MIDI Final
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
218 Terms
supine
left posterior oblique
left lateral decubitus
When looking at R kidney, what are the possible patient position options?
long axis, marker towards head
Probe orientation to view R kidney?
anterior axillary line
mid axillary line
mid clavicular line subcostal
What are the 3 possible acoustic windows to visualize the R kidney on US?
10th-12th
What approximate rib level is the probe at when viewing R kidney?
buildup of urine causes kidneys to swell/stretch
What is hydronephrosis?
anechoic "bear paw" with dilated calyces and renal pelvis
On US, how would the renal sinus appear in the setting of hydronephrosis?
potential space between liver and right kidney
What is Morrison's pouch?
curvilinear (can also use phased array)
What probe is used to visualize kidneys?
renal pyramids
The dots indicate:
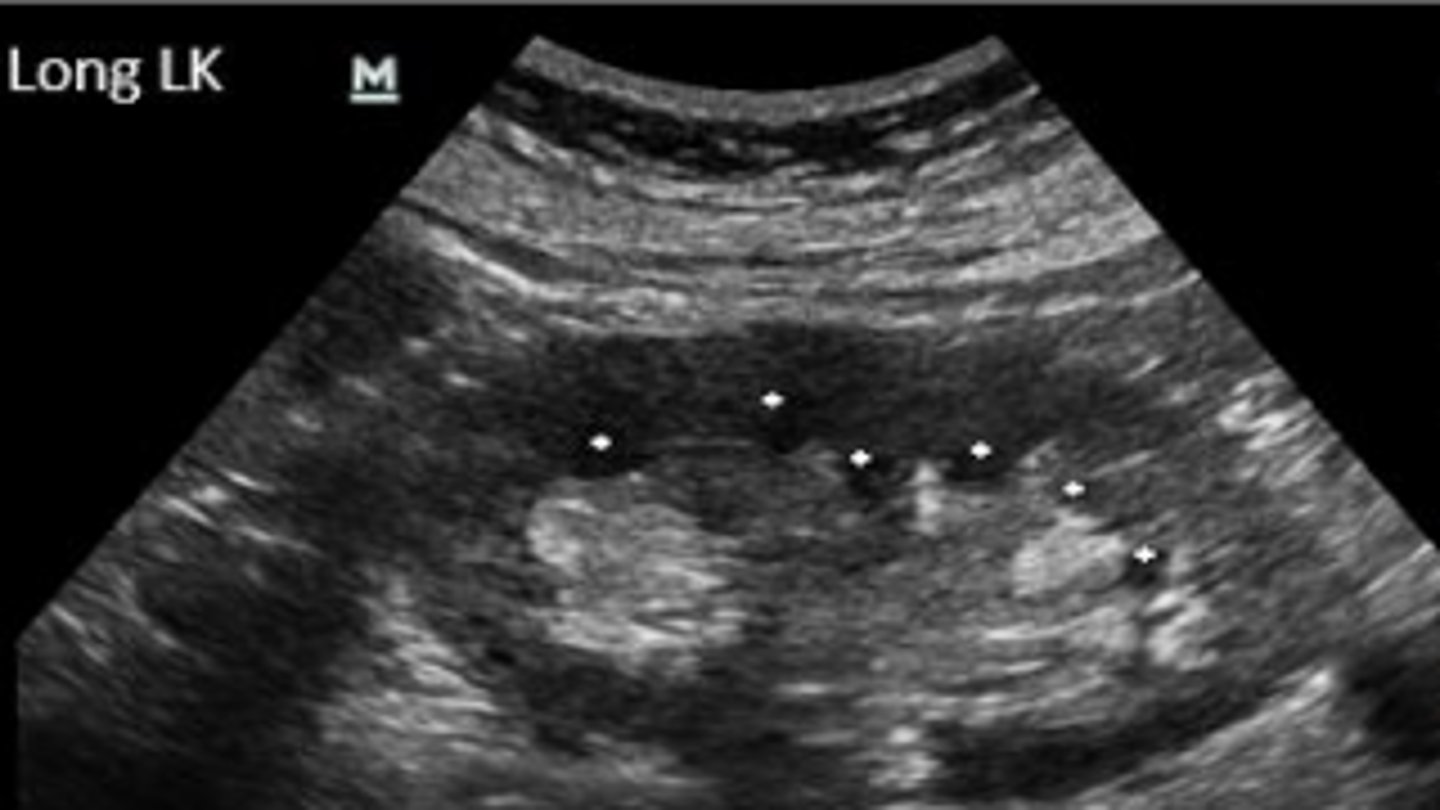
the ability of a surface to bounce back an echo, such as a sound wave in a medical ultrasound
What is echogenicity?
