
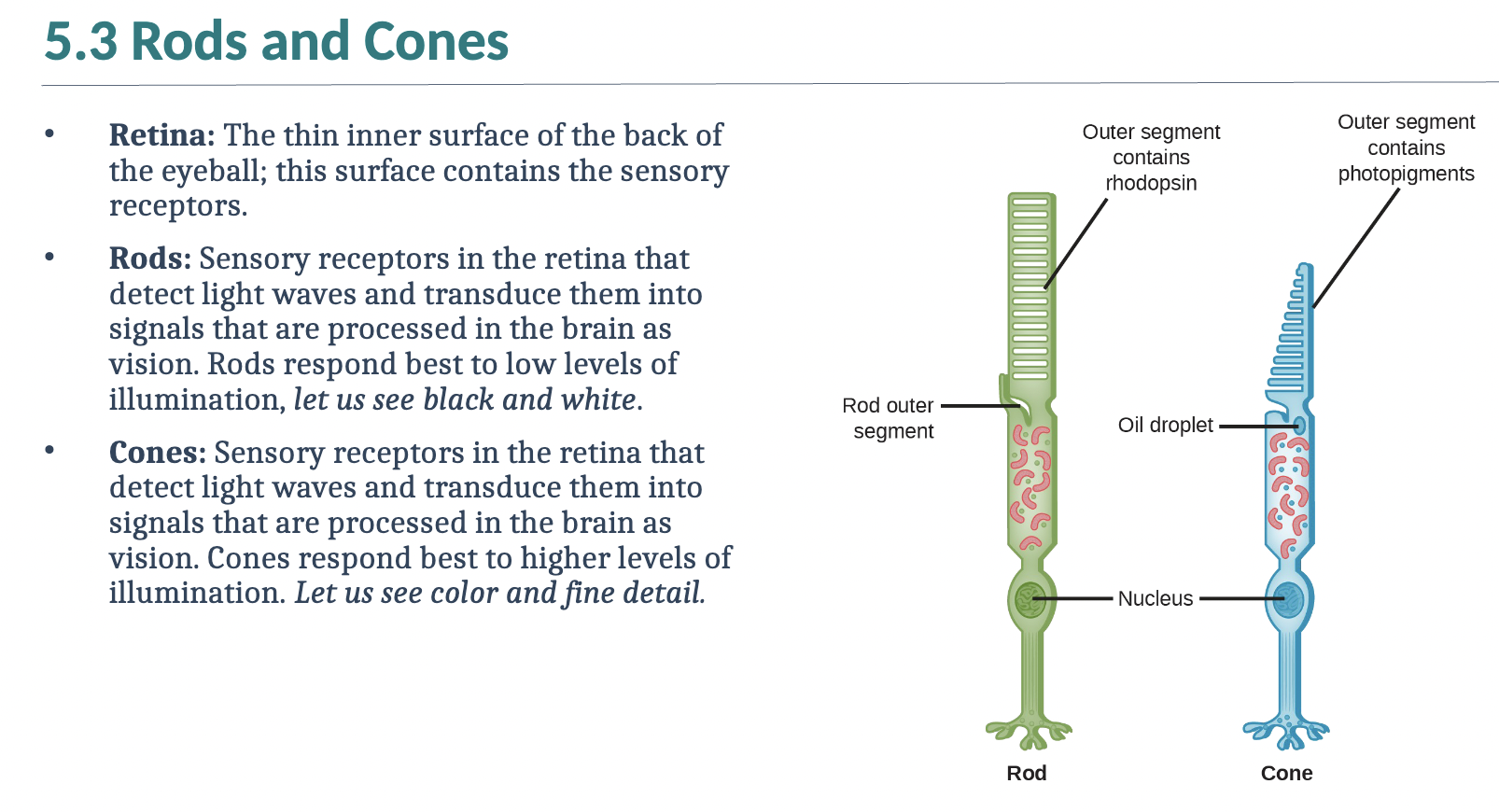
Review rods and cones
I’ve reviewed rods and cones
BLANK improves your physical health.
• It lowers the risk of cancer.
• People who BLANK are less likely to have heart problems, especially with aerobic exercise.
• People with better fitness in middle age are likely to live longer.
• Aids your thinking abilities. It improves memory, especially in older adults.
