FBS revision
1/197
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
198 Terms
Where does fertilisation occur?
Ampulla of the fallopian tube
what does the trophoblast become?
Cytotrophoblast + synctiotrophoblast
Placenta
What does the outer cell mass and inner cell mass differentiate into?
Trophoblast
Embryoblast
What are the three germ layers?
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
What does the ectoderm give rise to?
Epidermis and nervous system
What does the mesoderm give rise to?
Dermis, muscles, skeleton, circulatory system
What does the endoderm give rise to?
Digestive tract
When is an embryo most at risk?
3-8 weeks
What does the sclerotome give rise to?
Tendon, Cartlidge, bone
What does the myotome give rise to?
Muscles
What is a teratogen?
An agent or factor that causes malformation of an embryo leading to congenital abnormalities
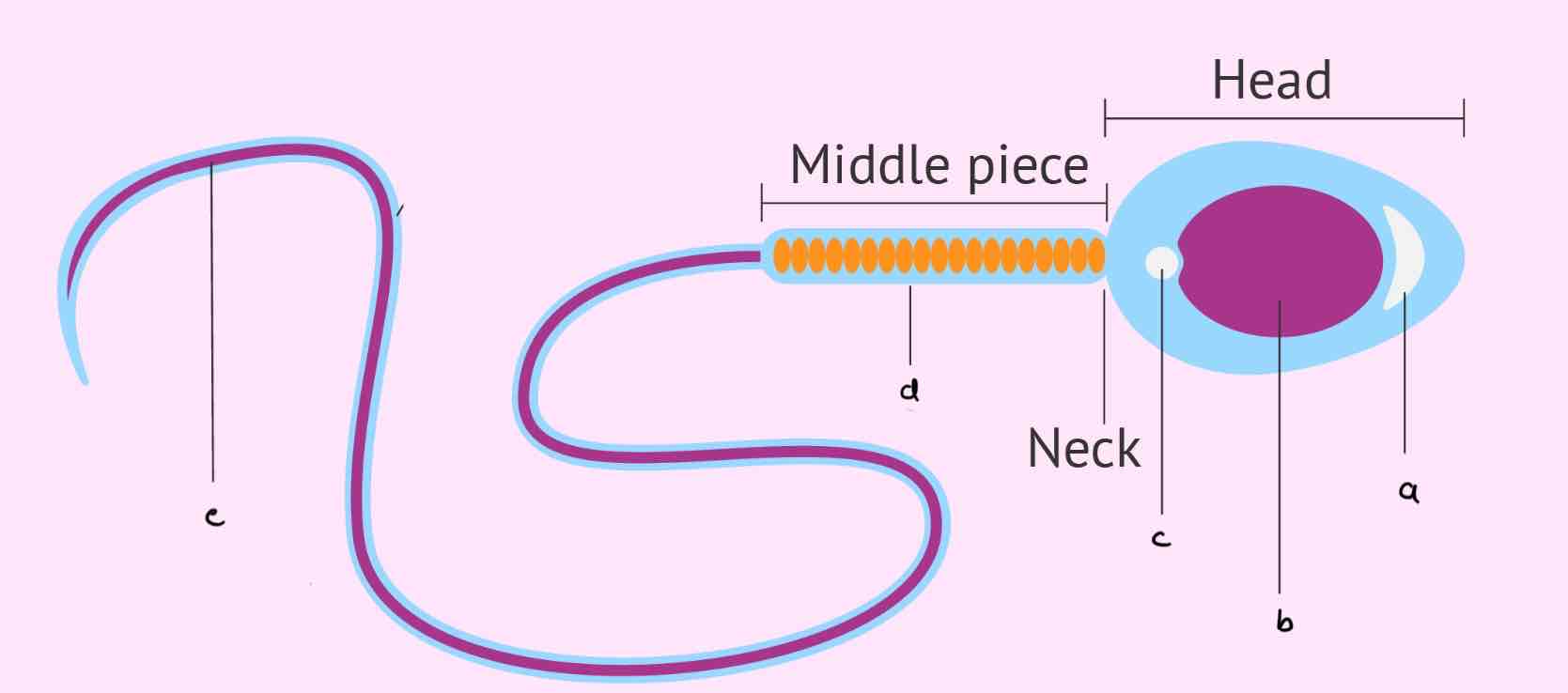
a. Acrosome
b. Nucleus
c. Centriole
d. Mitochondria
e. Flagellum
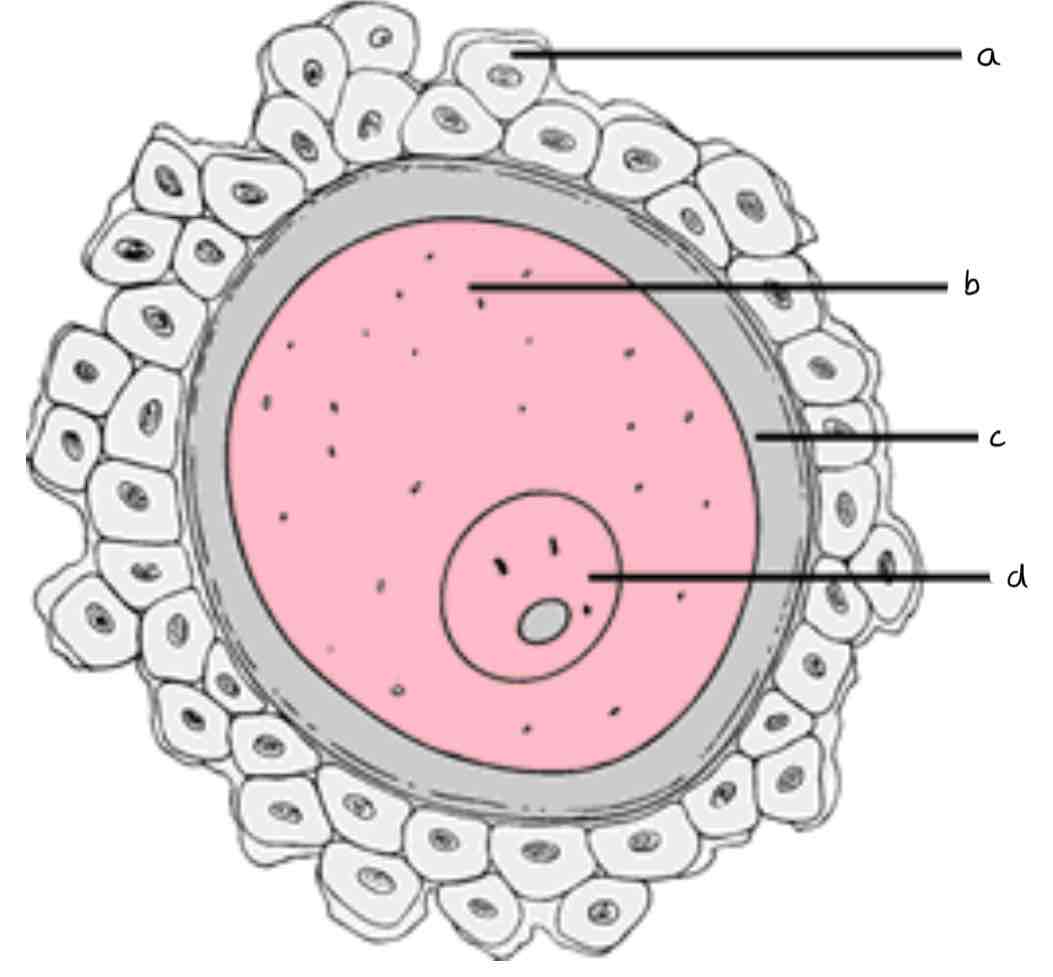
a. Corona radiata (follicle cells)
b. Cytoplasm
c. Zona pellucida (jelly coat)
d. Nucleus
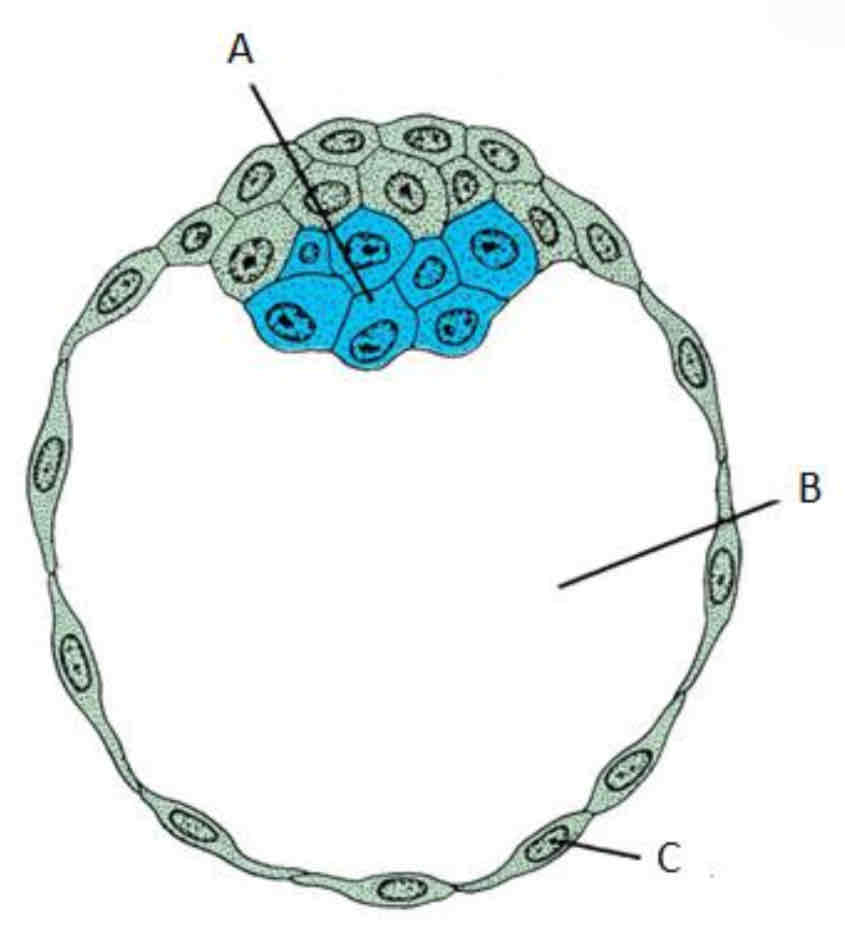
a. Inner cell mass/ embryoblast
b. Blastocoele
c. Outer cell mass/ trophoblast
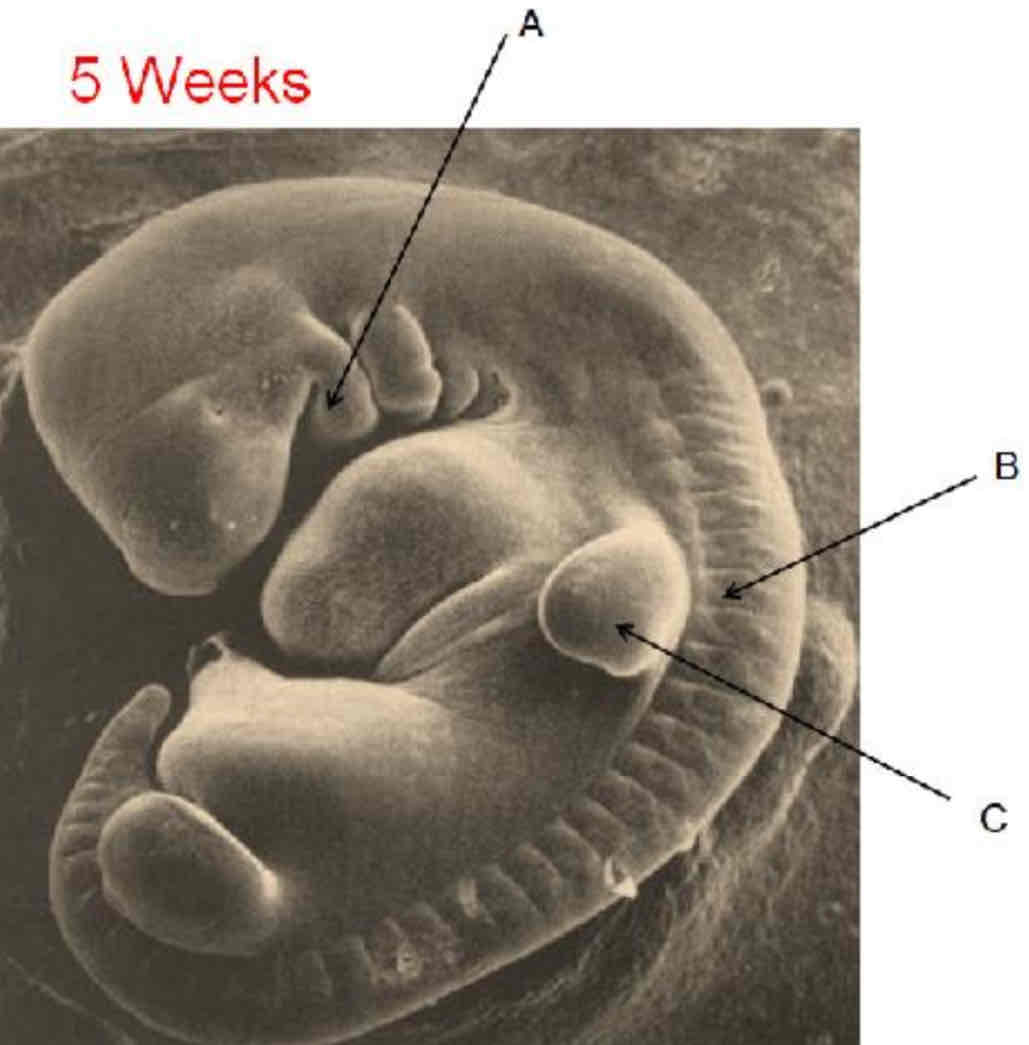
a. Branchial arches
b. Somite
c. Arm bud
What are the 2 germ cell layers before the 3 are formed?
Epiblast
Hypoblast
What cells line the oesophagus?
stratified squamous epithelium
What type of cells line the small intestine?
simple columnar epithelium
What type of cells line the respiratory system?
Cuboidal ciliated
What type of cells line the bladder?
Transitional epithelium
What type of fluid is normally found in the pleural space, and what is its function?
Serous fluid
Lubrication
What is the difference between desmosome and hemidesmosome?
A desmosome connects two cells together while a hemidesmosome connects a cell to the basal lamina
What are the different types of cell junctions?
tight junctions (occluding): seal cell together to prevent leakage
gap junctions (communicating) : allows passage of small molecules between cells
desmosomes (anchoring): connect cells together/ to the basement membrane
Difference between exocrine and endocrine glands
Exocrine: secrete onto surface via ducts
Endocrine: secrete directly into blood and controlled by hypothalamus and pituitary, ductless
What serous membrane covered the heart?
Pericardium
What is a serous membrane?
A thin, continuous membrane lining a closed cavity of the body and covering its organs
Parietal vs Visceral Membranes
PARIETAL - double-layered membrane attached to wall cavity (outer layer)
VISCERAL - double-layered membrane covering the internal organ (inner layer)
What do condition to cells used for microscopic slides need to be in?
