Energy, Metabolism, and Enzyme Function in Cells
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Enzyme
Biological catalysts that facilitate chemical reactions.
Active Site
Enzyme's catalytic site; substrate fits into active site.
Substrate
Reactant which binds to enzyme.
Product
End result of reaction.
Denaturation
Occurs when the protein structure is disrupted, eliminating the ability to catalyze reactions.
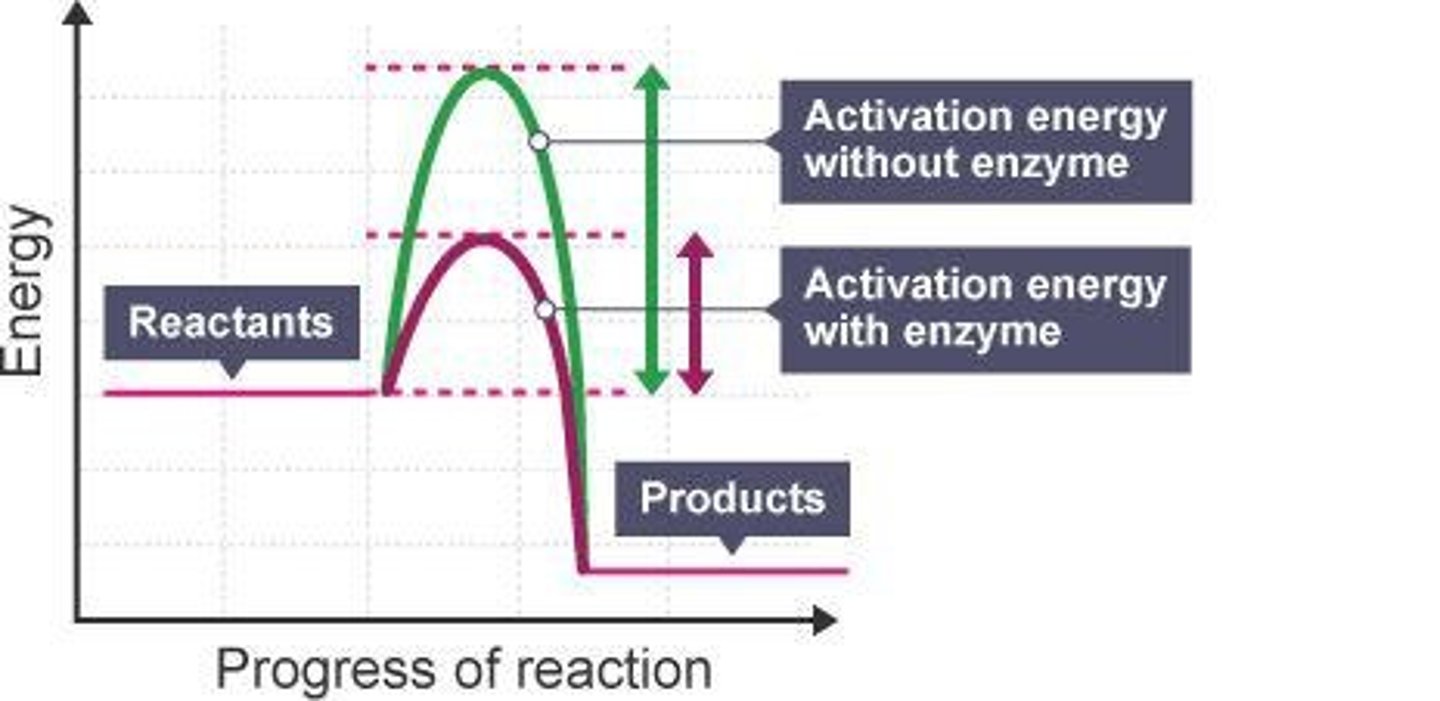
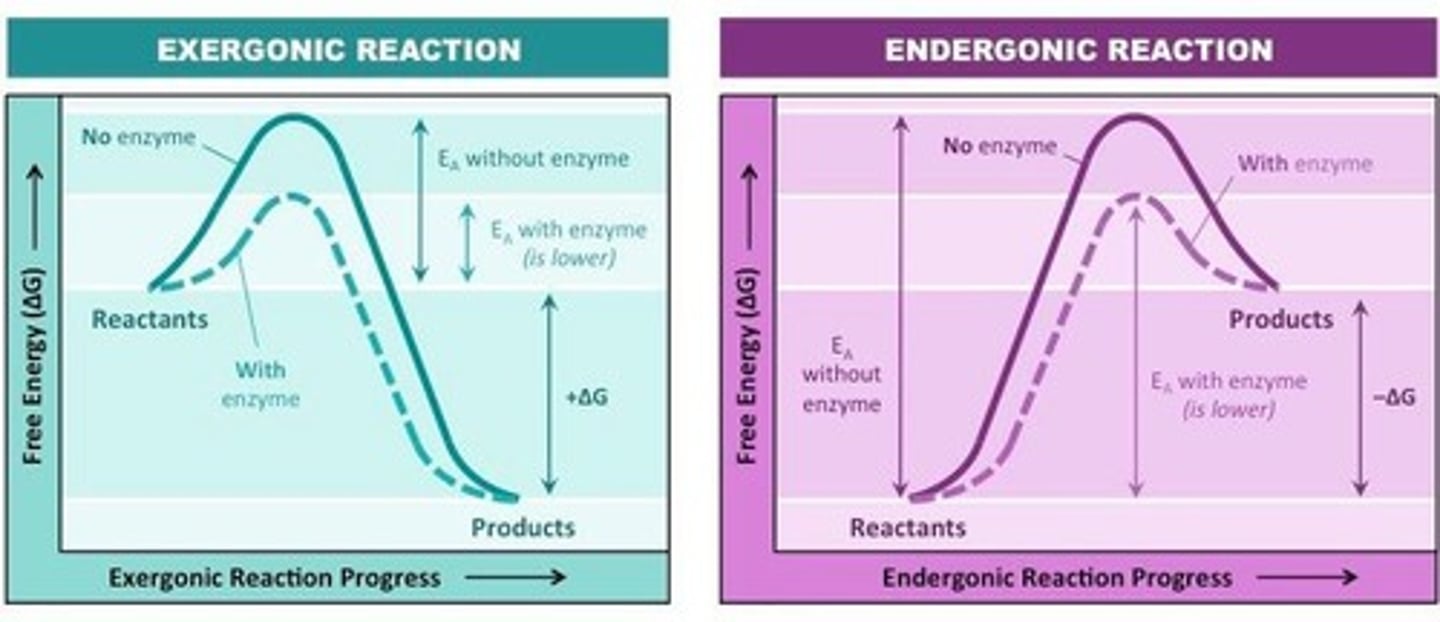
Activation Energy (Eₐ)
Initial energy investment required to break stable covalent bonds.
