Exam 3 - Molecular Genetics
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
location of DNA in prokaryotes
nucleoid (no membrane-bound organelles)
location of DNA in eukaryotes
nucleus (separates transcription and translation)
location of ribosomes in prokaryotes
cytoplasm
location of ribosomes in eukaryotes
endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and cytoplasm
how are genes organized in prokaryotes?
in operons - close together
how are genes organized in eukaryotes?
can be far apart - no operons
protein coding content on chromosome in prokaryotes
entire gene is coding
protein coding content on chromosome in eukaryotes
introns are removed and exons are coding
pre-translation mRNA processing in prokaryotes
minimal - some trimming and phosphates may be added to 3’ end
pre-translation mRNA processing in eukaryotes
splicing of exons
5’-cap (methyl group added to guanine)
3’-poly(A) tail
are transcription and translation coupled in prokaryotes?
yes they are
are transcription and translation coupled in eukaryotes?
no they are not
bacterial operon
clusters of co-regulated (all on or off) genes with related functions
why is there a correlation between transcription and translation in prokaryotes?
ribosomes start translating mRNA before transcription even finishes, so the rate of one process directly influences the other
What happens to transcription when translation is quick?
This ribosome movement blocks Rho-dependent termination, allowing transcription to continue (positive correlation)
What happens to transcription when translation is stalled or slow?
