Microbio Lab Quiz (7.1 and 7.2) and parasitology part 1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
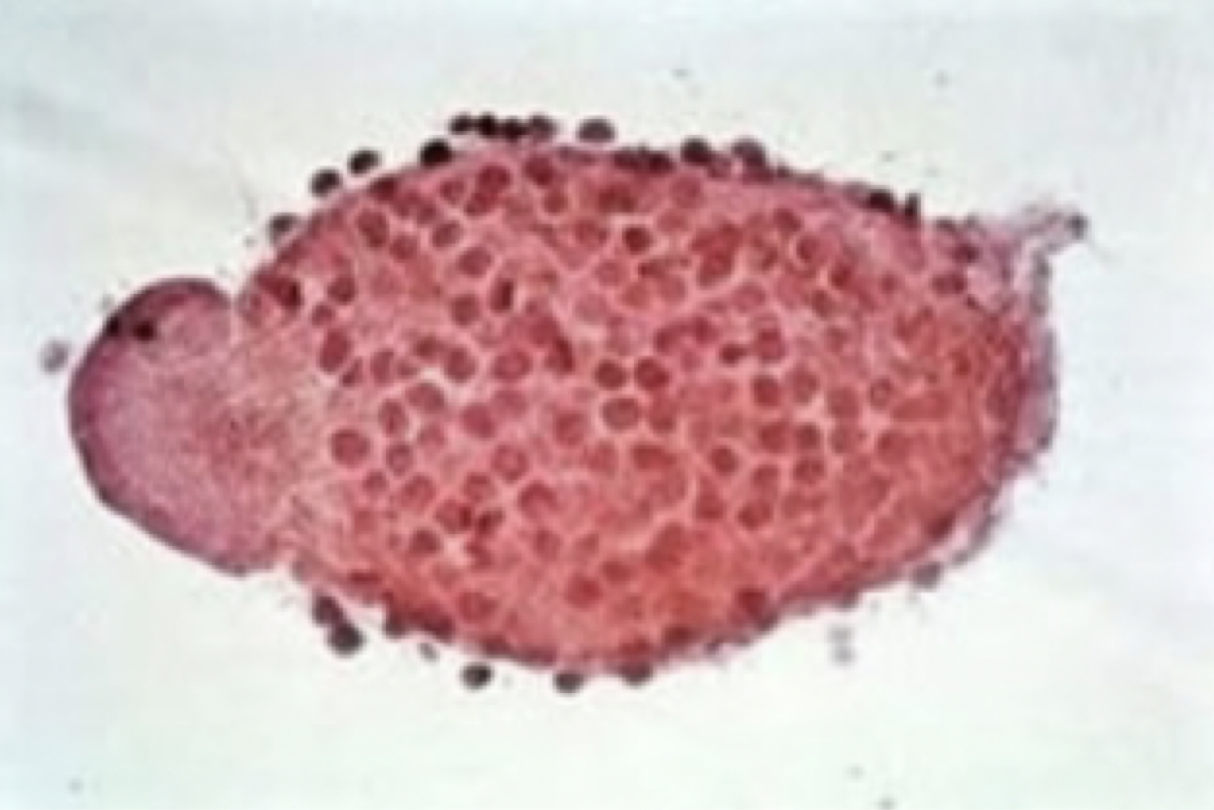
Entamoeba histolytica
Motility: pseudopod
Mode of transmission: fecal-oral
Infective stage: cyst
disease: amebiasis
parts to look for
central karyosome
bullseye nucleus
consumes red blood cells
look for RBCs inside organism
can eat through lining of GI tract and kill host
Entamoeba histolytica image
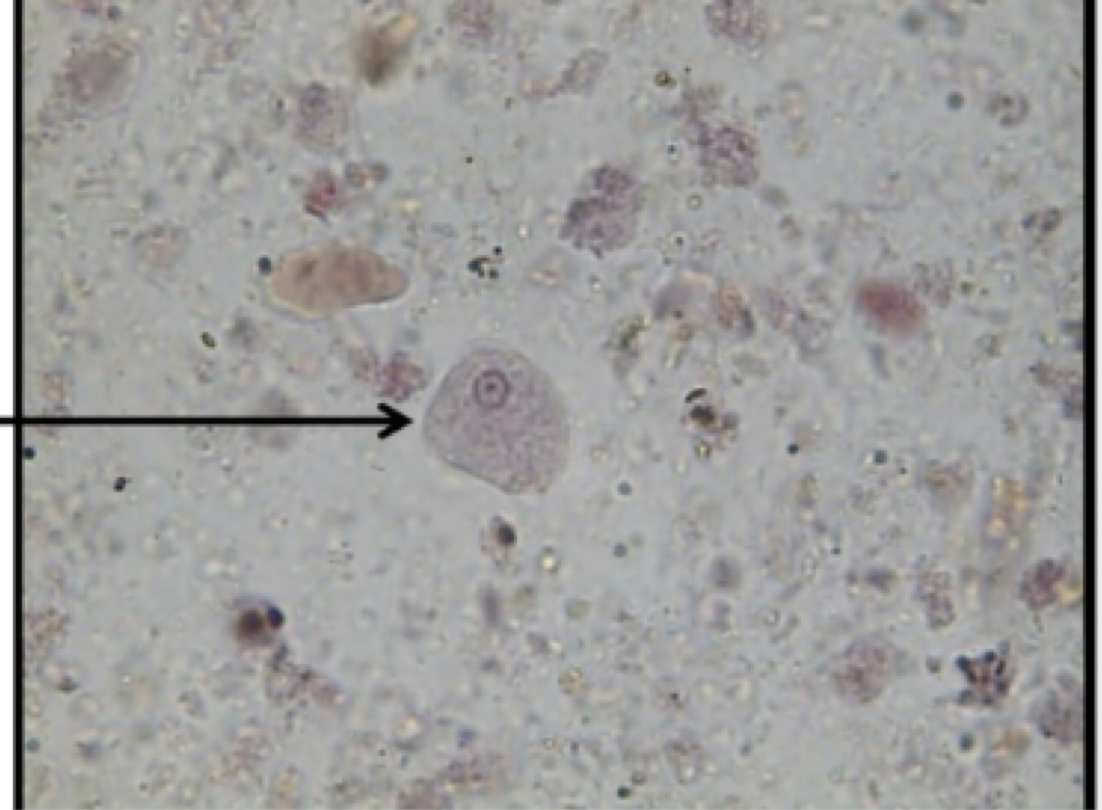
Naegleria fowleri
Motility: pseudopod
Mode of transmission: travels up the nose
water enters the nose of an organism then travels up olfactory nerve to the brain
Infective stage: trophozoite
disease: primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM)
parts to look for
large karyosome that take up whole nucleus
Naegleria fowleri image
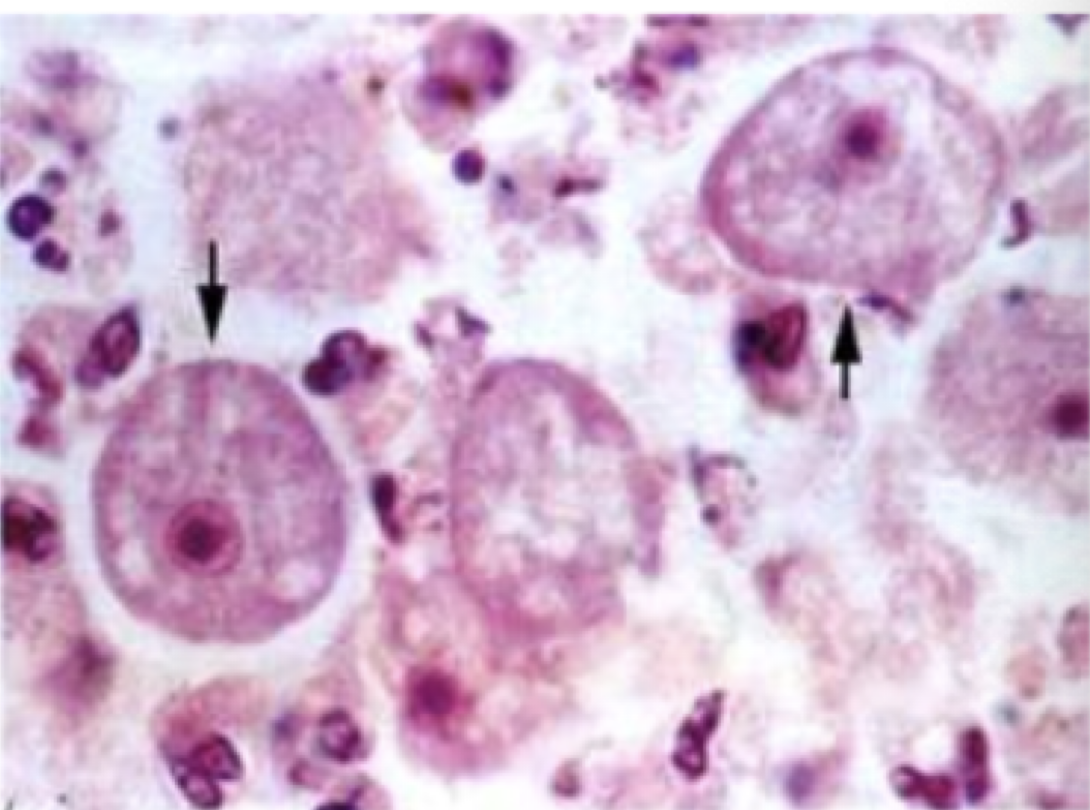
Acanthamoeba spp.
Motility: pseudopod
Mode of transmission: contaminated water or soil contact