Endergonic Reaction
Reactions that require energy input (+).
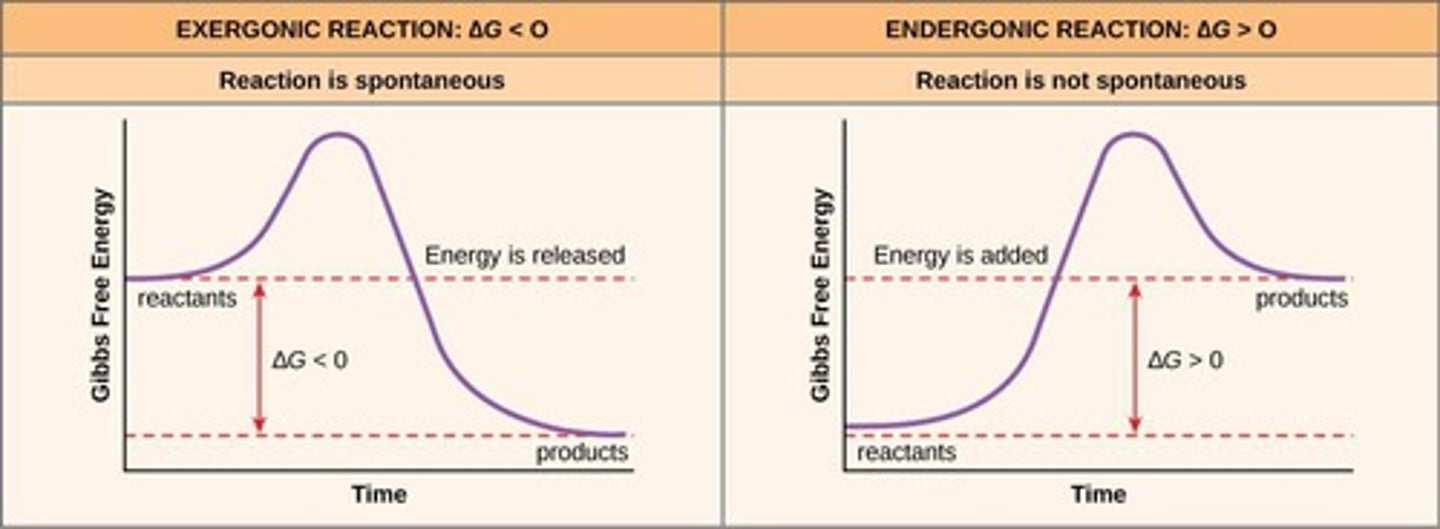
Exergonic Reaction
Reactions that release energy (-).
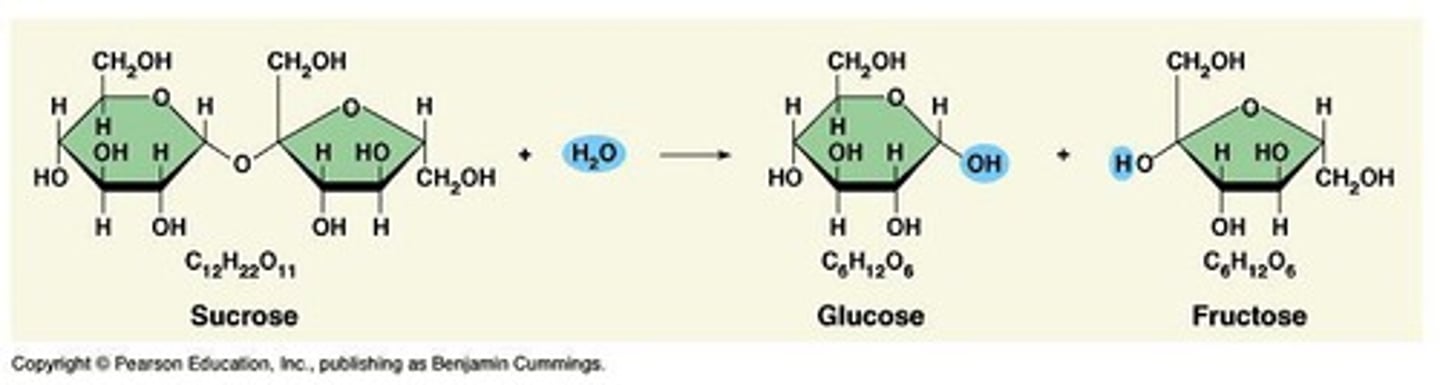
Hydrolysis
A catabolic process that breaks down molecules.
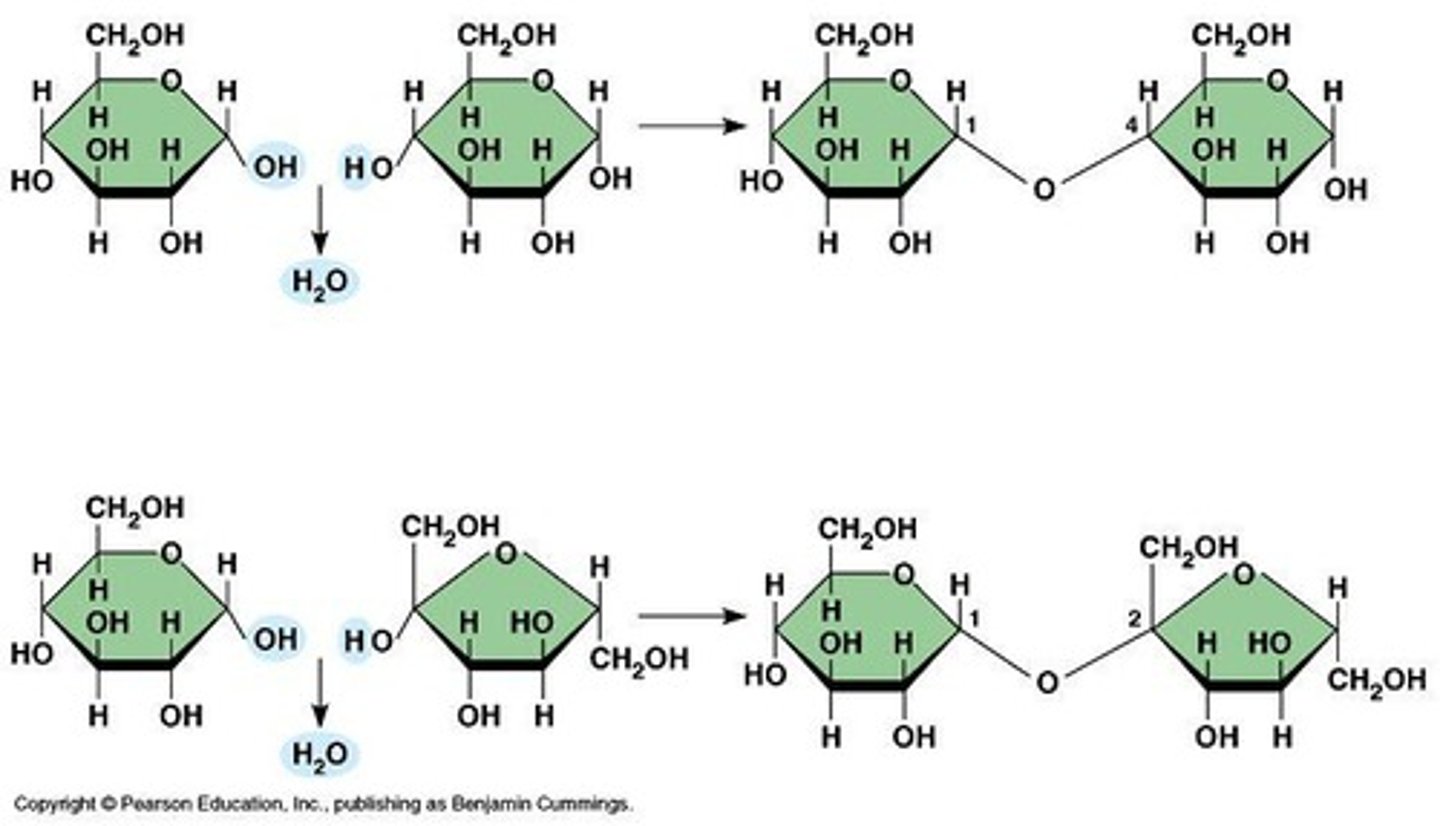
Dehydration Synthesis
An anabolic process that builds biomolecules.
