BIOL 107 FINAL EXAM
1/291
Earn XP
Description and Tags
EXAM #5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
292 Terms
Life continues through the formation of ________ and _________
new cells and new organisms
Reproduction ensures ____________
survival of species across genereations
Reproduction allows transfer of genetic __________ from ______ → _________
information from parent → offspring
2 Major Strategies of Reproduction
Asexual (clones)
Sexual (genetic variation)
What reproduction do humans use?
BOTH!
our body cells(somatic cells) undergo asexual reproduction – mitosis
The only cells that go sexual reproduction – gametes
DNA contains genes that ________
provide instructions for building proteins
DNA is packaged into __________
chromosomes
_____________ is characteristic for a species
Chromosome number
Humans have ____ chromosomes ( ___ pairs)
46, 23
Diploid (__n)
____ sets of chromosomes
____ set from each ________
Most human cells → ___n = ___
( 2n )
Two sets of chromosomes
One set from each parent
Most human cells → 2n = 46
Haploid (__n)
_____ set of chromosomes
Gametes ( ____ & ____ ) → ___n = ___
( 1n )
One set of chromosomes
Gametes (egg & sperm) → 1n = 23
2n = 4
meanings of 2, “n,” 4
4 = # of total chromosomes
2 = # of sets of chromosomes
n = # of chromosomes per set
Homologous Chromosomes
same _____
matching pair of chromosomes - one from each parent
same size, shape, genes/location
In Homologous chromosomes, though they have the same size, shape, genes, locations, they may carry ______ _________/_________
different versions/alleles
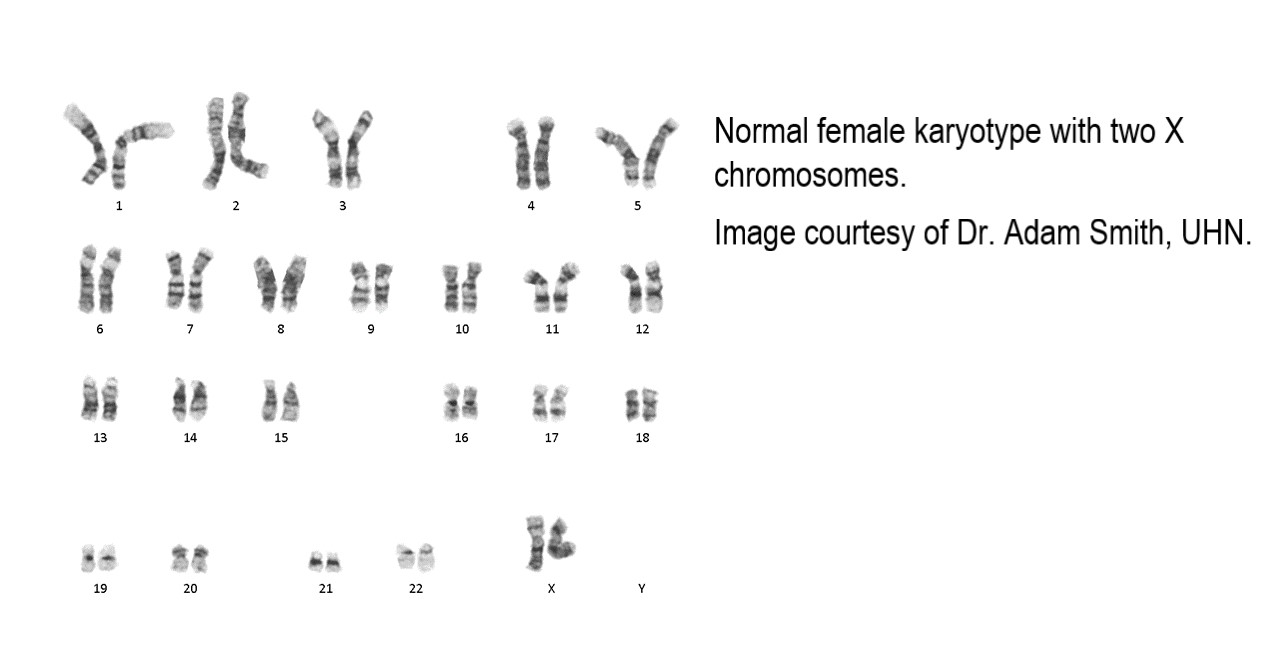
karyotype
Image showing chromosomes arranged by size and shape
Karyotype is used to detect
result from __-______
Chromosome number abnormalities result from non-disjunction
(e.g. Down Syndrome)
Structural changes
Chromosome number abnormalities result from ________________
non-disjunction
22 pairs of chromosomes are __________ ____________
2 pairs are ________ _____________
autosomal chromosomes, sex chromosomes
2 Major Phases of cell division
Interphase (G1, S, G2)
M phase (Mitosis + Cytokinesis)
Cells spend most of their time in _________
interphase
Cell division is regulated by ___________