Infective stage: trophozoite or cyst
disease: keratitis (eye), amebic encephalitis
parts to look for
karyosome takes up half of the nucleus
Acanthamoeba spp. image
Balantidium coli
Motility: cilia
Mode of transmission: fecal-oral
Infective stage: cyst
disease: Balantidiasis
also, may people go asymptomatic
parts to look for
large kidney bean shaped nucleus
Balantidium coli image
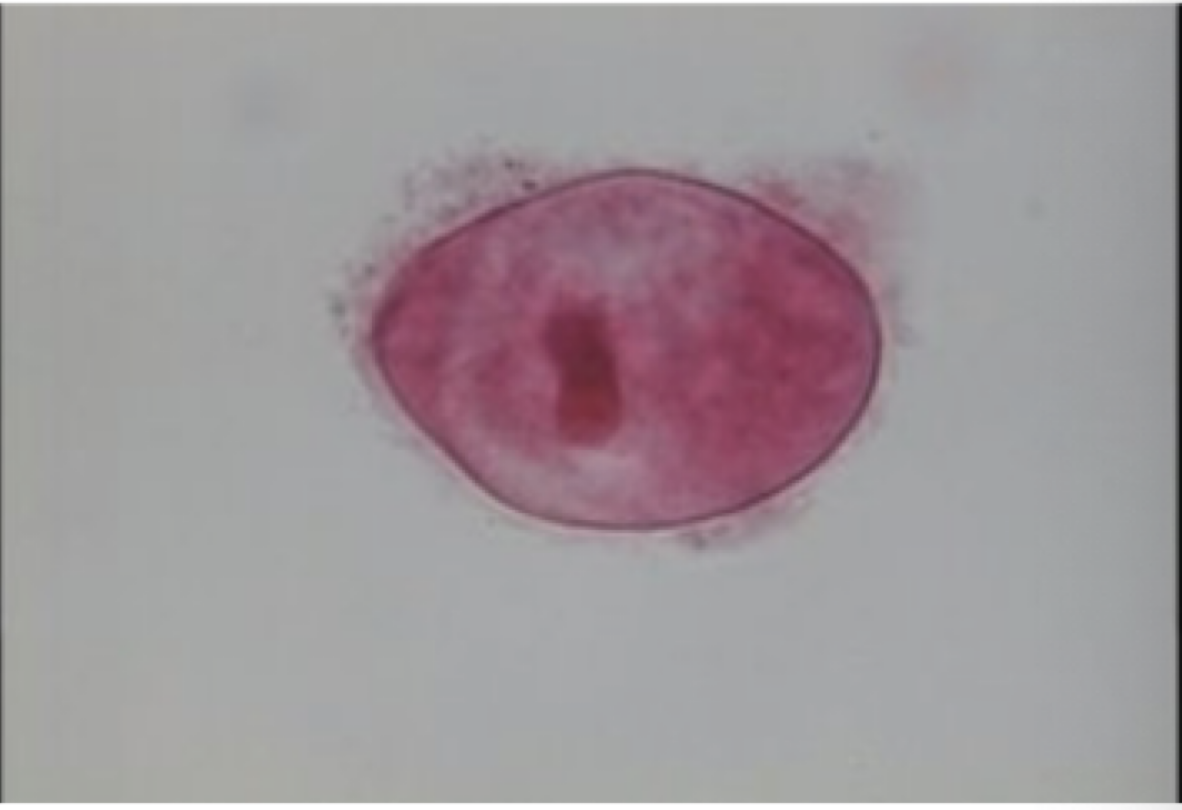
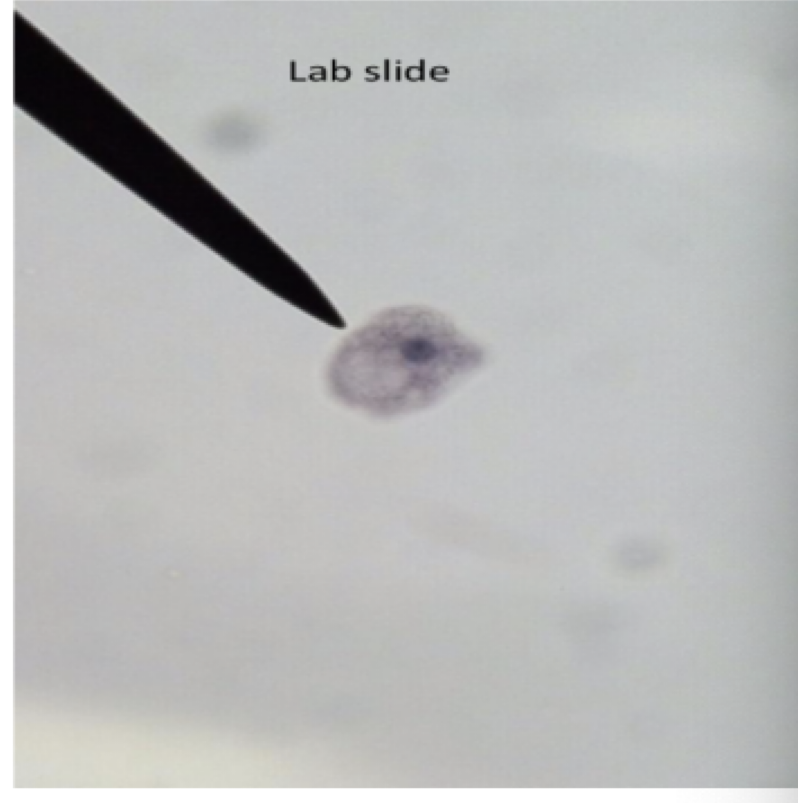
giardia lamblia
Motility: flagella
Mode of transmission: fecal-oral
Infective stage: cyst
disease: Giardiasis “Hikers’ diarrhea”
parts to look for
symmetrical heart shape
flagella
two nuclei
organelles positioned in such a way that it resembles a face
giardia lamblia image
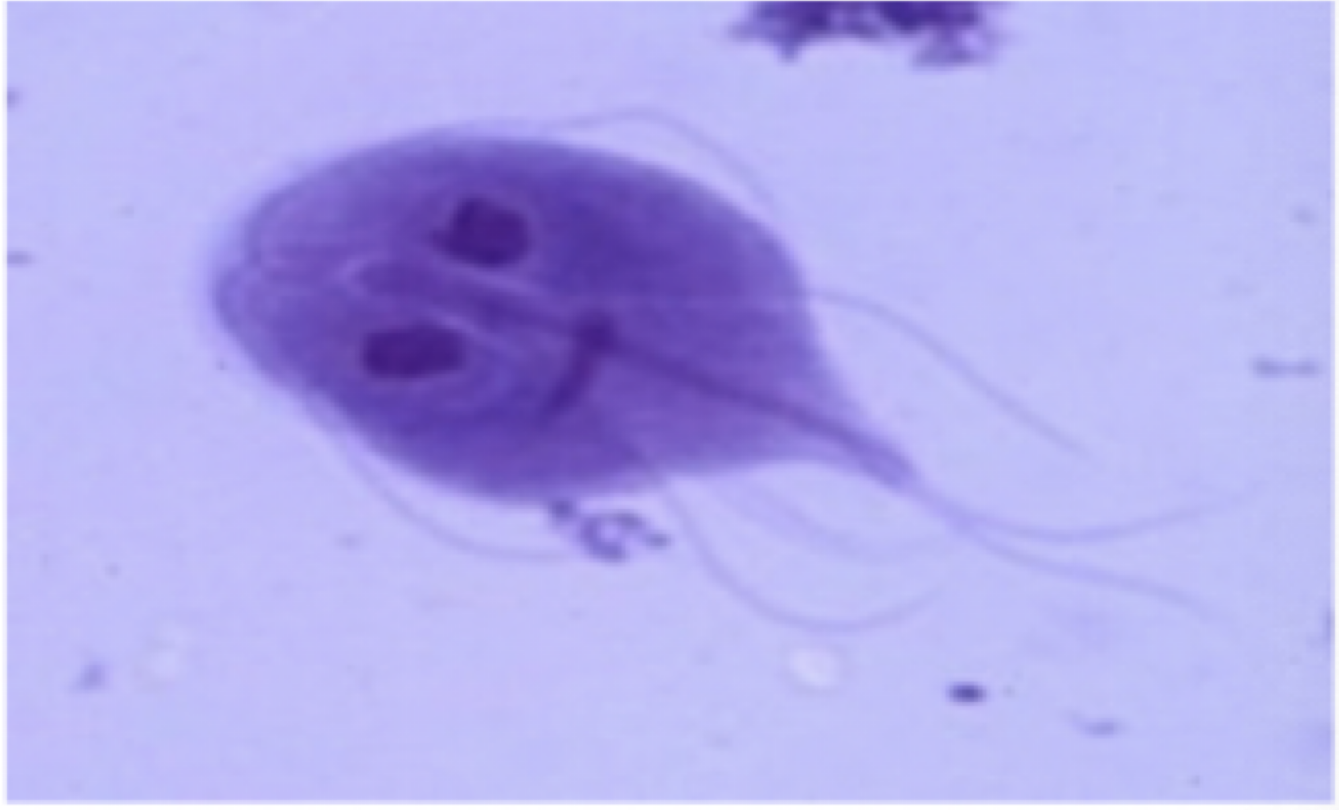
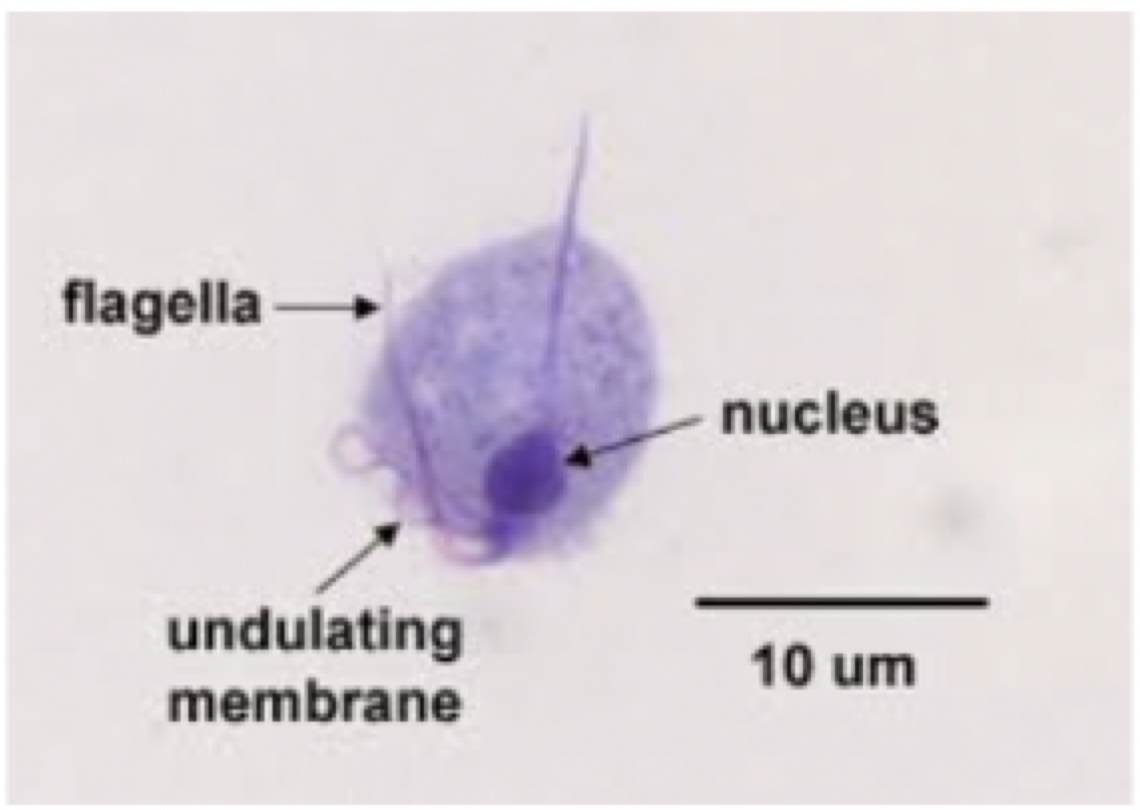
Trichomonas vaginalis
Motility: flagella
Mode of transmission: sexual intercourse
Infective stage: trophozoite
disease: Trichomoniasis
male: usually asynptomatic
female: vaginal discharge
