Atomic Structure
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:49 PM on 10/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
1
New cards
relative atomic mass definition
the average mass of an atom of an element compared to 1/12th of the mass of a Carbon-12 isotope
2
New cards
properties of isotopes
chemical properties are identical as they have the same number and arrangement of electrons
physical properties may differ due to different masses
physical properties may differ due to different masses
3
New cards
relative abundance formula
Ar = (mass x abundance)... / total abundance
4
New cards
finding the % abundance

5
New cards
s sub-shells
contain 1 s orbital holding a max of 2 electrons
6
New cards
p sub-shells
contain 3 p orbitals holding a max of 6 electrons
7
New cards
d sub-shells
contain 5 d orbitals holding a max of 10 electrons
8
New cards
f sub-shells
contain 7 f orbitals holding a max of 14 electrons
9
New cards
filling up energy levels
electrons occupy the lowest available energy level first (Aufbau principle)
10
New cards
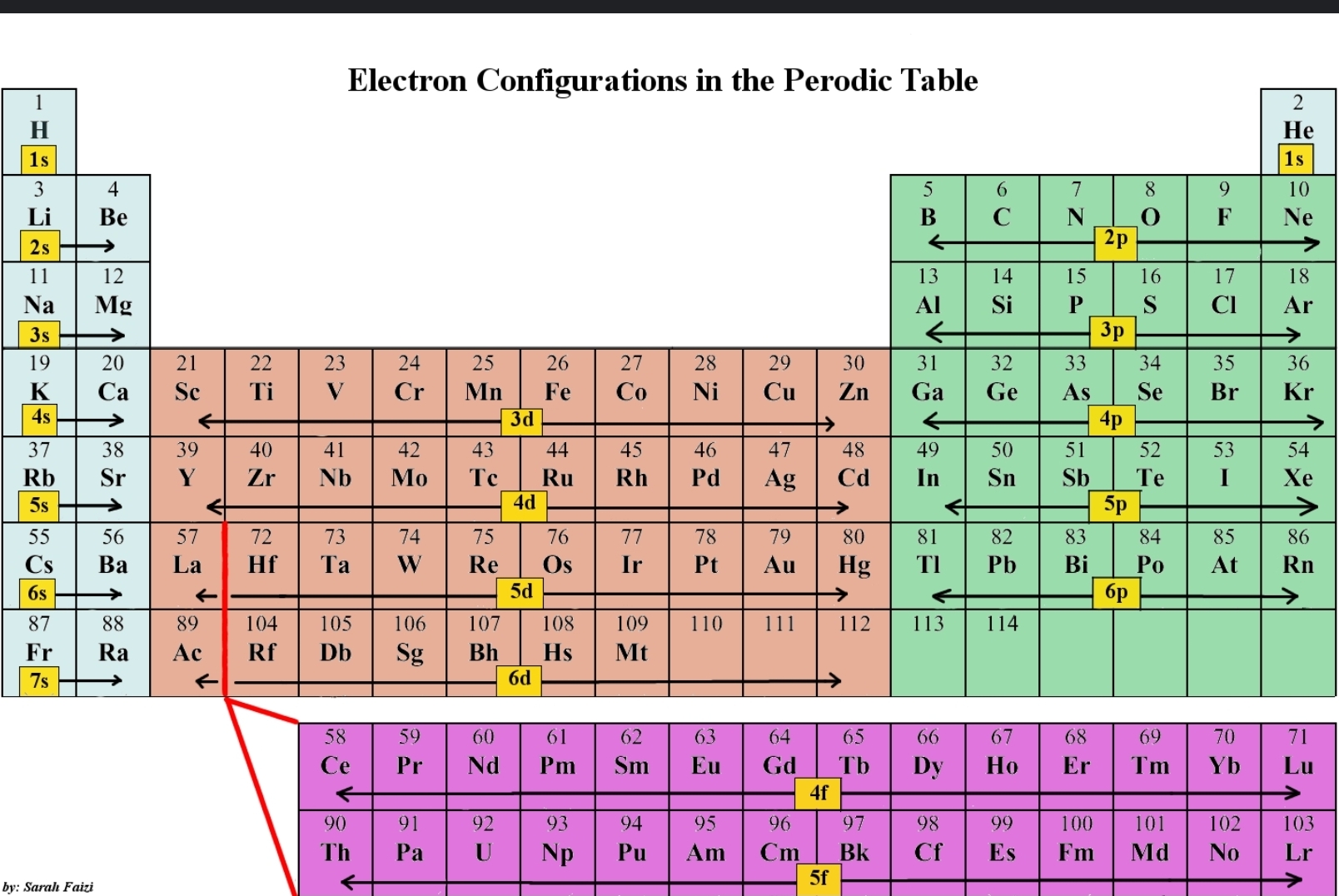
electronic configuration and the periodic table
an element's location on the periodic table gives its complete electronic arrangement - look on the table to find its outermost sub-shell (however far it is into the section is how many electrons in that shell)
all sub-shells before then are full
all sub-shells before then are full
11
New cards
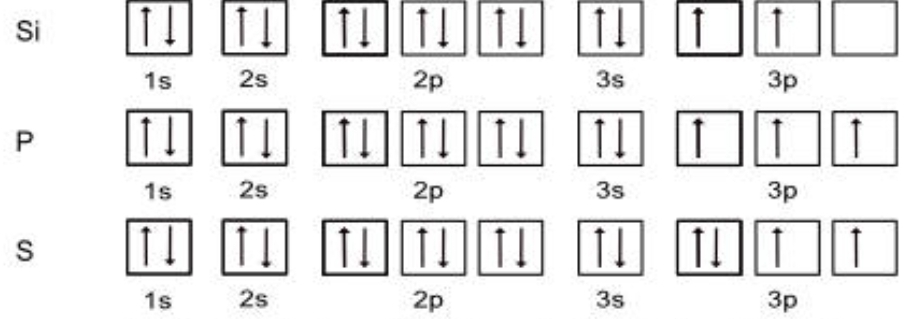
box and arrow notation
each box represents one orbital, each arrow represents an electron
always label the boxes
electrons prefer to be in an orbital alone, fill up all orbitals in subshell with one electron before pairing them
always label the boxes