Exercise
Treatment for psychological disorders in which a therapist works with clients to help them understand their problems and work toward solutions
o Therapists generally use BLANK to
change their clients’ patterns of thought or
behavior
Psychotherapy
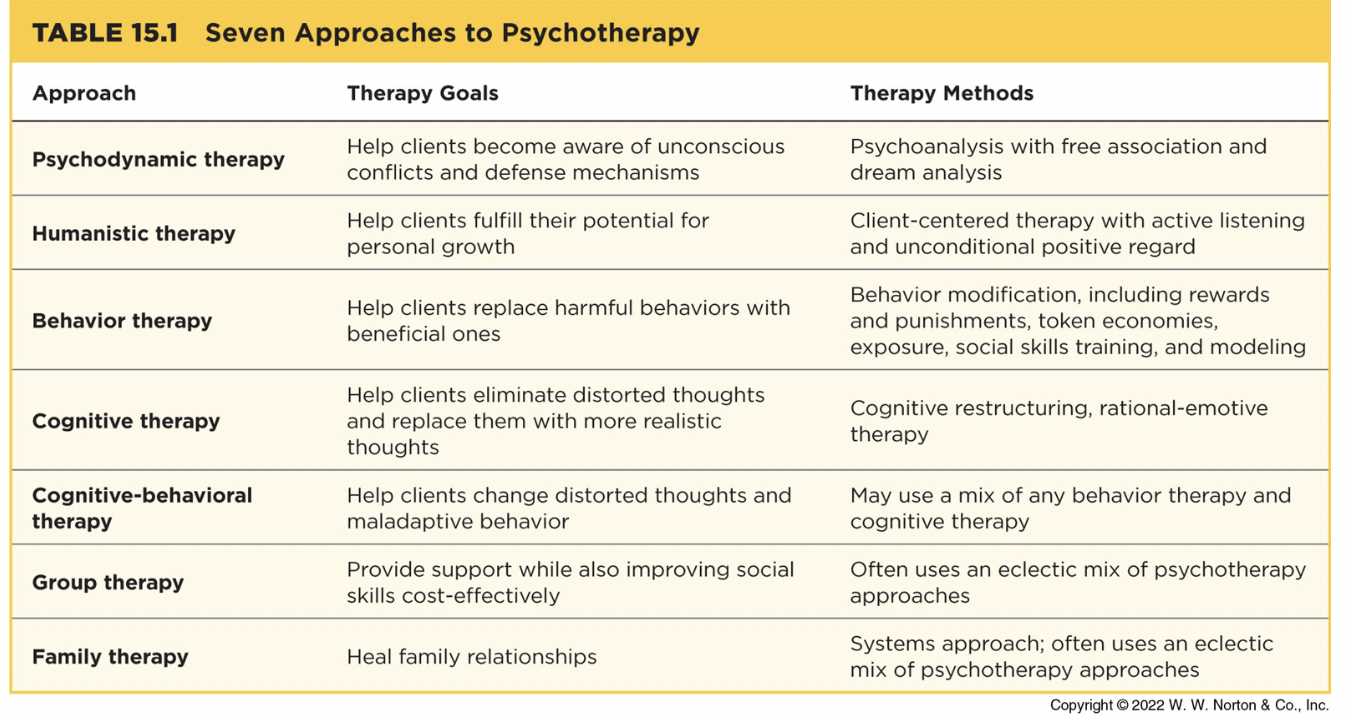
Review therapy types
I’ve reviewed therapy types
Treatment for psychological disorders in which a therapist works with clients to help them gain insight about how their unconscious processes may be causing inner conflict and impairing daily functioning
Along with Josef Breuer, Sigmund Freud pioneered the method of psychoanalysis. Freud’s techniques included free association and dream analysis
Psychodynamic therapy
Treatment for psychological disorders in which a therapist works with clients to help them change distorted thought patterns that produce maladaptive behaviors and emotions
o Aaron Beck has advocated cognitive
restructuring
o Albert Ellis introduced rational-emotive therapy
Cognitive therapy
A process by which sensory receptors change physical stimuli into signals that are eventually sent to the brain.
transduction
BLANK: The sense organs’ detection of external physical stimulus and the transmission of information about this stimulus to the brain.
Sensation
BLANK: The processing, organization, and interpretation of sensory information in the brain; these processes result in an internal neural representation of the physical stimulus.
Perception
A shortcut (rule of thumb or informal guideline) used to reduce the amount of thinking that is needed to make decisions
• There are three types of BLANK
• Availability
• Representativeness
• Affective
heuristics
BLANK:
• Tendency to believe you could have predicted something after you learn the outcome.
