Arthropathies: Developmental Arthropathies (Cram)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Fill in the blank: Arthropathies are diseases of the _______ system that most often involve _______ deficits or functional disorders
musculoskeletal, motion
What are the two most common arthropathy disorders?
Skeletal disorders
Articular disorders
What are the six causes of arthropathies?
Developmental
Infectious (or septic)
Degenerative
Neoplasia
Trauma
Immune mediated
What are the five developmental arthropathies?
Aseptic necrosis of the femoral head
Hip dysplasia
Osteochondrosis
Patellar luxation
Elbow dysplasia
Another term for aseptic necrosis of the femoral head
Legg–Calve–Perthes disease
Does aseptic necrosis of the femoral head occur in larger or smaller breeds more commonly?
Smaller breeds are more common
Fill in the blank: Aseptic necrosis of the femoral head is associated with _______ (limited blood supply) and _______ necrosis of the bone
ischemia, avascular
True or false: Aseptic necrosis of the femoral head is often bilateral
True. It often effects both femoral heads
Name some clinical signs of aseptic necrosis of the femoral head
Hindlimb lameness, atrophy of thigh muscles, pain during manipulation of the hip joint
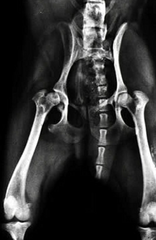
Why would you suspect aseptic necrosis of the femoral head on this radiograph?
Note: This radiograph is a unilateral case of aseptic necrosis of the femoral head
Irregular bone density, head fragmented, and shallow joint
What is the treatment for aseptic necrosis of the femoral head? It the prognosis good?
Surgical excision of the affected femoral head and neck. Prognosis is very good
Patellar luxation is a hereditary disorder in which three species?
Dogs
Cats
Horses
Fill in the blank: Patellar luxation is characterized by the ______ (in an abnormal position) development of the patella medial or lateral to the _______ _______ of the femur
ectopic, trochlear groove

What about this patient's hindlimbs indicate patellar luxation?
Bowed back legs
Do cats and small/miniature breeds typically have a medial luxation or a lateral luxation?
Medial luxation
Do large dogs typically have a medial luxation or lateral luxation?
Lateral luxation
What grade of patellar luxation is this: The dog experiences infrequent episodes of the patella slipping out of place. It goes back on its own
Grade I
What grade of patellar luxation is this: When the joint is flexed, the patella luxates out
Grade II
What grade of patellar luxation is this: The patella is more often out of the trochlear groove than in the trochlear groove. The patella can be helped back into the groove with assistance
Grade III
What grade of patellar luxation is this: The patella cannot be manipulated back into the trochlear groove, or can be with a lot of difficulty
Grade IV
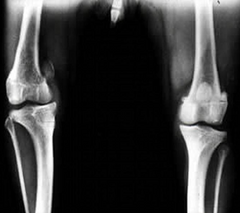
Is this a medial or lateral patellar luxation?
Medial patellar luxation
True or false: Patellar luxation happens because the patella was is too big to fit in the trochlear groove
False: A shallow trochlear groove is a factor. But it happens because the ligament is pulling the patella to the medial or lateral aspect of the leg
True or false: Patellar luxation is often treated with surgery, and the prognosis is good in mild or moderately affected animals
True. The surgeries involve deepening the trochlear groove, fascial releasing incisions, joint capsule imbrication, etc.
What structure in the legs tends to get damaged due to increased weight bearing because of a patellar luxation?
Note: Or medial meniscal injuries
Cruciate ligament
True or false: Cats are less severely affected by patellar luxation than dogs. They have a better prognosis
True
Abnormal endochondral ossification of epiphyseal cartilage
Osteochondrosis
Name some predisposing factors for osteochondrosis
Large/giant dog breed, excessive nutrition, rapid growth, trauma, and hereditary
Term for osteochondrosis that involves cartilage cracks, fissures, and flaps
Osteochondrosis dissecans
Fill in the blank: Osteochondrosis involves ______–itis, _____–itis, and _____ breakdown
synov, arthr, cartilage
Name some clinical signs of osteochondrosis
Lameness, effusion, and reduced range of motion
What class of drugs is frequently used to treat inflammation associated with osteochondrosis?
Note: Other treatment options include surgical, joint fluid modifiers, and hyaluronic acid
NSAIDS
What is the brand name of a very commonly used monthly joint fluid modifier?
Note: Generic is pentosan polysulfate
Cartrophen Vet®
Are horses more or less likely to recieve surgical treatment for osteochondrosis than small animals?
Horses are more likely to get surgical treatment, small animals are more likely to get drug therapies
Condition that effects young, large breed, rapidly growing dogs. It involves an ununited anconeal process
Elbow dysplasia
What are the three kinds of elbow dysplasisa?
Ununited anconeal process
Fragmentation of the medial coronoid process
Osteochondrosis of the medial humeral condyle
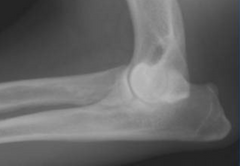
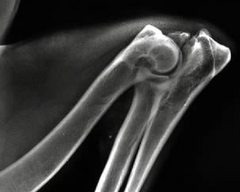
Circle the area of this radiograph that indicates elbow dysplasia. What kind of elbow dysplasia is it?
This is fragmentation of the medial coronoid process
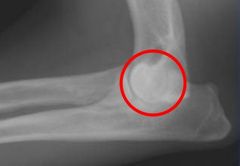
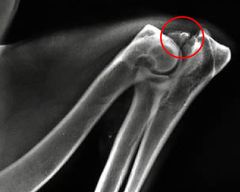
Circle the area of this radiograph that indicates elbow dysplasia. What kind of elbow dysplasia is it?
This is an united anconeal process
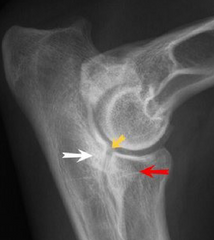
True or false: The lameness associated with elbow dysplasia is often easier to detect than lameness associated with hip dysplasia
False. The lameness assoiated with elbow dysplasia is harder to detect
You see this on a radiograph of a dog with fragmentation of the medial coronoid process. Can it be taken into surgery?
Once the bones have fractured to this extent, the integrity of the bone is comprimised and surgery is hard to preform. Early surgery is best in elbow dysplasia cases
Fill in the blank: Prognosis after surgery for elbow dysplasia is good if ______ ______ disease has not developed in the joint
degenerative joint
Conditont of abnormal development of the coxofemoral joint in large dogs
Hip dysplasia
A dog with hip dysplasia is said to sometime have what kind of gait?
Bunny–hopping
What is a common method of measuring the risk of hip dysplasia in dogs? It measures joint laxity and determines the risk of degenerative joint disease
Penn hip
What are some treatments for mild/nonsurgical hip dysplasia candidates?
Weight loss, restricted exercise on hard surfaces, physical therapy, NSAIDS, joint fluid modifiers