internal checkpoints
Checkpoints make sure that the _______________ for the cell to _______________
right conditions exist for the cell to go through cell division
Interphase
Preparing for division
G1 phase:
Cell grows
S phase:
DNA replication → chromosomes duplicated
G2 phase:
Final growth
Checks for DNA errors
Chromosomes are duplicated but not yet condensed
G1 Phase in Interphase
cell grows
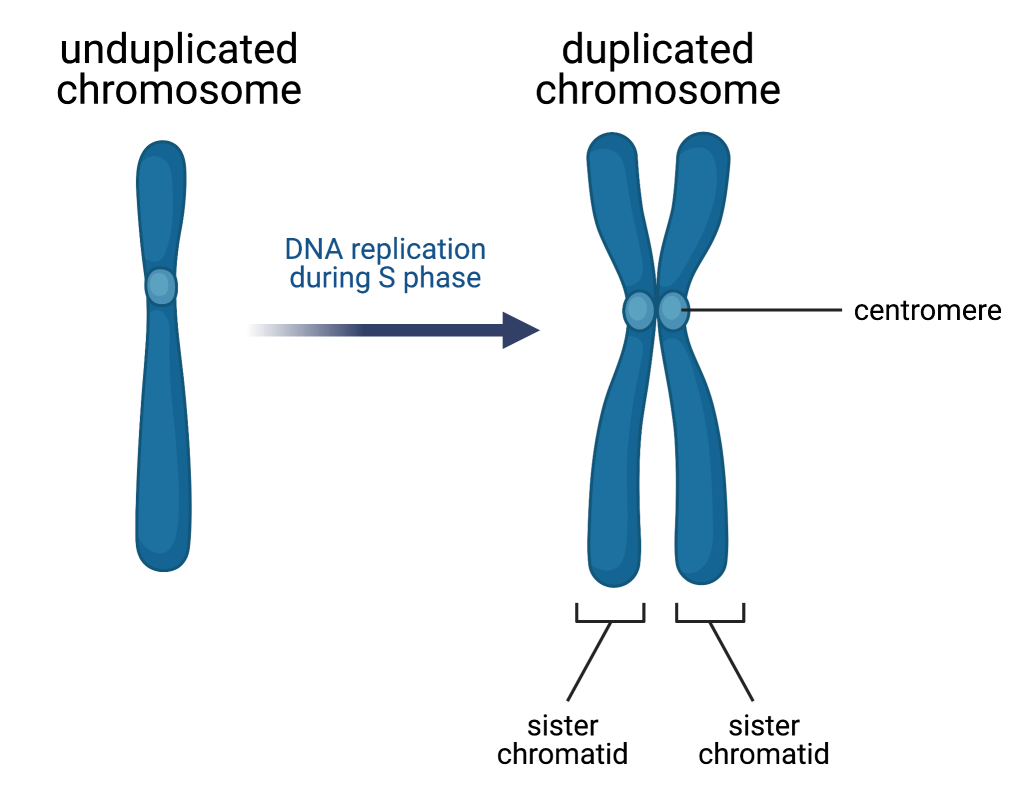
S phase in interphase
DNA replication → chromosomes duplicated
G2 phase in interphase
Final growth
Checks for DNA errors
Chromosomes are duplicated but not yet condensed
During G2 phase, chromosomes are ___________ but not yet _________
duplicated, condensed
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
Produces _________
Mitosis = division of the nuclear contents
Cytokinesis = division of the cytoplasm
Produces two identical daughter cells
Mitosis is the division of __________
nuclear contents
Cytokinesis is the division of the __________ and it produces ________________
cytoplasm, 2 identical daughter cells
Why cells perform mitosis
Growth and development
Tissue repair/healing
Asexual reproduction (in some organisms)
Purpose of Mitosis
Maintains chromosome number
(2n → 2n)
Phases of Mitosis
“I Peed Myself At The Circus”
Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis
Interphase - Mitosis
DNA was replicated
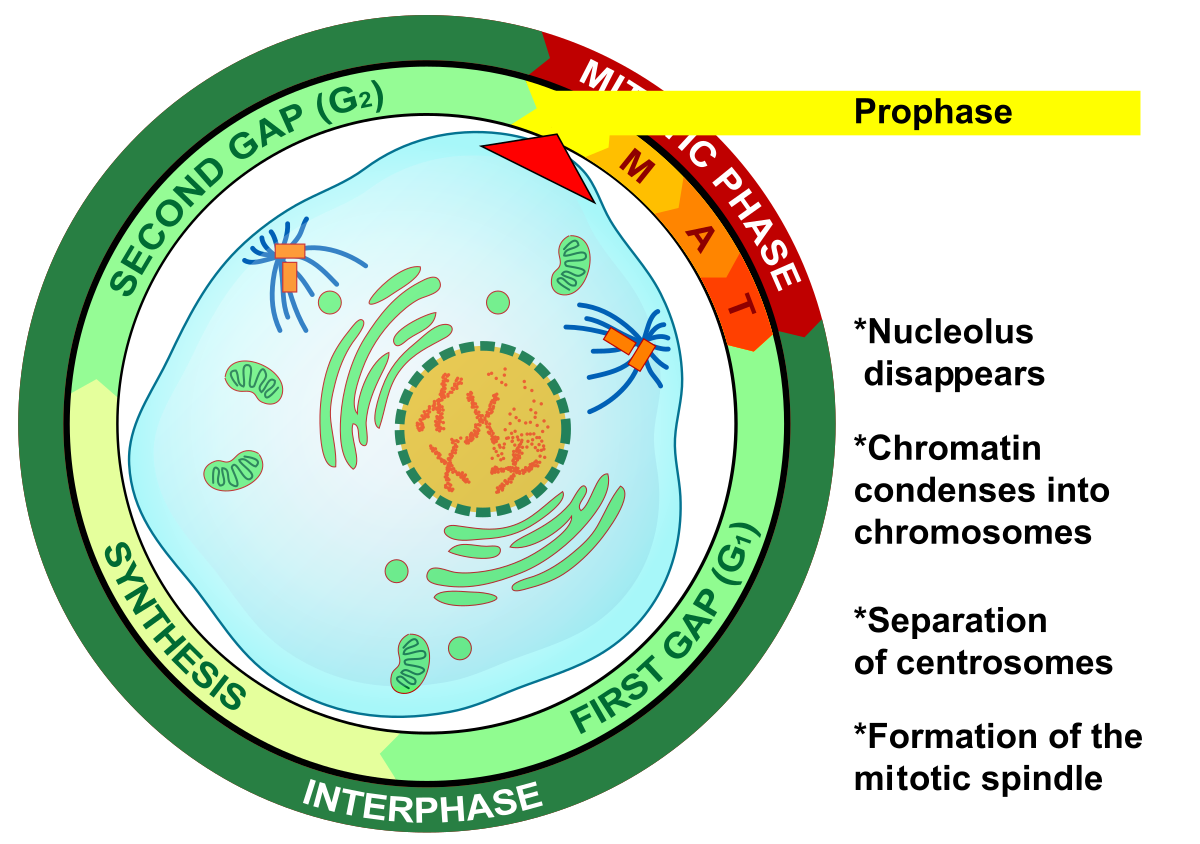
Prophase - Mitosis
Chromosomes condense; spindle aparatus develops/forms
Nuclear envelope breaks down
Centrosome (pair of centrioles), move towards opposite ends of the cell
During Prophase of Mitosis, the chromosomes _________, the spindle aparatus _____/_______
condense, develops/forms
During Prophase of Mitosis, the nuclear envelope ________ _______
breaks down
Mitosis - During prophase, centrosomes(pair of centrioles) move toward _____________
opposite ends of the cell
Prometaphase - Mitosis
(___ ______ attaches to _____ ______)
(spindle apparatus attaches to condensed chromosomes)
Metaphase - Mitosis
chromosomes line up at the cell’s equator
Anaphase - Mitosis
sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles
Mitosis - During anaphase, sister chromosomes _______ and move to _________?
