Lab #4 Review - Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lab #4 Review
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Activation Energy
Enzymes reduce ___, the amount of energy it takes to get a reaction started
Substrate
Enzymes work by binding to ____ then converting it into products
Enzymes
made of proteins, highly influences by factors such as temperature, pH, and osmotic pressure
biological catalysts that allow chemical reactions to run at normal cellular temp/conditions
Lab #4 tested what factors of enzymes
Influence of pH, enzyme concentration, and temperature
Denature
When enzymes lose their proper 3D shape, thus losing their function
Active Site
Where the substrate binds to the enzyme
Saturated
All active sites of enzymes present are ___ with substrate - rate of production can no longer increase
Saturation
As substrate concentration increases, the rate of product production will increase until the enzyme has reached a point of _____
Hydrogen Peroxidase
Enzyme found in aerobic cells which decompose toxic hydrogen peroxide (toxin found in aerobic cells, byproduct of metabolism)
2H2O2 —> 2 H2O + O2
Proteins
What macromolecular class do enzymes belong to?
Product
Enzymes convert substrate into ___ which is then released from the active site. The enzyme is unchanged and now ready for a new substrate molecule to begin the next cycle.
Neutralize
Hydrogen Peroxidase located inside of peroxisomes ____ H2O2 into H2O and O2
37 degrees Celsius
normal body temperature, therefore the optimal temp. for hydrogen peroxidase to function.
Example of Enzyme Graph
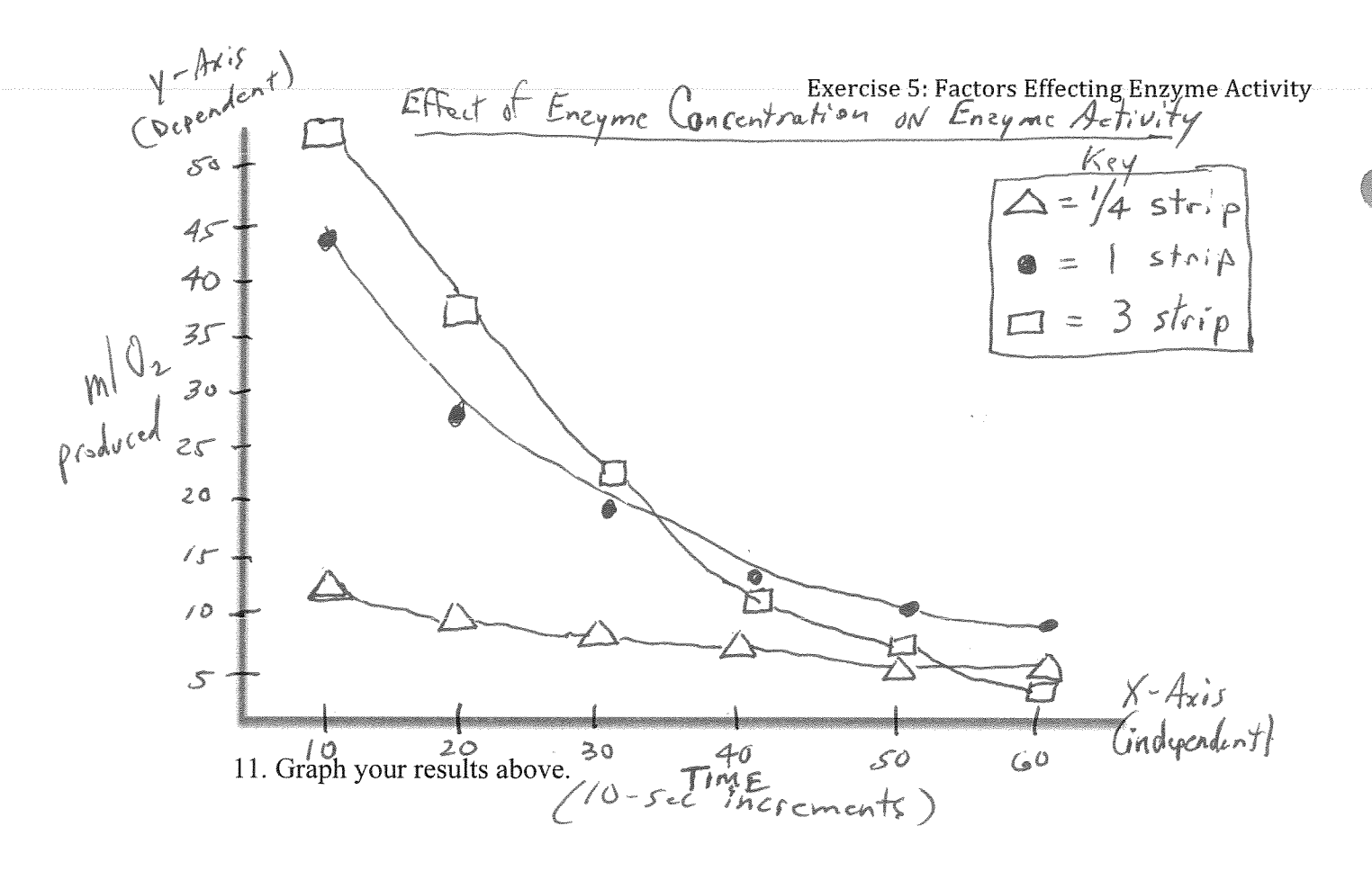
Note: Title, Label axises, Key, intervals
Increase in enzyme concentration = faster rate of converting substrate into products
Less enzyme concentration was still producing about the same O2 from beginning to end
Effect of enzyme concentration on enzyme reaction rates
Less enzyme concentration, O2 produced in 10 sec increments was relatively consistent throughout the 60 seconds.
Thus all enzyme molecules may have been “saturated”
Enzyme saturation vs. enzyme concentration
enzymes function most efficiently at near neutral pH, similar to the pH inside liver cells where hydrogen peroxidase would be found naturally
Effect of pH on enzyme function