Endocrine functions and Hypothalamic-pituitary axis
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Endocrinology
Branch of biology dealing with hormones, their glands and effects
Hormones
Chemical messengers released by endocrine glands
Enter the bloodstream and affect target tissues at very low concentrations
Help maintain homeostasis
Endocrine system
Hormones released in bloodstream
Slower response time but has long lasting effects
Widespread systemic influence (many organs/cells can respond)
Hormone roles
Developmental coordination - controls processes like puberty, pregnancy and sex determination
Environmental response - helps reaction to stress or sexual stimuli
What does classification by site of action mean
How far the hormone travles to reach its target and where it exerts its effects
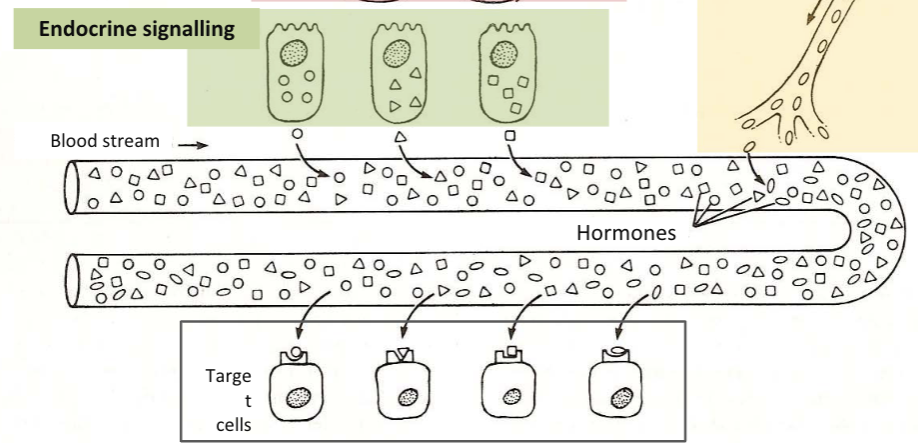
Classification by site of action - endocrine signaling
Hormones released in bloodstream and travels to distant target organs
e.g. insulin from pancreas acts on muscles and liver
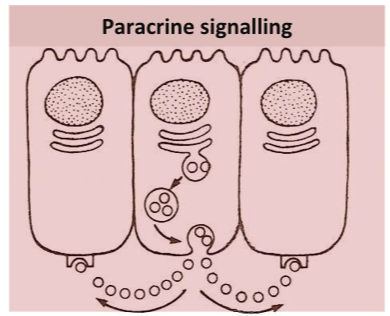
Classification by site of action - paracrine signaling
Hormones act on neighbouring cells (local signaling, not via blood)
e.g. growth factors released by one cell affect nearby ones
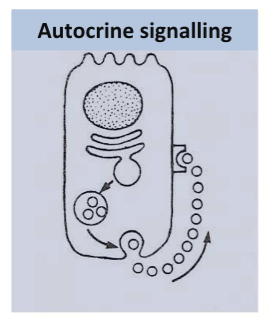