separate, opposite poles
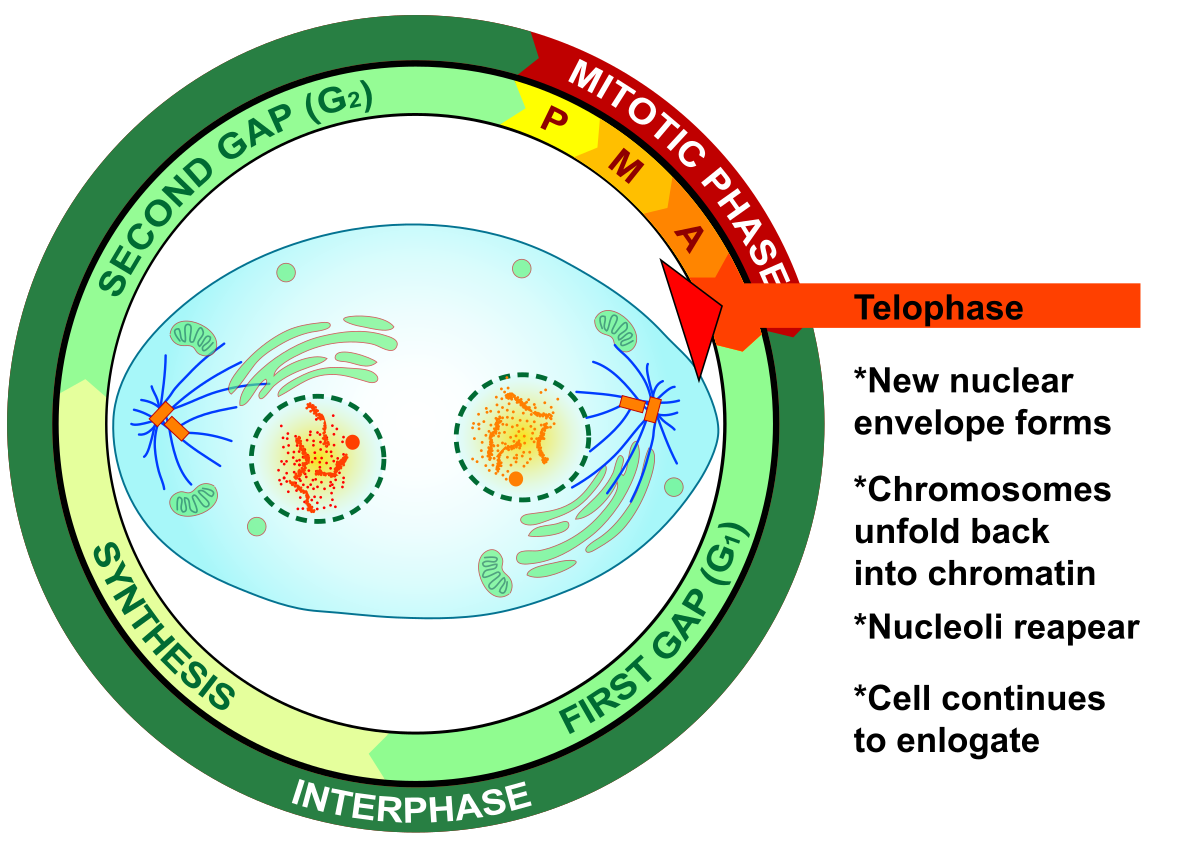
Telophase - Mitosis
reverse of _______
Chromosomes decondense, new nuclei form
cleavage furrow
reverse of prophase
During telophase, chromosomes ______ and new _______ form
decondense, nuclei
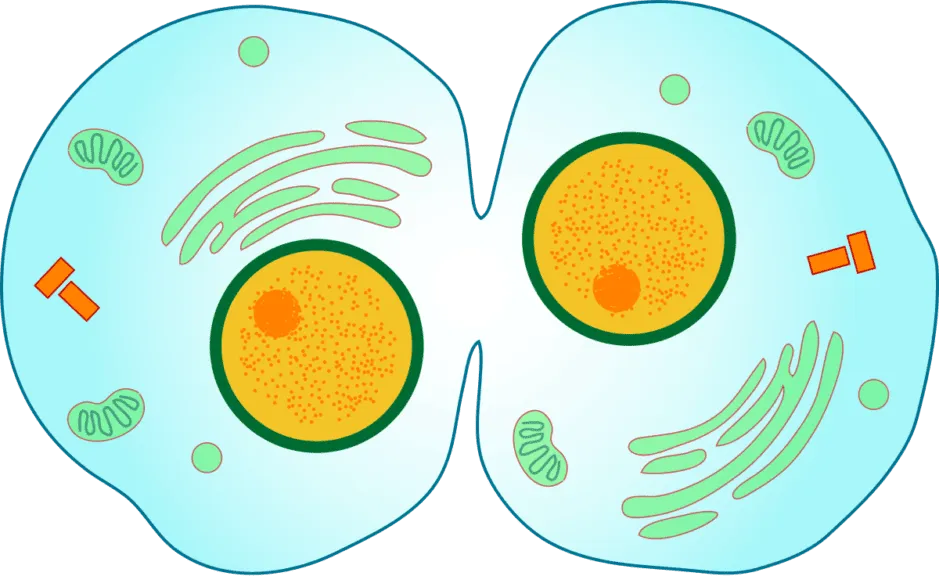
Cytokinesis
produces ________
cytoplasm divides; producing two daughter cells
What does cytokinesis produce?
two daughter cells
Key features of mitosis
Produces 2 genetically identical cells
Diploid → diploid
1 round of cell division
No homologous chromosome pairing
No crossing over
Mitosis produces
2 genetically identical cells
Mitosis has no __________ and no _________
homologous chromosome pairing, crossing over
Why does sexual reproduction requires meiosis?