pH
A measure of hydrogen ion concentration, calculated as pH = -log [H+].
Competitive Inhibitor
Molecules that can bind reversibly or irreversibly to the active site of the enzyme.
Noncompetitive Inhibitor
Molecules that can bind allosteric sites, changing the activity of the enzyme.
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
Temporary association between an enzyme and its substrate.
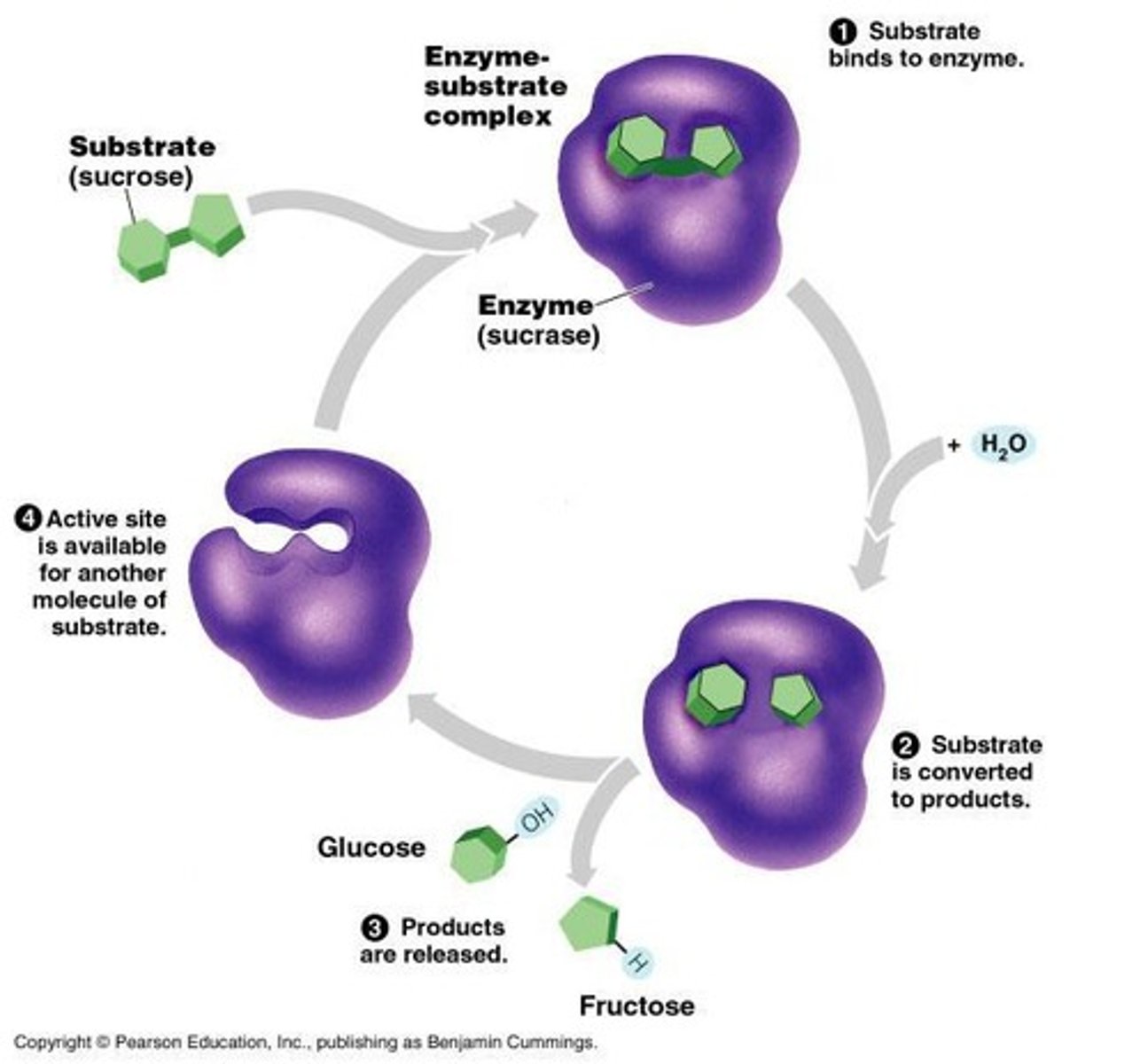
Induced Fit Model
More accurate model of enzyme action where substrate binding causes enzyme to change shape.
Lock & Key Model
Simplistic model of enzyme action where substrate fits into the enzyme's active site.
Metabolism
The general term for all of the chemical processes that occur in the body.
Catabolic Pathways
Metabolic pathways that break down molecules.
