Human Reproduction
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Spermatogenesis + where
Sperm production + seminiferous tubules in testes
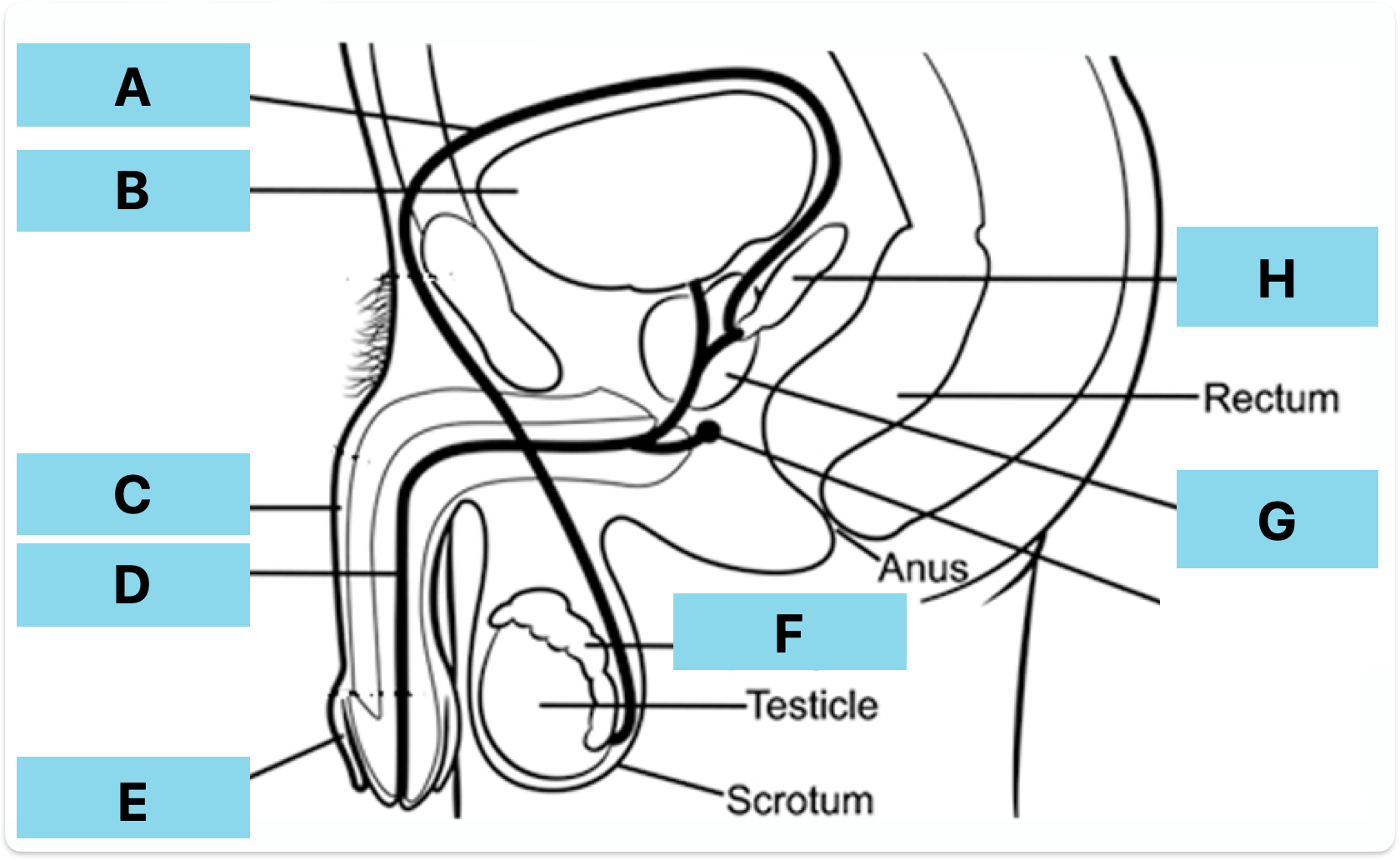
Label A-H
Vas deferens
Bladder
Penis
Urethra
Foreskin
Epididymis
Prostate gland
Seminal vesicle
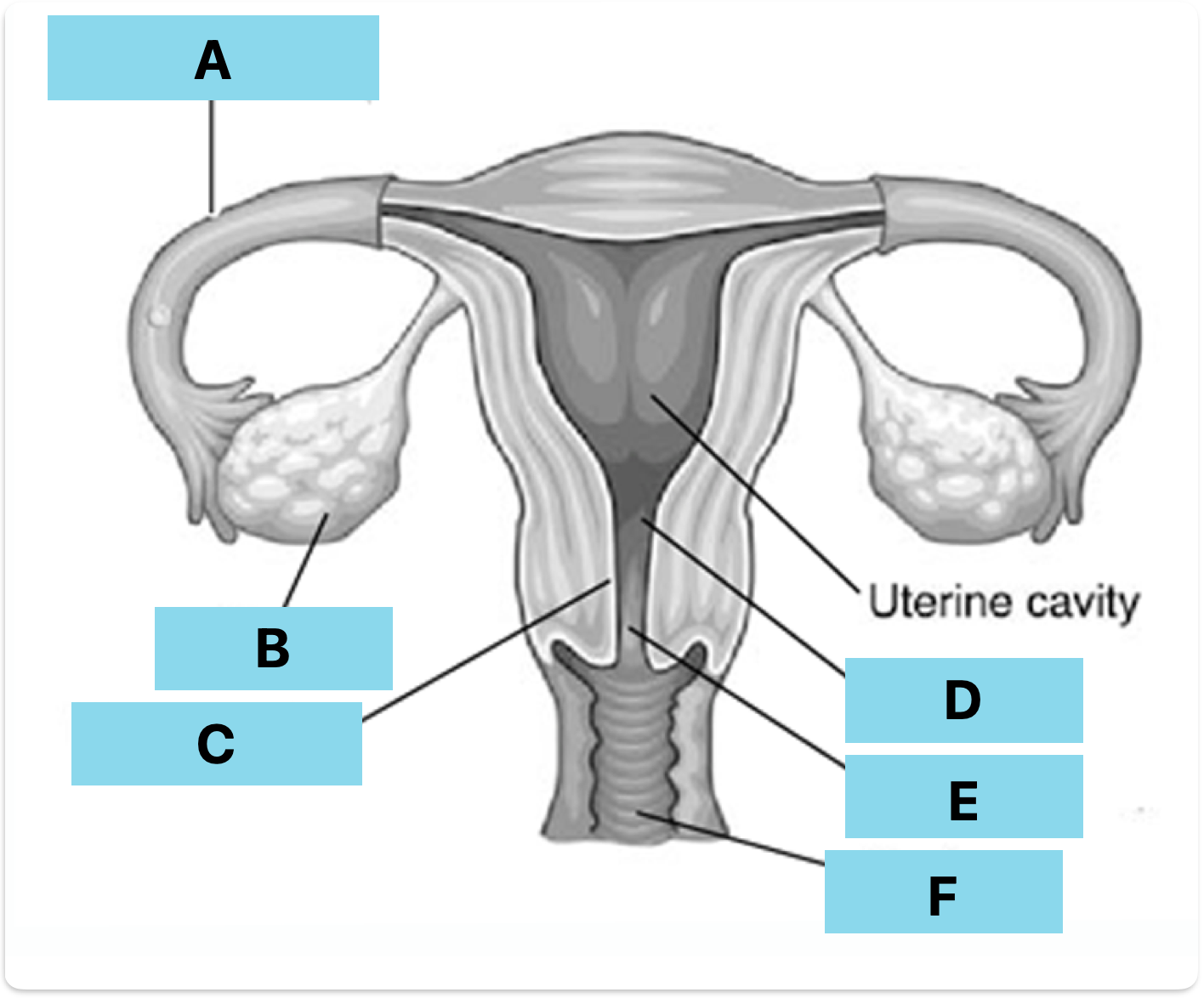
Label A-F
Fallopian tube
Ovary
Endometrium
Uterus
Cervix
Vagina
Urethra
Where sperm and urine leave penis
Why are testes kept outside the body
Require slightly cooler temperature than the body
Epididymis
Store sperm
What do tested produce
Adrenaline
Vas deferens
Transports mature sperm to penis
Seminal vesicles
Produce ejaculate fluid
prostate gland