electrons prefer to be in an orbital alone, fill up all orbitals in subshell with one electron before pairing them
12
New cards
first ionisation energy
energy required to remove an electron from each atom in 1 mole of gaseous atoms to form 1 mole of gaseous +1 ions
13
New cards
first ionisation energy equation
X (g) -> X+(g) + e-
always include state symbols
always include state symbols
14
New cards
second ionisation energy
energy required to remove an electron from each ion in 1 mole of gaseous +1 ions to form 1 mole of gaseous 2+ ions
15
New cards
second ionisation energy equation
X+ (g) -> X 2+ (g) + e-
16
New cards
is ionisation an endothermic or exothermic process?
removing electrons from atoms is an endothermic process as energy is needed to overcome the attraction of the nucleus on the outgoing electron. The stronger the attraction, the greater the ionisation energy
17
New cards
3 factors that affect ionisation energy
1) distance of the electron from the nucleus (closer to nucleus means stronger attraction so higher ionisation energy)
2) number of inner electron shells (repel outer electrons and shield positive charge of nucleus meaning lower ionisation energy)
3) number of protons in nucleus (more protons means greater attraction)
2) number of inner electron shells (repel outer electrons and shield positive charge of nucleus meaning lower ionisation energy)
3) number of protons in nucleus (more protons means greater attraction)
18
New cards
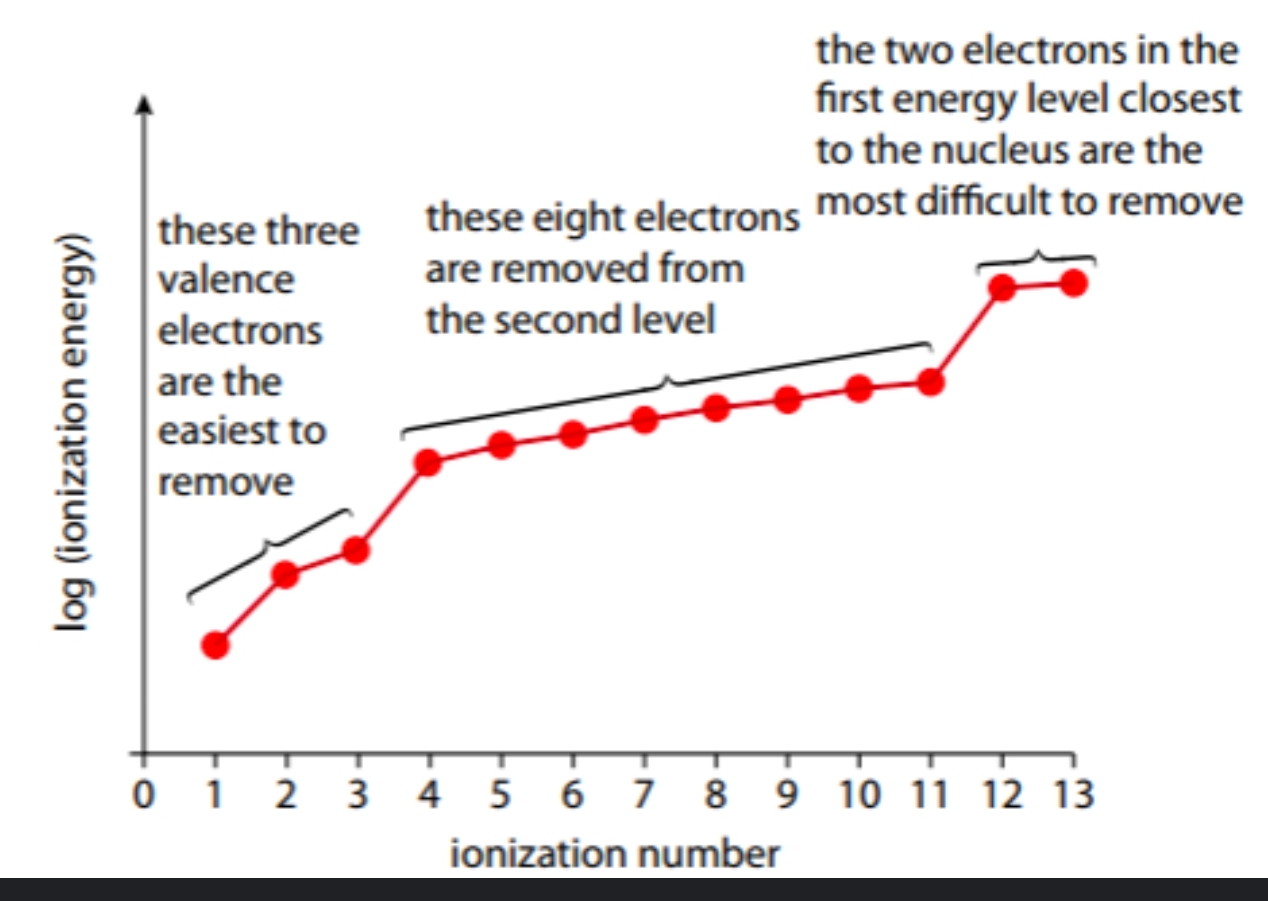
successive ionisation energies
how much energy is required to remove an electron from an atom until all electrons are removed
19
New cards
why are log ionisation energies plotted on successive ionisation energy graphs?
there are large differences between successive values (large range)
log=to power of 10
log=to power of 10
20
New cards
during successive ionisation, why do electrons in different shells have large differences in energy required?
as they are in different shells, they are different distances from the nucleus. Electrons in higher shells experience less attraction as they are further from the positive nucleus and there are more inner shells shielding them. This means that less energy is required to remove them
21
New cards
during successive ionisation, why do electrons in the same principle energy shell have similar values for energy but with small incremental increases?
as they are all in the same shell, they are the same distance from the nucleus with the same amount of inner level shielding. However, as each electron is removed, the ion becomes increasingly positive, meaning more energy is required to overcome the attraction (explaining the small differences)
22
New cards
trends in first ionisation down the groups in the periodic table
as you go down any group, 1st ionisation energy gets lower
although the number of protons in the nucleus increases, the electron being removed is further from the nucleus and experiences more inner electron shielding so less energy is required
although the number of protons in the nucleus increases, the electron being removed is further from the nucleus and experiences more inner electron shielding so less energy is required
23
New cards
patterns in atomic radius across a period
across a period, all atoms have the same number of shells and experience the same amount of shielding but the nuclear charge increases as there are more protons. The electrons are more strongly attracted to the nucleus, so the atomic radius decreases
24
New cards
which elements form ions which are smaller than the atom from which they are formed?
