CompTIA A+ 220-1101 - 3.2: Memory
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
RAM (Random Access Memory)
Memory that can be accessed at random - that is, memory that you can write or read from without touching the preceding address. This term is often used to mean a computers main memory.
DDR Notches
Physical feature of a DDR module that prevents the wrong model of module from being installed on a motherboard. Keeps it from fitting.
RAM details
RAM is not the only kind of memory.
It does not refer to hard drive or SSD storage.
- Don't mix up the two terms.
- Data is stored permanently on the drive.
Data and programs can only be used when moved to RAM.
Memory types have changed through the years.
- Driven by standardization and technology.
One of the most important components of your computer.
- Speed, speed, speed
Every motherboard is different, so check your documentation.
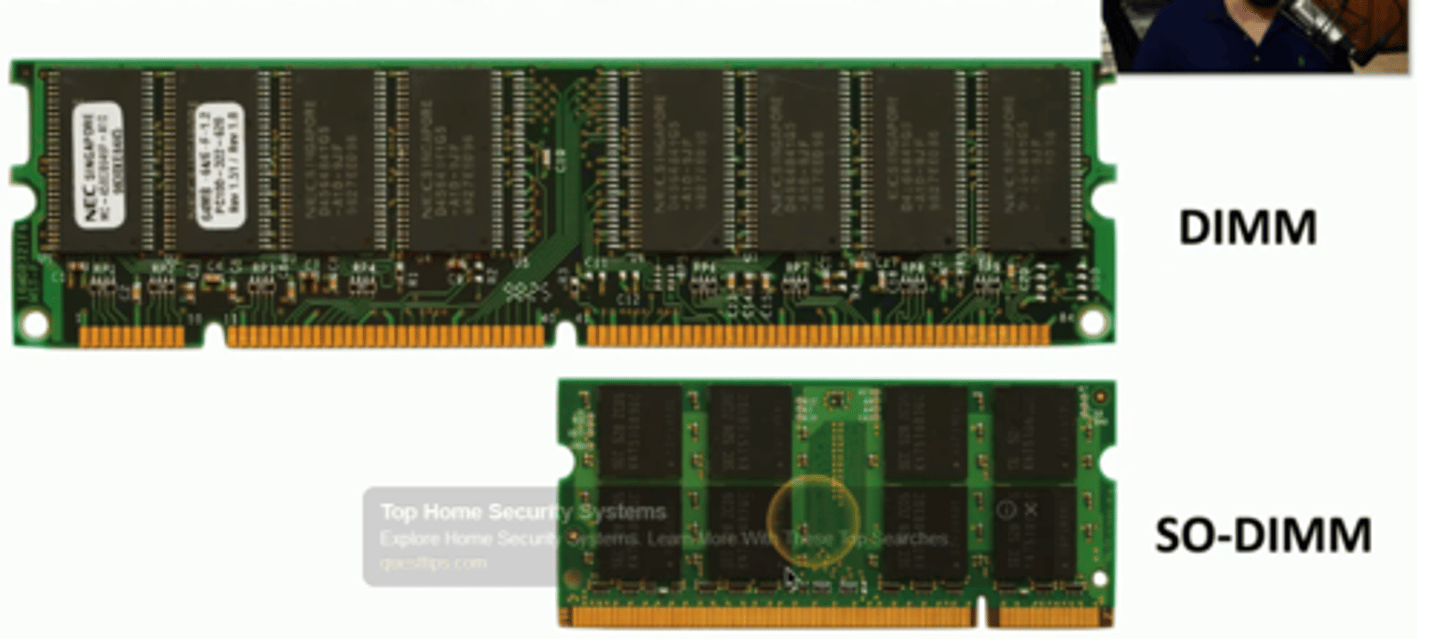
DIMM (Dual Inline Memory Module)
32- or 64-bit type of DRAM packaging
with the distinction that each side of each tab inserted into the system performs a separate function. DIMMs come in a variety of sizes, with 184-, 240-, and 288-pin being the most common on desktop computers.
DIMM details
Dual Inline Memory Module.
Electrical contacts are different on each side.
Information is moved in and out of the module in 64 bit data width.
SO-DIMM (Small Outline Dual Inline Memory Module)
Memory used in portable PCs because of its small size.
DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory)
Memory used to store data on personal devices. Stores each bit in a "cell" composed of a transistor and a capacitor. Because the capacitor in the cell can only hold a charge for a few milliseconds, DRAM must be continually refreshed, or rewritten, to retain it's data.