Fixed
Sliced
Stained
What are the layers of the epidermis? (From the top)
stratum corneum
stratum lucidum (only in thick skin)
stratum granulosum
stratum spinosum
stratum basale
What are the 4 cells of the epidermis?
keratinocytes
melanocytes
langerhans cells
merkel cells
What does a Meissner's corpuscle detect?
light touch and vibration
** found in papillary dermis
What does the parcinian corpuscle detect?
Deep pressure/vibration
** found in reticular dermis
What does the Ruffini corpuscle detect?
stretch of skin
** found in reticular dermis
What are the layers of the skin starting from the top?
Epidermis
Dermis
Hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue)
1st degree burn (superficial)
Only epidermis
2nd degree burn (partial thickness)
Epidermis and dermis
3rd degree burn (full thickness)
Epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
What cells line the trachea ?
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
Where do you find thick skin?
Heels and palms
What is the function of the stratum granulosum?
Water barrier
What does connective tissue consist of?
cells(Fibroblast, adipocytes,macrophages, mast cells ) +
extracellular matrix (collagen, elastin)
What type of collagen are reticular fibres made up of?
Type III
What is the point at which the trachea bifurcates called?
Carina T4/5
What is the difference between regular and irregular dense connective tissue?
Regular dense CT - collagen fibers are arranged parallel to each other with fibroblasts and strength is in 1 direction
Irregular dense CT - collagen fibers are arranged randomly and strength is in multiple directions
Difference between loose and dense connective tissue?
Loose is widely spaced with collagen and elastin and dense is tightly packed by collagen fibres
Skeletal muscle
striated and voluntary
Location: muscle attached to bone
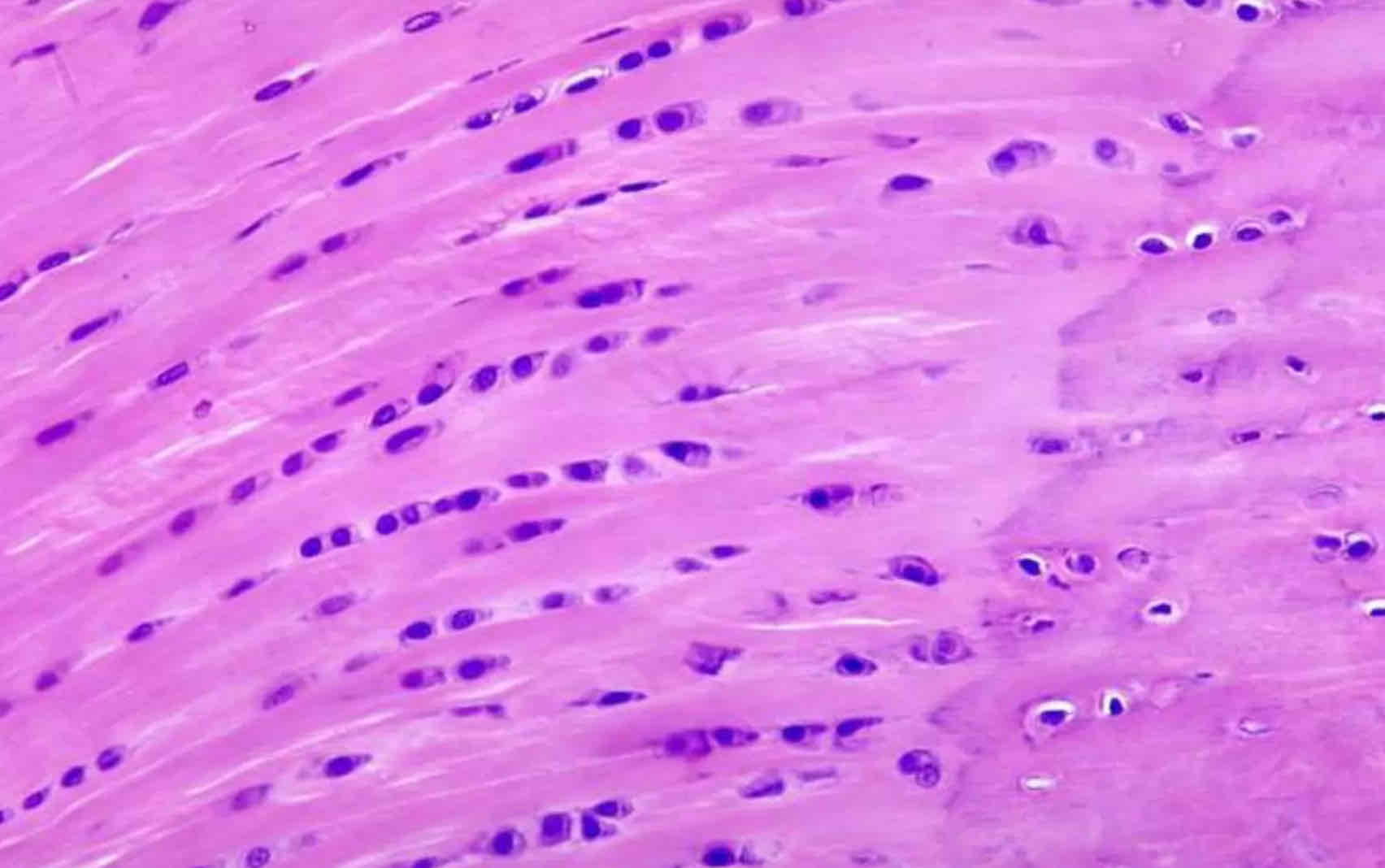
cardiac muscle
involuntary, striated
Location: heart
smooth muscle
involuntary, non-striated
Controls movement of hollow organs
Why does the trachea have c shaped cartilage?
Support and to allow it to move
Structure of tube in digestive tract (from the outside)
Adventitia
Smooth muscle
Submucosa
Mucosa
Lumen
What cells are found in the stomach?
Patietal (oxynitic) cells: produces HCl
Chief (Zymogenic) cells: produces enzymes
Endocrine cells: produces hormones
Where is the appendix located?
Outgrowth of the caecum
What cells make up cartilage?