parts to look for
pear shaped
undulating membrane
flagella
axostyle
Trichomonas vaginalis image
Selective media
media that contains one or more agents that inhibit the growth of certain microbe or microbes
Differential media
grows several types of microorganisms but are designed to bring out visible difference among those microorganisms
bacterial enzyme —> biochemical reaction —> color change
General Purpose Media
media that contains all the elements that most bacteria need for growth
not slective
no special growth requirement
complex media: contains milk protein (casein), soybean protein, sodium chloride
General Purpose Media examples
Tryptic Soy Agar
Brain Heart Infusion
Enriched Media
media that contains extra or higher concentrations of nutrients, vitamins, trace elements, and other growth factors that allows fastidious microbes to grow
thioglycolate
blood agar
chocolate agar
what media forms are Enriched Media
blood agar
enriched and differeintial
base: cryptic soy agar
additive: 5% sheep blood
differential: base on the ability to break down red blood cells or not
Types of blood agar red blood cells
alpha hemolytic
beta hemolytic
gamma hemolytic
alpha hemolytic
partially able to catabolize RBCs
brown to green outline around the colonies
beta hemolytic
completely catabolize RBCs
clear center around colonies
gamma hemolytic
no hemolysis
area adjacent to colonies will remain clear
Chocolate agar
enriched media
base: tryptic soy agar
additive: hemolyzed (lysed) sheep blood
used for going fastidous organisms
Thioglycolate broth
enriched media
base: tryptic soy broth
additive: thioglycolate binds with oxygen
enriched media because it allows anaerobes to grow
growth patterns based on oxygen requirements
Thioglycolate broth examples
obligate aerobe: top
obligate anaerobe: bottom
facultative anaerobe: mostly on top and some throughout
microaerophile: just below the top surface
areotoleraat aerobe: throughout
what are forms of selective media?