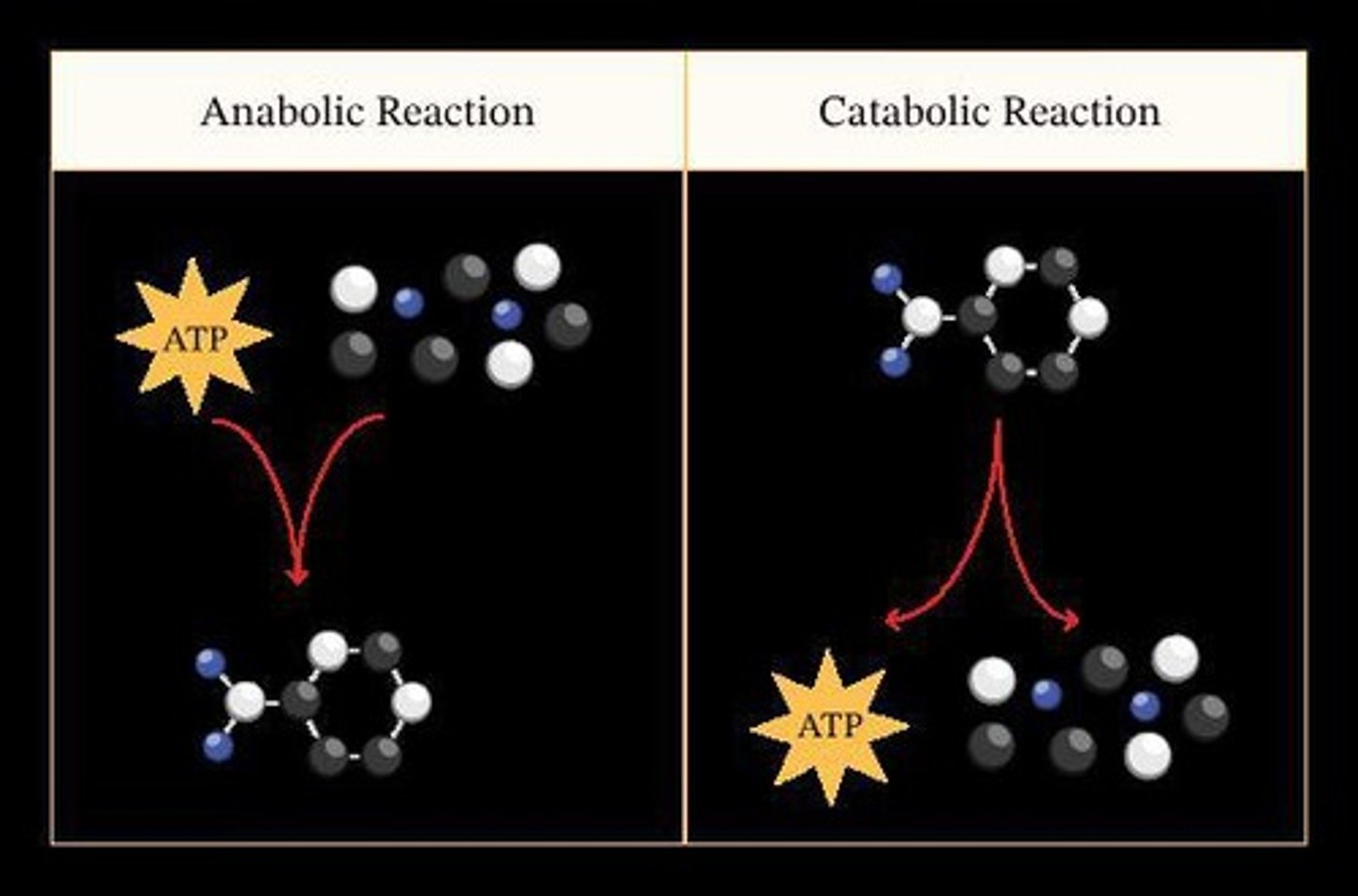
Anabolic Pathways
Metabolic pathways that build up molecules.
Environmental Factors
Conditions such as temperature, pH, and salinity that affect enzyme activity.
Enzyme Naming
Enzymes are named for the reaction they catalyze.
Reaction Specificity
Each enzyme works with a specific substrate.
Chemical Fit
The interaction between the active site and substrate through hydrogen and ionic bonds.
Conformational Change
The change in shape of an enzyme upon substrate binding.
Energy Coupling
Using exergonic reactions to fuel endergonic reactions.
Hydrogen Bonds
Interactions that help maintain enzyme structure and can be disrupted by environmental changes.
Efficiency of Enzyme Activity
Determined by environmental pH and relative concentrations of substrates and products.
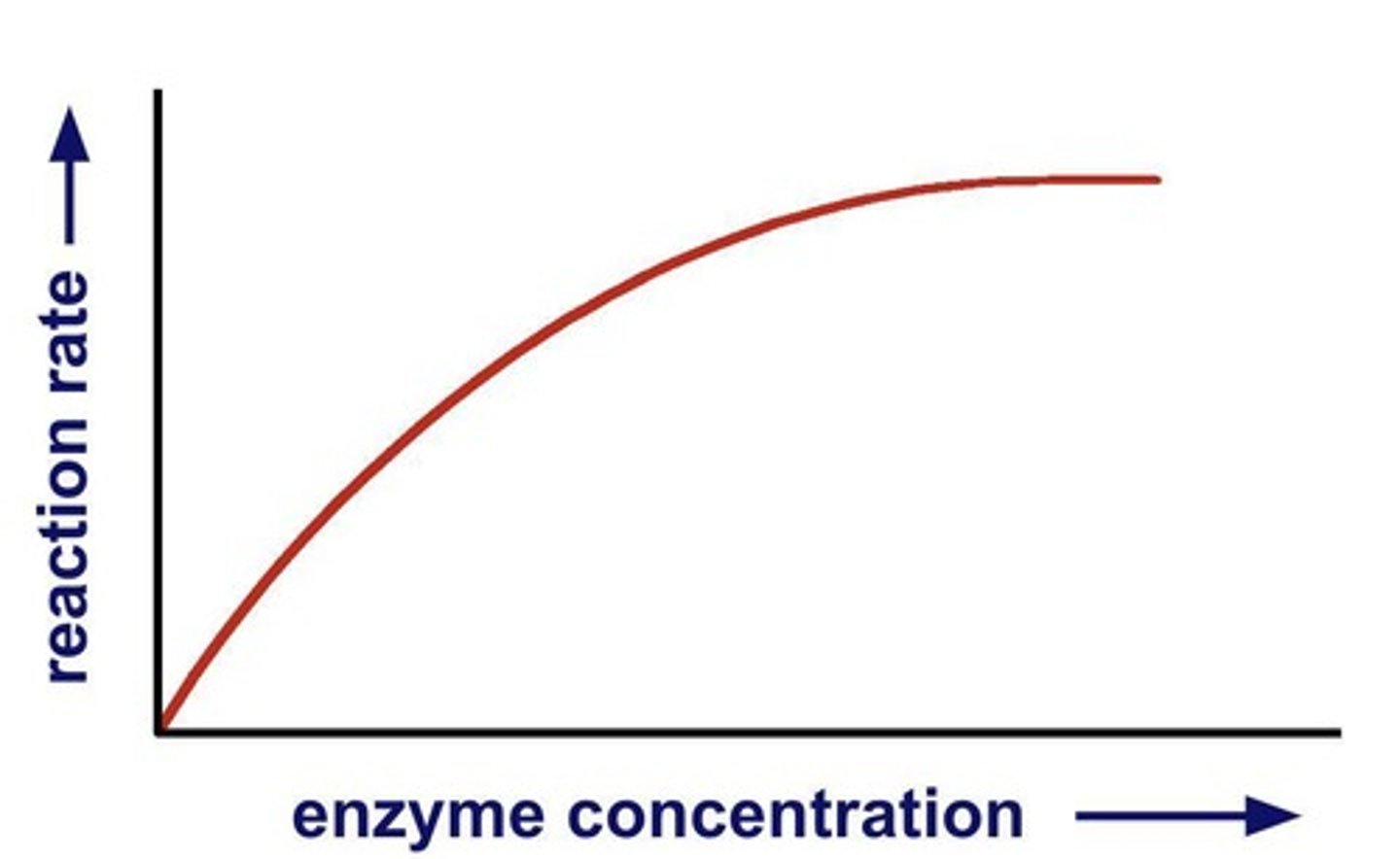
Enzyme concentration
Higher concentration increases reaction rate.
