162_Lesson 1: To Err is Human
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Patient Safety
A framework of organized activities that creates cultures, processes, procedures, behaviors, technologies and environments in health care that consistently and sustainably lower risks, reduce the occurrence of avoidable harm, make errors less likely and reduce the impact of harm when it does occur
Patient safety
Practices that reduce the risk of adverse events related to exposure to medical care across a range of diagnosis or conditions
Patient safety
A discipline in the healthcare professions that applies safety science methods towards the goal of achieving a trustworthy system of healthcare delivery
C. Both statements are true.
I. In healthcare, mistakes can happen because healthcare workers are human, but mistakes are serious in this field because they can harm patients.
II. Patients expect high-quality care, and it’s their right to receive it.
A. The first statement is true. The second statement is false.
B. The first statement is false. The second statement is true.
C. Both statements are true.
D. Both statements are false
there must be a culture of safety and policies and guidelines to enable this.
Humans are bound to make mistakes. However, when tackling patient safety, we must reduce the risk of errors. How can we achieve this?
Patient safety
Patient safety is an overarching definition different safety problems in a healthcare institution. It may include patient diagnosis, bedside care, surgical procedures, medication safety, etc.
freedom from accidental injury
C. Both statements are true.
I. Safety in healthcare means protecting patients at every level of the system.
II. If safety fails at any level, it can create a "hole" in the system, leading to errors and potentially harming patients.
A. The first statement is true. The second statement is false.
B. The first statement is false. The second statement is true.
C. Both statements are true.
D. Both statements are false
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
AHRQ?
Using scientific methods to create reliable healthcare systems.
Reducing the number of harmful events.
Helping patients recover quickly when adverse events happen.
According to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), patient safety is a healthcare discipline focused on: [3] ?
Temporary injury
Permanent injury
Two types of harm
Harm
any physical or psychological injury that damages health of person that can be temporary or permanent
Healthcare quality
What goes hand in hand when we talk about patient safety?
SEPTEE
Safe
Effective
Patient-centered
Timely
Efficient
Equitable
Provided by AHRQ. It should be present at all levels:
🔉 Microlevel - Interprofessional and intraprofessional teams
🔉 Mesolevel - institutional (are there adequate policies for patient safety)
🔉 Macrolevel - National Safety Program
Domains of Healthcare Quality [6]
Safe
[Domains of Healthcare Quality]
avoiding harm to patients from the care that is intended to help them
Effective
There should be no underuse or misuse of health care services
[Domains of Healthcare Quality]
providing services based on scientific knowledge to all who could benefit and refraining from providing services to those not likely to benefit
Patient-centered
[Domains of Healthcare Quality]
providing care that is respectful of and responsive to individual patient preferences, needs, and values and ensuring that patient values guide all clinical decisions
Timely
In other countries that already implement the UHC and free-for-all healthcare, kahit maliit lang na sakit pupunta na sila. Because of this, masyadong marami pupunta so mahirap na magset ng consultation, so considering the wait time is important.
[Domains of Healthcare Quality]
reducing waits and sometimes harmful delays for both those who receive and those who give care
Efficient
Kaya gumagawa ng mga CQI(Continuous Quality Improvement) when we talk about healthcare quality.
[Domains of Healthcare Quality]
avoiding waste, including waste of equipment, supplies, ideas and energy
Equitable
[Domains of Healthcare Quality]
providing care that does not vary in quality because of personal characteristics such as gender, ethnicity, geographic location and socioeconomic status
Engage patients and families as partners in safe care
Achieve results through collaborative working
Translate evidence into actionable and measurable improvement
Base policies and action on the nature of the care setting
Use both scientific expertise and patient experience to improve safety
Instill a safety culture in the design and delivery of health care
Ex. we have healthcare teams that work interprofessionally
🔉 It shud not always be the doctor who is leading the team. There can be different people who will. It shud be built into the culture.
🔉 There are times where healthcare professionals (HCPs) work for long hours, would they still be able to do their work properly? How can we correct the problem?
Ex. Medical interns - from 72hrs to 36hrs.
🔉 We are waiting for associations to do smth about it coz it really is a problem
Ex. While counseling patients, we may fall asleep from the lack of it
🔉 Overall, it will affect how we treat our patients
Global Patient Safety Action Plan 2021-2030
Guiding principles of implementation: [6]
False.
Leadership can vary among healthcare individuals.