Phenylethyl alcohol agar
mannitol salt agar
MacConkey’s Agar
Eosin Methylene blue agar
Phenylethyl alcohol agar (PEA)
selective media
selective for gram positive bacteria
Phenylethyl Alcohol dissolves the lipopolysaccharide layer in the gram-negative
inhibits gram negative growth
Mannitol salt agar
selective differential media
selective: contains 7.5% NaCl
NaCl favors the growth of staphylococci
differential: ability to ferment mannitol
media contains mannitol
pH indicator Phenol red
MacConkey’s agar
selective and differential media
Selective: contains bile salts and crystal violet
selects gram negative enteric bacteria
inhibits gram postive bacteria
differential: ability to ferment lactose
media contains lactose
pH indicator neutral red turns pink/ purple when pH is less than 6.8
Eosin Methylene Blue agar
selective differential media
Selective: contains eosin and methylene blue
selects for gram negative enteric bacteria
inhibits gram positive bacteria
responsible for the color changes
differential: ability to ferment lactose
E. coli is able to ferment lactose to produce a green metallic streak
CHROMagar
Differential Media
Differential: contains chromogens
artificial substrates in the media that develop specific colors when broken down
if bacteria have the enzymes needed to ultilize a substrate
specific color develops
CLED agar
differential media
Cystine: amino acid
Lactose: carbohydrate
Electrolyte Deficient: prevent swarming
-designed grow and quantify pathogens in urines
-pH indicators help colonies develop different colors to identify organism
Trypanosoma bruceli
motility; flagella
mode of transmission: bite from tsetse fly
infective stage: trypanomastigtoe
Host: Tsetse fly —> human
ideas; African Sleeping sickness
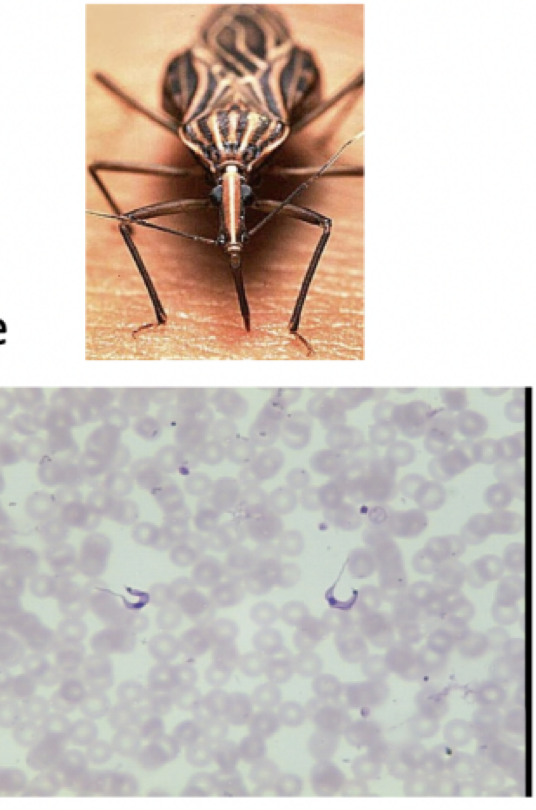
Trypanosoma cruzi
molitty: flagella
mode of transmission: bite from kissing bug
infective stage: trypomastigote
Host: kissing bug —> human
Disease; chaga’s disease
sickness is different
location of contraction is different
insect vector is different
differences between T. brucei and cruzi
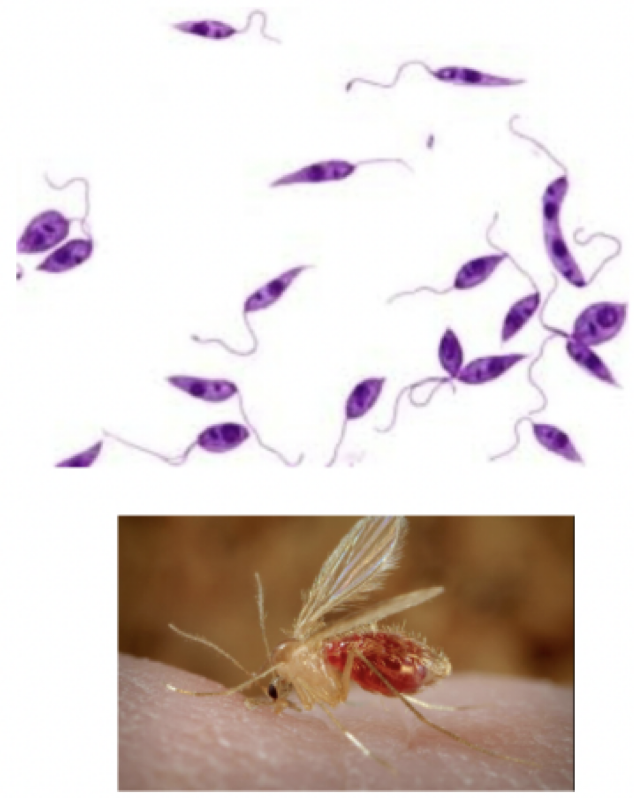