echogenicity --> aka less clear picture is indicative of disease
There is ________ of the renal cortex in medical renal disease
supine
right posterior oblique
right lateral decubitus
Possible patient positions to visualize left kidney?
posterior axillary line at approx 9th-11th rib
MC acoustic window to visualize the left kidney?
hydronephrosis --> dilated calicies and pelvis
What is seen here?
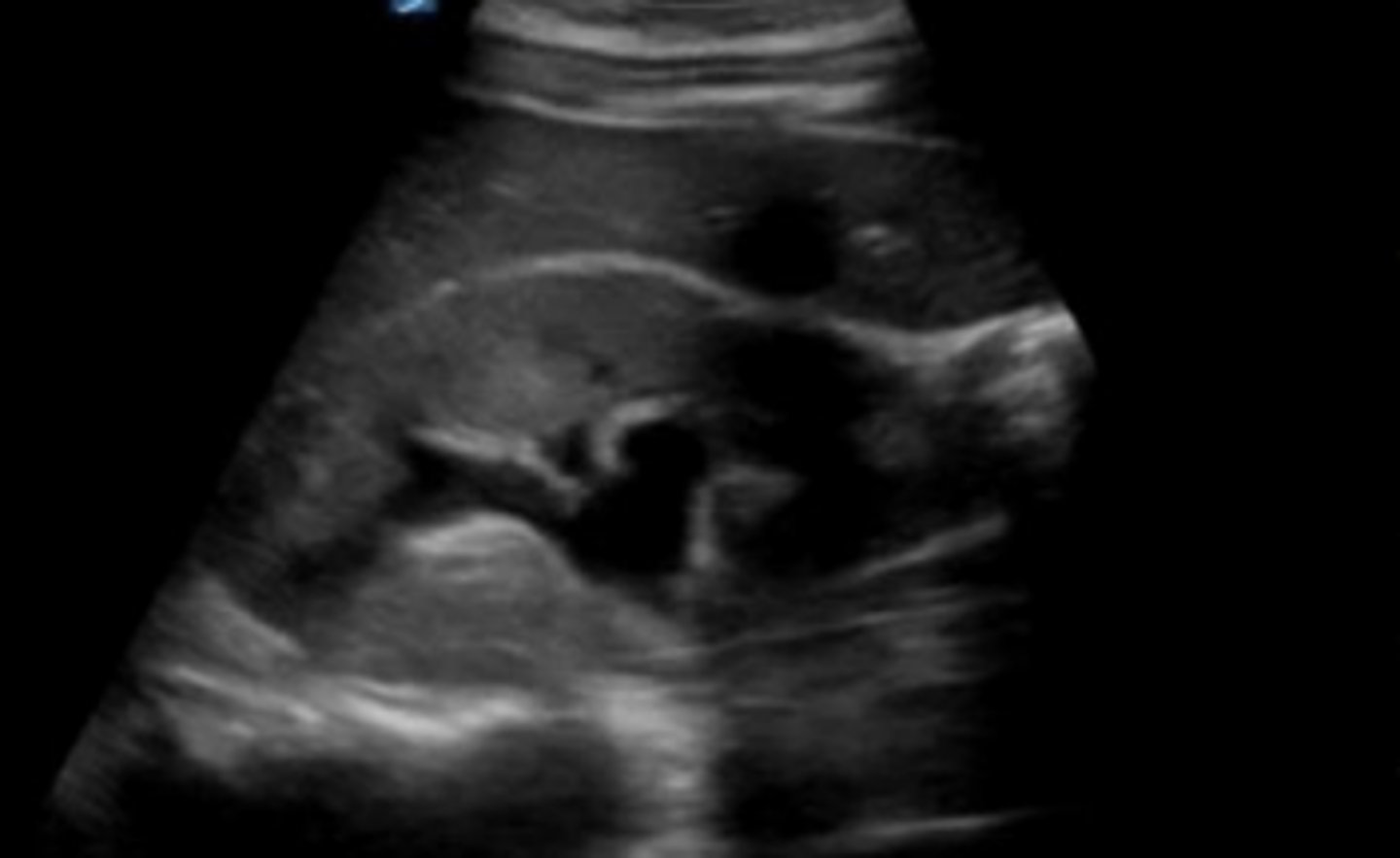
medical renal disease--> increased cortical echogenicity
What is seen here?
abdominal
What US setting is used to visualize the kidneys?
men; flank
Nephrolithiasis is more common in _______ and presents with ______ pain
calcium
75% of renal stones contain ______
uric acid
struvite
cysteine
Less commonly, renal stones contain: (3)
Non-contrast CT
DX standard of care to ID nephrolithiasis (non-pregnant patients)
IV pyelography
Before non-contrast CT, ______ was used to DX nephrolithiasis
degree
US allows us to quantify ________ of hydronephrosis
size
Hydronephrosis correlates with ______ of nephrolith
5 mm
A ______ nephrolith will pass spontaneously 90% of the time
8 mm
A ______ nephrolith will pass spontaneously 5% of the time
degree of hydronephrosis
POCUS can evaluate the size of the nephrolith based upon the ______________ and not the actual size of the stone (non-contrast CT can do this)
greater than 3 months
CKD is an abnormality of renal structure or function that lasts
HTN and diabetes
Most significant risk factors of CKD
pre-renal
intrinsic
post-renal
How is CKD classified?
decreased perfusion
Pre-renal CKS is related to
vascular disease or interstitial kidney disease
Intrinsic CKD is related to
obstruction
Post-renal CKD is related to
renal size
cortical echogenicity
parenchymal thickness
Most helpful tools in obtaining DX of CKD:
9-13 cm
Normal renal size
hyperechoic
A ________ cortex is associated with CKD
15-20 mm
Normal kidney thickness
curvilinear (can also use phased array)
What probe should be used to visualize the bladder?
supine
What position should the patient be in to view the bladder?
just above pubic symphysis
When visualizing the bladder, where should the probe be placed to start?
