CH4710 RM26
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
gene
a segment of a DNA molecule that contains the information required for the synthesis of a functional biological product, whether protein or RNA
4 classes of RNA
ribosomal (rRNA): components of ribosomes
messenger (mRNA): intermediates on protein synthesis
transfer (tRNA): translate info in mRNA into amino acid sequence
noncoding (ncRNA): wide variety of functions
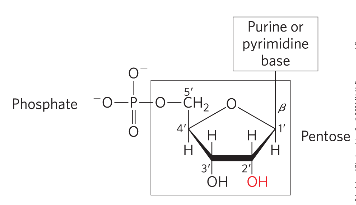
3 components of nucleotides
nitrogenous base (pyrimidine or purine)
pentose
1+ phosphates
nucleoside
nucleotide without phosphate group
Identify
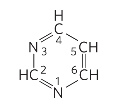
pyrimidine
Identify
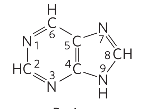
purine
bond within nucleotide
a N-beta-glycosyl bond covalently joins the 1’ carbon of pentose to the base
phosphate is bonded at 5’ carbon of pentose
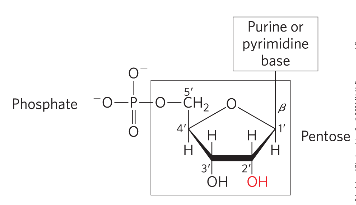
pyrimidine vs purine bonding to pentose
pyrimidine bond at N-1
purine bond at N-9
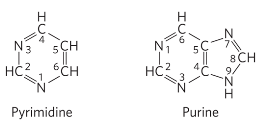
nitrogenous bases, purine vs pyrimidine
purine: A and G
pyrimidine: C, T, and U
what are the structural units of DNA
deoxyribonucleotides
“deoxy-”
adenosine
guanosine
thymidine
cytidine
what are the structural units of RNA
ribonucleotides
adenosine
guanosine
uridine
cytidine
process of nucleotides carrying chemical energy
hydrolysis of nucleoside phosphates provides chemical energy (similar to ATP)
nucleotides and enzyme relationship
adenine is component of enzyme cofactors
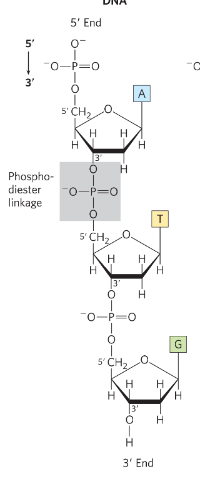
what joins nucleotide chains in DNA and RNA
phosphodiester linkage
describe phosphodiester linkage
between 5’ phosphate of one nucleotide and the 3’ OH of the next nucleotide
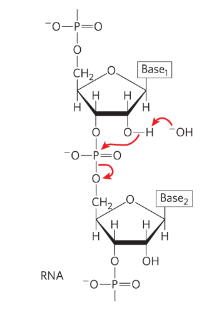
why is RNA rapidly hydrolyzed and DNA is not
RNA nucleotides contain 2’ OH groups and DNA does not
OH- can attack that OH group to break phosphodiester linkage
oligonucleotide
short nucleic acid (less than 50 nucleotides)
polynucleotide
longer nucleic acid