Classification by site of action - autocrine signaling
The cell that secretes the hormone is also its own target
e.g. immune cells release cytokines that act back on themselves
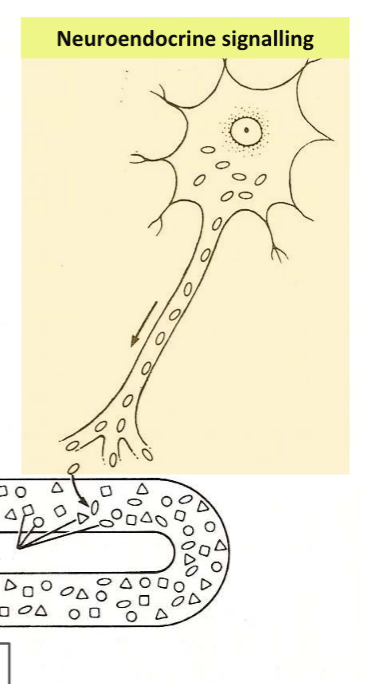
Classification by site of action - neuroendocrine signaling
Neurons release hormones (called neurohormones) into the blood, not into synapse
e.g. hypothalamic neurons releasing oxytocin or ADH into circulation
What does classification by chemical structure mean
Molecular makeup of the hormone
Determines how the hormone is stored, transported and acts on target cells
Liposoluble (fat soluble) hormones
Hormones that dissolve in fat, not water (pass through cell membranes, which are made of fat (lipid layer)
They can bind to receptors inside the cell and change gene expression
Liposuble - Steroid hormones
Made from cholesterol, which is a type of fat
Steroid hormones - Adrenocortical hormones
Glucocorticoids - like cortisol (stress and metabolism)
Mineralocorticoids - like aldosterone (salt/water balance)
Androgens - like DHEA (precursor to sex hormones)
Steroid hormones - Sexual hormones
Adrogens, estrogens, progesterone, testosterone…
Liposoluble hormones - Thyroid hormones
Made from an amino acid called tyrosine
Thyroid hormones
T3 - Triiodothyronine (metabolism)
T4 - Thyroxine (metabolism, growth, development)
