ARL MIDTERMS MEGA PEYZ
1/288
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
289 Terms
lewis keeble
who thinks urban planning is “art and science of ordering the use of land and siting of building and communication routes so as to secure maximum practicable degree of economy, convenience, and beauty”?
john ratcliffe
who thinks urban planning is “allocation of resources, particularly land, in such a manner as to obtain a maximum efficiency, while paying heed to the nature of the built environment and the welfare of the community.”?
john friedmann
who thinks urban planning is “a way of thinking about socio-economic problems oriented predominantly toward the future, is deeply concerned with the relation of goals to collective decisions and strives for comprehensiveness in policy and program.”?
paul davidoff and thomas reiner
who thinks urban planning is “a process for determining appropriate future action through a sequence of choices.”
the achievement of ends, exercise of choice, orientation to the future, action, comprehensiveness
characteristics of planning
law regulating the environmental planning profession in the philippines
what is PD 1308
PD 1308
According to ____ environmental planning is activities concerned with the management and development of land as well as the preservation, conservation, and rehabilitation of the human environment.
environmental law of 2013
what is RA 10587
RA 10587
According to ___ environmental planning is the multidisciplinary art and science of analyzing, specifying, clarifying, harmonizing, managing, and regulating the use and development of land and water resources, in relation to their environs, for the development of sustainable communities and ecosystems.
economic development, equity/social justice, environmental protection
what are the three corners of planner’s triangle
property conflict
what type of conflict formed between social justice and economic development
development conflict
what type of conflict formed between social justice and environmental protection
resource conflict
what type of conflict formed between economic development and environmental protection
people, sovereignty, territory, government
a state must have
planning as state intervention
Refers to the collective action involving the legitimate coercive powers of the government. It encourages, prescribes, discourages, or prohibits private action
power of taxation, police power, power of eminent domain
inherent powers of state are
supplier of public, regulator and facilitator of operations in marketplace, social engineer, arbiter, agent
according to dear and clark, role of state are
social inequality, environmental degradation
Land is used for greed and needs leading to _____ and _______
public control, incentive
Land use planning is used by government as _____ and ______
legal, physical, social
Land use planning constraints are
DENR, LLDA
Who monitors the land use planning constraints (Public)
DHSUD
Who monitors the land use planning constraints (Private)
NCIP
Who monitors the land use planning constraints (Ancestral)
CLUP, PPFP
Who monitors the land use planning constraints (LGU)
local government code of 1991
According to __________, planning is a political activity supported by the services of technical people.
property owners, state, electorate
Land use stakeholders
conquest and settlement in newly discovered territories
What are the westerners’ pov of land
notion of stewardship. Man as caretaker of God’s creation
What are the biblical pov of land
land
_____ refers to the ground, soil, or earth that can be owned or possessed by a person, group, or entity.
air rights like tree branches and roof lines
extent of land ownership above
include underground rights like minerals
extent of land ownership below
barlowe
According to ________… land is the sum total of natural and man-made resources… control of which is achieved by possession of the Earth’s surface.
71, 29
In earth, ___ % is water while land is ___%
factor of production, consumption, or both
in economic perspective, land is _____
natural environment or earth’s surface
in ecological perspective, land is _____
macro/microclimate, hydrology, geology, topography, plants and animals living on it
attributes of land
forest and wildlife
“Green” land is known as
aquatic
“Blue” land is known as
socio-economic
“Brown” land is known as
location
Since land is immovable, its ____ determines its value and subsequent land use
land use is distributed efficiently to avoid conflict, develop urban centers in disadvantageous areas
What are the ideal distribution of land
development is forced to adapt where its available, develop urban centers on disadvantageous areas requires huge investment capital
What are the realities of distribution of land
true
Land is not reproducible
topography, soil content, minerals, oil, gas, sub surface structure and composition
Physical and climatic characteristics of land
load-bearing capacity and location
urban implications of land
urban implication
this implication is less dependent in nature but more productive
accessibility, amenity, topography, utilization, historical factors
Eugene Brigham’s Five Determinants of Land Value
rural implication
this implication is more dependent on nature
soil fertility, climate, water quality, nutrient, quality and quantity of mineral
rural implications of land
natural resource, economic good, property, territory
land is known as
inland and territorial waters, airspace above, subsoil below
state owns the land’s
forest land
Type of land that is declared for forestry purposes. Production and protection of forests, shouldn’t be titled.
timber land
Portion of forestland lease by state to operators of commercial forestry production
mineral land
Portion of forestland that is declared by DENR – Mines and Geosciences bureau to have rare mineral
ancestral land
Portion of forestland that is occupied by indigenous people
pasture land
Portion of forestland for raising livestock
alienable and disposable land, commonwealth act 141
Land that is not needed for forest purposes thus for disposition according to __________ amended by public lands act (No land 18% or over slope shall be classified as A or D nor titled)
arable land
Land theoretically good for agriculture, fisheries, and livestock according to FAO standards. (Not currently cultivating)
crop land
Land good for intensive/extensive agriculture (Actually cultivating)
marginal land
Land not readily useful for agriculture, forestry, or settlement
industrial land
Land for manufacturing, processing, construction, storage, distribution by at least 10 people
land use conversion
It is defined by natural/man-made activities in, on, over or under land surface
kaiser, edward, j.