elements that form cations as they lose the outer shell
25
New cards
which elements form ions which are larger than the atom from which they are formed?
elements that form anions have a bigger atomic radius
they don’t gain shells (they fill the outer shell) yet the electrons repel from each other making the ion larger
they don’t gain shells (they fill the outer shell) yet the electrons repel from each other making the ion larger
26
New cards
isoelectronic
same electronic configuration
27
New cards
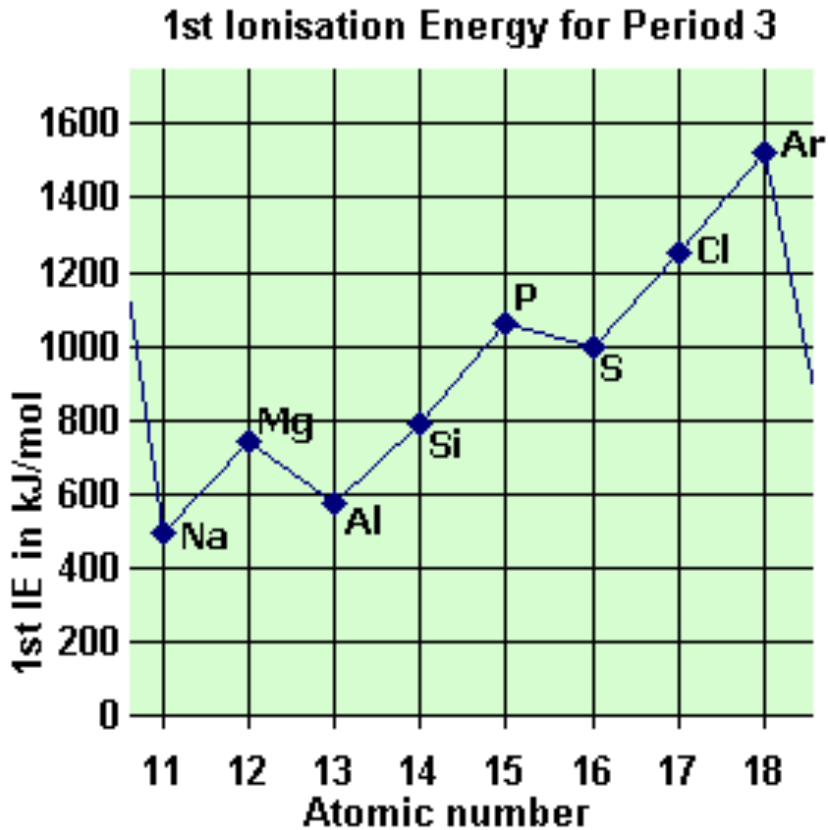
trends in first ionisation energy across a period
general increase as proton number increases (more attraction)
there are drops after new shells and sub shells with significant drops between periods
there are drops after new shells and sub shells with significant drops between periods
28
New cards
explain the drop between magnesium and aluminium