Leishmania donovani
motility: flagella
mode of transmission: bite from sand fly
infective stage: promastigote
Host: sand fly —> human
disease: Leishmaniasis
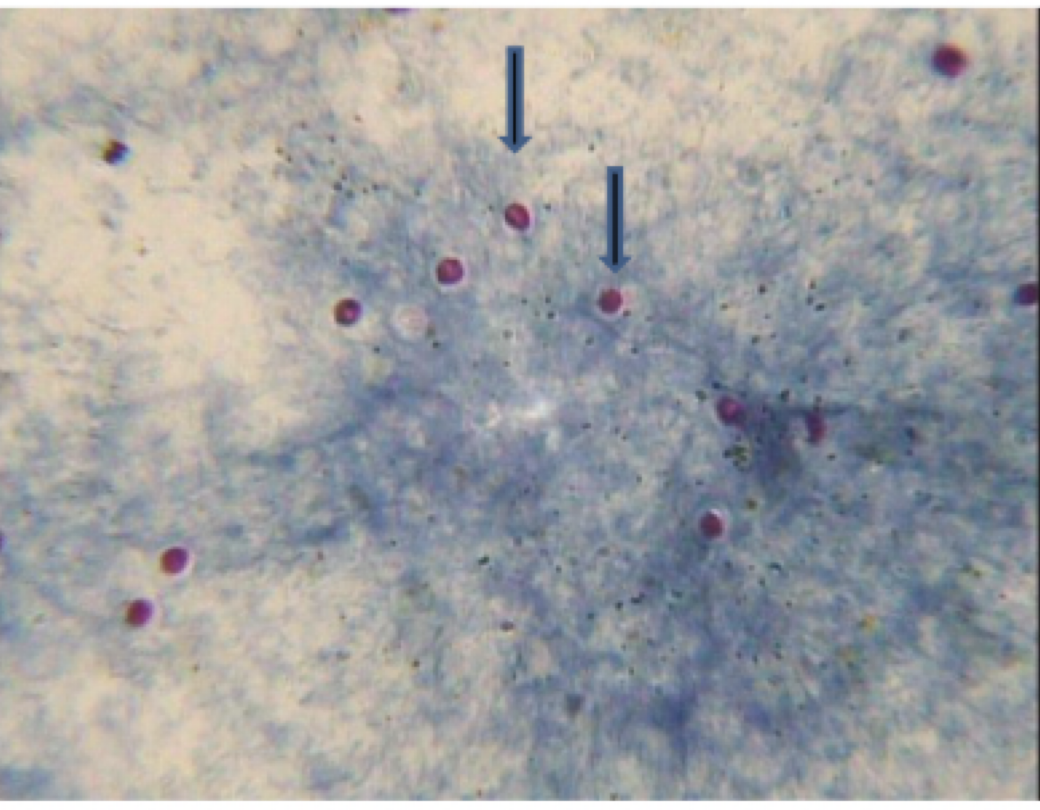
Cryptosporidium parvum
motility: none
mode of transmission: females oral, ingestion of oocyst
infective stage: oocyst
host: humans and other animals
disease: cryptosporidiosis
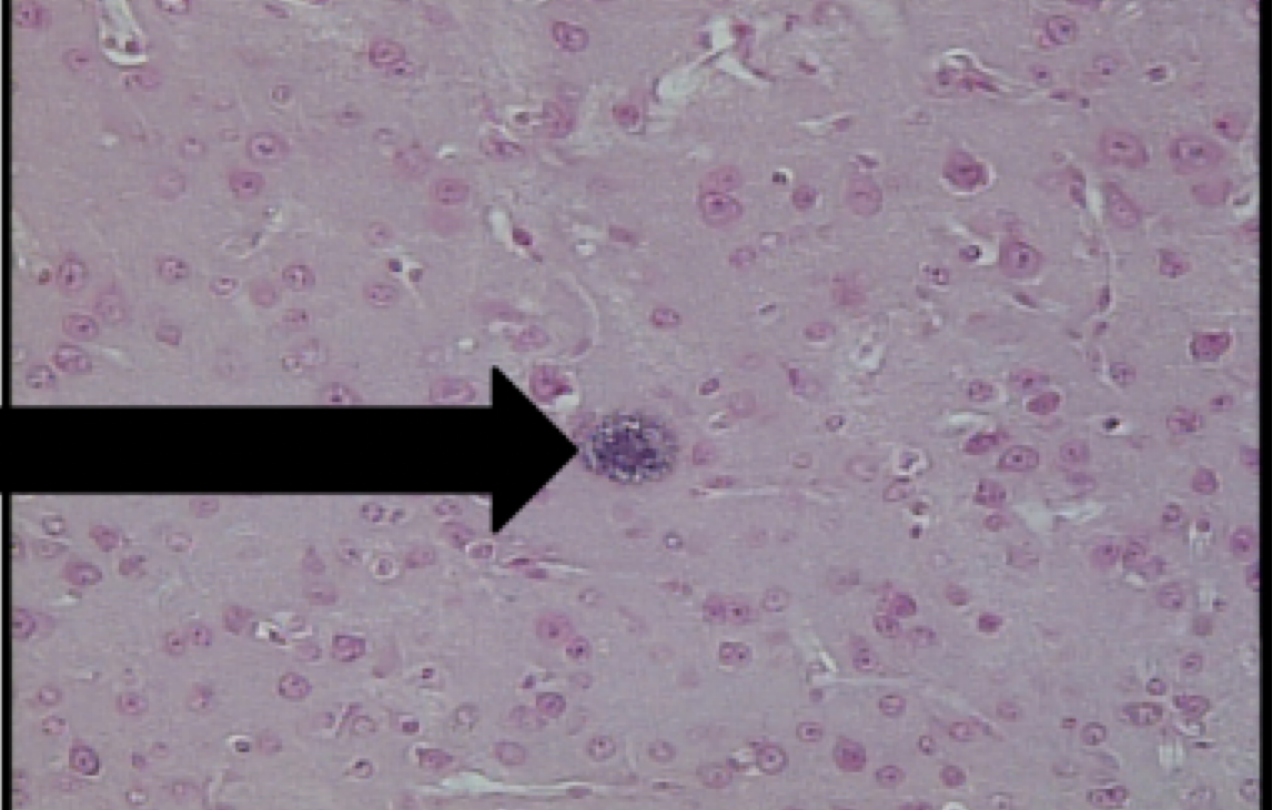
toxoplasma gondii
motility: none
mode of transmission: ingestion of oocyst
infective stage: oocyst
host: feline —> rodent, bird, human
disease: toxoplasmosis
plasmodium species
motility: none
mode of transmission: bite from female anopheles mosquito
infective stage: sporozoite
host: female anopheles mojito —> human
disease: malaria
plasmodium lIfe cycle 1-3
1) sporozoites in mosquito saliva
2) injected into human hosts when mosquito take a blood meal
3) sporozoites invade the cells of the liver (hepatocytes)
plasmodium lIfe cycle 4-6
4) undergo division in the liver cells and become Merozoites
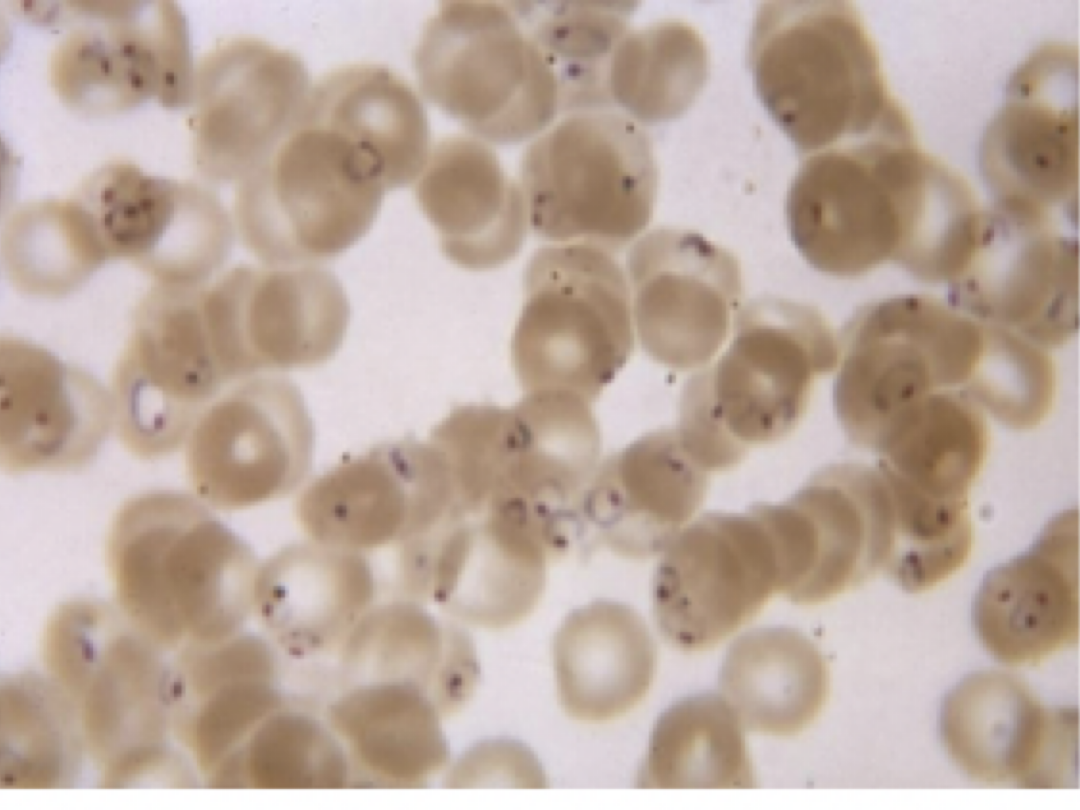