He defined the natural/man-made activities in, on, over or under land surface
nature-attached activities
In this activity, land has capacity to renew itself (erosion, volcanic eruption)
man-made activities
In this activity, land is usually irreversible (construction)
reversible
A type of land conversion that define landform are not substantially changed
irreversible
A type of land conversion that define original land condition is difficult to attain
reversible
Land used as a site, changed to another use as a site = ?
reversible
Land used as a soil, changed to another use as a soil = ?
irreversible
Land used as a soil, changed to another use as a site = ?
land use capacity
Also known as the limits of land to be used productively
profit return, sustainability, socio-cultural values
What are the considerations to determine the land use capacity
land use compatibility
It talks about that different land uses should coexist harmoniously.
economic harmony, ecological sustainability, socio-cultural sensitivity
Different types of land use compatibility
exclusionary, mixed-use zoning
Types of land use zoning according to its compatibility
exclusionary
A type of land use zoning that keeps incompatible activities separated
mixed-use zoning
A type of land use zoning that allows compatible activities to coexist productively
land use capacity
Relative ability of a unit of land to produce a surplus (excess) of returns above the cost of utilization (use)
carrying capacity
It is about how much of a kind of use can an area sustain without significant damage, such as soil compaction, soil erosion, and nutrient loss.
land misuse
It is about improper use of land (Contradiction with recommend use or environmental characteristics)
land disuse or nonuse
It is the act of letting the land lie idle, vacant, and unproductive
walt whitman rostow
Rostow’s stages-of-growth was developed by
rostow’s stages-of-growth
This theory believes that a country passes through sequential stages in achieving development
traditional society, pre takeoff, takeoff, drive to maturity, age of high mass consumption
Stages of Rostow’s stages of growth
harrod-domar growth model
Theory wherein functional economic relationship which growth rate of gross domestic product (g) depends on the national savings-income ratio (s) and inversely on the national-capital output (c)
level of savings, productivity of investment
In harrod domar model, economic growth depends on
capital-output ratio
Ratio that shows that units of capital are required to produce a unit of output over a given period
labor, capital
In harrod domar model, Economic growth depends on the amount of _____ and _____
physical capital
In harrod domar model, The least developed countries often have abundant supply of labor; it is a lack of ________ that holds back economic growth and development
income
In harrod domar model, higher ____ allows higher levels of saving
structural change theory
A theory that focuses on mechanisms by which underdeveloped economies transform their economic structures from a heavy emphasis on traditional subsistence agriculture to a more modern, more urbanized, and more industrially diverse manufacturing and service economy.
underutilization of resources
In structural change theory, It Hypothesizes that underdevelopment is due to _______ arising from structural or institutional factors that have their origins in both domestic and international dualism.
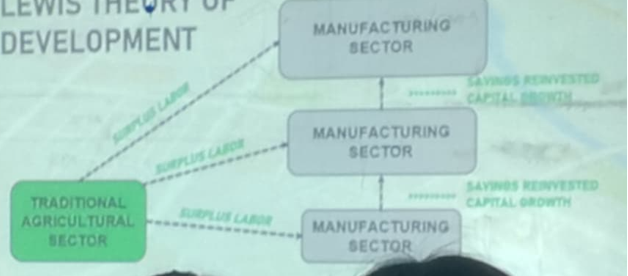
two-sector surplus labor model
A model in Which surplus labor from agricultural sector is transferred to the modern industrial sector
structural transformation
Also known as lewis turning point, it is the Process of transforming an economy in such a way that the contribution to national income by the manufacturing sector eventually surpasses the contribution by the agricultural sector.
two-sector surplus labor model
What model is this
patterns of development analysis by chenery et al.
An attempt to identify characteristic features of the internal process of structural transformation that a typical developing economy undergoes
patterns of development analysis by chenery et al.
In this theory, Increased savings and investment are perceived as necessary but not sufficient conditions for economic growth
physical, human
According to the patterns of development analysis of chenery et al., ___ and ____, along with interrelated changes in economic structure of a country is required in transitioning from traditional economic system to modern.
international dependence revolution
This revolution was built from growing disenchantment with both the stages and structural change models
developing countries
In the international dependence revolution, it Views ______ as beset by institutional, political and economic rigidities, both domestic and international, and caught up in a dependence and dominance relationship with rich countries