Reduces chromosome number (diploid → haploid)
Produces gametes (egg & sperm)
Increases genetic variation
Sexual reproduction requires meiosis to reduce _________ _______ ( _____ → _______ )
chromosome number (diploid → haploid)
Meiosis increases genetic variation through:
Crossing over
Independent assortment
Random fertilization
Mitosis makes _____ cells
somatic cells(body cells)
*makes MY TOES*
Meiosis makes ______
gametes (reproductive/sex cells)
*makes ME*
Crossing over - 3 steps
HcDP
Homologous chromosomes pair up in synapse
DNA exchanged through crossing over
Produces recombinant chromosomes
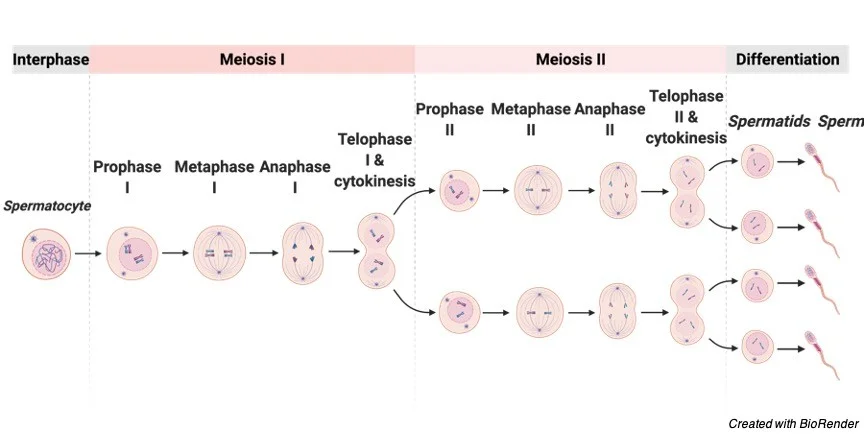
Meiosis Phases
Interphase, Meiosis I, Meiosis II
Meiosis I
separation of ______
_______ reduces ( __ → __ )
Separation of homologous chromosomes
Ploidy reduces (diploid → haploid)
Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I & Cytokinesis
Meiosis I is a separation of _____________
homologous chromosomes
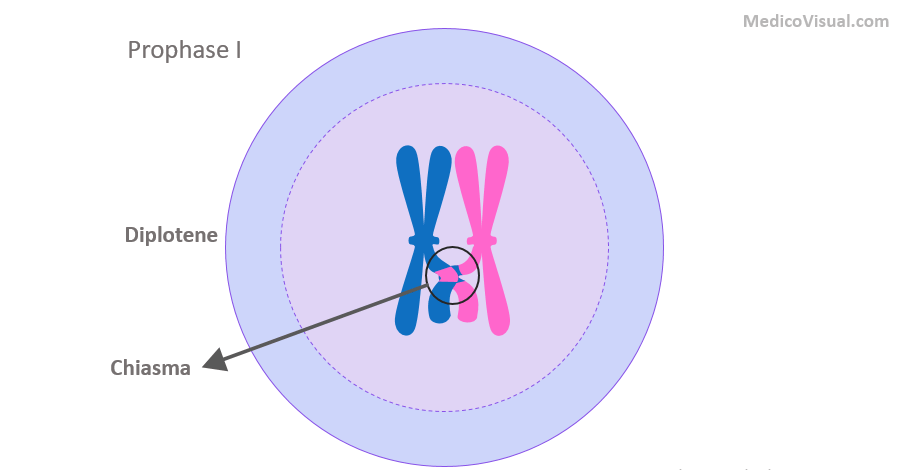
Prophase I - Meiosis I
homologous chromosomes pair (snapsis); crossing over occurs
2n
Metaphase I - Meiosis I
tetrads align at metaphase plate
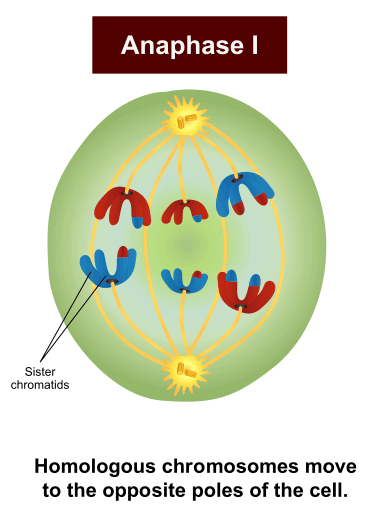
Anaphase I - Meiosis I
homologous pairs separate
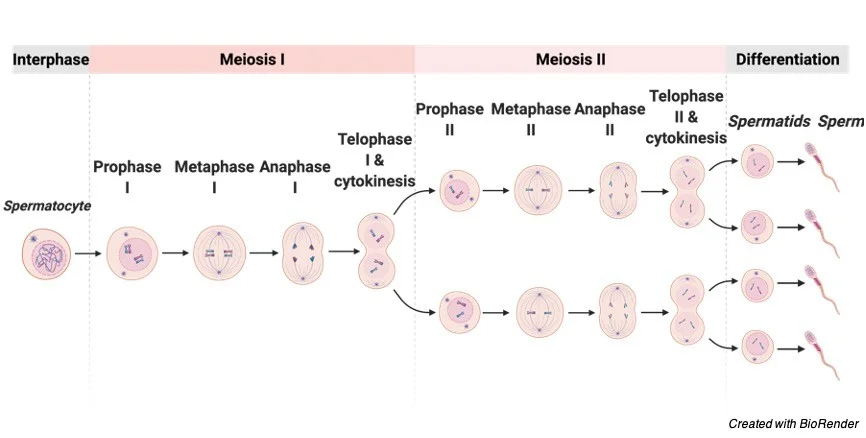
Telophase I & Cytokinesis - Meiosis I
2 cells, each haploid, form; chromosomes still duplicated
Sister chromatids *no longer identical due to crossing over
Meiosis I produces