Naked mRNA is exposed, so Rho binds and prematurely terminates transcription (negative correlation)
In bacteria, what molecule causes premature termination when translation slows?
Rho factor
promoter
DNA sequence (100-1000 bp long) upstream of structural genes - where RNA polymerase will bind to initiate transcription
operator
region of DNA between promoter and structural genes where a repressor (regulatory protein) will bind (stops transcription)
regulatory genes
encode transcription factor proteins that influence transcription rate of the operon
repressor
turns off transcription in response to external stimuli
activator
increases transcription in response to external stimuli
What 3 regions of the promoter does RNAP recognize and bind to?
-35 region, -10 region (TATA/Pribnow box), +1 region (start site)
Which RNAP subunit interacts with the -10 and -35 promoter regions?
sigma
What happens to the sigma subunit of RNAP once transcription begins?
It falls off the core RNAP.
Beta subunit of RNAP
Has the main catalytic domain - separates DNA strands and polymerizes RNA synthesis
Beta’ subunit of RNAP
helps stabilize the DNA-RNA hybrid during transcription
Alpha subunits of RNAP
involved in assembly and stability of RNAP transcription complex
Omega subunit of RNAP
stabilizes core subunits, essential for holoenzyme assembly
Sigma subunit of RNAP
essential for promoter recognition and binding (not part of core)
Transcription - Step 1 - Initiation
sigma subunit binds to core RNA polymerase subunits
sigma subunit binds to promoter
beta subunit separates DNA strands at start site, creating a transcription bubble