from an s -> p sub shell
p sub shells are further from nucleus so less energy is needed to remove electrons
p sub shells are further from nucleus so less energy is needed to remove electrons
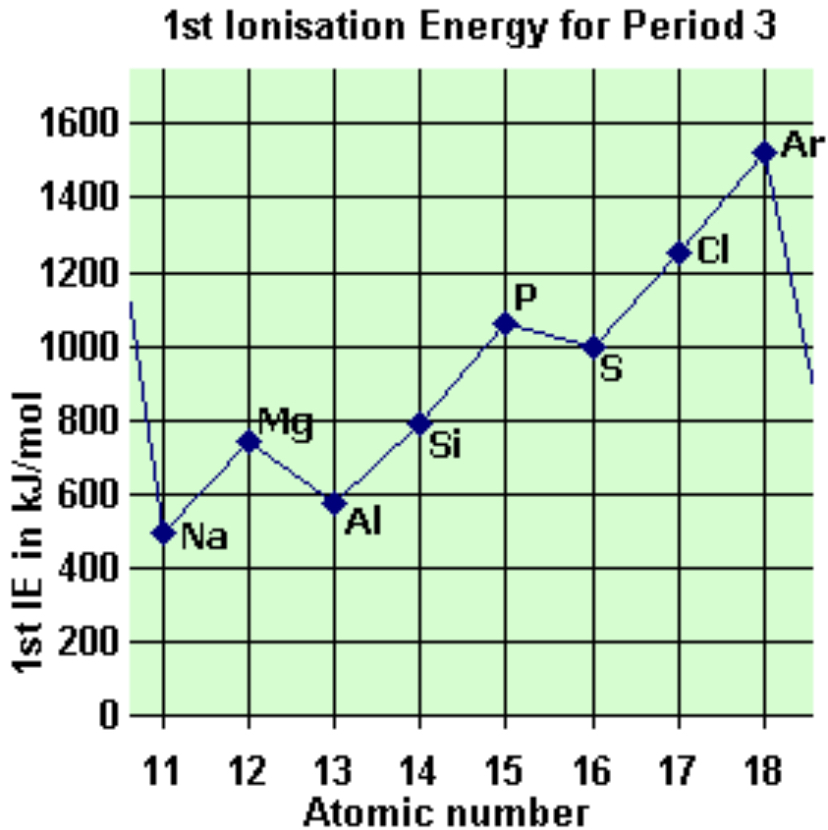
29
New cards
explain the drop between phosphorous and sulphur
this is the 1st time electrons are paired in p sub shell
increased repulsion so less energy is needed to remove electrons
increased repulsion so less energy is needed to remove electrons
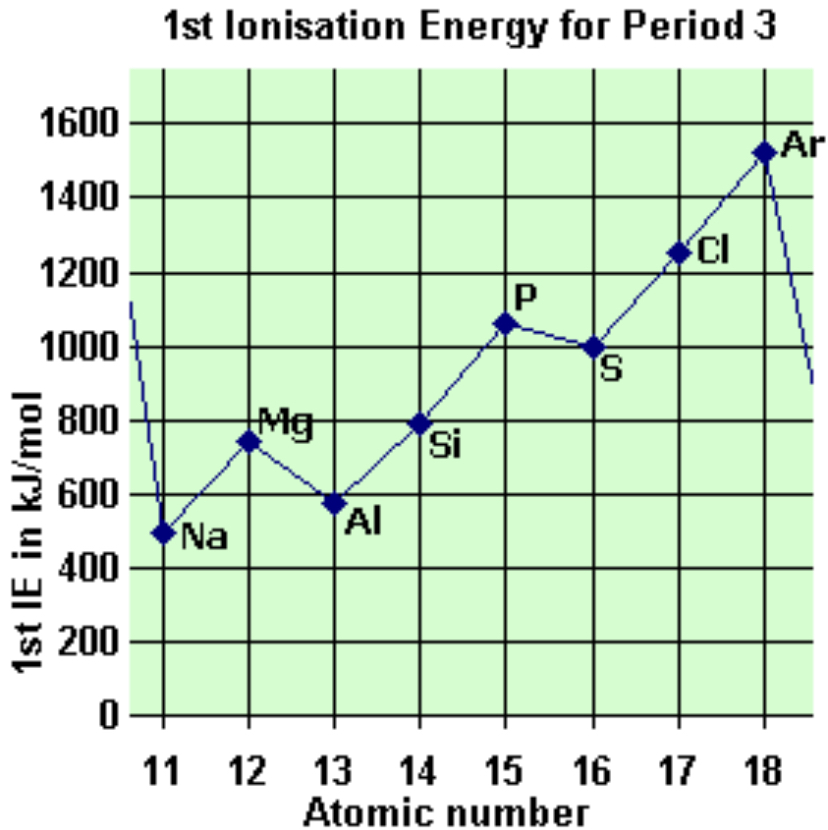
30
New cards
in period 2, why is the first ionisation energy of oxygen less than that of nitrogen?
in oxygen, electron is removed from a paired 2p orbital whereas in nitrogen, the electron is removed from a singularly occupied orbital
31
New cards
X and Zn are different elements. Explain why the chemical properties of 70-X and 70-Zn
they don’t have the same electronic configuration