Produces additional fluid to ejaculate to increase sperm mobility when in vagina
Uterus
Site of implantation and development of foetus
Ovaries
Produce female eggs as well as oestrogen and progesterone
Fallopian tubes
Attaches ovaries to uterus - where fertilisation occurs
What happens during fertilisation (simple)
Secondary oocyte fuses with sperm cell to form a zygote
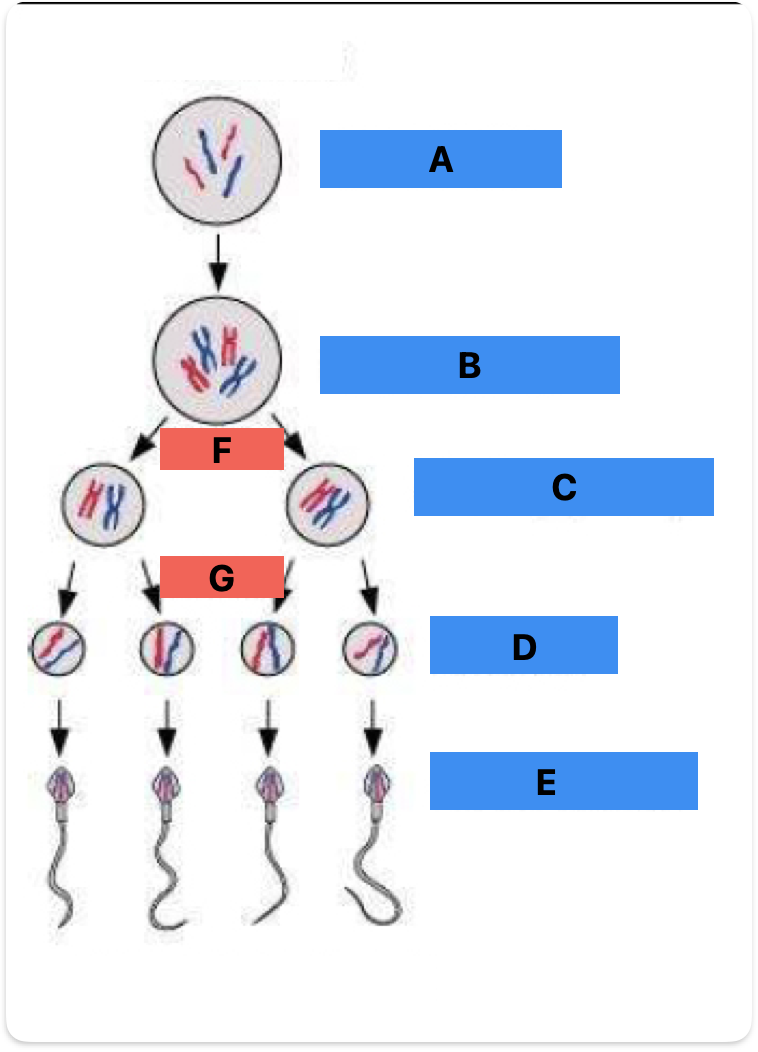
Label A-F
Spermatogonium (mitosis)
Primary spermatocyte (meiosis 1)
Secondary spermatocyte (meiosis 2)
Spermatid
Spermatozoa
Meiosis 1
Meiosis 2
3 parts of sperm cell + functions
Head - contains nucleus + acrosome (hydrolytic enzymes)
Midpiece - contains mitochondria