[T/F] It’s always the doctor who’ll lead during interprofessional collaboration of HCPs.
Governments
Health care facilities and services
Stakeholders
Global Patient Safety Action Plan 2021-2030
Key delivery partners [3]
Governments
Ex. Antimicrobial stewardship programme (AMS programme) used to be just hospital base but now it is required in the LGUs since there are primary health care facilities there
[Global Patient Safety Action Plan 2021-2030 - Key Delivery Partners]
Ministries of health and their executive agencies at both national and subnational levels, legislative institutions, other concerned ministries, and regulatory bodies?
Health care facilities and services
Hospital are required to have patient safety programs and their respective patient safety health officers
These patient safety programs need to create projects based on the problems (medications, etc.) that will correct them
[Global Patient Safety Action Plan 2021-2030 - Key Delivery Partners]
All health care facilities ranging from primary health centers to large teaching hospitals, irrespective of ownership and scope of services
Stakeholders
UPM has a biannual patient safety congress and opens it to other institutions about the projects that can apply to their institutions to solve their problems + make other hospitals talk about their programs to share their ideas
Other than that, the education is also improving by having this as a separate subject 🔉 Ex. patient safety was just part of dispensing but now it is integrated into the curriculum + equip students with this knowledge so it can be used further in their education and internships.
[Global Patient Safety Action Plan 2021-2030 - Key Delivery Partners]
Nongovernmental organizations, patients and patient organizations, professional bodies and scientific associations and societies, academic and research institutions and civil society organizations
1. Make zero avoidable harm to patients a state of mind and rule of engagement in the planning and delivery of health care everywhere.
HCPs learn to be mindful of their actions, instead of saying it’s alright to make a mistake. They shud know that patients shud be treated in a proper way
🔉 In terms of institutions and planning, there are the US Institute of Medicine (IOM) and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ)
🔉 There are also orgs who grade the patient safety of institutions based on indicators
🔉 AHRQ - also has monitoring forms for internal audits to measure the effectiveness of their patient safety programs
2. Build high-reliability health systems and health organizations that protect patients daily from harm.
Dito pumapasok yung quality improvement, system perspectives and design
3. Assure the safety of every clinical process.
Ex. If there is a Cardiotocography (CTG) that can be used, it shud be used
4. Engage and empower patients and families to help and support the journey to safer health care
5. Inspire, educate, skill and protect every health worker to contribute to the design and delivery of safe care systems.
6. Ensure a constant flow of information and knowledge to drive mitigation of risk, reduction in levels of avoidable harm and improvements in the safety of care.
7. Develop and sustain multisectoral and multinational synergy, partnership and solidarity to improve patient safety and quality of care.
Global Patient Safety Action Plan 2021-2030
Strategic objectives [7]
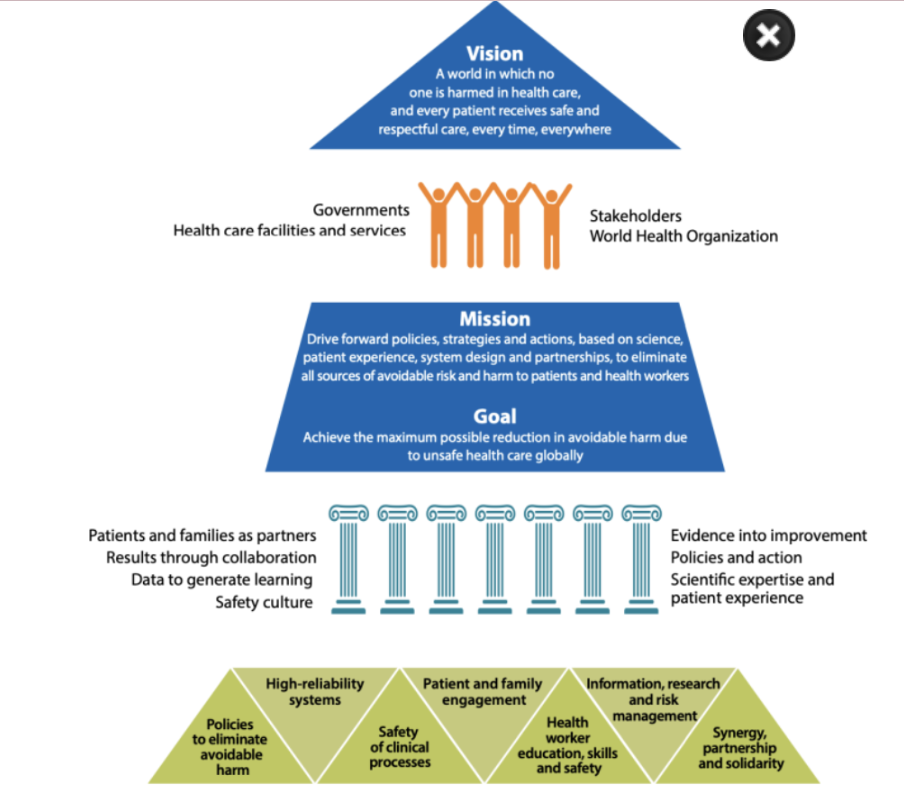
Global Patient Safety Action Plan 2021-2030
1. Promotion of culture of safety through operational and managerial strategies
2. Assessment of the nature and scale of adverse events
There are lists of indicators that they collect from health facilities, example is the number of adverse events
3. Training and capacity building of health workforce sensitive to patient safety
All training are toward creating a better patient safety program
4. Prevention and control of healthcare-associated infection
In the PH, there are lots of healthcare-associated infections, with HAIs being the primary reason why they die