two haploid cells that are genetically unique from the original parent cell
Meiosis II is a separation of ______________
sister chromatids
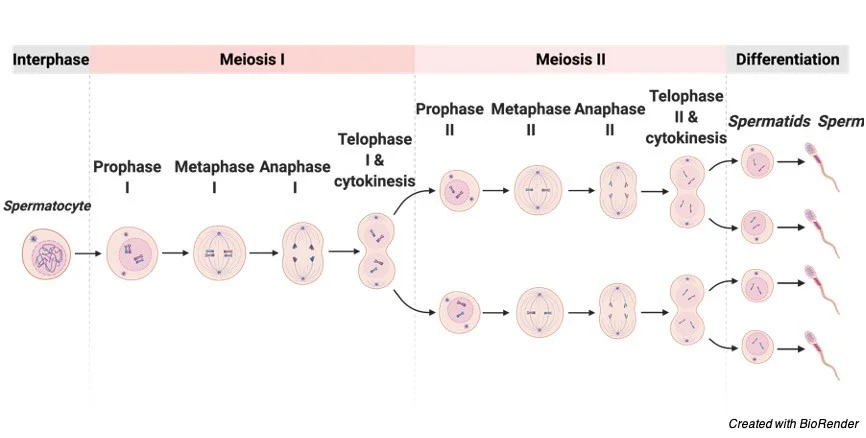
Meiosis II
______ _______ separated → 4 ______ ______
Similar to meiosis
Sister chromatids separated → 4 haploid cells
Each gamete is genetically unique
essentially mitosis for a haploid cell
Meiosis II produces
four genetically unique haploid daughter cells from the two haploid cells that entered the stage
purpose of mitosis
growth/repair
purpose of meiosis
gamete production
Reproductive System is responsible for:
Production of gametes
Protection/nourishment of developing fetus (in females)
Releasing hormones
the reproductive system provides ________/_____ of developing fetus (in _____)
Protection/nourishment of developing fetus (in females)
Sexual maturity occurs between
8-13 in females
9-14 in males
Production of human somatic cells
produces _____ cells and _________
______ cell division
produces 2 ____________
______ chromosomes in human somatic cells
Mitosis
Produces somatic (body) cells AND diploid germ cells
One cell division
Produces 2 genetically identical, diploid (2n) cells
46 chromosomes in human somatic cells
Production of human somatic cells produces
2 genetically identical, diploid (2n) cells
there are ______ chromosomes in human somatic cells
46
Production of human sex cells
produce ________ cells
involved in _________
