Lipids: Types, Functions, and Heart Health Impacts
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are the main classes of lipids?
Triglycerides, phospholipids, and sterols.
What health risks are associated with dietary fat?
Health risks arise from both excessive and insufficient dietary fat.
What is the primary role of body fat?
Lipids provide energy and support various bodily functions.
What is adipose tissue?
Masses of fat-storing cells that store/release lipids and secrete hormones.
What percentage of the body's ongoing energy needs during rest is supplied by adipose tissue?
60%.
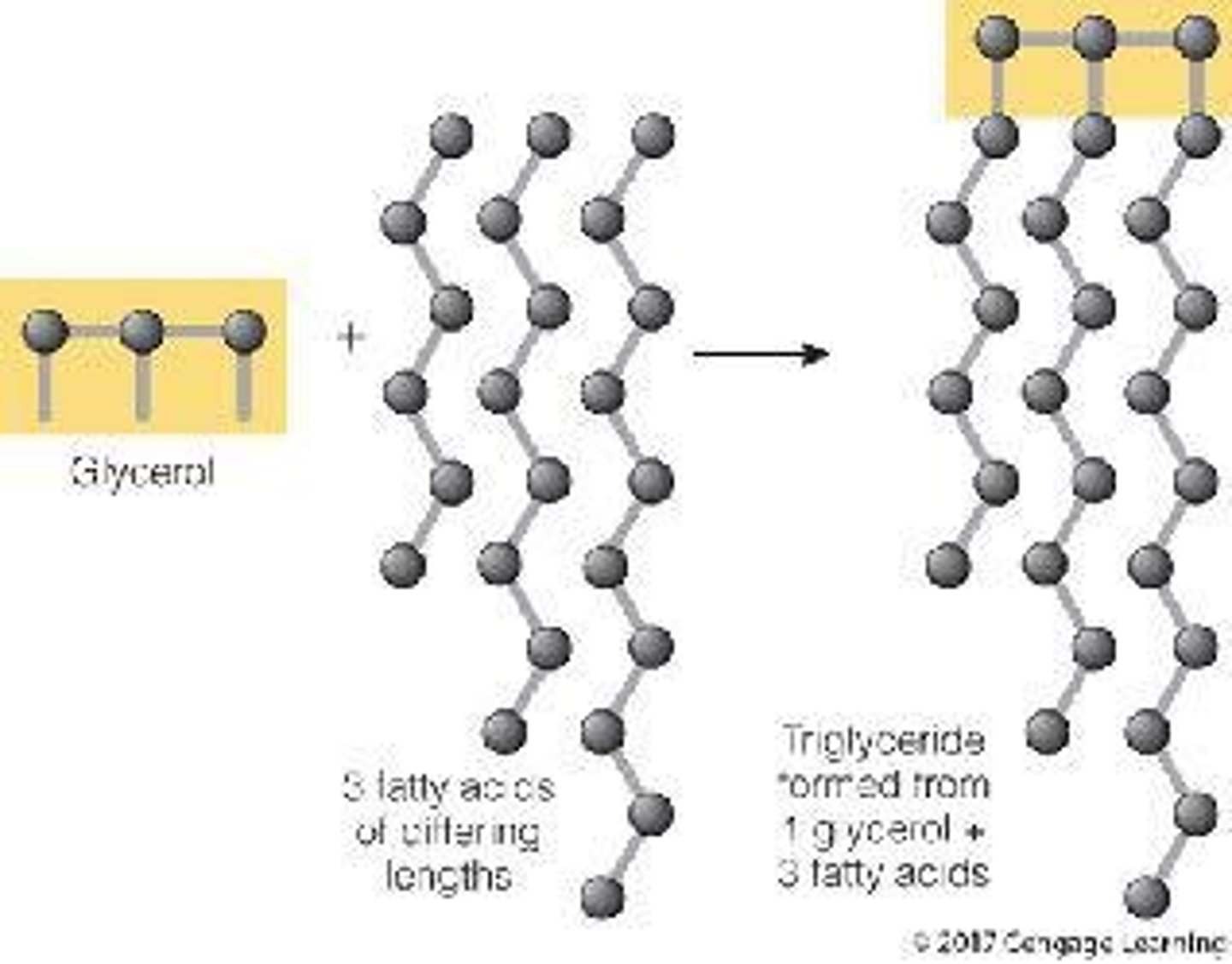
What is the structure of triglycerides?