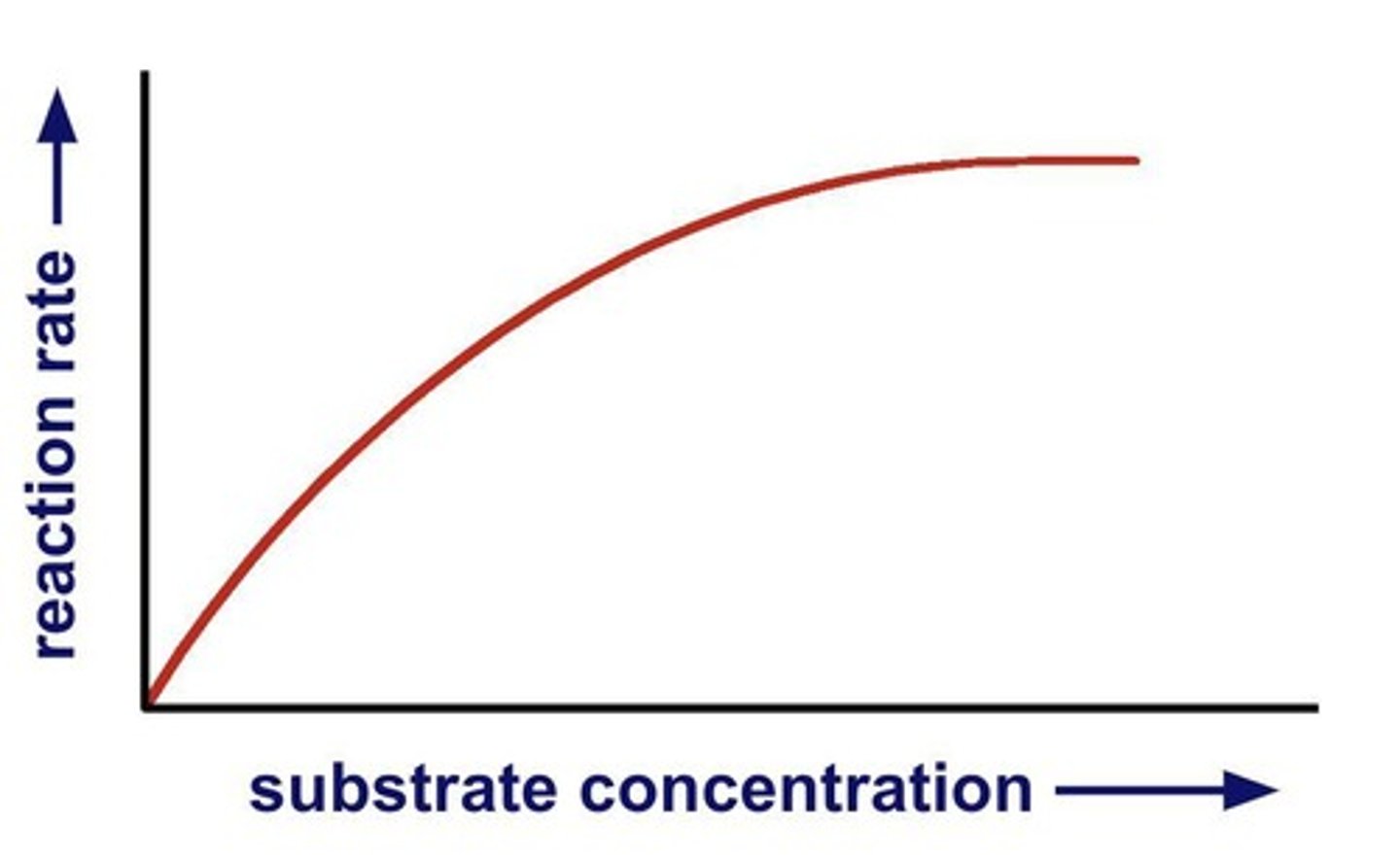
Substrate concentration
More substrate leads to more frequent collisions.
Reaction rate
Speed at which reactants convert to products.
Active site
Region where substrate binds on an enzyme.
Saturation
All enzyme active sites occupied by substrate.