Tail - flagellum
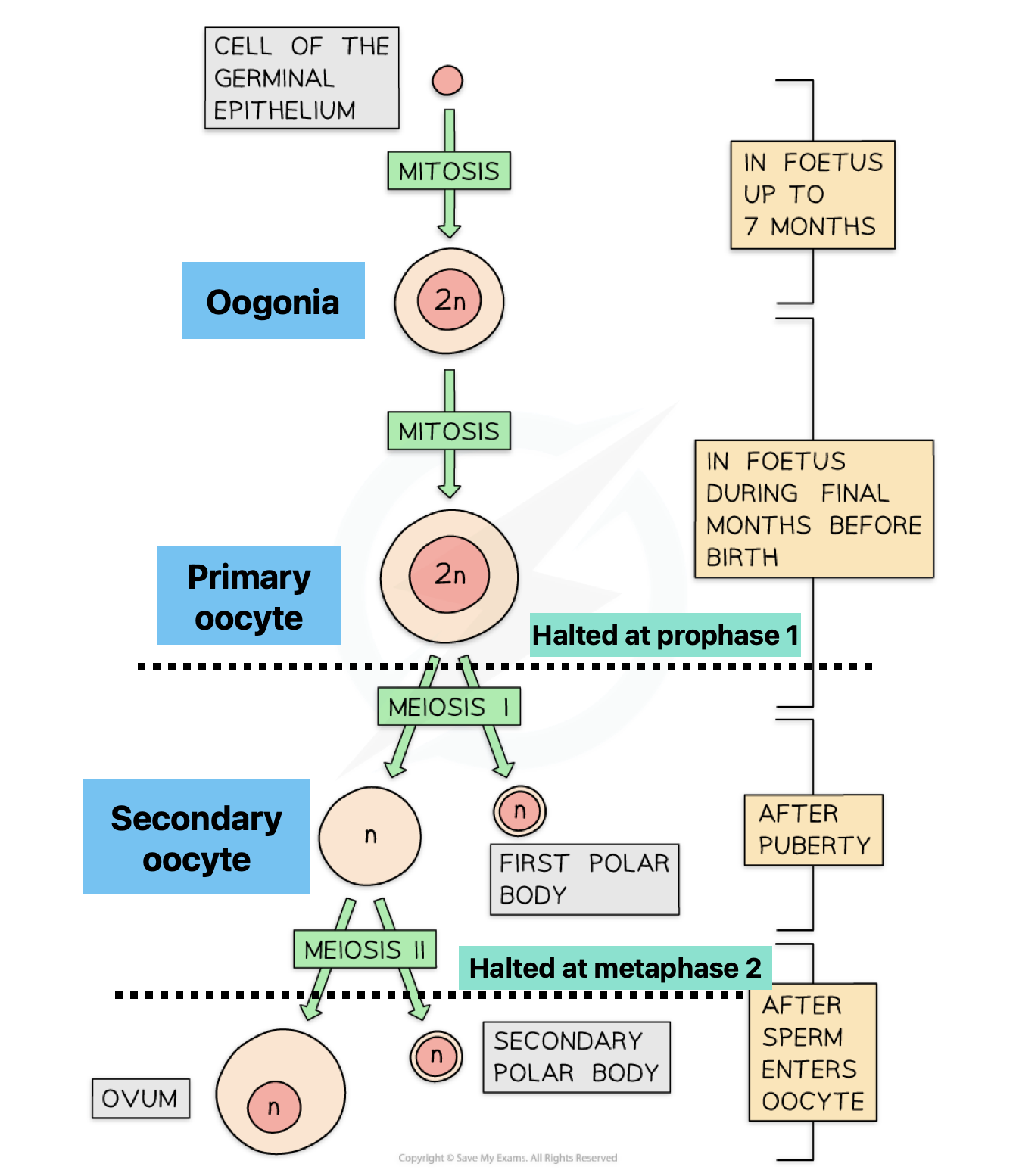
Describe oogenesis
(foetal)
Oogonium - primary oocyte
Begins meiosis - halts at prophase 1
(post puberty)
Primary oocyte - secondary oocyte
Each month follicle develops and completes meiosis 1
(ovulation)
Secondary oocyte is released
Starts meiosis 2 and is released from ovary into fallopian tube
(If fertilisation occurs)
Quickly completed meiosis 2 to form ovum
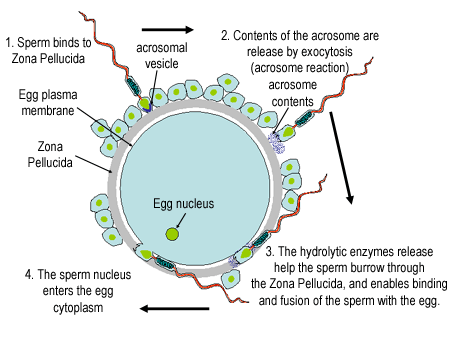
Describe fertilisation
Sperm travels to fallopian tube
Sperm burrows through corona radiata and binds to zone pellucida
Acrosome reaction creates a path for sperm to bind to secondary oocyte