Hydrosoluble hormones
Dissolve in water, not fat
They cannot cross cell membranes so they work outside the cell
Hydrosoluble hormones - peptide hormones
Made of chains of amino acids
Includes - insulin (blood sugar), oxytocin (birth/milk), growth hormone, LH FSH TSH (reproductive and thyroid reg)
Hydrosoluble hormones - amine hormones
Small and made from amino acids like tyrosine or tryptophan
Includes - adrenaline, dopamine, melatonin…
Classification by site of synthesis
Which gland or tissue produces the hormone
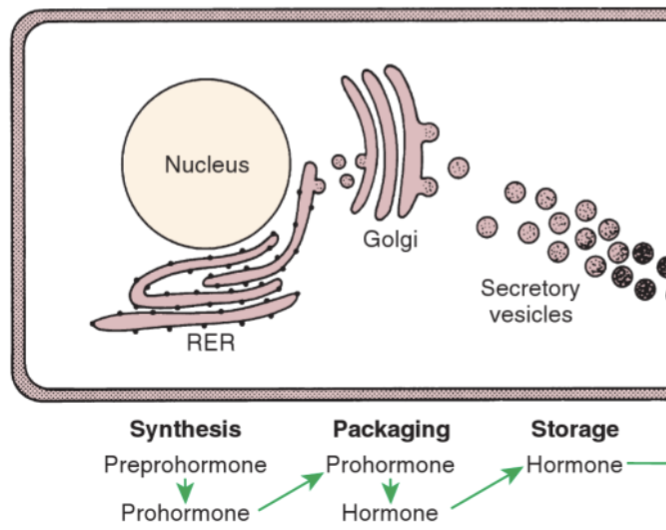
Peptide hormones synthesis
Preprohormone - synthesis in RER, contains extra amino acid segments (signal peptide)
Prohormone - after signal peptide is removed, transferred to golgi apparatus
Active hormone - final process occuring in secretory vesicles
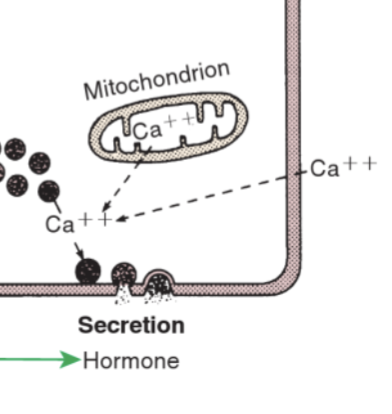
Peptide hormones secretion
Released by exocytosis when cell is stimulated
Requires ATP and calcium
Amine derived hormones synethesis and storage
Adrenal medulla (water soluble) - made in adrenal medulla, stored in vesicles and released by exocytosis
Thyroid hormones (fat soluble) - made in thyroid follicles, stored as part of thyroglobulin and released by diffusion when TSH stimulates thyroid
Melatonin - made in pineal gland, stored and secreted rhythmically