_____ cell divisions (________)
produces 4 __________
_____ chromosomes in human gametes
Meiosis
Produces sex cells (gametes)
Involved in sexual reproduction
Two cell divisions (Meiosis I & II)
Produces 4 genetically unique, haploid (1n) cells
23 chromosomes in human gametes
Meiosis produces
4 genetically unique, haploid (1n) cells
there are ____ chromosomes in a human gamete
23
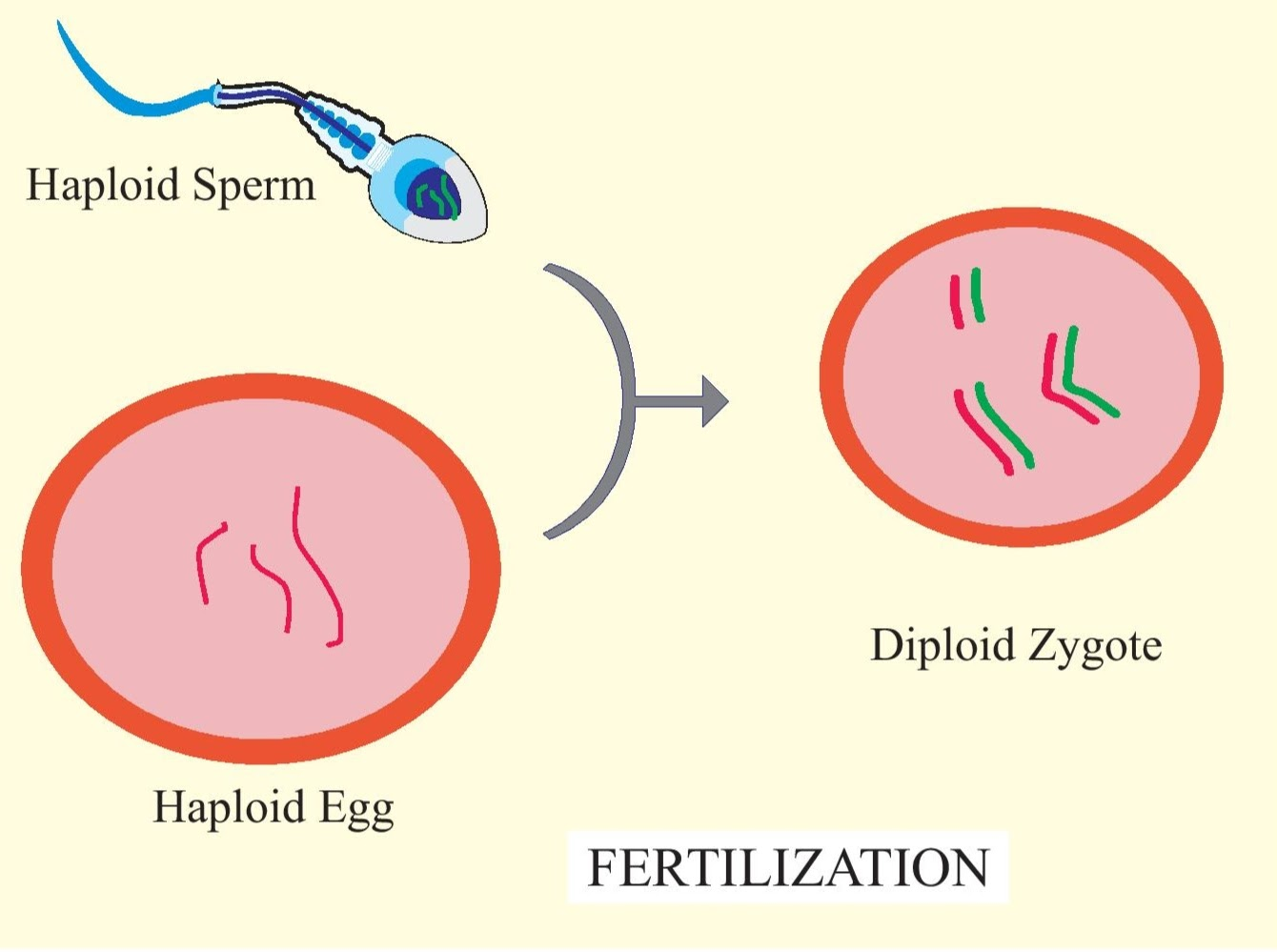
Fertilization
Restores the diploid state
Produces a zygote
Formed when a sperm cell (1n) fertilizes an ovum (1n)
Contains a complete set of chromosomes (2n) – half from each parent
Fertilization restores the _________
diploid state
Fertilization produces ___________
zygote
Fertilization is formed when ______________
a sperm cell (1n) fertilizes an ovum (1n)
Fertilization contains __________
a complete set of chromosomes (2n) – half from each parent
Zygote
Represents the first cell of new organism
Undergoes rapid cell division (cleavage) to begin embryonic development
a zygote undergoes ____ ____ ______ (____) to begin embryonic development
rapid cell division (cleavage)
Cleavage
rapid cell division – the cells are dividing without really growing in between
Female reproductive organs
O Of U C
Ovaries, Oviduct (fallopian tube), Uterus, Cervix
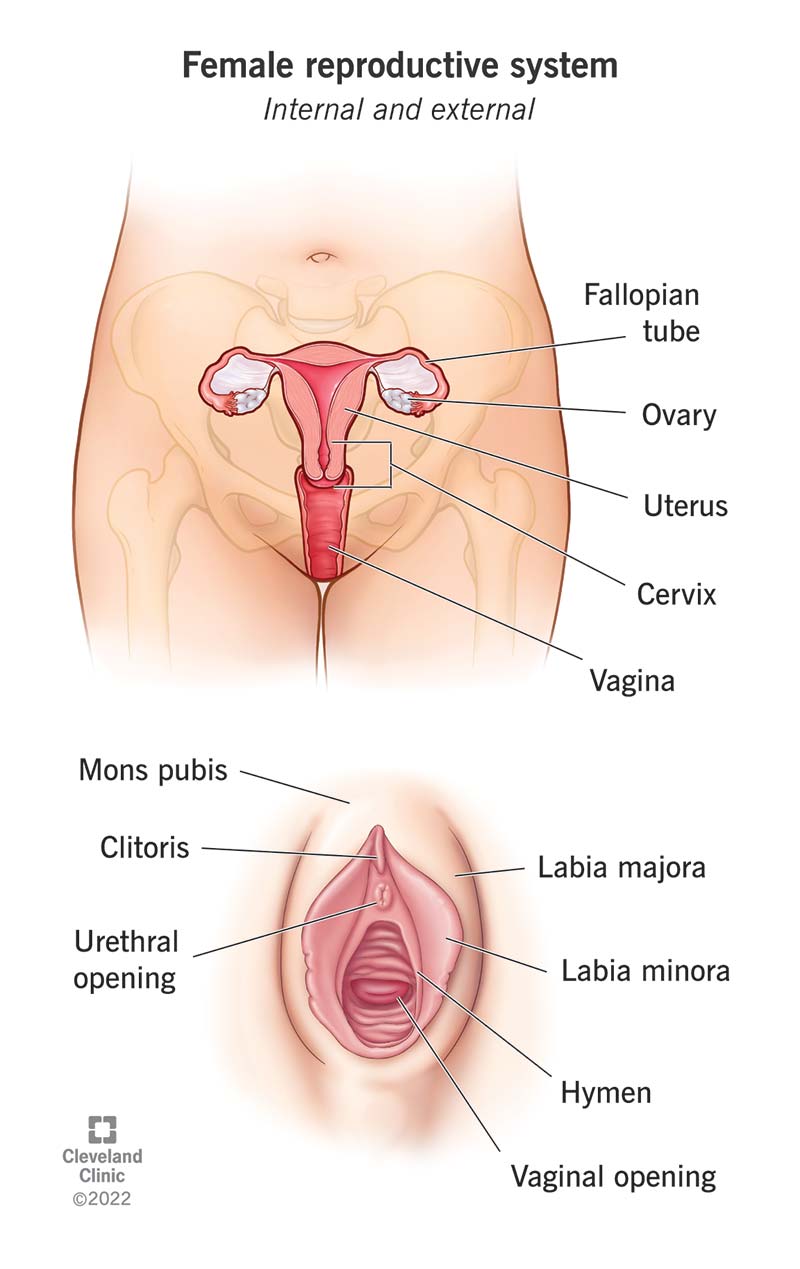
Ovaries
Produce hormones and oocytes, immature eggs
Oviduct (fallopian tube)
Transport oocyte to uterus
Site of fertilization
what is the site of fertilization?