SO-DIMM details
Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Module
- About half the width as a DIMM.
Used in laptops and mobile devices.
SO-DIMM vs DIMM
SO-DIMMs are used in laptops and mobile devices.
DIMMs are used in desktop computers.
"Dynamic"
An aspect of DRAM.
- Needs constant refreshing.
- Without refreshing, the data in memory disappears.
- Requires a constant power source.
"Random"
An aspect of DRAM.
- Any storage location can be accessed directly. No fast forward or rewind.
- Unlike magnetic tape.
SDRAM (synchronous DRAM)
DRAM that is synchronous, or tied to a system clock. This type of RAM is used in all modern systems.
- Queue up on process while waiting for another.
- Classic DRAM didn't wait for a clock signal.
DDR SDRAM (double data rate SDRAM)
Type of SDRAM that makes two processes for every clock cycle.
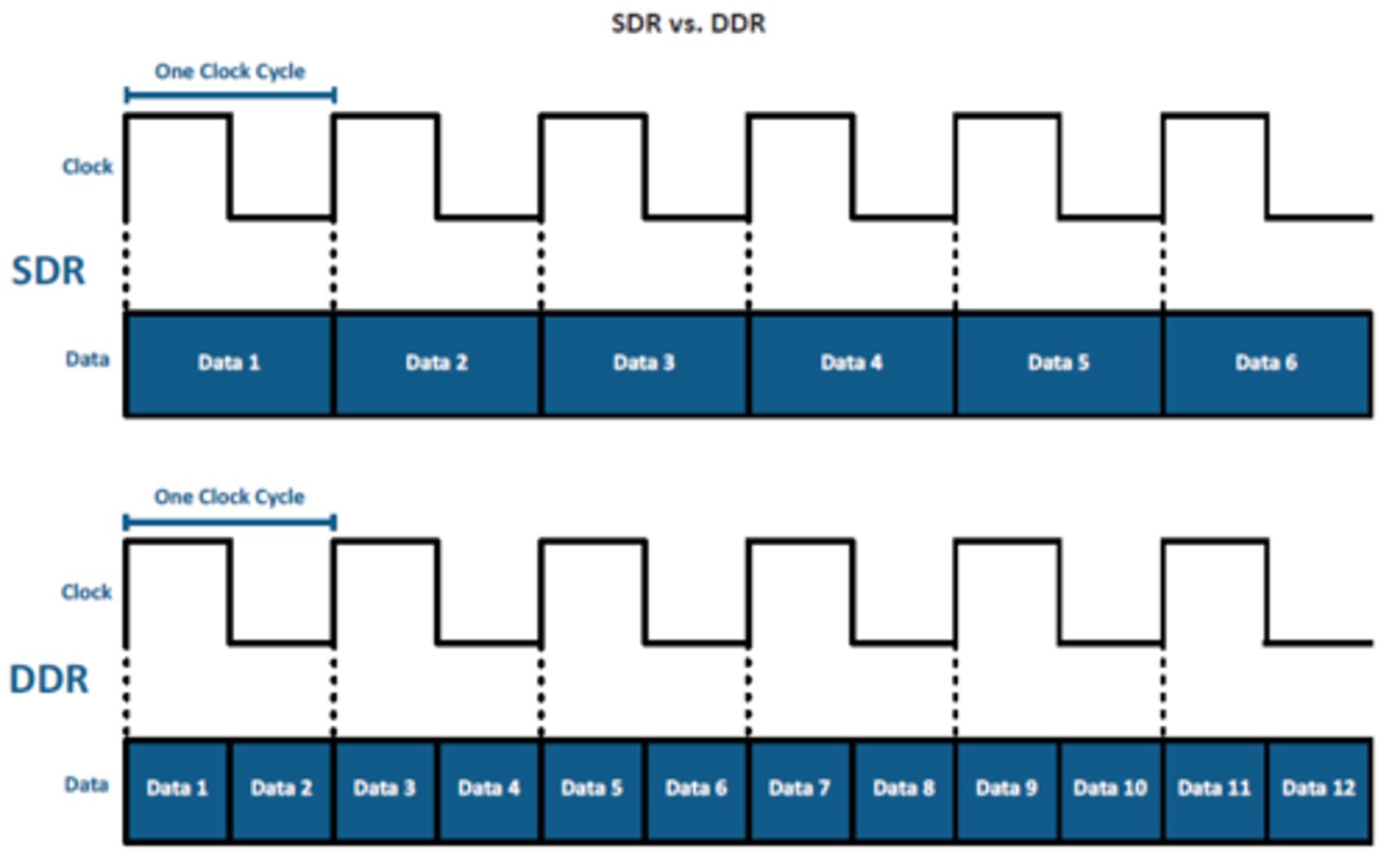
SDR vs DDR
SDR = single data rate memory 1 clock cycle = one bit of data
DDR = double data rate = twice in a single clock cycle
DDR2 SDRAM
Type of SDRAM that sends 4 bits of data in every clock cycle.