Steroid hormones synthesis, storage and secretion
All made from cholesterol, conversion involves specific enzymes found in mitochondria and SER
Not stores, synthesised on demand
Diffuse through the cell membrane into bloodstream
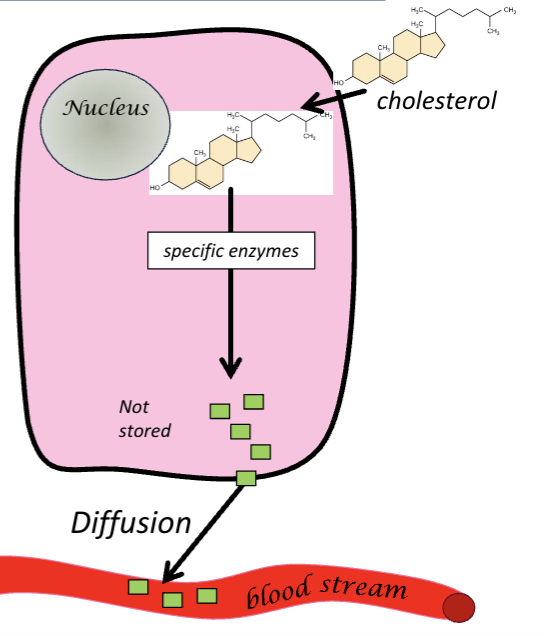
Liposoluble hormones
Cholesterol enters cell and is converted into hormone by specific enzymes
Hormones not stored so they diffuse directly out of the cell
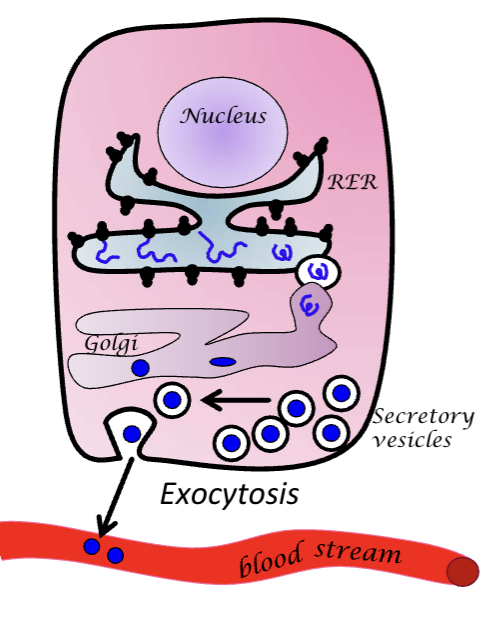
Hydrosoluble hormones
Hormone made in nucleus and RER
Goes to golgi aparatus and is packaged into secretory vessicles
Stored until signal arrives and exocytosis
Negative feedback regulation
When desired effect is achieved the hormone production shuts down
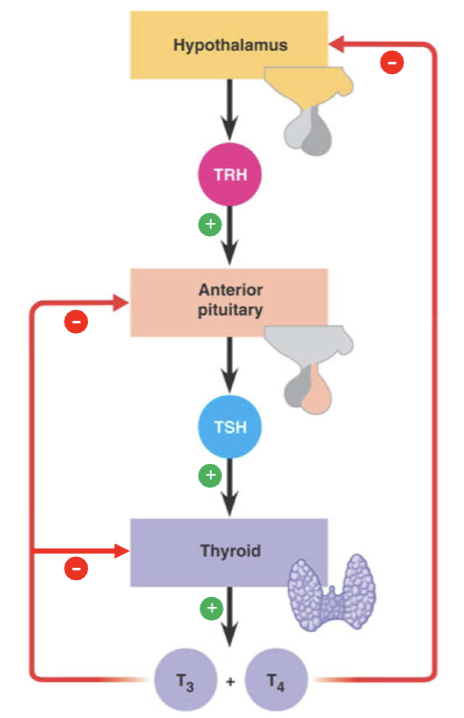
Negative feedback regulation example
Hypothalamus tells pituitary to make TSH
TSH tells thyroid to make T3 and T4 which control metabolism
When there is enough T3 and T4 in blood, they go back to tell the pituitary and hypothalamus there is enough
TSH and TRH production slows down (inhibited)
Positive feedback regulation
The hormone stimulates more of itself until an external loop happens
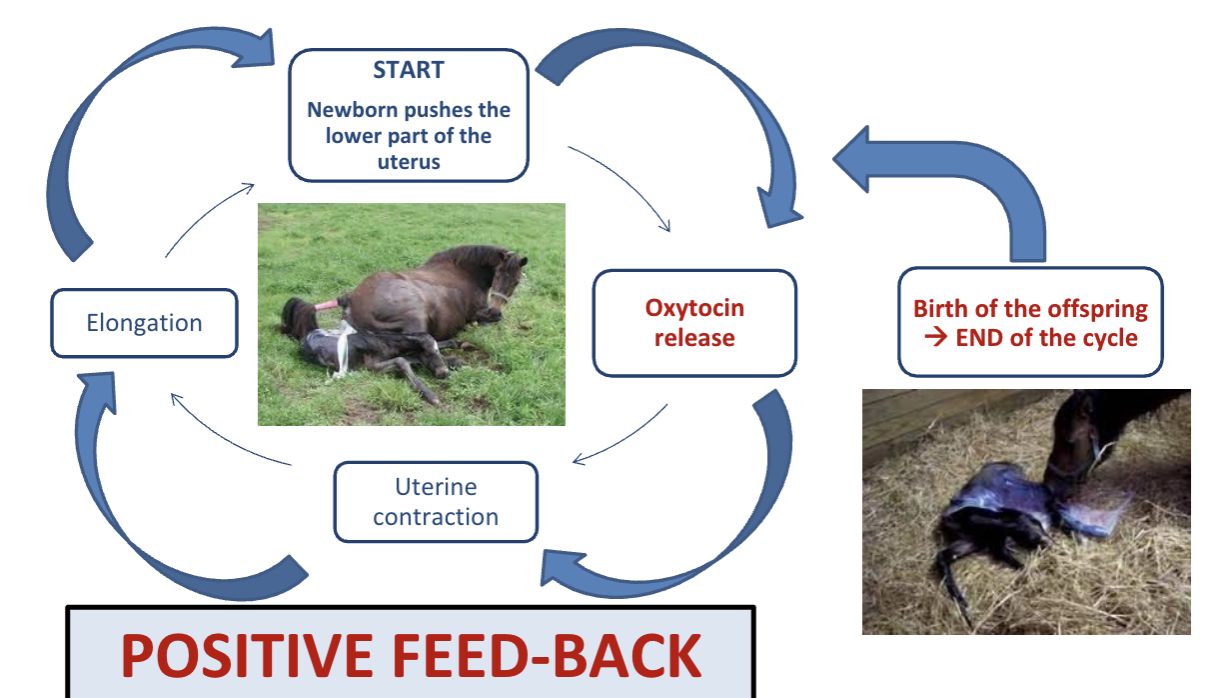
Positive feedback regulation example
Baby stretches cervix → triggers oxytocin release
Oxytocin causes stronger uterine contractions