Oviduct (fallopian tube)
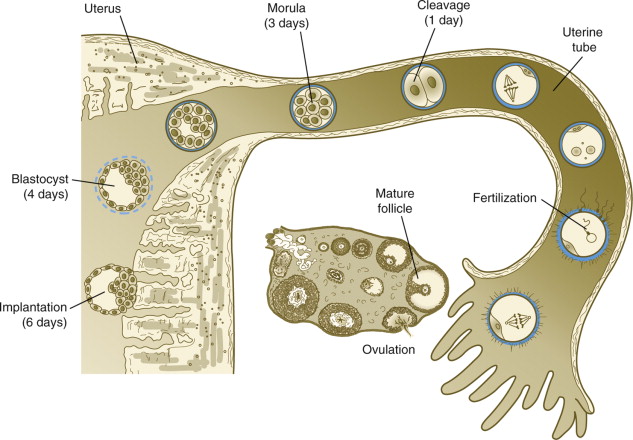
the Oviduct (fallopian tube) transports
______ → _______
oocyte → uterus
Uterus
Muscular organ
Supports embryo development
Walls include:
Myometrium = muscular layer
Endometrium = inner lining; thickens and sheds during menstrual cycle
the uterus supports ______ ________
embryo development
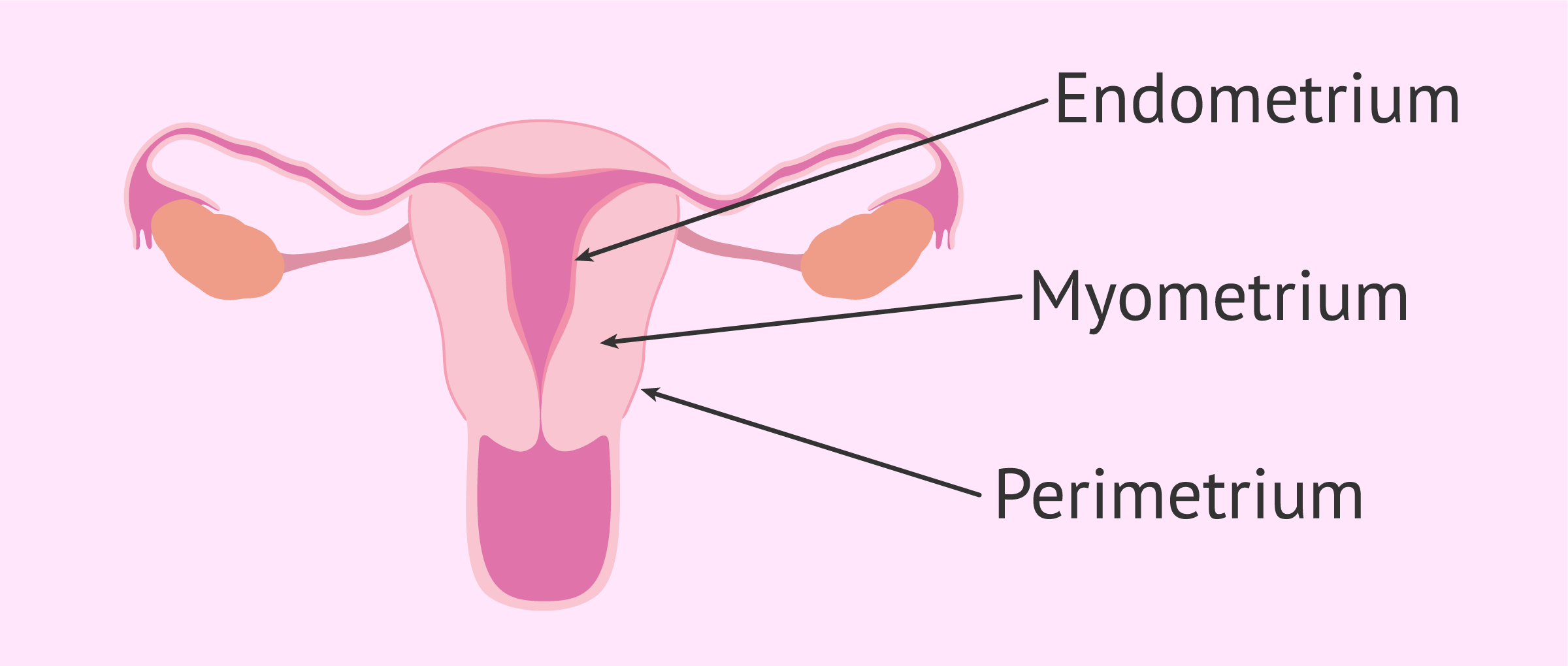
Myometrium
muscular layer in the walls of uterus
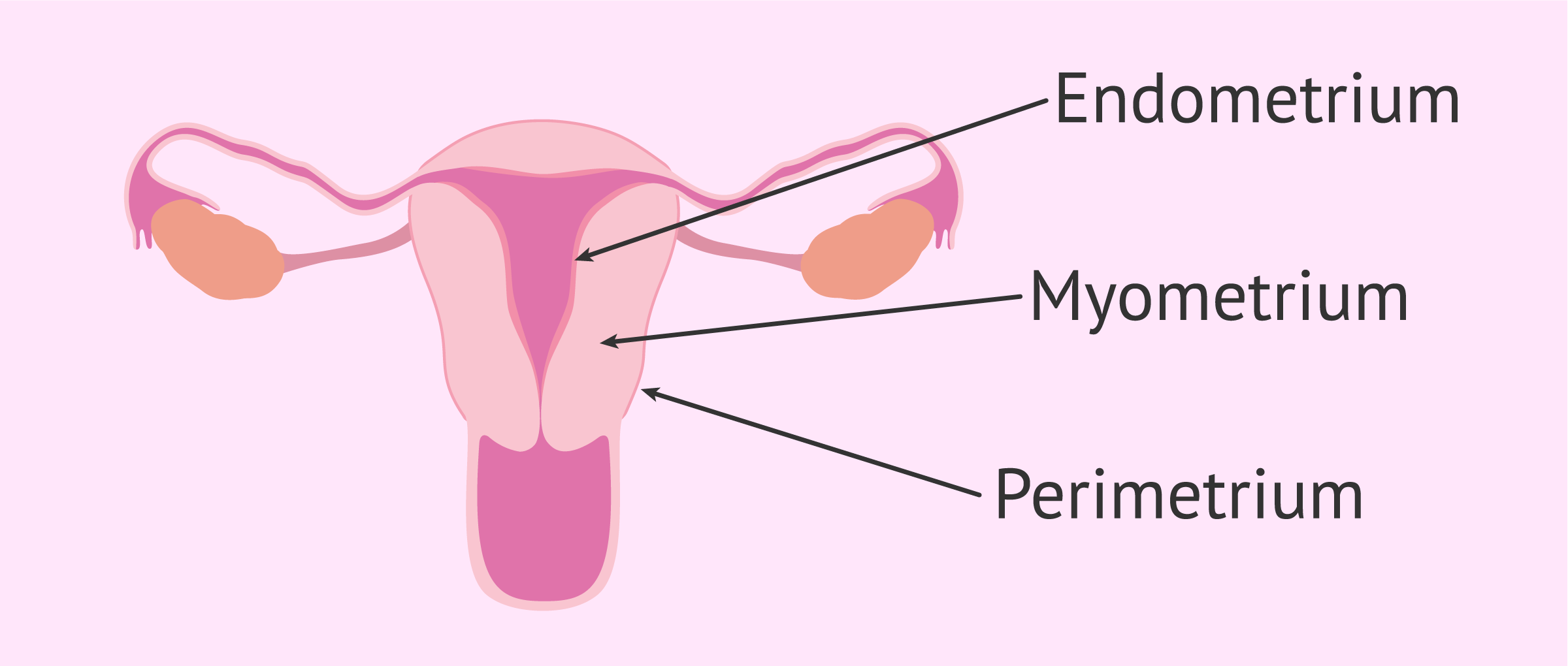
Endometrium
inner lining of the uterus; thickens and sheds during menstrual cycle