Chondocytes
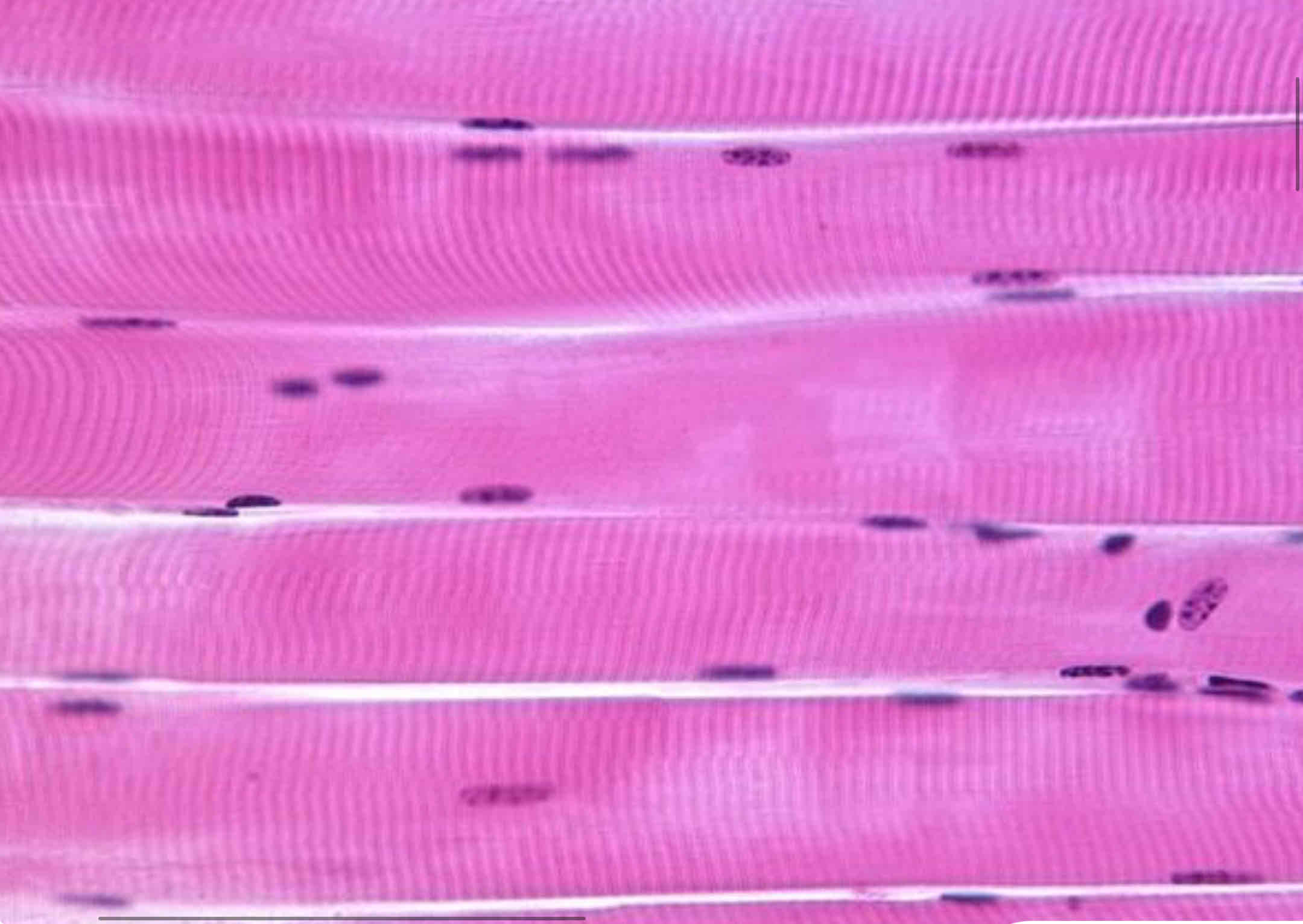
Skeletal muscle
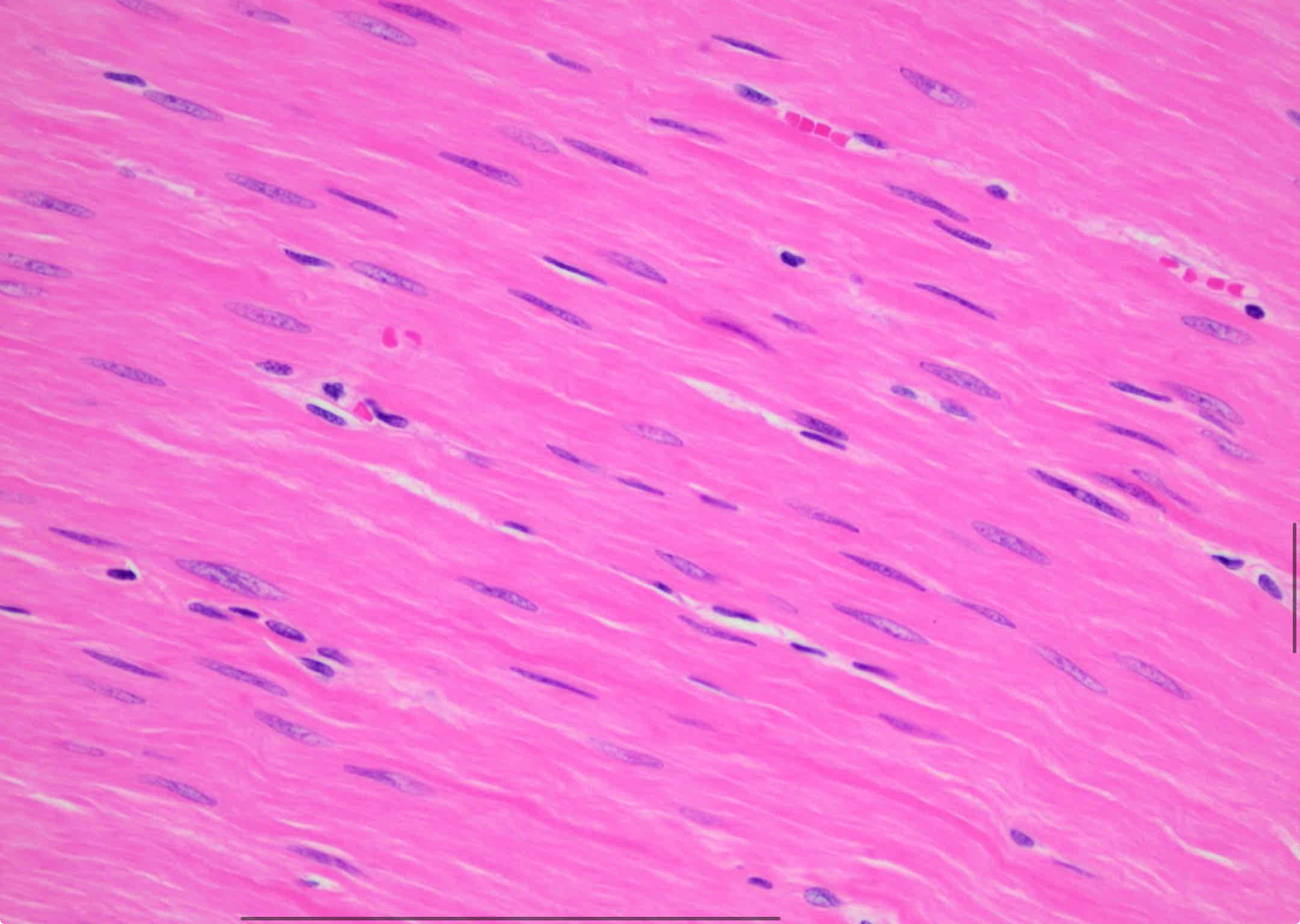
Smooth muscle
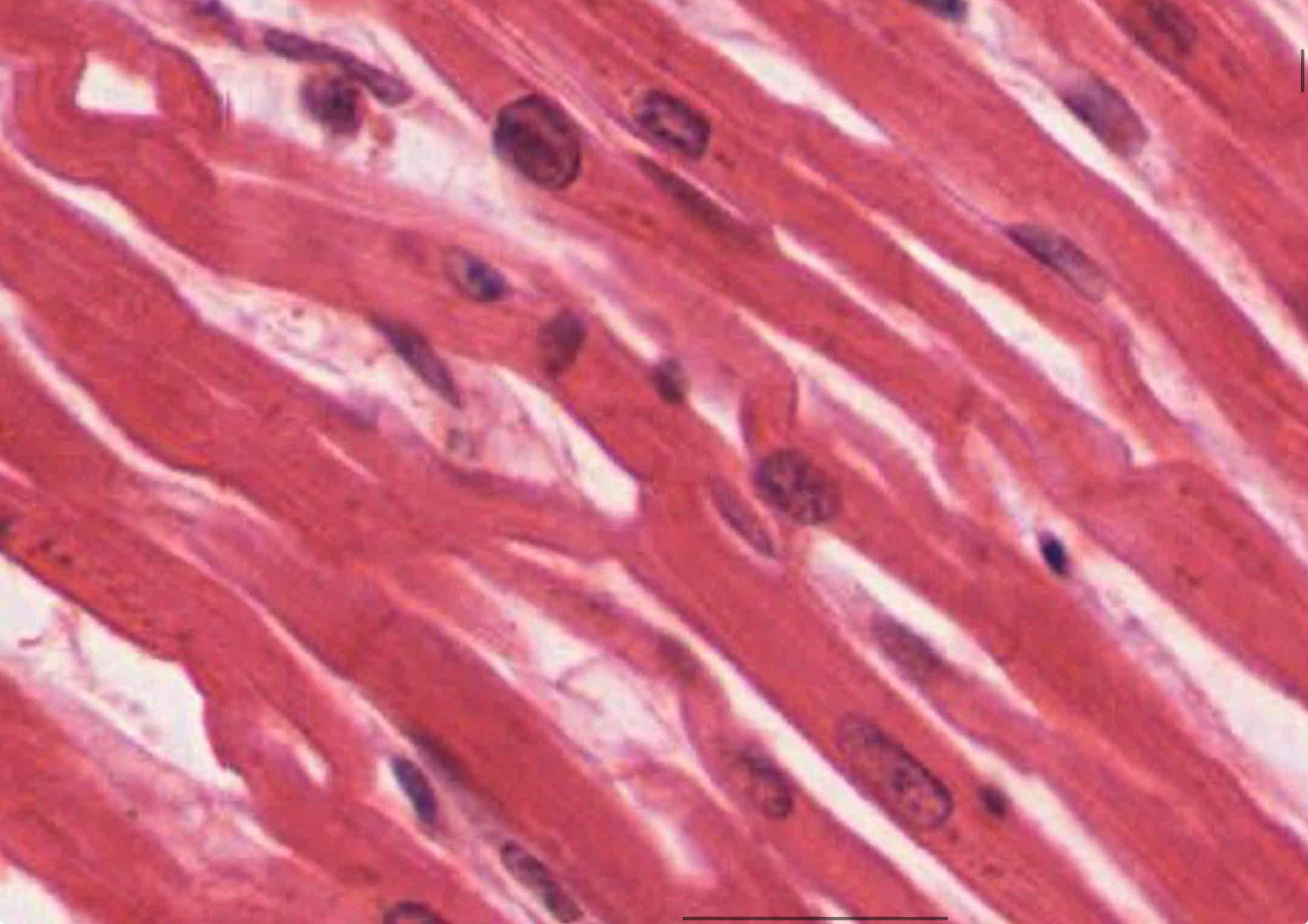
Cardiac muscle
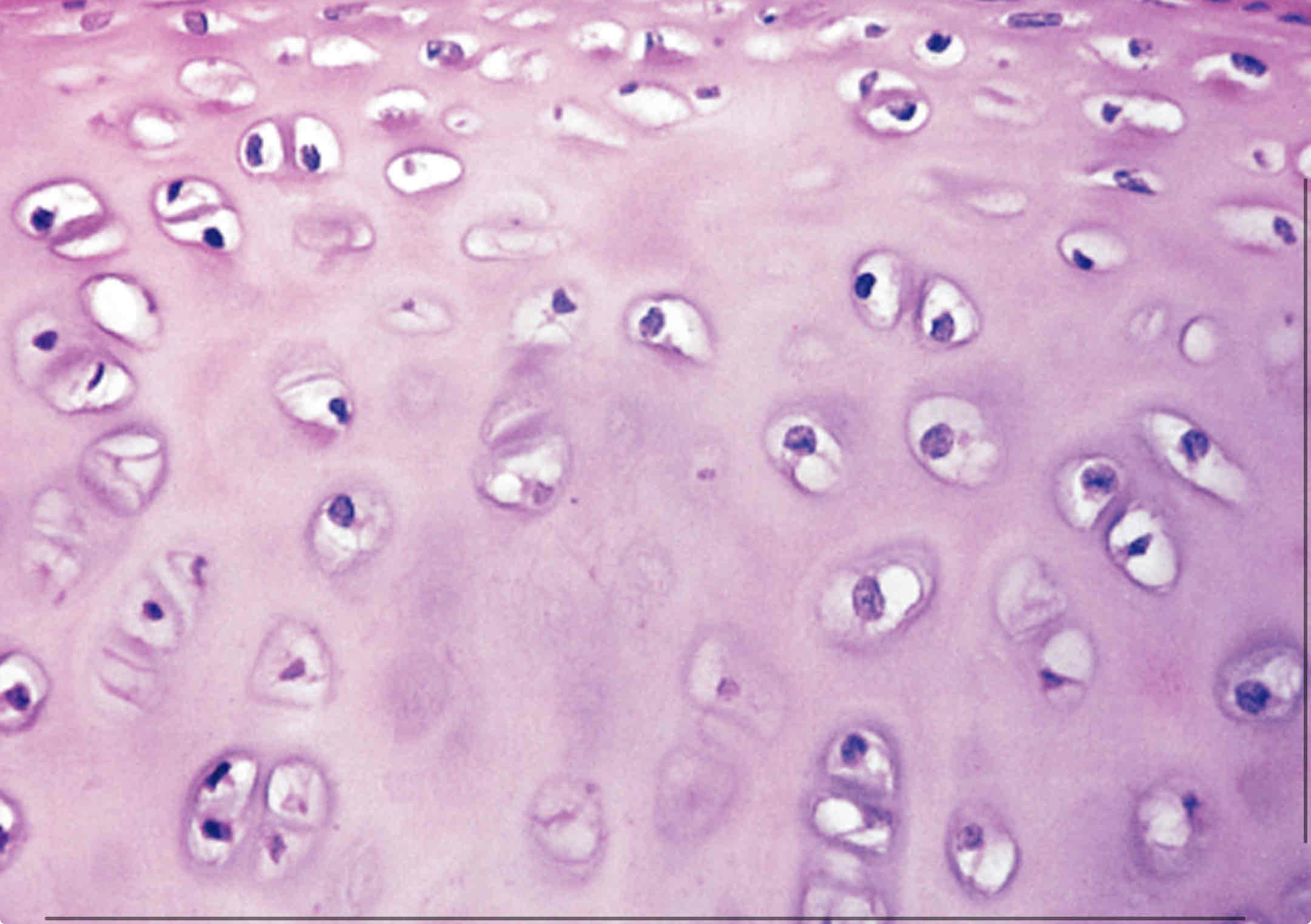
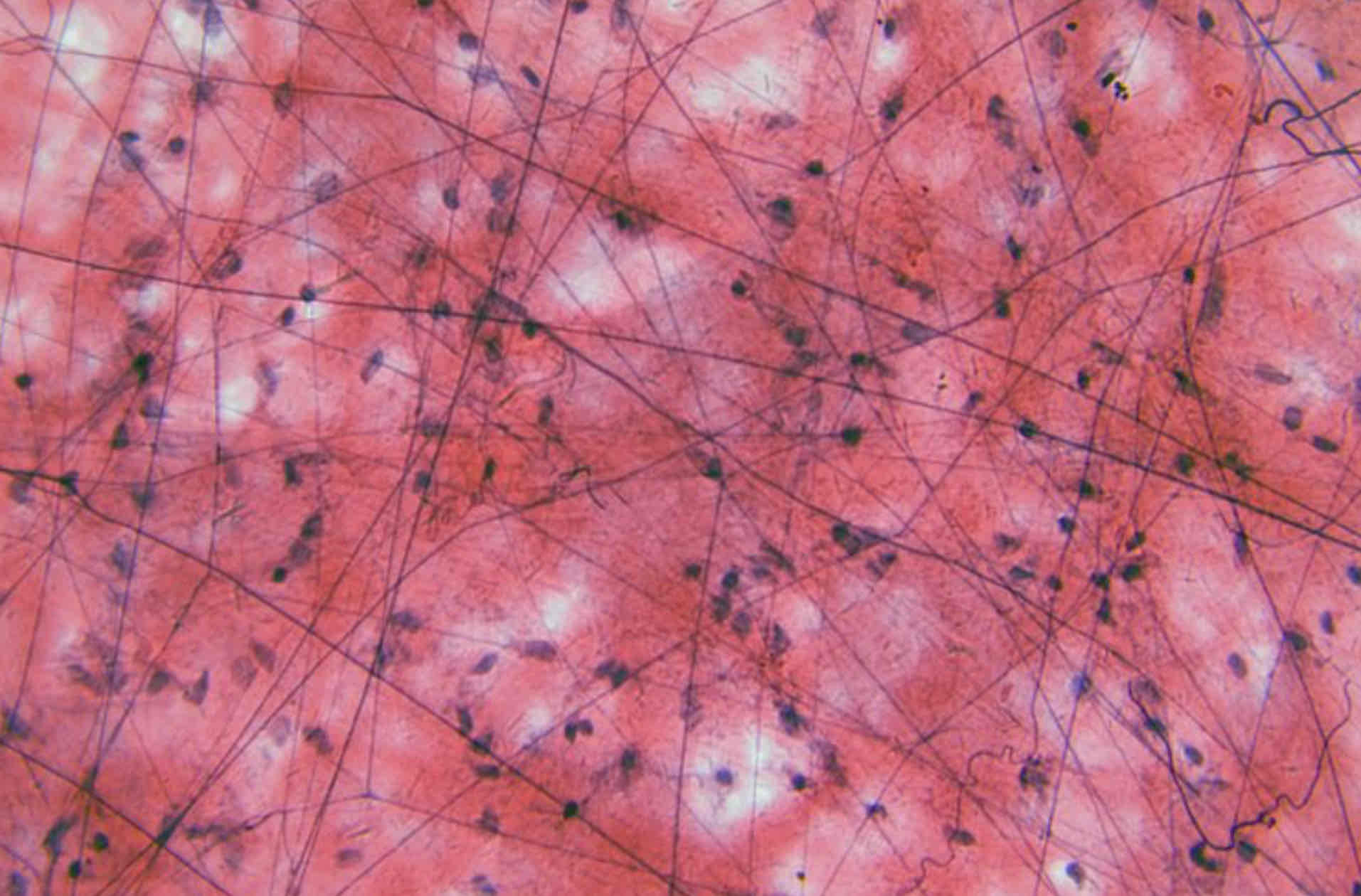
Hyaline cartilage
Fibrocartilage
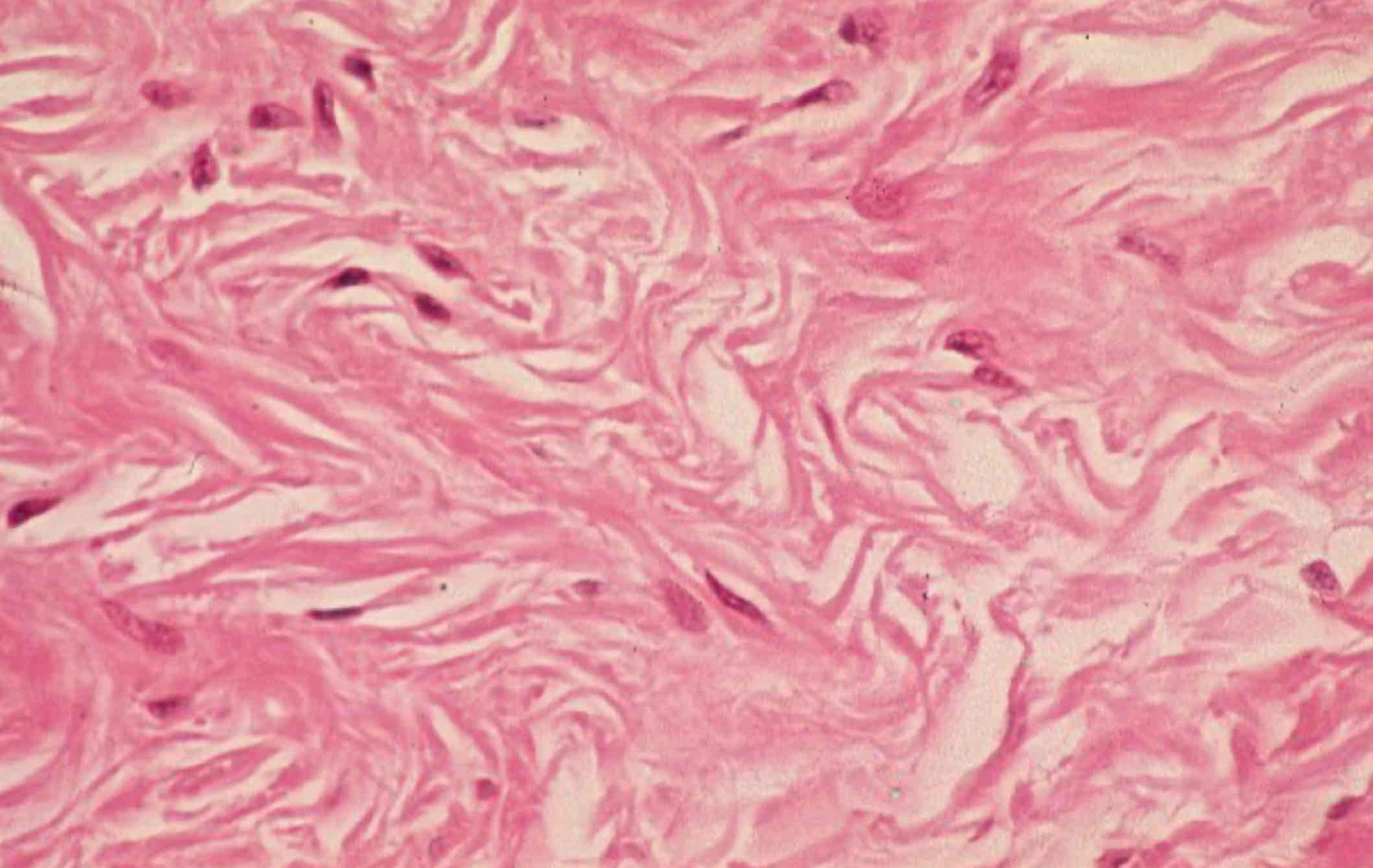
Loose connective tissue
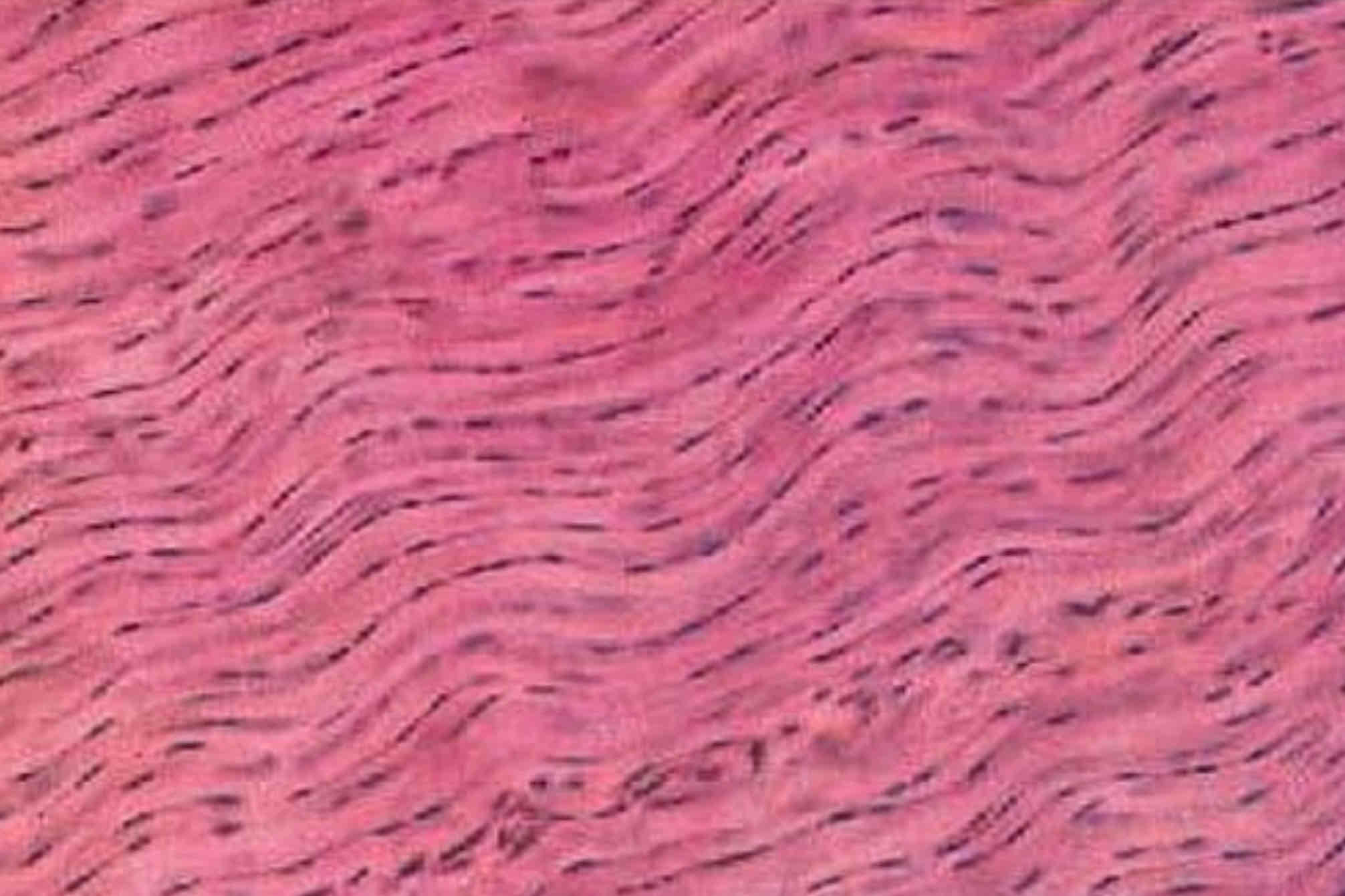
Dense regular connective tissue
Dense irregular connective tissue
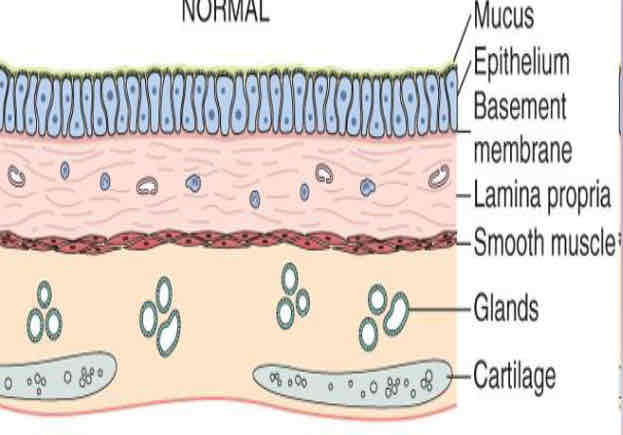
What are the airway layers?
Respiratory epithelium: pseudostratified columnar, ciliated + BM. Also contain goblet cells which form mucus.
Lamina propria: contain connective tissue, blood and lymph - give nutrients and structural support.
Submucosa: seromucus glands, smooth muscle/elastin fibres.
Cartilage: hyaline cartilage - C-shaped in trachea, but less prominent as tubes get smaller.
What vessels make up the portal triad?
the hepatic artery, the hepatic portal vein and the bile duct
Describe the lovers dual blood supply