More stretching → more oxytocin
Ends when the baby is delivered
Circadian rhythms regulation
Hormone release follows a 24-hour cycle
Regulated by supraschiasmatic nucleus in the hypothalamus
Melatonin peaks at night and cortisol peaks in the morning
Neuroendocrine reflex regulation
Nervous system triggers hormonal release under stress of stimuli
Transport of hormones in blood
Hydrosoluble - circulate freely
Liposoluble - carrier protein needed
Liposoluble hormones mechanism
Diffuse through plasma membrane, bind to intracellular receptors
Hormone-receptor complex interatcs with DNA in nucleus and acts as a transcription factor that regulates gene expression
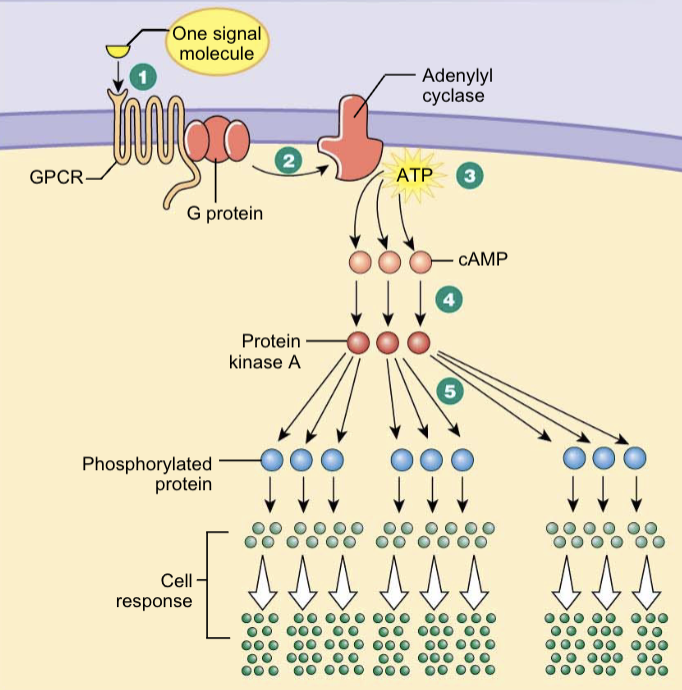
Hydrosoluble → cell membrane action
1 - hormone binds to receptor on cell surface (specific to hormone)
2 - receptor activates G-protein (molecular switch that has subunits)
3 - G-protein activates enzyme adenynyl cyclase which converts ATP into cAMP (second messenger)
4 - cAMP activates protein kinase A (PKA) which adds phosphate groups to proteins (phosphorylation) which activates/inactivates enzymes, ion channels or transcription factors
5 - final outcome depends on the target cell
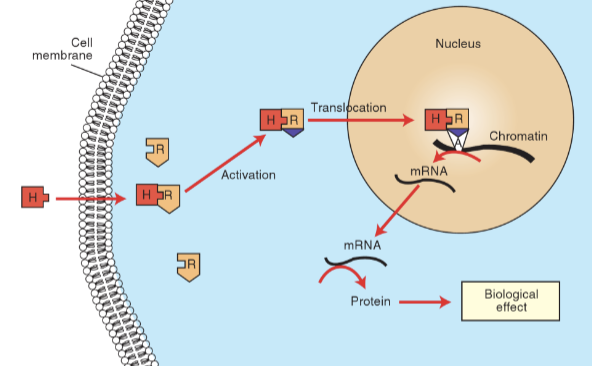
Liposoluble → steroid hormone action
1 - enters cell by diffusion through membrane