anechoic
Urine appears _______ on US
6 mm
Normal bladder thickness
posterior
The trigone area is the _______ aspect of the bladder
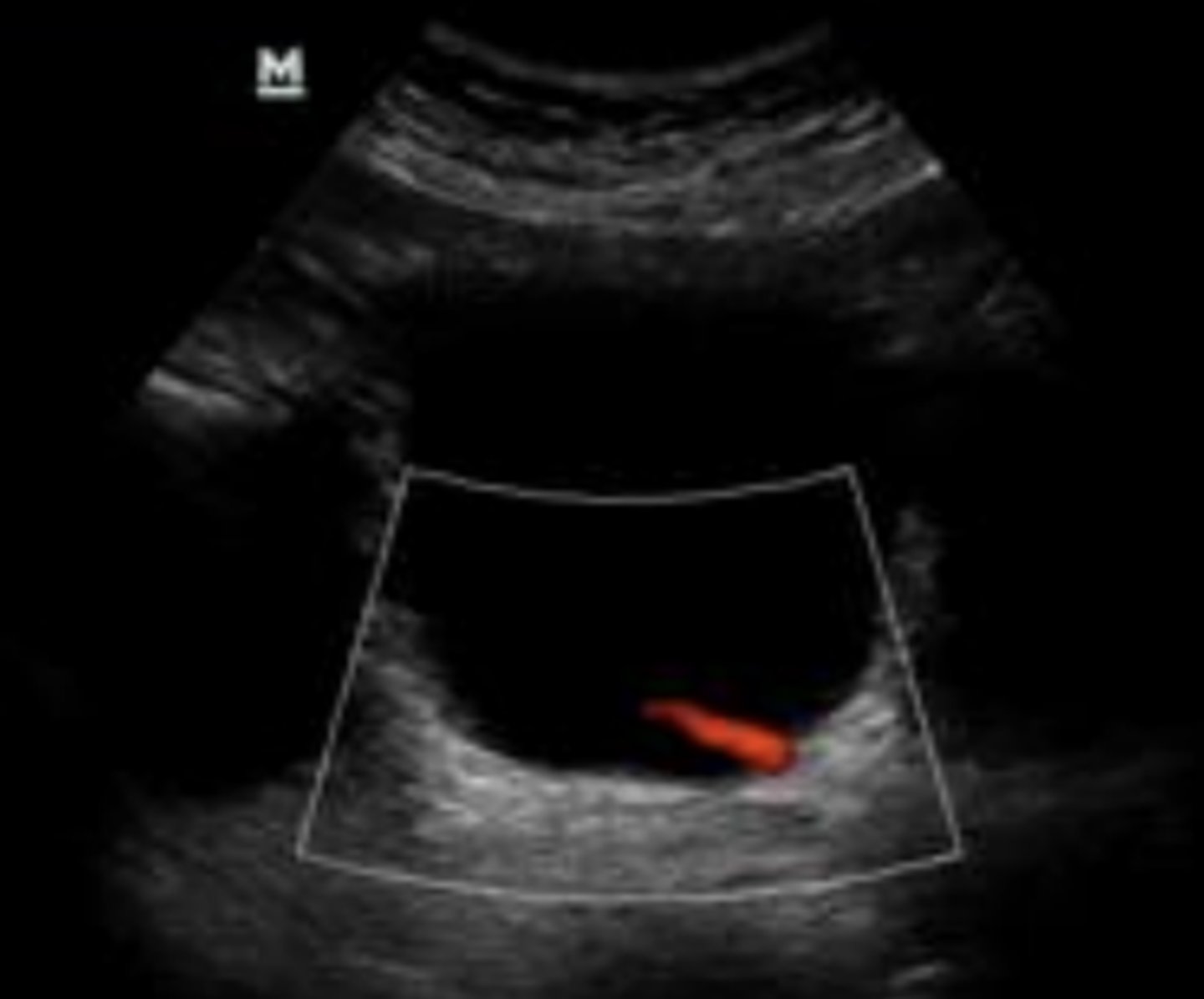
in; out
On color doppler, red indicates fluid moving _______ and blue indicates fluid moving ______
complete or partial obstruction of the ureter
In setting of hydronephrosis, observing urine jets may aid in determining:
rectouterine pouch
In females, what area in the pelvic region do we observe for free fluid?
rectovesical space
In males, what area in the pelvic region do we observe for free fluid?
left
This urine jet is coming from what ureter?
long axis subxiphoid
Where should the probe be oriented to observe the aorta?
posterior
The aorta passes _____ to the diaphragm
by major anterior branches --> celiac axis and SMA
How is the aorta differentiated from IVC in abdominal region?
proximal; distal
Diameter of aorta tapers from _____ to ______
anterior
The aorta appears more ____ when you move inferiorly
infrarenal
Abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA) are most often _______ in location
fusiform
Abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA) are most often _______ in morphology
>/= 3 cm
Abdominal aortic aneurysms are greater than ____ in diameter
celiac axis and its branches (hepatic and splenic arteries)
What is the seagull sign on US?