The hepatic artery delivers oxygenated blood from the general circulation.
the hepatic portal vein delivering deoxygenated blood from the small intestine containing nutrients
Which muscle that controls the diameter of the trachea
Trachealis muscle
What is part of the axial skeleton?
Vertebral body, ribs, sternum, skull
What is part of the appendicular skeleton?
pelvic girdle, pectoral girdle, bones of limbs
Where is compact bone usually found?
Exterior of bone, surrounding the spongy (cancellous) bone
What part of the bone contains bone marrow?
Medullary cavity
How are foetal bones transformed into adult bones?
Endochondral ossification
Hyaline cartilage → adult bone
What is a pneumatic bone?
Bone filled with air
Usually found in the face
What is intramembranous ossification?
ossification spreads through a sheet of mesenchyme tissue (ossification of bones in the membrane)
** only for flat bones
Name the type of cartilages
Hyaline
Fibrocartilage (yellow)
Elastic (white)
What is endochondral ossification
Cartilage is infiltrated by 3 blood vessels forming 3 ossification centres - 2 epiphysial (ends) and 1 diaphyseal
Where is the primary ossification centre in long bones?
Diaphysis
What do osteoblasts do?
Secrete collagen to build bone matrix
What do osteocytes do?
Maintain bone tissue
What do osteoclasts do?
Breakdown old/damaged bone
What is a compact bone made up of?
Bony lamella strongly packed together
Haversian systems (concrete rings surrounding a central canal that contains blood vessels, nerves, osteocytes)provide strength to the bone
What are the steps of fracture repair?
Inflammation(haematoma): Immune cells clean up debris
Soft callus formation: Fibrous tissue and collagen stabilise
Hard callus formation: Osteoblast produce new cells forming woven bone
Remodelling: Woven bone is turned to Lamella bone (stronger)
What are the different types of joints?
Fibrous: Fixed
Cartilaginous: Slightly movable
Synovial: Highly movable
At what level is the larynx?
C3-6
What does the larynx contain and do?
Vocal cords
Prevents food entering trachea
At what level is the trachea?
C6-T4/5
Where does the trachea bifurcate?
Carina T4-5
At what level is the sternal angle?
T4-5 (2nd rib)
At what level is the diaphragm?
T10
At what level is the oesophagus?
C6-T10/11
How many lobes does the right and left lung have?
R: 3
L:2
Why does the left lung only have 2 lobes?
To leave space for the heart
Process of inspiration
1. External intercostal muscle contracts
2. Diaphragm contracts (flattens)
3. Chest wall expands (lung volume increases)
4. Atmospheric pressure > lung pressure
What is found in the superior mediastinum?
oesophagus, trachea,thymus, aortic arch, brachiocephalic trunk, L common carotid artery, L subclavian artery
What is found in the middle mediastinum?
pericardium, heart, ascending aorta, pulmonary trunk, superior vena cava, phrenic nerves
What is found in the posterior mediastinum?
descending aorta, oespohagus, vagus nerve
How do the right and left bronchi differ from each other and why important?