2 - inside cytoplasm, binds to intracellular receptor
3 - hormone receptor complex enters nucleus
4 - binds to specific DNA region called ‘acceptor site’ on chromatin
5 - activates transcription, forming mRNA → new protein synthesis
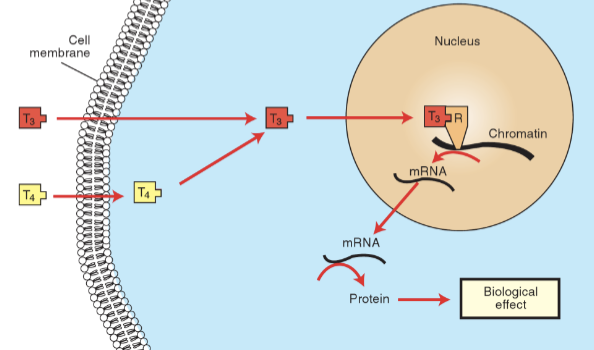
Liposoluble → thyroid hormone action
1 - enter the cell easily through diffusion
2 - go straight to nucleus without binding in cytoplasm
3 - inside nucleus, bind to intranuclear receptor already attached to DNA
4 - T3-receptor complex activates transcription → mRNA → protein synthesis
How are hormones eliminated
Metabolism - mainly in liver and kidney, hormones chemically altered (broken down or into inactive form) → no longer fits in the receptor
Excretion - mainly through urine (kidneys) but also bile (liver), hormones or broken down products are filtered by kidney and excreted, some fat-soluble hormones may be excreted in bile
Enzymatic degradation - enzymes at target tissues break down hormone after binding to receptor
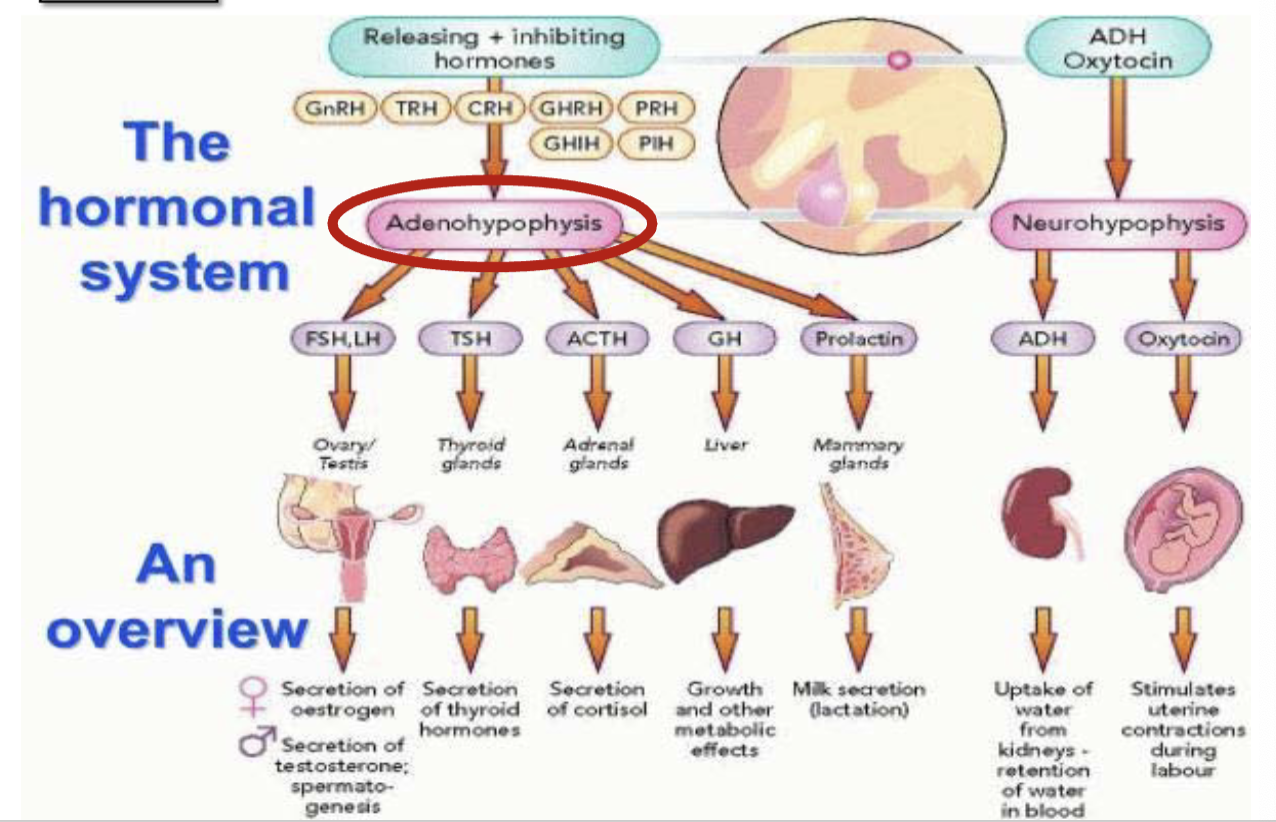
Function of pituitary and hypothalamic axis
Critical component of endocrine system
Coordinates hormonal signals between hypothalamus and pituitary gland
Pituitary gland
Located at the base of the brain in region called Sellaturcica