Three fatty acids attached to a glycerol backbone.
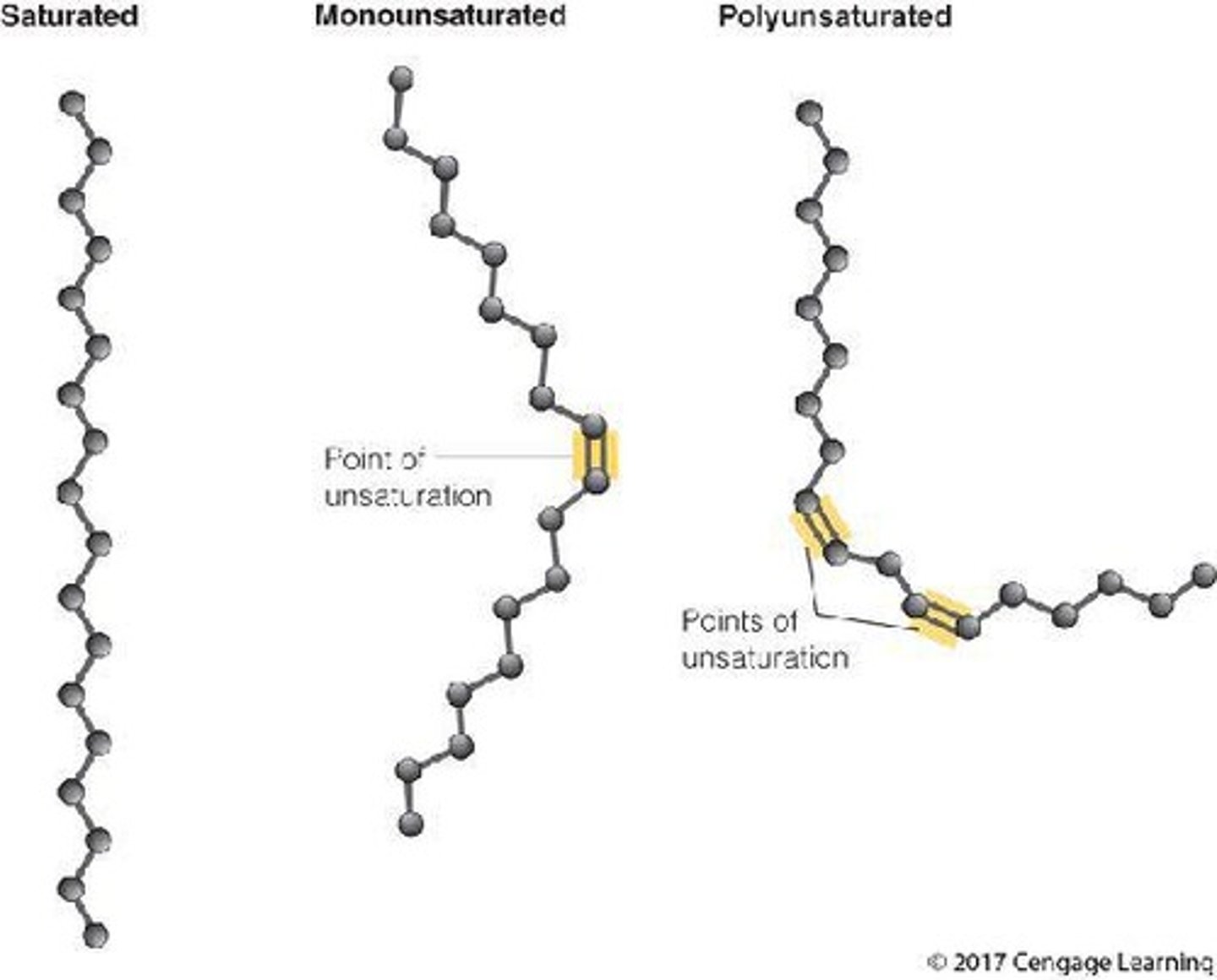
What distinguishes saturated fatty acids from unsaturated fatty acids?
Saturated fatty acids have maximum hydrogens and only single bonds between carbons, while unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double bonds.
What are the characteristics of hard and soft fats?
Hard fats, like lard, are more saturated, while soft fats, like safflower oil, are more unsaturated.
What is hydrogenation?
A process that alters fats to protect against oxidation and increase solidity.