Hindsight bias
BLANK: people show a strong tendency to pay greater attention to evidence that supports their beliefs and ignore or downplay evidence that does not
Confirmation bias
BLANK behavior pattern: Personality
traits characterized by being noncompetitive, relaxed, easygoing, and accommodating.
Type B
BLANK behavior pattern: Personality Traits characterized by competitiveness, achievement orientation, aggressiveness, hostility, restlessness, impatience with others, and an inability to relax.
o Men who exhibit these traits are much more likely to develop heart disease.
Type A

Review efficacy
I’ve reviewed efficacy

Review evidence-based
I’ve reviewed evidence-based
BLANK: Everyday irritations that cause small disruptions, the effects of which can add up to a large impact on health.
Daily hassles
BLANK: Large disruptions, especially unpredictable and uncontrollable catastrophic events, that affect central areas of people’s lives.
Major life stressors
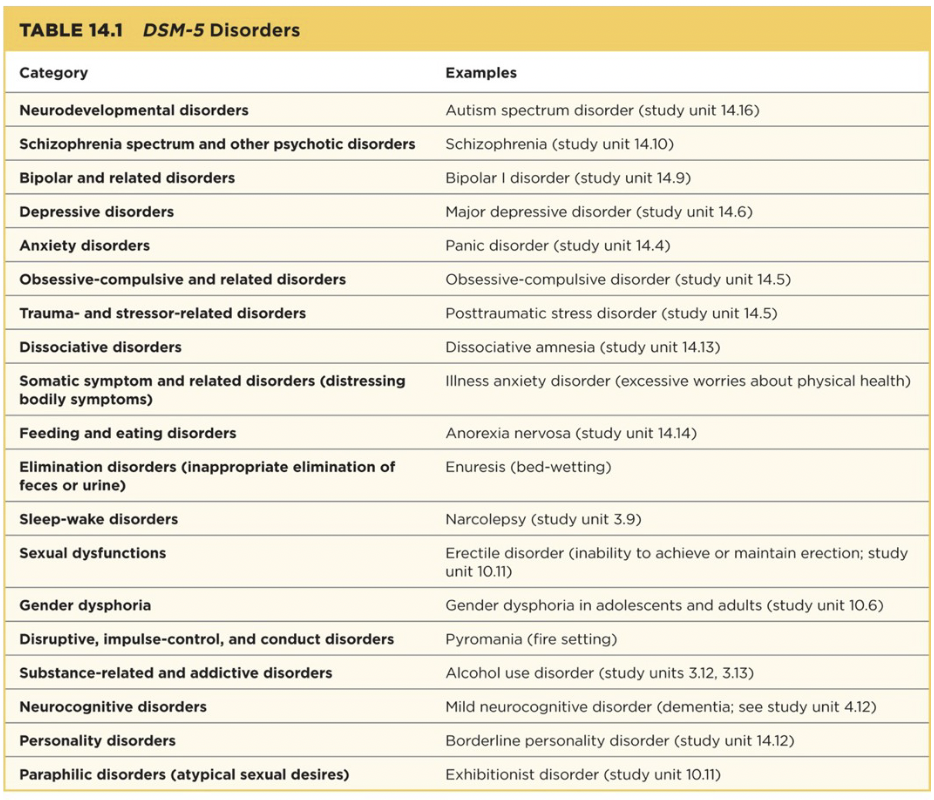
Review psychological disorders
I’ve reviewed psychological disorders
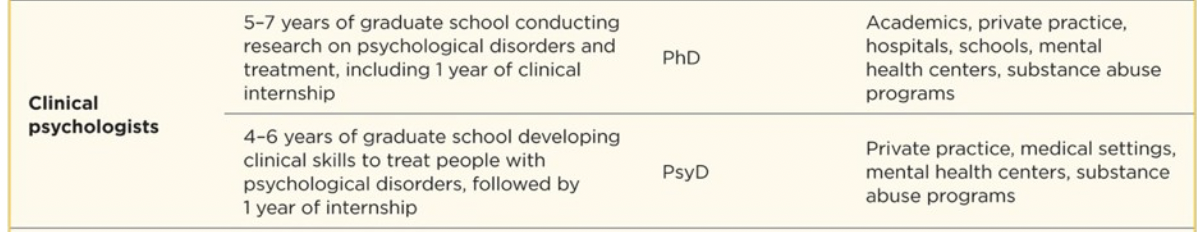
Review providers
I’ve reviewed providers

Review providers
I’ve reviewed providers
Part of the limbic system; relay station for incoming and outgoing brain messages, like a "mailroom"
Thalamus
BLANK treatments for phobias often include anti-anxiety drugs that are calming
Psychotropic medication
BLANK are the treatments of choice for phobia (OCD)
treatment of panic attacks
CBTs
BLANK may be useful for social phobia (social anxiety disorder)
Antidepressants
Psychotropic medications for BLANK disorders
depressive
FOR DEPRESSION & ANXIETY: SSRIs
Since selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) have the fewest serious side effects, they tend to be used as the first-line BLANK
medication
The most common treatment for ADHD is a central nervous system stimulant, such as BLANK.
Symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
methylphenidate (Ritalin) or Adderall
Early antipsychotic drugs called BLANK reduced the positive symptoms of schizophrenia, such as delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized speech and behavior
conventional antipsychotics

Review Eysenck’s trait theory
I’ve reviewed Eysenck’s trait theory

Review how to find therapist
I’ve reviewed how to find therapist
Openness to experience
Conscientiousness
Extroversion
Agreeableness
Neuroticism
OCEAN (Big Five)
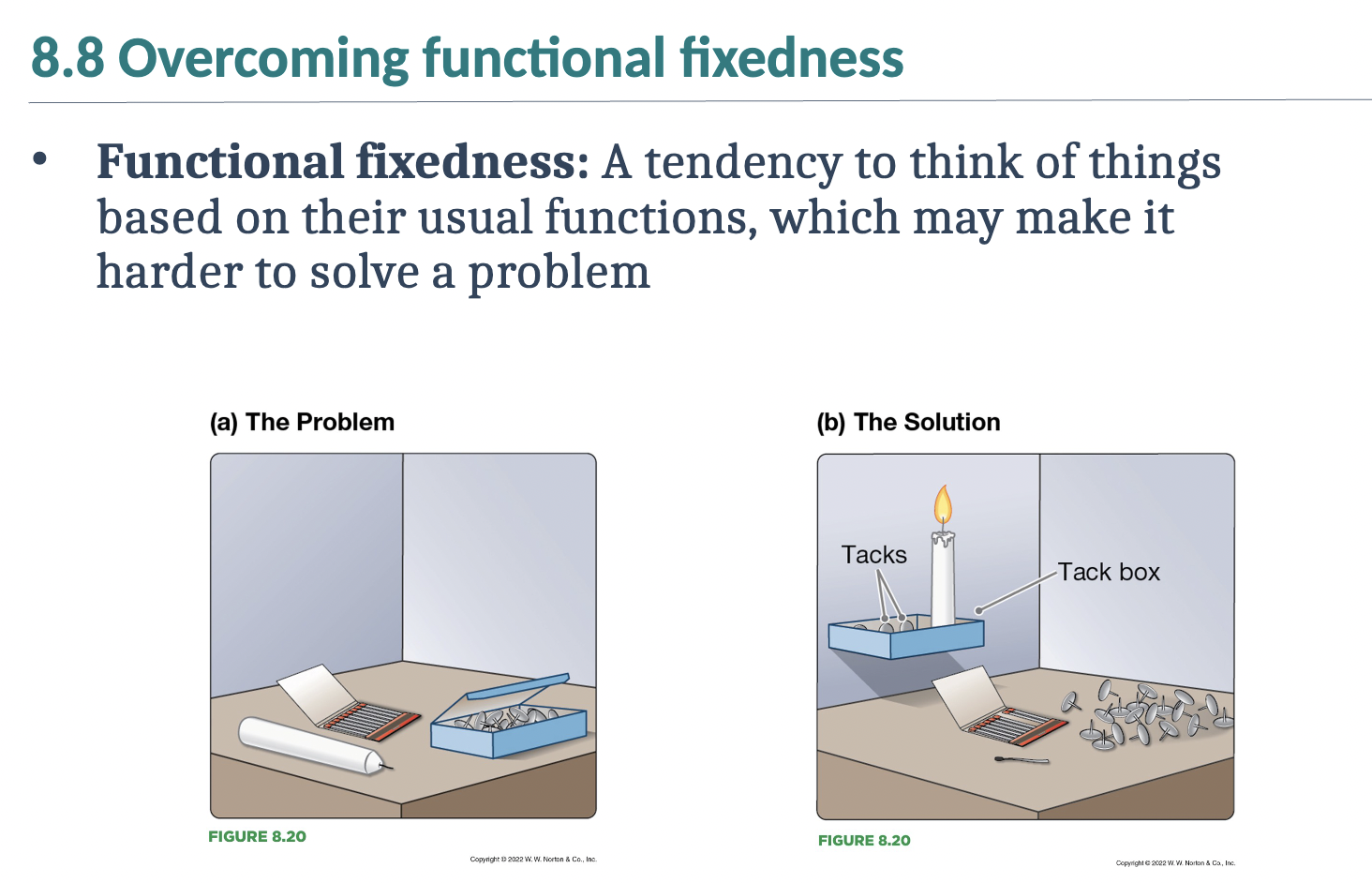
Box of tacks, candle, and matches experiment
Duncker's candle problem
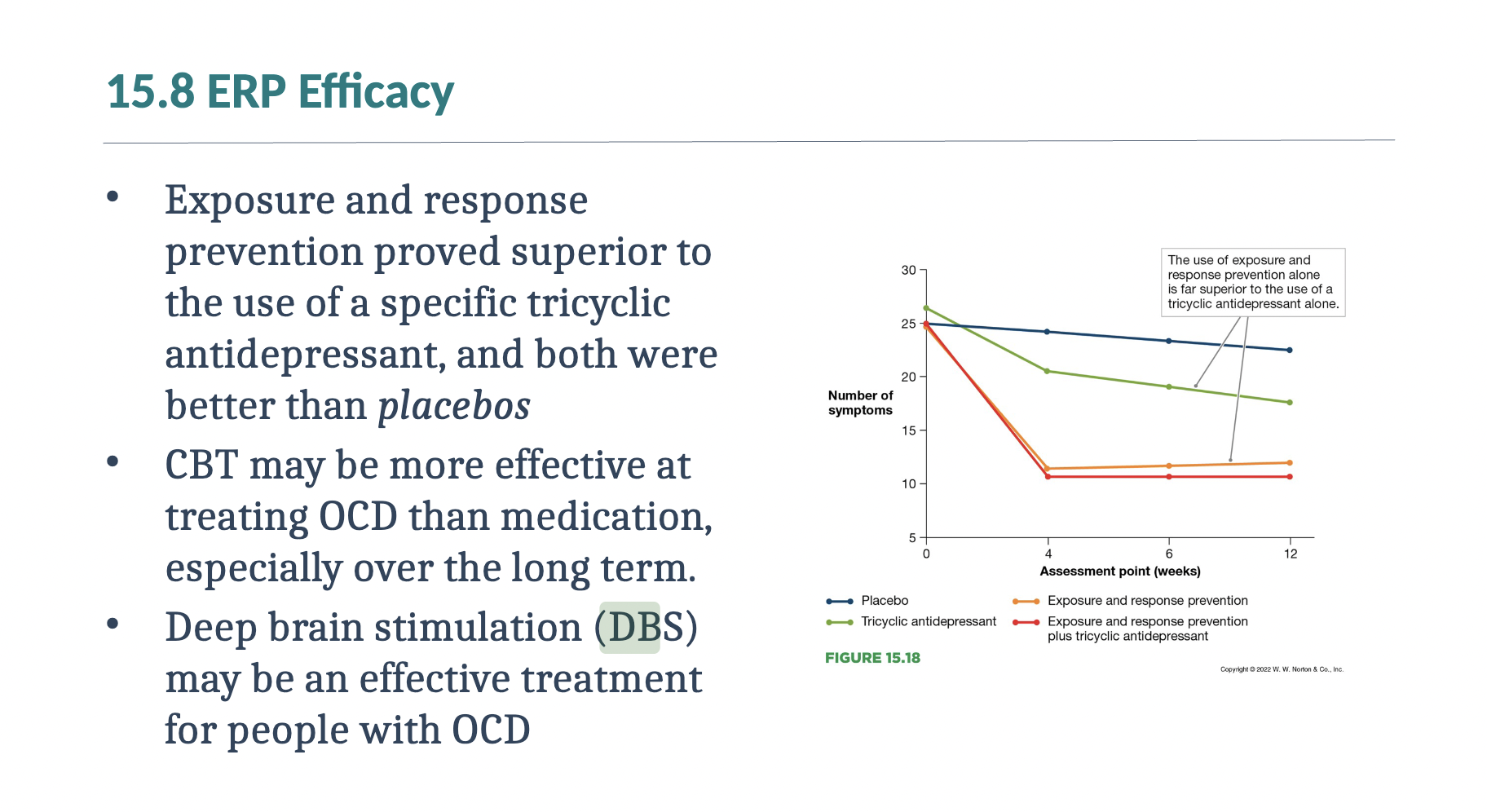
Review 15.8