DDR3 SDRAM
Type of SDRAM that transfers data at twice the rate of DDR2 SDRAM.
- Larger chip capacities - Maximum 16 GB per DIMM
- No backwards compatibility - Speed brings sacrifice.
DDR4 SDRAM
Type of SDRAM that offers higher density and lower voltages than DDR3, and can handle faster data transfer rates.
- Maximum 64 GB per DIMM.
- No backwards compatibility - Speed brings sacrifice.
DDR5 SDRAM
Type of SDRAM that offers faster data transfers between the memory module and the motherboard.
- Maximum of 64 GB per DIMM
- No backwards compatibility
Virtual Memory (Virtual RAM)
Space on a hard disk or other storage device that simulates RAM.
- Slower than true RAM.
Swap currently unused application data to storage.
- Free up space for other applications.
Managed automatically by the OS.
- Some configurations are available.
Multi-Channel Memory
Takes the throughput that normally would be sent to one single memory module, and spreads that load across multiple memory modules.
Dual-channel, triple channel, or quad channel.
Memory combinations should match.
- Exact matches are best.
Memory module slots are often colored differently.
Memory that checks itself
Used on critical computer systems
• VM servers, database servers, any server
Parity memory
• Adds an additional parity bit
• Won't always detect an error
• Can't correct an error
Error Correcting Code (ECC)
• Detects errors and corrects on the fly
• Not all systems use ECC
• It looks the same as non-ECC memory
Parity RAM
Earliest form of error-detecting RAM; stored an extra bit (called the parity bit) to verify the data.
ECC RAM
RAM that uses special chips to detect and fix memory errors. Commonly used in high-end servers where data integrity is crucial.
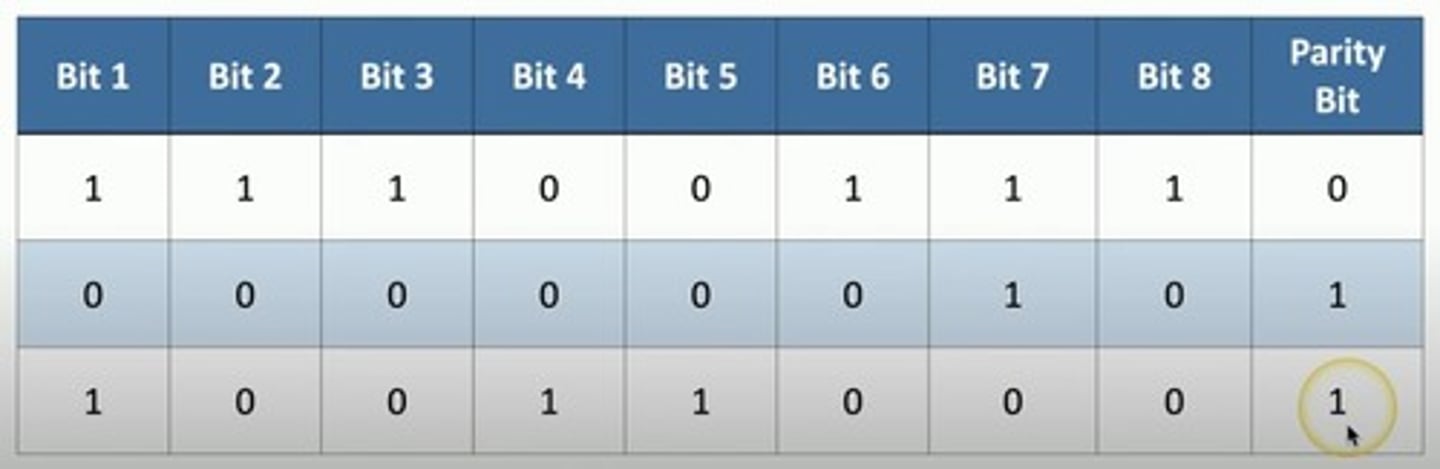
Parity
Early method of error detection where a small group of bits being transferred is compared to a single parity bit set to make the total bits odd or even. The receiving device reads the parity bit and determines if the data is valid, based on the oddness or evenness of the parity bit.