Posterior - neurohypophysis, develops from nervous tissue and is connected to hypothalamus via nerve fibers
Anterior - adenohypophysis, develops from epithelial tissue, grows upwards from roof of the mouth (Rathke’s pouch)
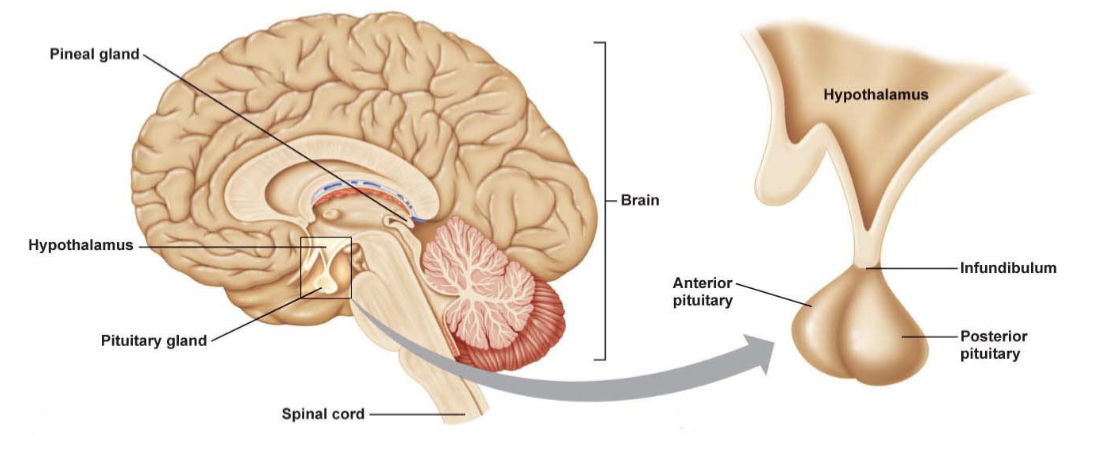
Posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) and hypothalamus
Hypothalamus sends nerve impulses to posterior
Hormones are produced in the hypothalamus but stored and released from the posterior pituitary when hypothalamus sends nerve impulses
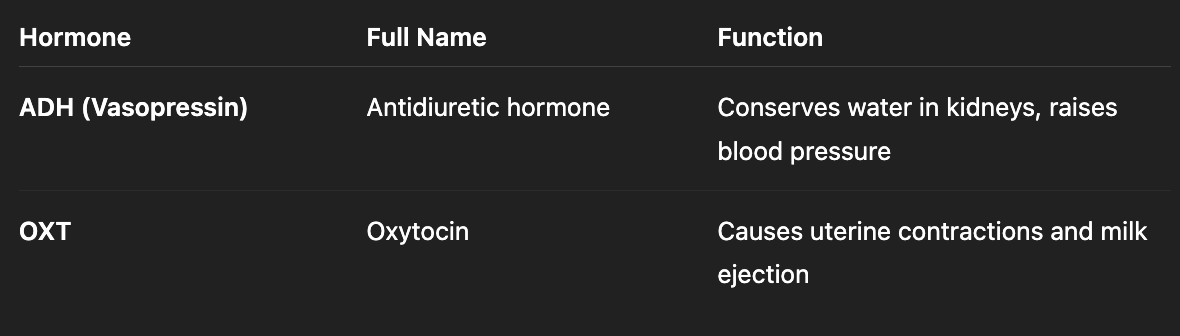
For instance oxytocin (OXT) and ADH (antidiuretic hormone) are stored and later released in the bloodstream
Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) and hypothalamus
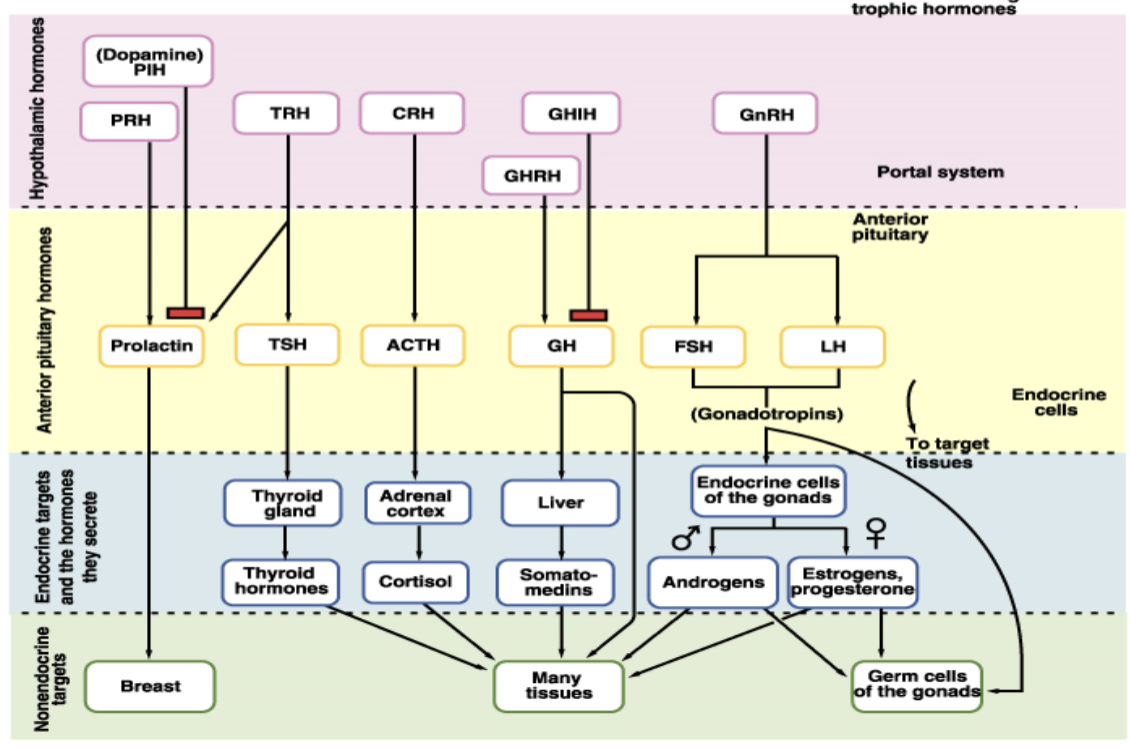
Hypothalamus released chemical messengers called ‘releasing or inhibiting hormones’ into blood supply between the anterior and hypothalamus
Travel through a portal blood system where they stimulate or inhibit the release of other hormones called ‘tropic hormones’ into the bloodstream
Tropic hormones act on other endocrine glands to release their own hormones like the thyroid, adrenal glands, gonads…
Neurohypophysis
Oxytocin and Antidiuretic hormone are stored in nerve terminals
When hypothalamus receives signal, it sends nerve impulses down axon terminal → triggers release of hormones in bloodstream → neurosecretion
Paraventricular nucleus - produces mainly oxytocin, PNV axons extend into posterior and release hormones in bloodstream
Supraoptic nucleus - produces mostly ADHand releases hormones the same way as PNV
Tropic hormones
Hormones that target other endocrine glands to produce own hormones:
FSH (follicle stim) - targets gonads, helps regulate reproductive functions
LH (luteinizing) - works with FSH in regulating reproductive functions (ovulation or testosterone prod)
TSH (thryoid stim) - stim thyroid gland, thyroid hormones, metabolism
ACTH (adrenocorticotropic) - adrenal glands to produce cortisol, used for body stress response
Non tropic hormones
Directly affect target cells without stimulating other glands:
GH (growth) - promotes growth, cell reproduction and repair, bones+muscles
PRL (prolactin) - milk production in females after childbirth
MSH (melanocyte-stim) - skin pigmentation by stimulation the production of melanin in melanocytes
Hypothalamus hormones
Travel to anterior and tells it to ‘release’ or ‘hold back’ certain hormones
Adenohypophysis hormones
Produces and releases own hormones in response to signals from hypo

Neurohypophysis hormones
Does not make its own hormones, but stores and releases from hypo
Overview
Overview