This has to be controlled through continuous quality improvement, but there are not much as of this current time
5. Implementation of key priority areas (patient identification protocols, effective communication, fall prevention, medication safety, safe surgical care, blood safety, safe childbirth, and safe injections)
6. Prioritization, promotion and facilitation of patient safety research
Only ONE (1) research for patient safety has been conducted by the DOH; more to come with future data and collaboration with DOST
National Policy on Patient Safety in HFs [6]
errors can lead to significant harm or death, making immediate attention and prevention crucial. The rapid identification and mitigation of risks help protect patients and uphold trust in healthcare systems. Ensuring safety is essential to prevent cascading impacts on both patients and healthcare providers.
Why is patient safety considered a medical emergency?
(from worksheet 1)
Clinically, medical errors can result in severe the financial burden on healthcare systems.
Patient harm, prolonged hospital stays, disability, or death.
Economically, they increase healthcare costs through extended care, additional treatments, legal liabilities, and loss of patient trust. Preventing errors not only improves patient outcomes but also reduces the financial burden on healthcare systems.
Explain the clinical and economic effects of medical errors based on the film.
(from worksheet 1)
The Swiss Cheese Model illustrates that errors occur when weaknesses in multiple layers of defense align, creating a pathway for harm. By identifying and strengthening each layer (e.g., protocols, training, communication), organizations can reduce vulnerabilities. Continuous feedback and addressing gaps in the system help prevent adverse events.
Explain how the Swiss Cheese Model (SCM) can be utilized in preventing errors.
(from worksheet 1)
Medication Reconciliation: Pharmacists can review patients' medication histories during transitions of care to prevent errors like duplication or contraindications.
Interprofessional Collaboration: Healthcare teams, including nurses and physicians, can use standardized communication tools (e.g., SBAR) to ensure accurate information sharing and timely interventions.
How can pharmacists and other health care professionals work to minimize preventable harm? Provide at least two (2) concrete examples.
Patient safety initiatives such as testing medical students and healthcare professionals through simulations will help healthcare professionals to remember and be alert in identifying the errors that can take place in patient care. For example, the implication of the Doom Room is a way for medical students and healthcare professionals to study and fully prepare themselves by utilizing active recall, in which the trainees can spot their mistakes and try to improve themselves once more.
Choose and research on one of the patient safety initiatives discussed in the film and explain how it can improve health care quality.
(from worksheet 1)
Degree of harm
the severity and duration of harm, and any treatment implications, that result from an incident.
Error
failure to carry out a planned action as intended or application of an incorrect plan
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
an approach that seeks to find and identify possible failures in the system and implement strategies to prevent the failures from occurring
Adverse event
an incident that resulted in harm to a patient
Incident
An event or occurrence that may cause or causes an interruption or a crisis. In safety, an incident of workplace illness or injury.
Incident reporting
collecting and analysing information about an event that could have harmed or did harm a patient in a health-care setting.
Patient safety
: the reduction of risk of unnecessary harm associated with health care to an acceptable minimum
Quality of care
degree to which health services for individuals and populations increase the likelihood of desired health outcomes.
Risk
: the probability that an incident will occur