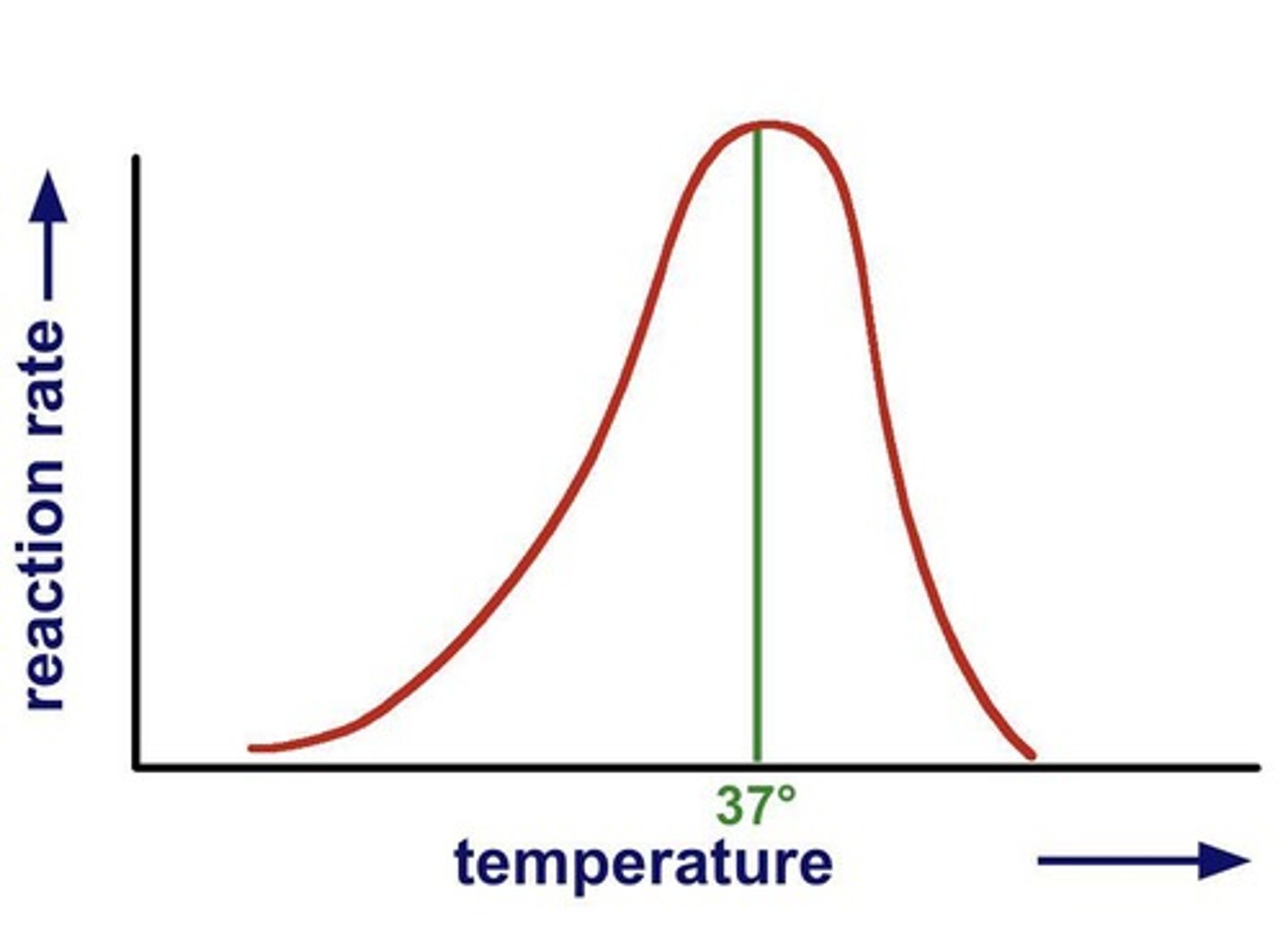
Optimum temperature
Temperature for maximum enzyme activity.
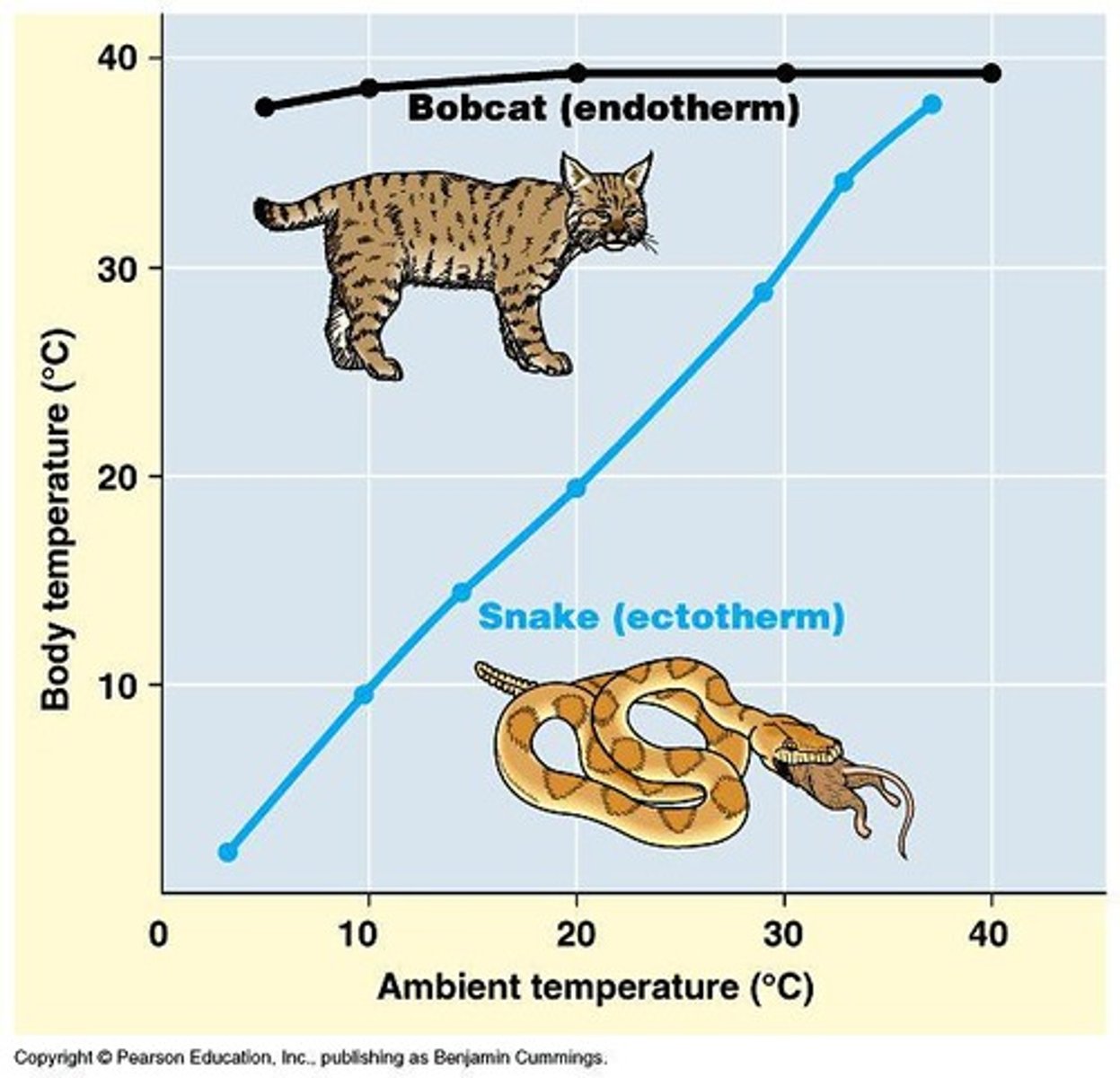
Ectotherms
Organisms relying on environmental temperature.
