Theory (4.2 types of trade protection)
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What are the reasons for implementing a tariff?
Protecting Domestic Industries: By making foreign goods more expensive, tariffs encourage consumers to buy local products.
Generating Government Revenue: Tariffs provide a source of income for governments, especially in developing countries.
Reducing Trade Deficits: By discouraging imports, tariffs can help balance a country's trade by reducing the gap between imports and exports.
National Security: Protecting industries vital to national security, such as defense or technology.
Stakeholder impacts of a Tariff
Domestic producers are better off as they sell a higher quantity (Q3) and a a higher price (Pw+t)
Consumers are worse off as they pay a higher price (Pw+T) for a lower quantity (Q4). They also have fewer choices due to less imports.
Forgein producers are worse off as they sell at a lower quantity at the same price) and loses market shares to domestic producers.
Government earns tax revenue of Tx(Q4-Q3)
Total welfare decreases as more units are being produced by the relatively inefficient producers and consumers must pay a higher price while consuming a lower quantity (consumption reduces/inefficiency ersists due to reduced competition).
Why might a quota be implemented?
To protect domestic industries from foreign competition
To preserve jobs in specific sectors
To reduce reliance on foreign goods
To improve the trade balance by limiting imports
Stake holder impacts of a quota
Domestic producers are better off as they sell a higher quantity and at a higher price.
Consumers are worse off as they pay a higher price and consume a lower quantity.
Foreign producers may generate higher or lower sales revenues depending on the PED, PES, and the size of the quota.
The government does not earn any revenue.
Total welfare decreases. More units of products are being produced by the relatively inefficient producers, and consumers must pay a higher price while consuming a lower quantity.
Why might a subsidy be implemented?
National Security: Protecting vital industries (e.g., steel, agriculture).
Employment: Maintaining jobs in key sectors.
Infant Industry Protection: Supporting emerging industries until they become competitive.
Stake holder impact of a subsidy
Domestic producers are better off as they sell a higher quantity (Q3) and receive a higher price (Pw+sub).
Consumers are unaffected by the subsidy as they still pay Pw and consume Q2 units.
Foreign producers generate lower sales revenues due to falling exports (Q2"–"Q3).
The government/taxpayers must pay for the subsidy ((Pw+sub – Pw) × Q3).
Total welfare decreases. More units are being produced by the relatively inefficient producers, leading to a misallocation of resources.
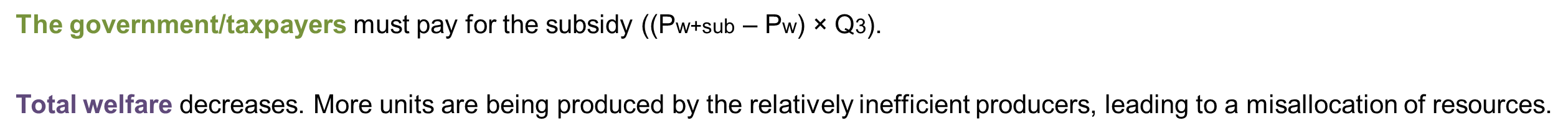
Negative effects of a subsidy
Resource Misallocation: Encouraging production in less efficient industries.
Opportunity Cost: Government funds could be used for education, healthcare, etc.
Trade Distortions: Unfair competition in international markets.
Examples of administrative barriers
EMBARGOES AND EXCHANGE CONTROLS along with:
Product Standards: Requirements for safety, quality, or environmental impact.
Licensing and Permits: Importers must obtain special permissions, often limited in number.
Customs Procedures: Lengthy inspections or documentation requirements that delay imports.
Labeling Requirements: Specific rules about how products must be labeled, such as language or content disclosures.
Effects on different stake holders for different
Domestic Producers
Increased Protection: Local firms benefit from reduced foreign competition, allowing them to capture a larger market share.
Potential Inefficiency: However, without competition, domestic firms may lack incentives to innovate or improve efficiency.
Foreign Producers
Higher Costs: Complying with additional regulations increases production and administrative costs.
Market Access Challenges: Some foreign firms may be unable or unwilling to meet the standards, losing access to the market entirely.
Disadvantages of administrative barriers
Higher Consumer Costs: Prices may rise due to increased production costs or reduced competition.
Inefficiency: Domestic firms may become complacent without foreign competition.
Trade Tensions: Other countries may retaliate with their own barriers.
Advantages of administrative barrier
Consumer Protection: Ensures imported goods meet safety and quality standards.
Environmental Benefits: Regulations can promote sustainable practices.
Support for Domestic Industries: Protects jobs and local businesses from foreign competition.