Parity details
Even parity
- The parity bit makes an even number.
- If there is already an even number, the parity bit is 0
Evaluating Parity
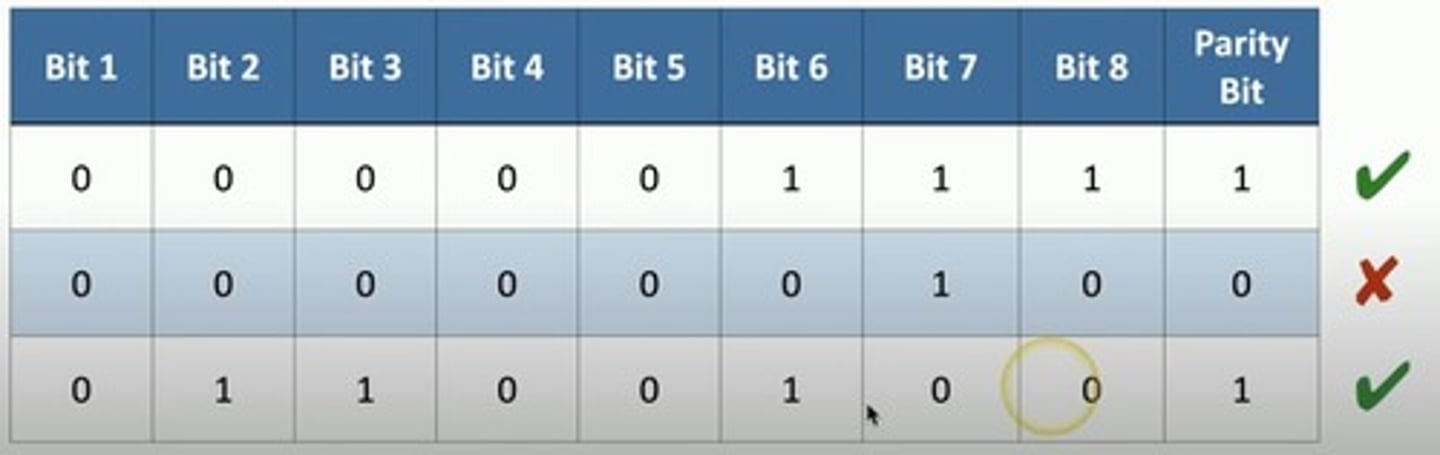
Valid or error
- Even parity bit.
Dual-Channel Architecture
A chipset feature, whereby two identical sticks of RAM (either RDRAM or DDR) are used (and required) to increase throughput.
Triple-Channel Architecture
A chipset feature similar to dual-channel RAM, but requiring three matched sticks instead of two.
Quad-Chanel Architecture
A chipset feature similar to dual-channel RAM, but requiring four matched sticks instead of two.
Single-Channel Architecture
A chipset feature, whereby a single stick of RAM is used. One of the most common memory channels available today.
Page File (Swap File)
A system file that creates a temporary storage space on an SSD or HDD when the system runs low on memory. This file swaps for a section of RAM storage from an idle program and frees up memory for other programs.
Swap/Page Partition
A special partition found on Linux and UNIX systems that behaves like RAM when your system needs more RAM than is installed.
SRAM vs DRAM
SRAM
Faster than DRAM
More expensive than DRAM
Utilized for CPU cache memory chips.
SDRAM
Slower than SRAM
Cheaper than SRAM
Both are Volatile.
Volatile Memory
Memory that must have constant electricity to retain data.
184 Pins
DDR SDRAM DIMMs
200 Pins
DDR SDRAM SO-DIMMs
DDR2 SDRAM SO-DIMMs
204 Pins
DDR3 SDRAM SO-DIMMs
240 Pins
DDR2 SDRAM DIMMs
DDR3 SDRAM DIMMs
260 Pins
DDR4 SDRAM SO-DIMMs
288 Pins
DDR4 SDRAM DIMMs