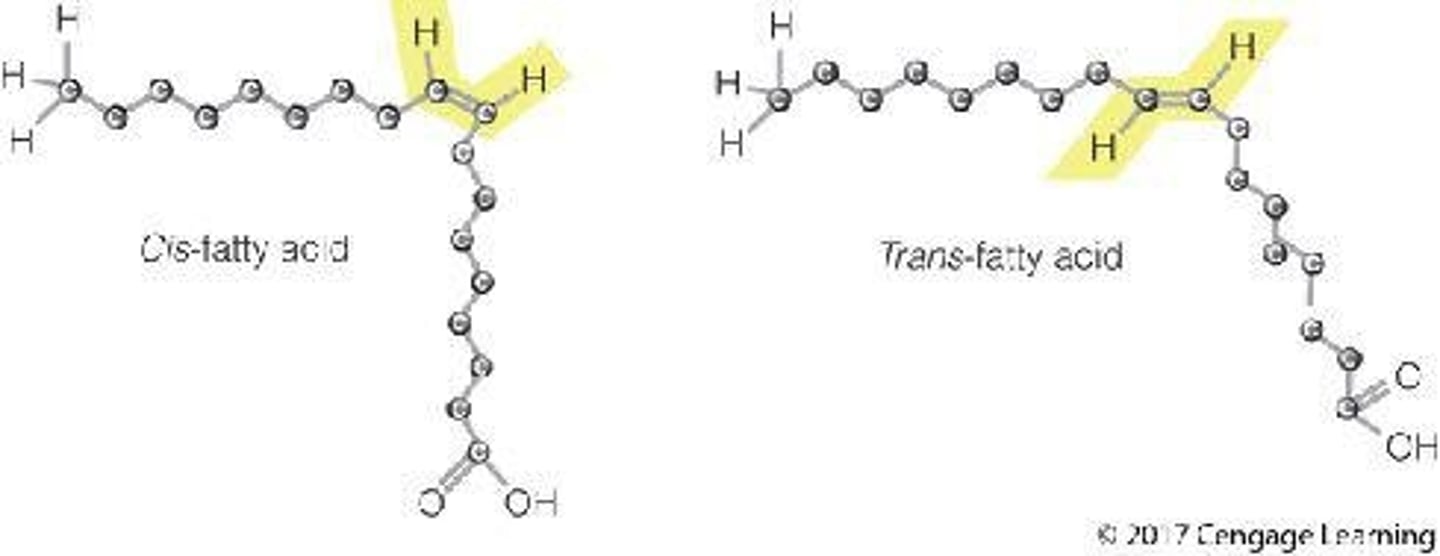
What are trans-fatty acids?
Fats that result from hydrogenation, altering some double bonds from cis to trans shape, increasing heart disease risk.
What are essential fatty acids?
Fatty acids that the body cannot synthesize, such as linoleic acid (omega-6) and linolenic acid (omega-3).
What is the role of phospholipids in the body?
They form cell membranes and act as emulsifiers in food.
What are sterols?
Large, complex molecules with interconnected rings of carbon, including cholesterol and vitamin D.
How is cholesterol synthesized in the body?
It is manufactured in the liver from energy nutrient fragments.
What are the two routes cholesterol takes in the body?
Incorporated into bile for digestion or released into the bloodstream to travel to cells.
What is the goal of fat digestion?
To break triglycerides into monoglycerides, fatty acids, and glycerol for absorption.
What dietary factors increase the risk of cardiovascular disease?
High intake of saturated fats and trans fats.
What is the recommended intake of total fat as a percentage of daily energy?
20% to 35%.
What are the recommended limits for saturated and trans fats?
Less than 7% of kcalories from saturated fat and less than 1% from trans fat.
What is the effect of monounsaturated fatty acids on blood cholesterol?
They may prevent heart disease when substituted for saturated fats.
What are the benefits of omega-3 fatty acids?
They lower blood triglycerides, prevent blood clots, and protect against irregular heartbeats.
What are some sources of omega-3 fatty acids?
Fish oils, particularly EPA and DHA.
How can one find fats in foods?
High-fat foods are typically high in calories, and many solid fats are invisible in the diet.
What is the recommended serving of protein foods per day for adults?
5 to 7 ounces.
How can one reduce intake of solid fats?
By replacing them with liquid oils and selecting foods low in saturated and trans fats.