Optimal pH
pH range for maximum enzyme activity.
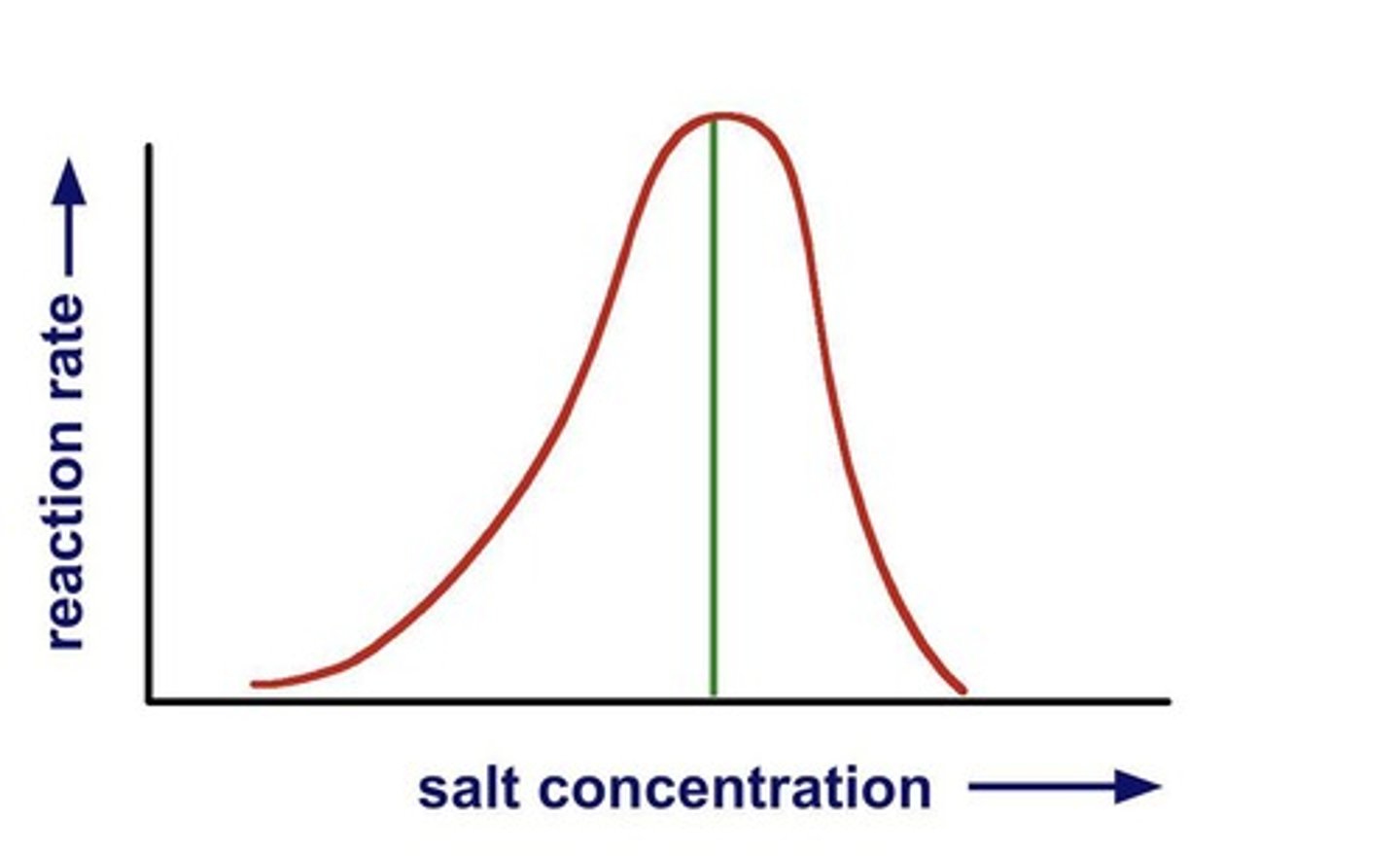
Salinity
Concentration of salts affecting enzyme function.
Cofactors
Inorganic compounds aiding enzyme function.
Coenzymes
Organic molecules that assist enzyme activity.
Non-competitive inhibitors
Bind away from active site, altering shape.
Competitive inhibitors
Compete with substrate for active site binding.
Irreversible inhibition
Permanent binding of inhibitor to enzyme.
Feedback inhibition
Final product inhibits an earlier pathway step.
Metabolic pathways
Series of chemical reactions in living organisms.
Energy coupling
Linking exergonic and endergonic reactions.
Thermodynamics
Study of energy transformations in systems.
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Entropy increases in energy transformations.
Human enzyme temperature range
Optimal activity between 35°C and 40°C.
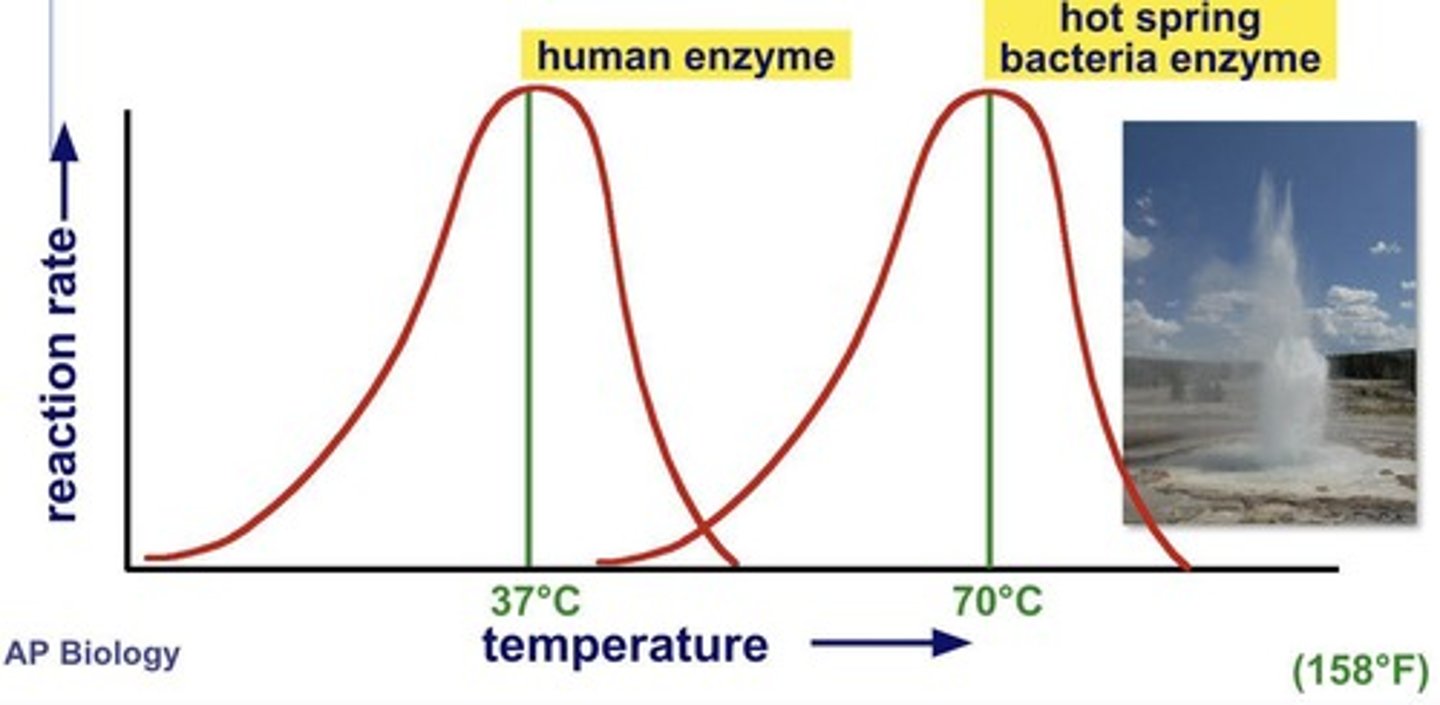
Pepsin
Enzyme active at pH 2-3 in stomach.