SMA and renal vessels
What can be visualized at level of pancreas?
distal aorta
Where do most AAAs occur?
AAA
What is seen here?
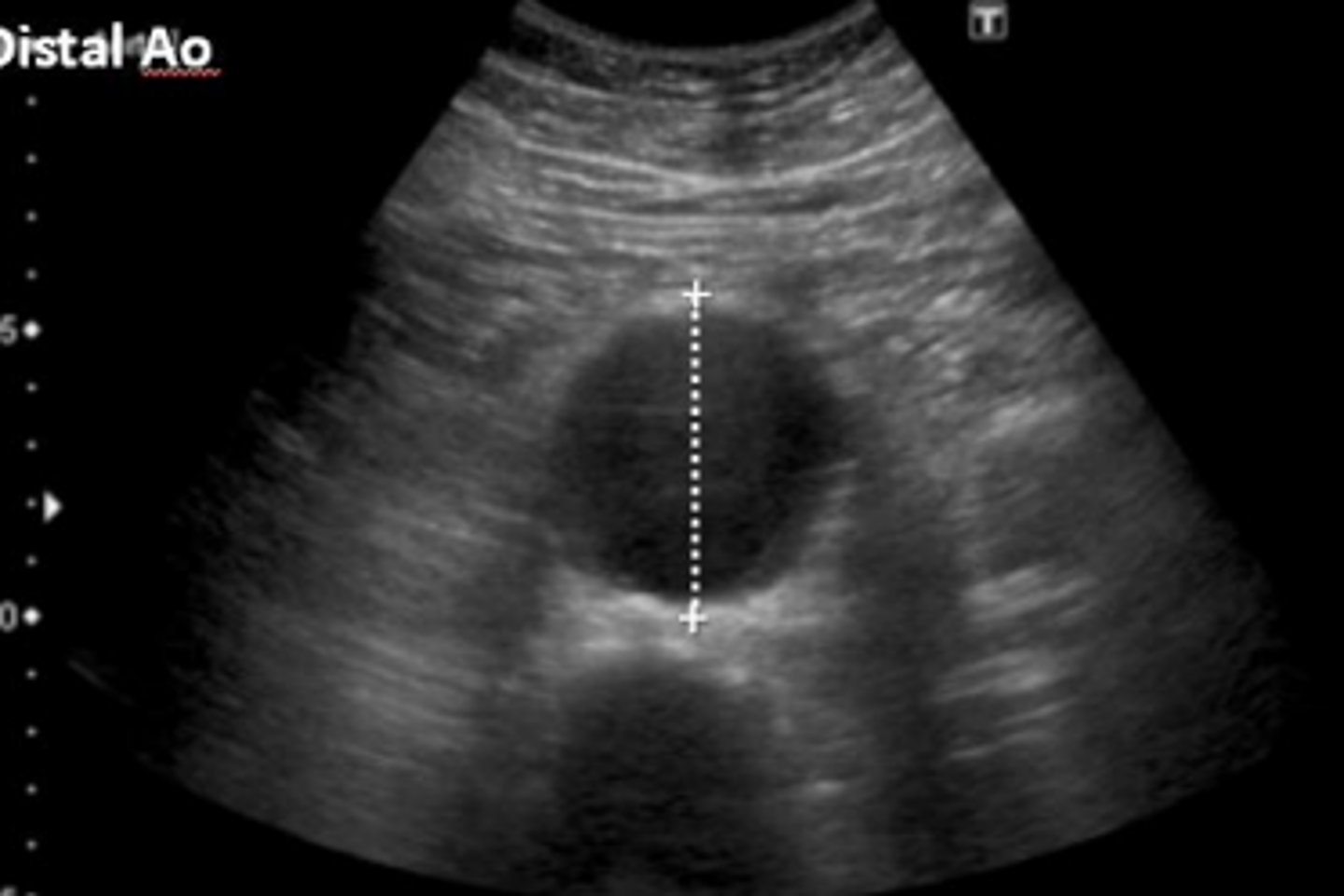
seagull sign
What can we observe in this image?