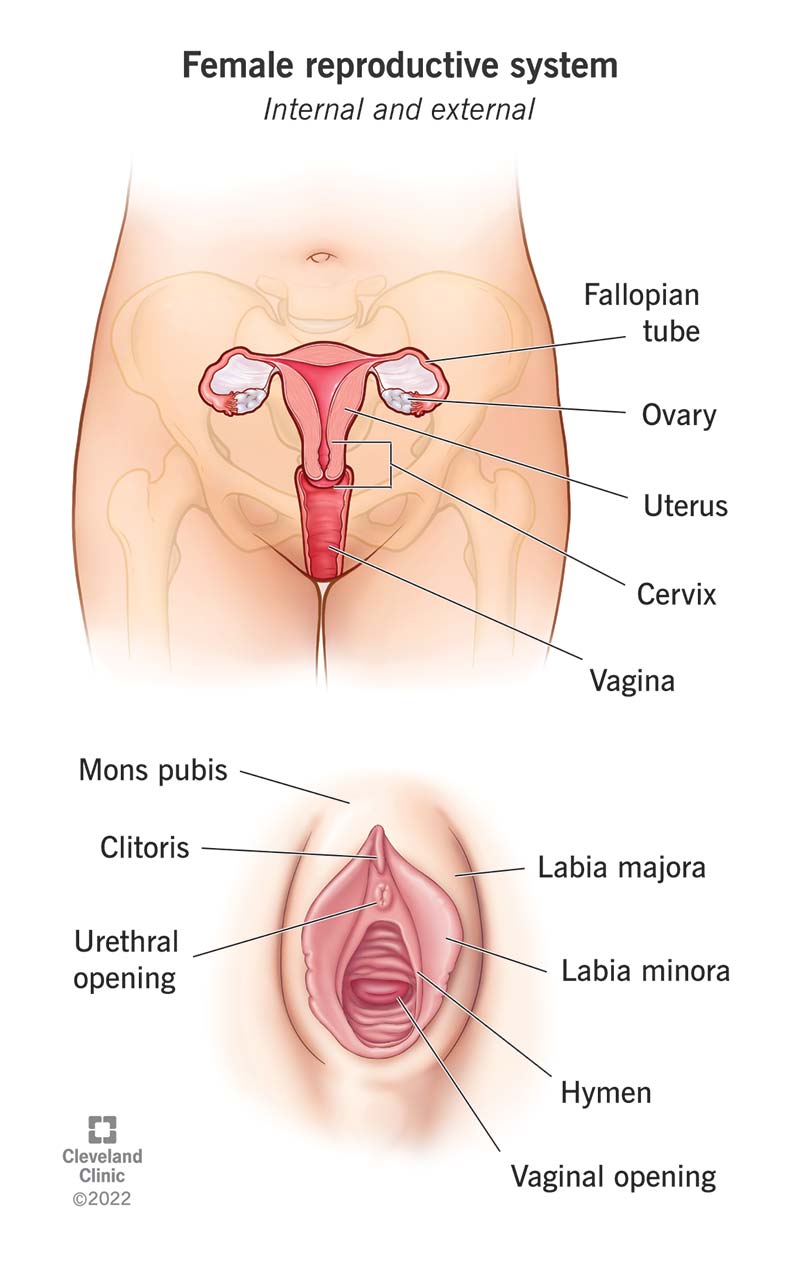
Cervix
Gateway between uterus and vagina
Oogenesis
development of the ovum
Oogenesis: Before birth
Oogonia → primary oocytes
Primary oocytes begin meiosis I and arrest in prophase I
~1–2 million present at birth
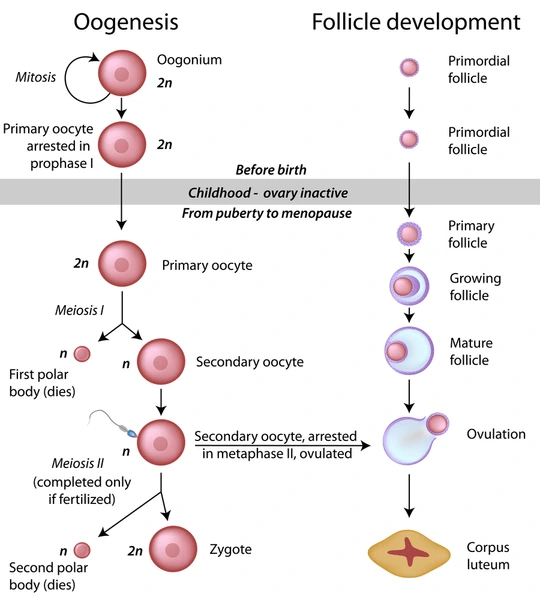
In Oogenesis, Primary oocytes begin ________ and arrest in ________
meiosis I, prophase I
Oogenesis: At puberty
Monthly hormonal signals resume meiosis I
Primary oocyte → secondary oocyte + first polar body
At puberty, month hormonal signals resume _______
Meiosis I