I’ve reviewed 15.8
DBS may be especially valuable for treating severe obsessive- compulsive disorder (OCD) and depression

Review 15.12
I’ve reviewed 15.12

Review 14.6
I’ve reviewed 14.6

Review 14.4
I’ve reviewed 14.4

Review 14.10
I’ve reviewed 14.10
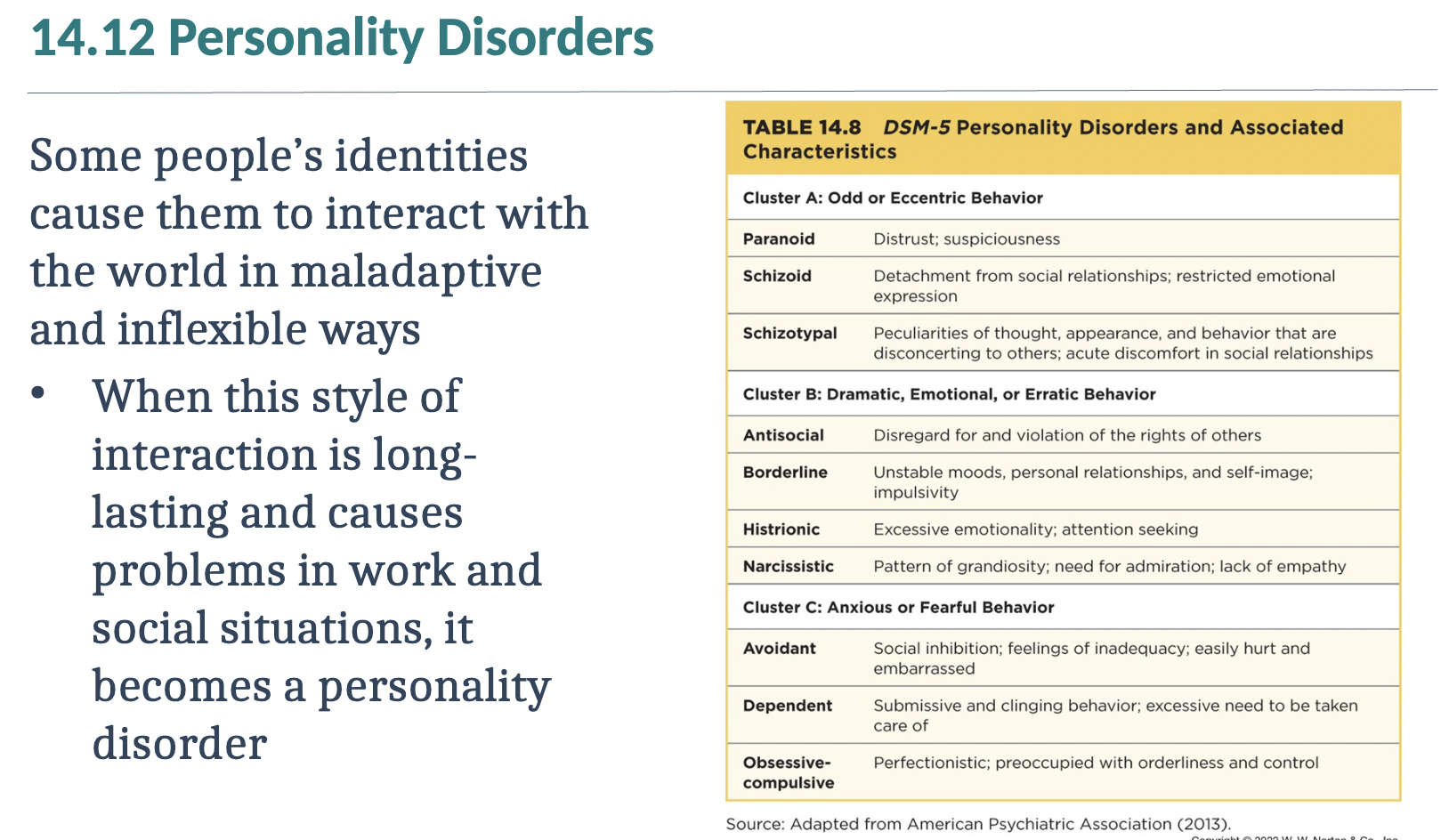
Review 14.12
I’ve reviewed 14.12

Review 14.13
I’ve reviewed 14.13