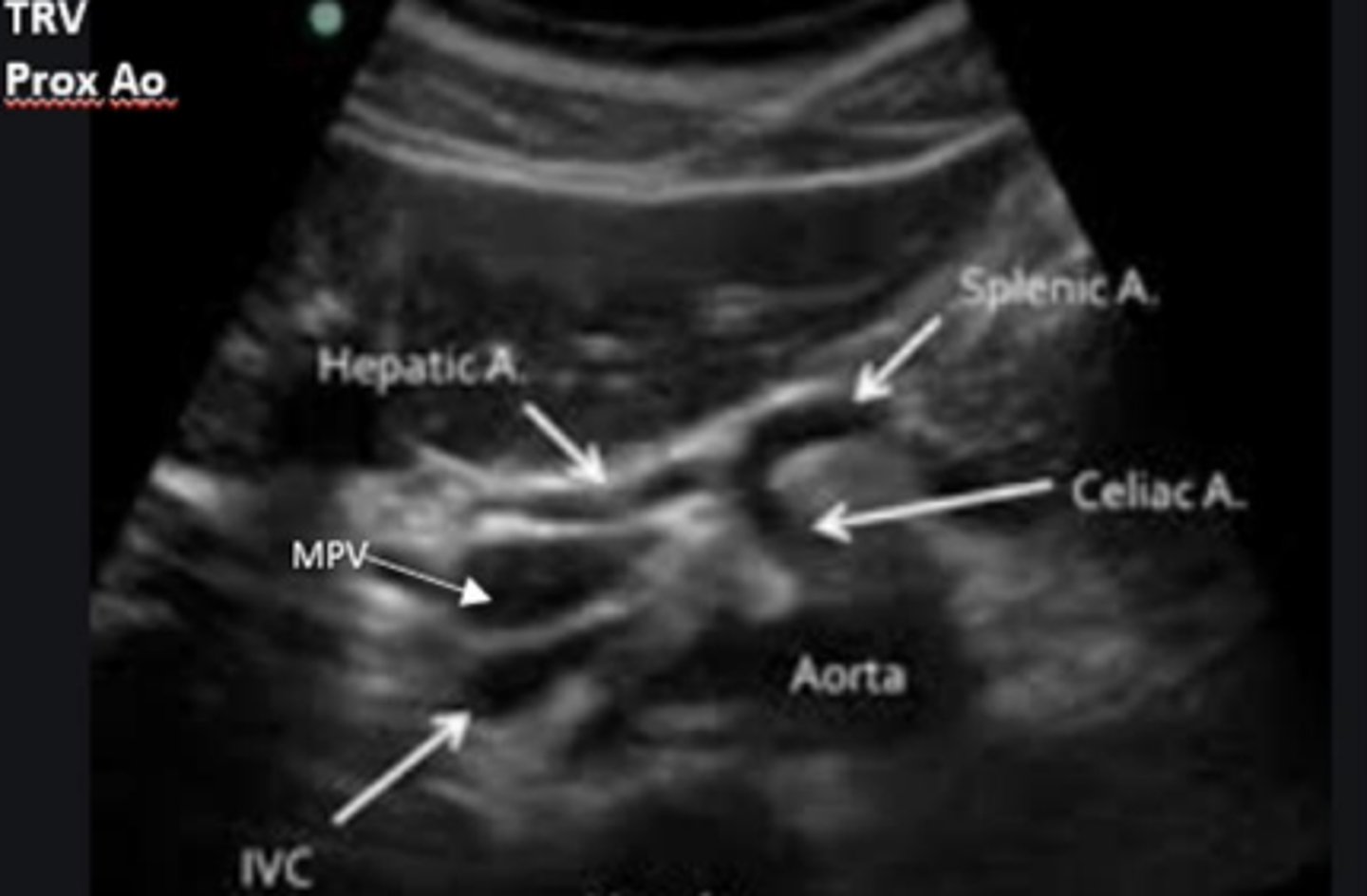
5th
Intrauterine pregnancy should be visible on transvaginal POCUS at the ______ week of gestation
fallopian tubes, caruna, ovary
Extrauterine/ectopic pregnancy can be present in:
sagittal view of empty uterus
MOst significant POCUS view to obtain DX of extrauterine pregnancy is:
systematic assessment of pelvis to ID location of implantation
If an extrauterine pregnancy is ID on US, what is the next step?
