9 - histogenesis of dental pulp - origin and development. development of the dental papilla - cells, blood vessels and nerves. Anatomy of dental pulp
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
origin of dental pulp
derived from mesenchyme and ectomesenchyme
development of dental pulp
beginning of pulp histogenesis is at the bud stage of the tooth and the end is at the completion of the tooth root
The pulp chamber narrows with deposition of dentin and finally forms a canal containing blood vessels and nerves of the tooth
cells involved in the development of the dental papilla
odontoblasts
fibroblasts
undifferentiated mesenchymal cells
immunocompetent cells
odontoblast in development of dental papilla
outermost part of pulp is a layer of odontoblasts
they form single layer, with cell body in pulp and long cytoplasmic odontoblastic processes extending into the dentinal tubules
fibroblasts in development of dental papilla
most numerous connective tissue cells in the pulp
can synthesise and maintain connective tissue matrix
main function in pulp is to synthesise type 1 and 3 collagen
undifferentiated mesenchymal cells in development of dental papilla
distributed throughout the cell rich zone and pulp core, they are stellate shaped cells
after receiving stimuli they can give rise to fibroblasts or to odontoblasts
immunocompetent cells in development of dental papilla
these cells are recruited from bloodstream
are an active participant in host defence (lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils, plasma cells and mast cells)
blood vessels role in pulp
it is microcirculatory system due to lack of true arteries and veins
Largest vessels observed in pulp are arterioles and venules
Pulpal blood flow is more rapid than in most areas in body
Pulpal pressure is amongst highest of all tissues
Walls of pulpal vessels are very thin as the pulp is protected by a hard underlying sheath of dentin
One or more small arterioles enter the pulp via apical foramen and ascend through radicular pulp of root canal, once they reach the pulp chamber they branch out peripherally to form a dense capillary layer
Circulatory system of pulp has a number of structures regulating amount of blood recquired for its function
Such as sphincters, shunts or arterio-venous anastomoses, collaterals, fenestrated capillaries and microcirculatory system
TA - terminal arterioles
PC precapillary sphincters
PCV - postcapillary venules
AVA - arterio-venous anastomoses
LC - lymphatic capillaries
what are some structures of the circulatory system that help regulate the amount of blood required for the functions of the pulp?
Such as sphincters, shunts or arterio-venous anastomoses, collaterals, fenestrated capillaries and microcirculatory system
why are the walls of pulpal vessels very thin?
as the pulp is protected by a hard underlying sheath of dentin
is pulpal pressure amongst the lowest or highest of all tissues ?
amongst the highest
is pulpal blood flow more or less rapid than that in most areas of the body?
more rapid
what is the primary function of the blood vessels ?
Primary function - regulate local interstitial environment via transport of hormones, nutrients, gases and removal of metabolic waste products
what are the largest vessels observed in pulp?
arterioles and venules
Nerves in development of dental papilla
enter pulp via apical foramen along with afferent blood vessels and form a neurovascular bundle
Once in pulp chamber they ascend through radicular pulp of root canal, once they reach the pulp chamber they branch out
Each nerve fibre may provide at least 8 terminal branches forming a plexus known as plexus of Raschkow
The nerve entering the pulp consists of sensory afferents of the trigeminal nerve and sympathetic branches
Delta fibres - unmyelinated fast conducting are associated with a sharp localised pain
Myelinated fibres - slower in conducting and are associated with a dull diffuse pain
what is the sensory afferents nerves that enter the pulp?
Delta fibres - unmyelinated fast conducting are associated with a sharp localised pain
Myelinated fibres - slower in conducting and are associated with a dull diffuse pain
how do nerves enter the pulp?
enter pulp via apical foramen along with afferent blood vessels and form a neurovascular bundle
anatomy of dental pulp
dental pulp in crown is surrounded by hard shell made of enamel and dentin and in root - by dentin and cementum
pulp has a peripheral and central zone: peripheral zone consists mainly of cells - odontoblasts and fibroblasts, as well as the peripheral branches of vessels and nerves
Central zone mainly contains arteries, veins, nerves, collagen fibers located from the apex to the periphery of the pulp
anatomically, the pulp is divided into coronal and radicular
anatomically what is the pulp divided into?
coronal and radicular
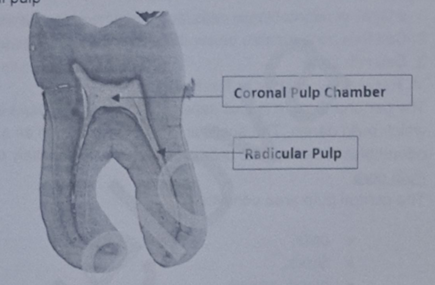
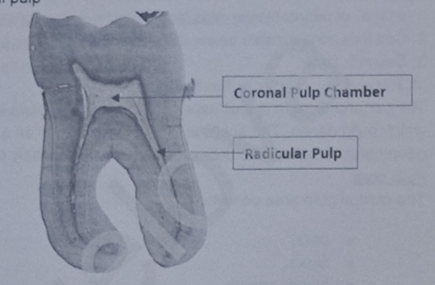
describe the coronal and radicular pulp
coronal pulp - larger and contains many more elements than root pulp
Radicular pulp - acts as a conducting tube to carry blood to and from the coronal area to the apical canal
Both pulpal areas contain the same elements although the cells, fibres, blood vessels and nerves are more numerous in coronal pulp
what are the zones of the pulp/
pulp has a peripheral and central zone:
peripheral zone consists mainly of cells - odontoblasts and fibroblasts, as well as the peripheral branches of vessels and nerves
Central zone mainly contains arteries, veins, nerves, collagen fibers located from the apex to the periphery of the pulp