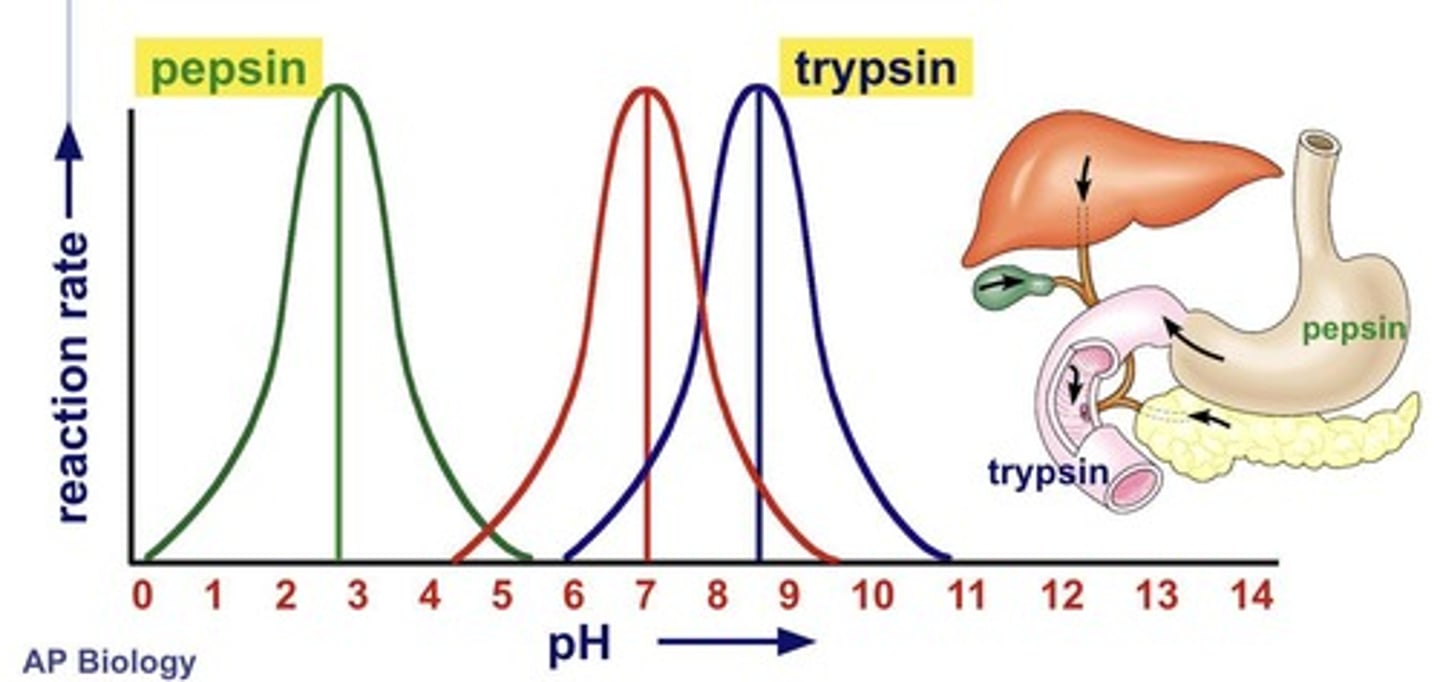
Trypsin
Enzyme active at pH 8 in small intestine.
Dead Sea
High salinity prevents enzyme function.
Aspirin
Irreversible inhibitor binding to active site.
Sarin
Allosteric inhibitor permanently altering enzyme shape.
Vitamin B12
Essential for red blood cell production.
Gibbs Free Energy (ΔG)
Indicates spontaneity of chemical reactions.
ΔH
Change in total energy of a system.
ΔS
Change in entropy of a system.
T
Absolute temperature in Kelvin (K).
Entropy
Measure of disorder in a system.
Photosynthesis
Process converting solar energy into organic molecules.
Kinetic Energy (KE)
Energy of motion; measured by temperature.
Potential Energy (PE)
Stored energy based on position or arrangement.
Chemical Energy
Potential energy in molecular atomic arrangements.
Calorie
Energy needed to raise 1 mL water by 1°C.
Kilocalorie
1,000 calories; energy measurement in food.
ATP
Primary energy currency of the cell.
ADP
Adenosine diphosphate; product of ATP hydrolysis.
Phosphorylation
Transfer of phosphate group to another molecule.
ATP Hydrolysis
Breakdown of ATP releasing energy for work.
Metabolic Rate
Speed of biochemical reactions in organisms.
ATP Cycle
Regeneration of ATP from ADP and Pi.
Mechanical Work
Movement-related work in cells.
Transport Work
Pumping substances across cell membranes.
Chemical Work
Synthesis of molecules from smaller units.
Entropy Tax
Energy loss due to inefficiency in transformations.
2,4-Dinitrophenol (DNP)
Weight-loss drug causing metabolic disruption.
Hyperthermia
Elevated body temperature due to metabolic issues.
Metabolic Acidosis
Condition of increased acidity in body fluids.