R: shorter and wider
More likely for particles to get dislodged and entering R lung
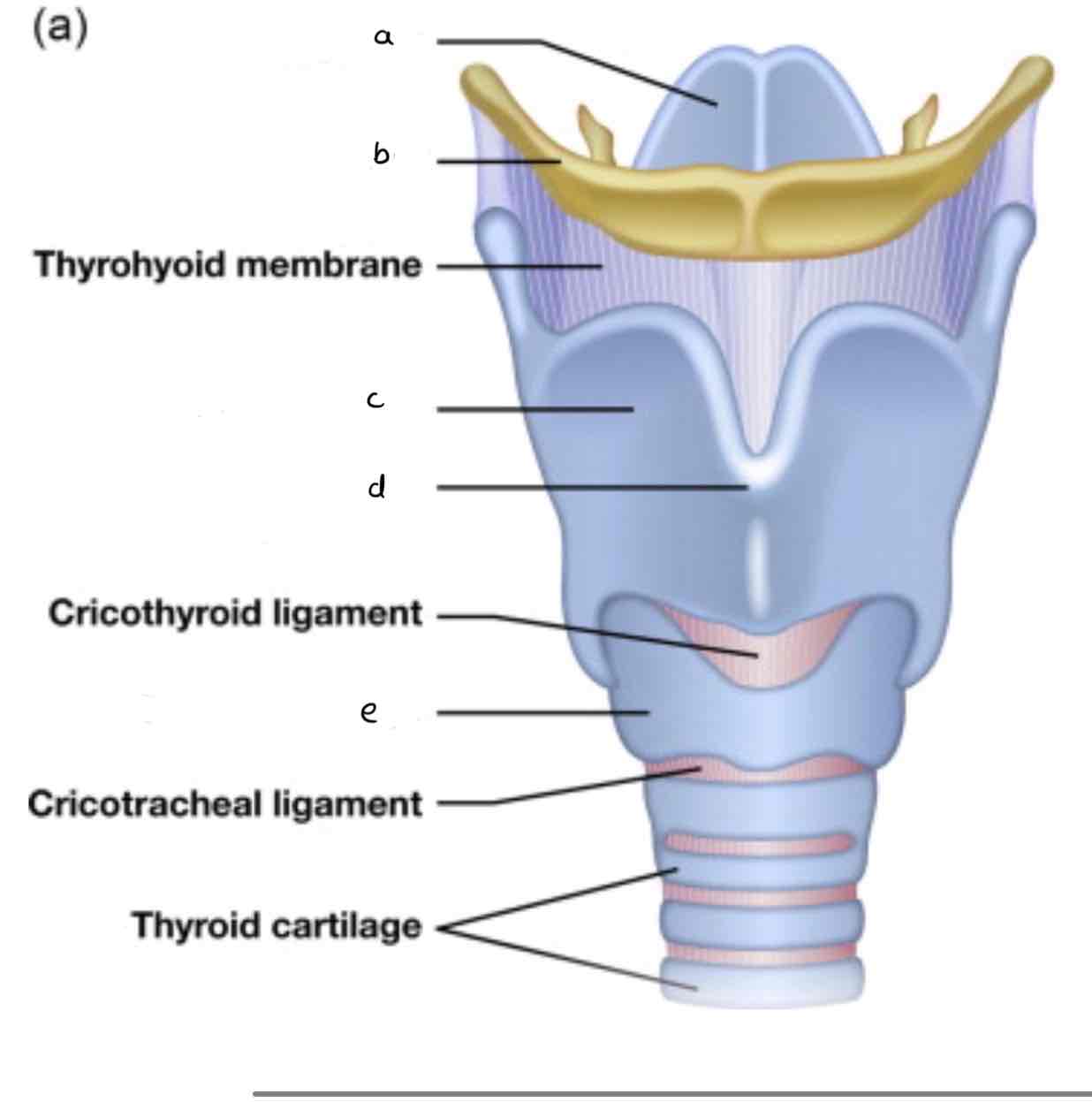
a. Epiglottis
b. Hyoid bone
c. Thyroid cartilage
d. Laryngeal prominence (Adam’s apple)
e. Cricoid cartilage
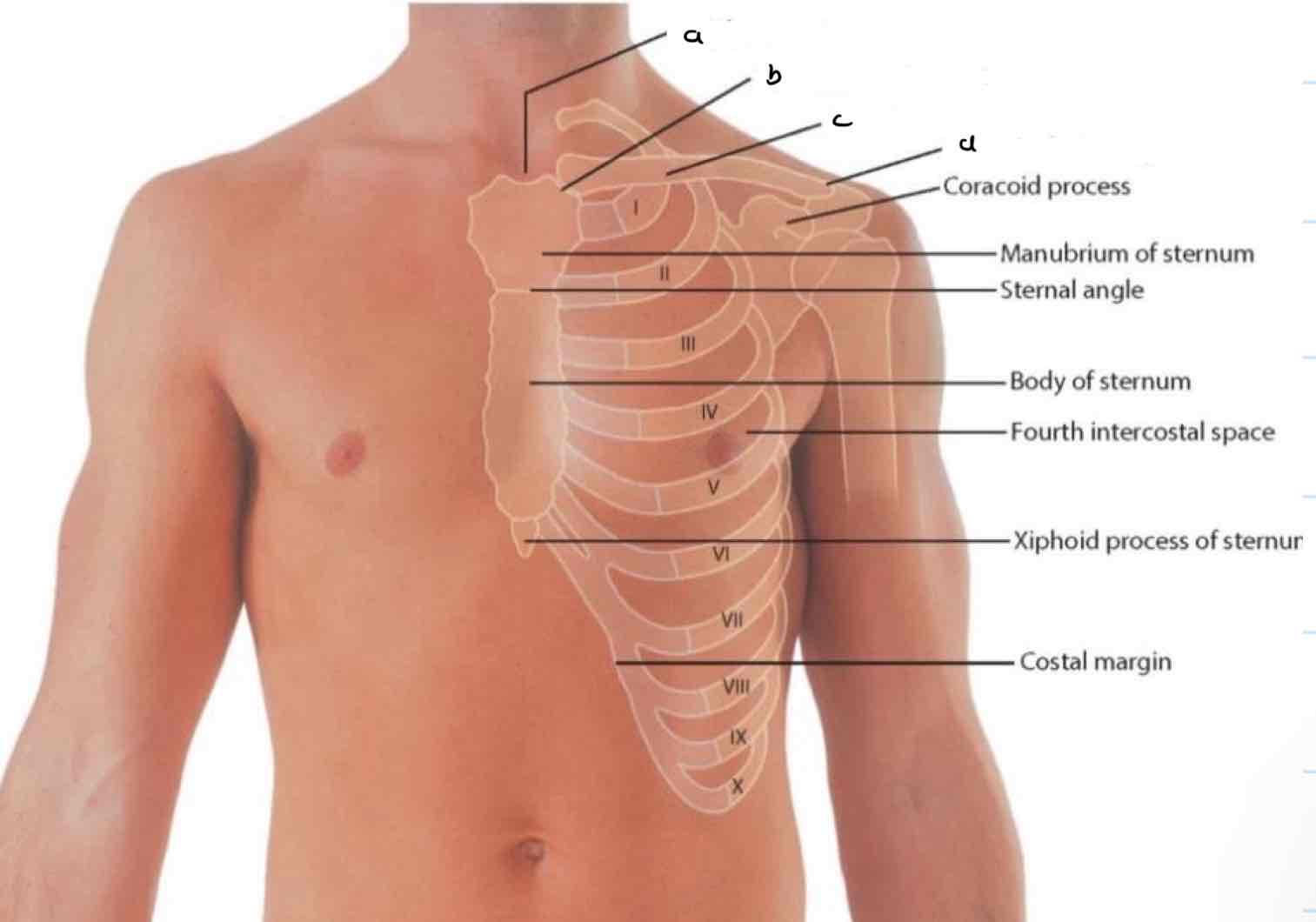
a. Jugular notch
b. Sternoclavicular joint
c. Clavicle
d. Acromioclavicular joint
What is the name of the space between the lungs and diaphragm?
Costodiaphragmatic recess
** safest place to collect fluid
What are the margin of the lung?
6th rib midclavicular
8th rib midaxillary
10th rib midscapula