5) Merozoites exit liver cells and invade red blood cells
6) Inside red blood cells a merozoite forms a Trophozoite ring
plasmodium lIfe cycle 7-9
7) Ring stage grows and precedes more Merozoites
8) Merozoites rupture REd Blood cell and the cycle continues
9) Merozoite enters red blood cell
a) Trophozoite-merozoite path
b) Produce gametocytes
*gametocytes do not rupture RBC and are where gametes develop
plasmodium lIfe cycle 10-12
10) Mosquito will take up gametocytes with their blood
11) Gametocytes release gametes that unite in the gut of mosquito to form a zygote
12) zygote then forms an ookinete that penetrates the midgut wall
plasmodium lIfe cycle 13-14
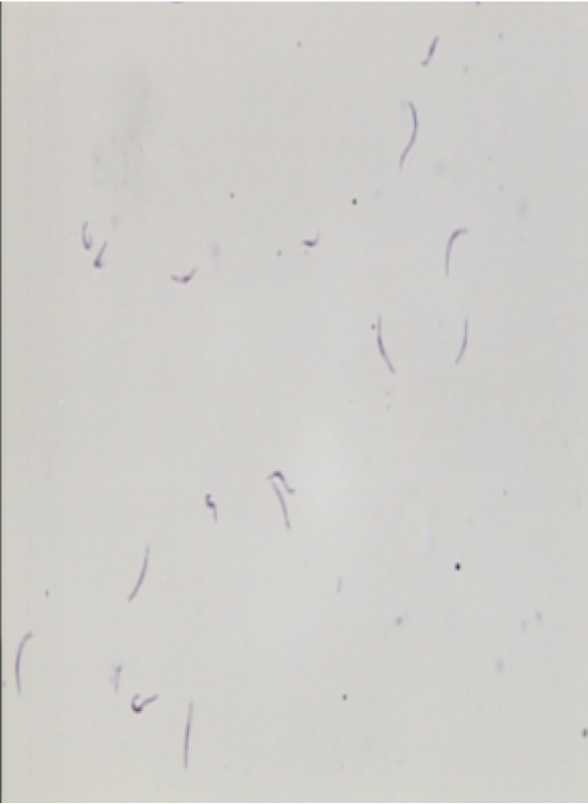
13) the ookinete develops into an oocyst that produces sporozoites
14) sporozoite migrate to salivary glands of the mosquito
Trypanosoma bruceli
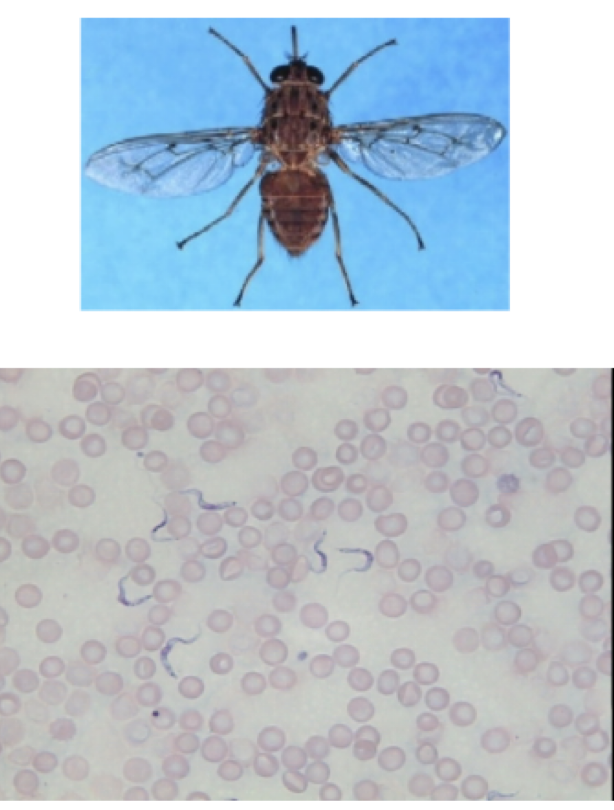
Trypanosoma cruzi
Leishmania donovani
Cryptosporidium parvum
Toxoplasma gondii
Plasmodium species
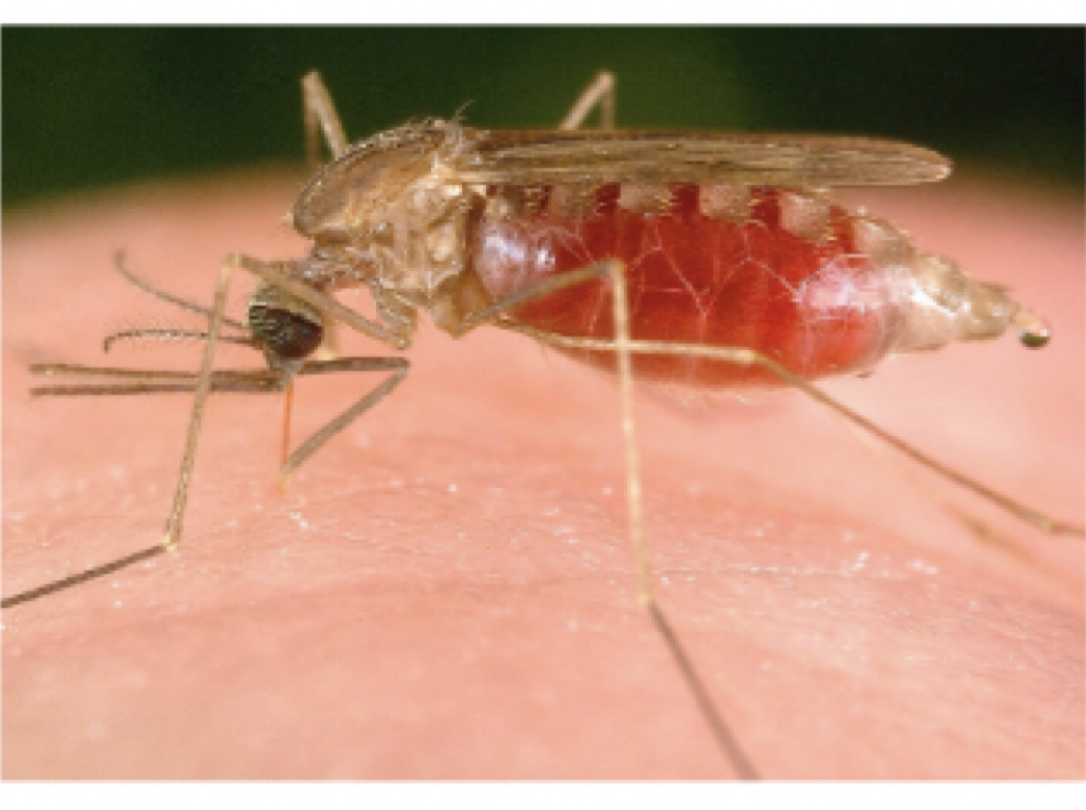
Sporozoites
Trophozoite rings
ookinete

oocyst