Cortical reaction - Releases enzymes which harden the zona pellucida preventing polyspermy
Zygote then formed
What happens after the zygote is formed in fertilisation (implantation)
Mitosis occurs to increase cell devisions
Cells divide unevenly and eventually form the blastocyst
This then embeds in the endometrium
What happens after implantation of the blastocyst
(outer layer)
Outer layer is called trophoblast
Trophoblast develops into chorion
Placneta function (3)
Secrete hormones
Exchange of gas / waste
Allows maternal antibodies to protect foetus
Adaptation of placenta
Counter current
Bloods do not mix to prevent mother developing an immune response and killing it
Pressure in capillaries is much higher - this forces substances into the intervillous space
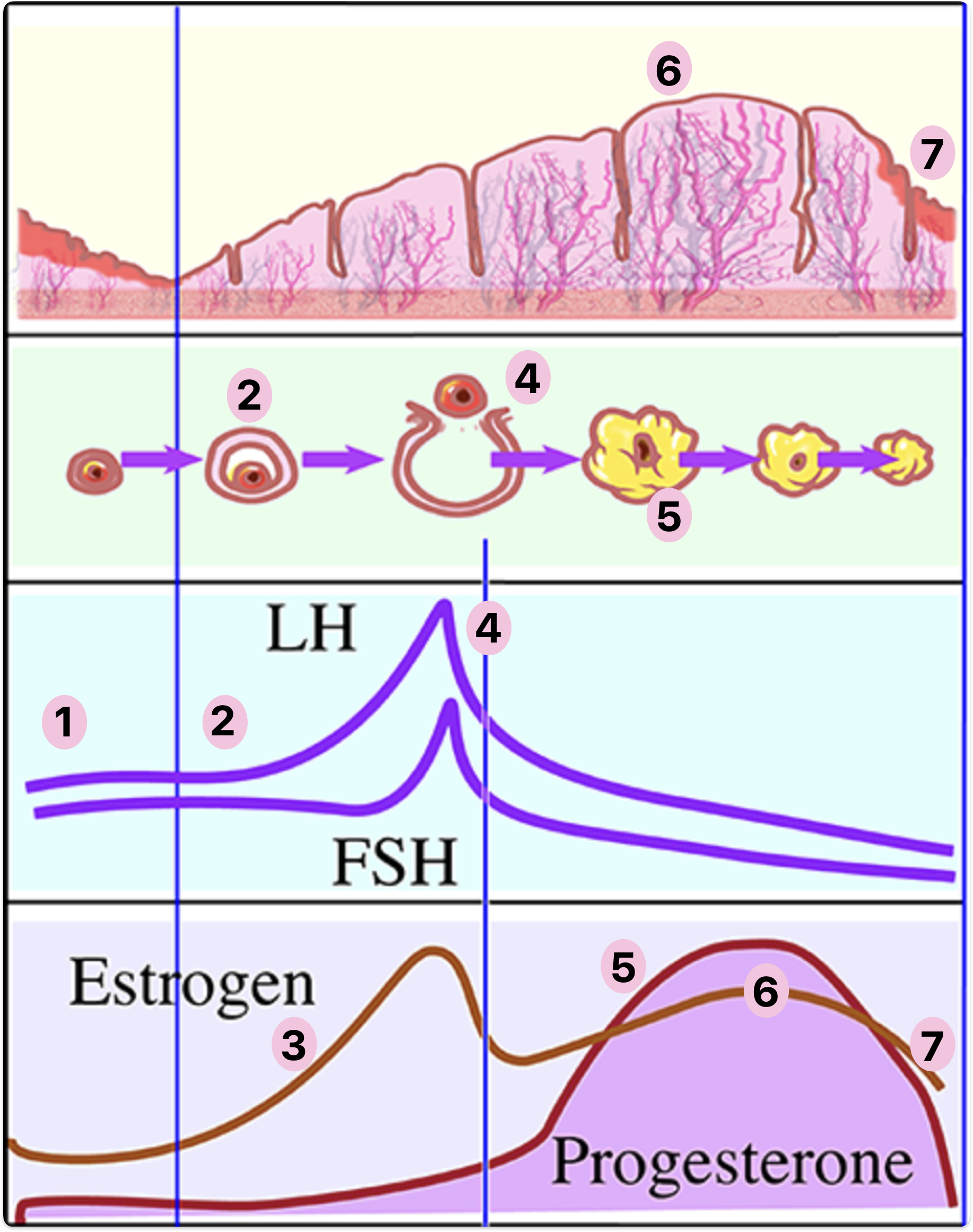
Describe 1-7
FSH + LH produced by anterior pituitary and induces the cycle
FSH stimulates follicle development
Building follicle produced oestrogen + Ve- effect on FSH + LH
LH induces ovulation - Graafian follicule releases secondary oocyte
GF retained as corpus luteum + produce progesterone
Progesterone stimulates growth of endometrium
If no fertilisation progesterone drops and endometrium sheds
Oestrogen dropping causes FSH + LH increase so cycle restarts
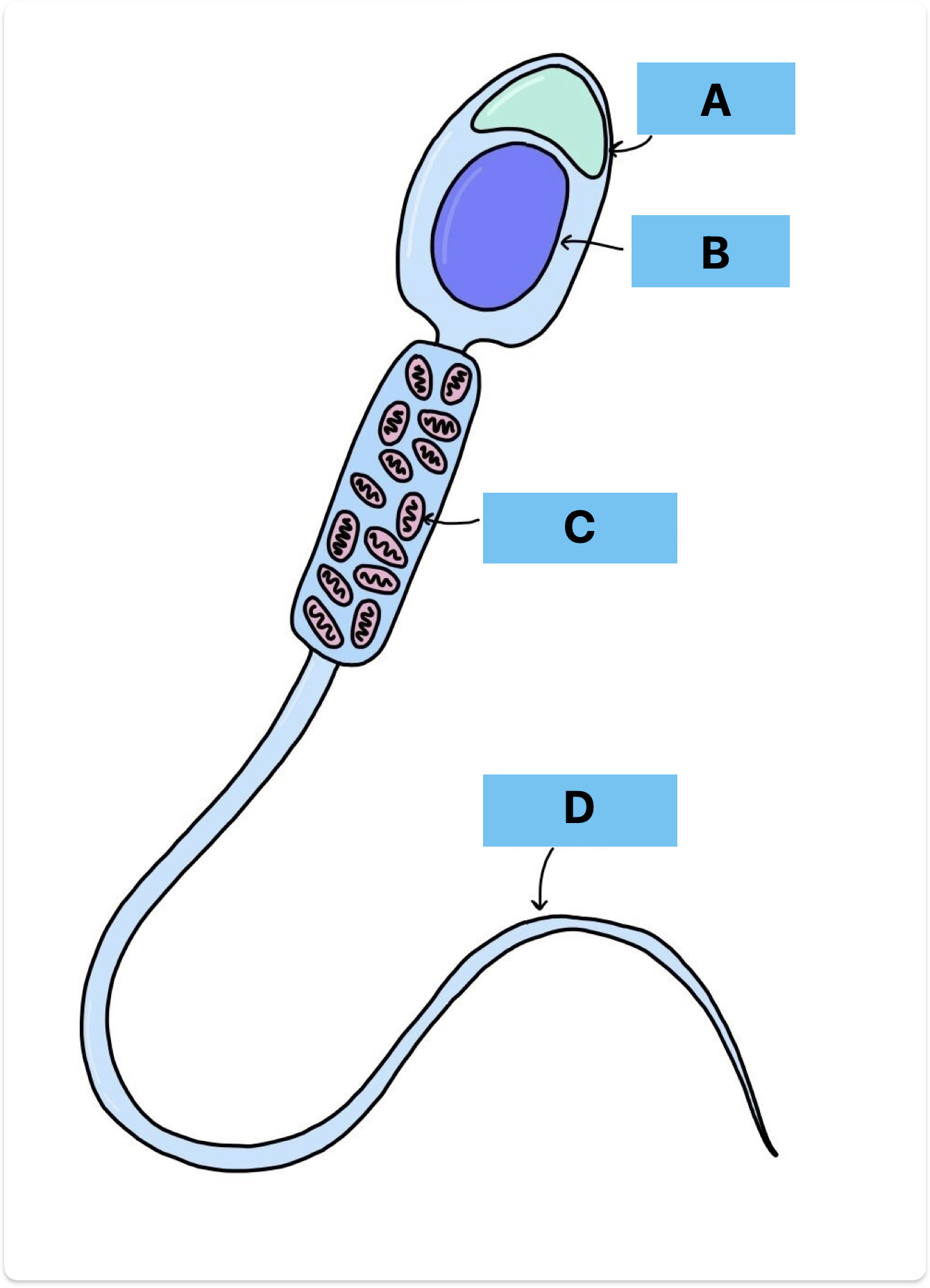
Label A-D
Acrosome
Nucelus
Mitochondria
Flagellum
Amnion + later function (4)
Membrane derived from inner blastocyst
Amniotic fluid then accumulates
Maintaining temperature
Provide lubrication (between foetus and tissue)
Allowing movement
Shock absorber
What produces hormones during pregnancy + function of hormones
Placenta
Progesterone inhibits uterine walls ability to contract
Oestrogen stimulates growth of uterus
What happens to the hormones just before birth
Progesterone decreases allowing uterine wall to contract
Decrease in progesterone allows secretion of oxytocin and prolactin
Oxytocin contracts myometrium
Prolactin stimulates mammary glands to synthesise milk
Most common cause of female infertility + treatment
Blocked fallopian tubes
IVF