attaches first nucleotide of RNA (A or G)
Transcription - Step 2 - Elongation
Beta subunit adds nucleotides to growing mRNA strand
sigma subunit is displaced by RNA strand and falls off.
Core RNAP subunits move in 5’-3’ direction
beta’ stabilizes DNA/RNA hybrid
alphas bind to upstream region of DNA (UP element at -50) to help stabilize complex
Transcription elongation complex (TEC)
DNA enters pincers of beta and beta’
Free nucleotides enter through beta secondary channel
beta active site = site of polymerization
RNA exits through beta exit channel
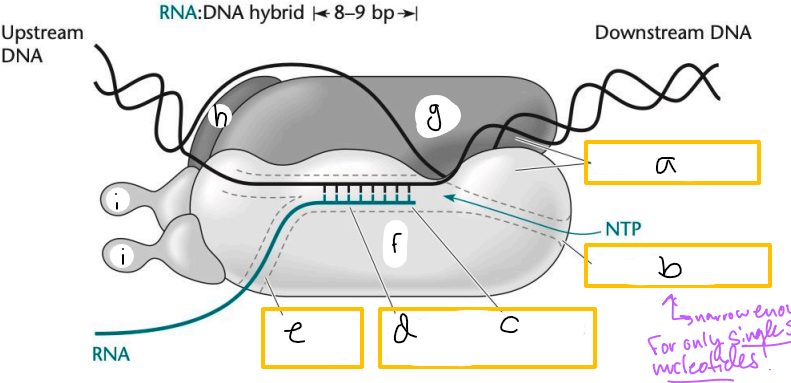
a? (TEC)
downstream jaws
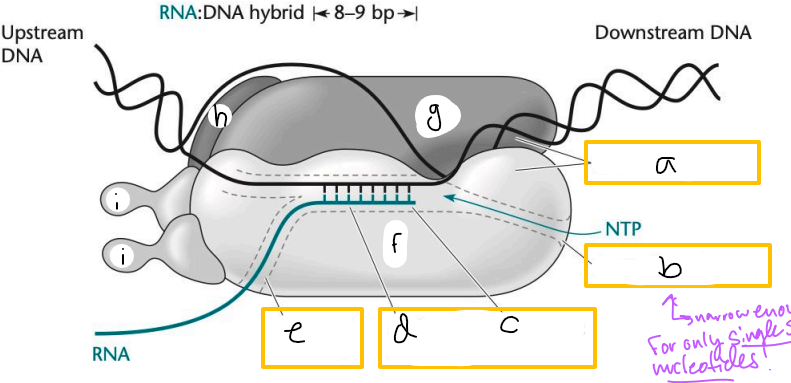
b? (TEC)
secondary channel
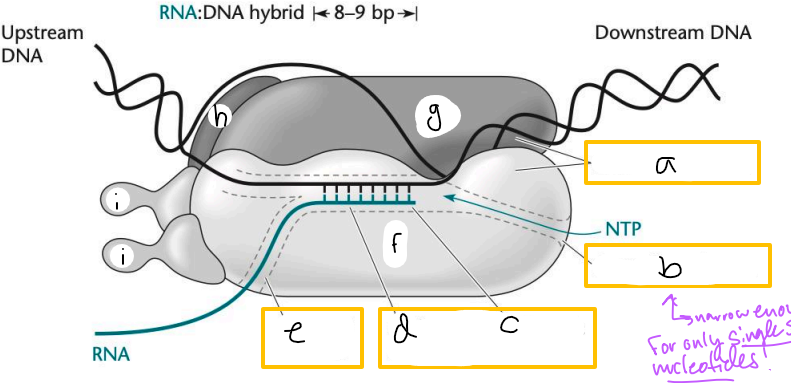
c? (TEC)
active site
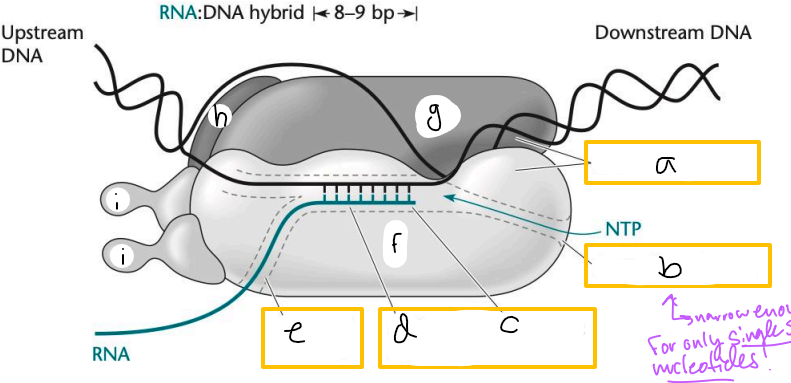
d? (TEC)
active site channel
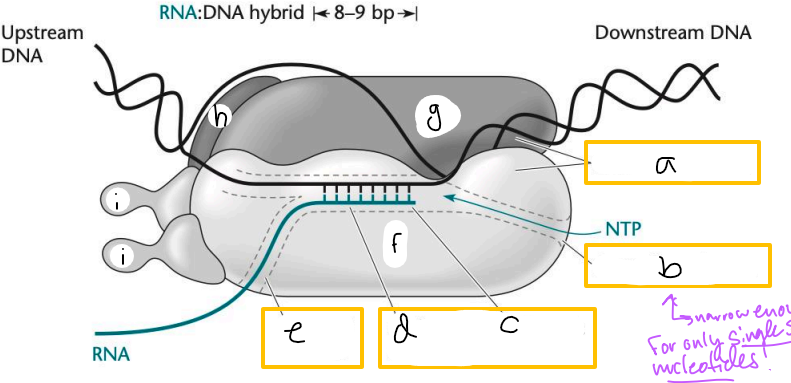
e? (TEC)
RNA exit channel
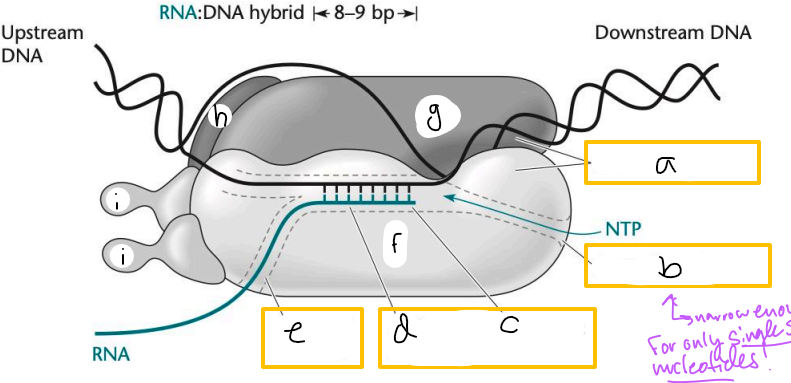
f? (TEC)
beta subunit
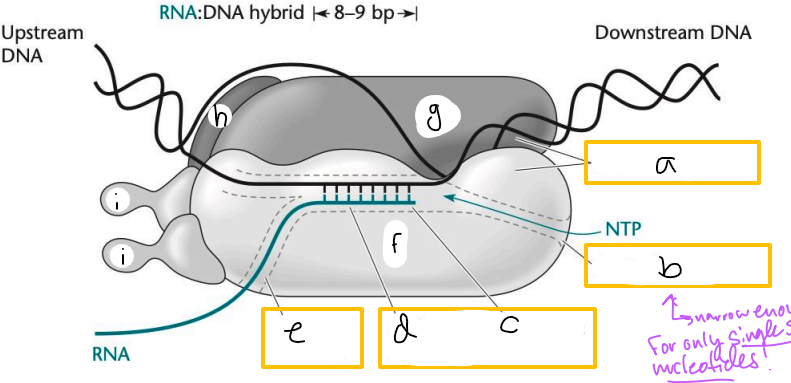
g? (TEC)
beta’ subunt
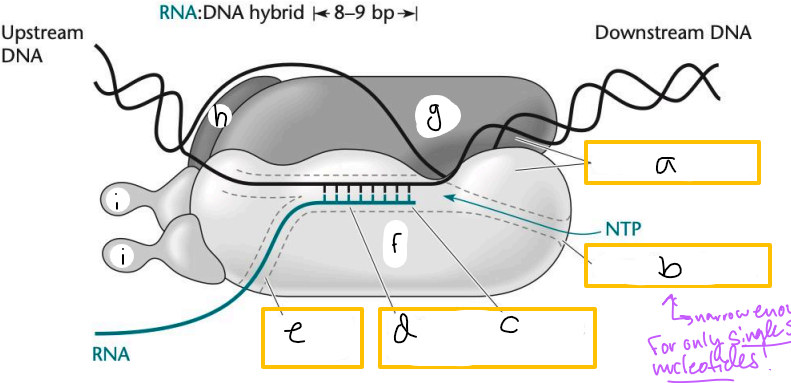
h? (TEC)
omega subunit
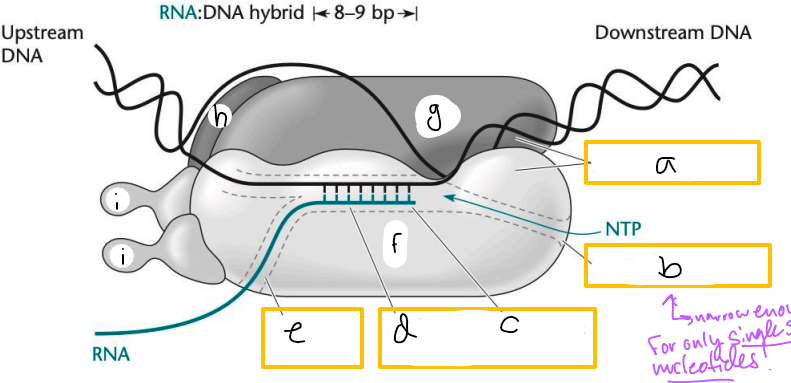
i’s? (TEC)
alpha subunits
Which strand is the template strand that RNAP creates a compliment of?
the 3’-5’ strand
Which strand is the RNA product identical to with U’s replacing T’s?
the coding strand (5’-3’)
Transcription - Step 3 - Termination
polymerization continues until RNAP encounters terminator region of DNA
RNAP pauses after transcribing string of Us
Inverted G-C repeats bind to each other and form hairpin
Hairpin causes RNAP to dissociate