cysts and leiomyomas
What other things can be found on the ovaries in US?
transvaginal US
What is the gold standard for assessment of ovarian cysts?
dermoid cyst
cystadenoma
endometrioma
What are some of the potential classifications of ovarian cysts?
leiomyomas
What are the MC gynecological tumors in the world (present in 20-50% of women)?
transvaginal
Is transabdominal or transvaginal superior in cases involving pelvic pathology?
focal dilations of the aorta at least 50% larger than normal
AAAs are described as:
Smoking
HTN
hyperlipidemia
presence of CT disorder
What are risk factors for AAA?
smoking
Most significant RF of AAA?
aneurysmal rupture
What is the most serious complication of an AAA?
80-95%
Mortality of AAA rupture
patients that have never smoked
Screening for AAA category 1:
patients that smoke
Screening for AAA category 2:
men 65-75 years based on HX and other RF
When should category 1 patient's be screened for AAA?
no
Is it recommended to screen for AAA in female patients who have never smoked?
men 65-75
When should category 2 patients be screened for AAA?
no
Is it recommended to screen for AAA in female patients who have ever smoked?
size and rate of expansion
Monitoring of known AAA is based upon:
4,0-5.5 cm
What is considered a "small" AAA?
6-12 months; 5.5 cm
Small asymptomatic AAAs are followed every _________ until they reach ______
when it is greater than 5.5 cm in diameter
When is SX or endovascular repair of AAA indicated?
0.5 cm
AAA with growth rate of greater than ______ during a 6 month period should be treated DESPITE their size
emergently treated
All symptomatic AAAs should be:
When evaluating the heart in Parasternal Long Axis (PLAX) where should the probe marker be oriented?
Right shoulder
During US evaluation of the cardiac cycle, you observe the atrioventricular valves to be open. Which part of the cardiac cycle represent?
Diastole
During the evaluation of the Inferior Vena Cava (ICV) what is the proper orientation of the probe marker?
Head
How many chambers of the heart should be will be observed during evaluation with the Subxiphoid view?
4
What US preset can be used during Subxiphoid evaluation of the heart?
Abdominal
Which transducer is the most appropriate for US evaluation of the lungs and pleura?
Linear array
What is the proper probe marker position during Apical-4-Chamber cardiac view?
Left axilla
What transducer is most appropriate to obtain an adequate POCUS view of the heart?
Phased array
When evaluating the right lung / pleura in zone one (1) you do not observe the normal "sliding" motion. What should you do next?
Slide the transducer caudally to scan zone 2 on the right
Which ultrasound mode is required to evaluate the "Sandy Beach Sign" of normal sliding pleura?
M-Mode
When can an Intrauterine Pregnancy (IUP) first be recognized by transvaginal ultrasound?
5 weeks
What best describes the identification of urine in the bladder?
Anechoic
Which of the following is the most significant risk factor associated with the development of an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA)?
smoking
Which of the following patients would be the most appropriate to obtain AAA sonographic screening?
68-year-old female that smoked for 10 years
65-year-old-male that stopped smoking 10 years ago
75-year-old-male that has never smoked
70-year-old-female that currently smokes
65-year-old-male that stopped smoking 10 years ago