Global Dimensions Midterm Study Guide - Kimmel
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Globalization
trend away from distinct national economic units and toward one huge global market
Globalization of Markets
Moving away from an economic system in which national markets are distinct entities, isolated by trade barriers and barriers of distance, time, and culture, and toward a system in which national markets are merging into one global market.
Globalization of Production
Trend by individual firms to disperse parts of their productive processes to different locations around the globe to take advantage of differences in cost and quality of factors of production.
land
labor
capital
energy
factors of production?
Service Learning
a credit-bearing, educational experience in which students participate in an organized service activity that meets identified community needs and reflect on the service activity in such a way as to gain further understanding of course content, a broader appreciation of the discipline, and an enhanced sense of civic responsibility.
Mississippi Development Authority
Service Learning Partner is the...
market economy
An economic system in which the interaction of supply and demand determines the quantity in which goods and services are produced.
Command Economy
An economic system where the allocation of resources, including determination of what goods and services should be produced, and in what quantity, is planned by the government.
Mixed Economy
an economic system combining private ownership and free market mechanisms landing between market and command economies.
Collectivism
a political system that emphasizes collective goals as opposed to individual goals
Socialism
A system in which society, usually in the form of the government, owns and controls the means of production.
(roots with Karl Marx)
Individualism
An emphasis on the importance of guaranteeing individual freedom and self-expression
Representative Democracy
a political system in which citizens periodically elect individuals to represent them in government.
Communist Totalitarianism
a version of collectivism advocating that socialism can be achieved only through a totalitarian dictatorship
Theocratic Totalitarianism
a political system in which political power is monopolized by a party, group, or individual that governs according to religious principles
tribal totalitarianism
A political system in which a party, group, or individual that represents the interests of a particular tribe (ethnic group) monopolizes political power.
right-wing totalitarianism
A political system in which political power is monopolized by a party, group, or individual that generally permits individual economic freedom but restricts individual political freedom, including free speech, often on the grounds that it would lead to the rise of communism.
Pseudo-Democracies
-Many nations lie between pure democracy and complete totalitarianism
--Authoritarian elements capture much of the machinery of state and use this in an attempt to deny basic political and civil liberties
--Russia under Vladimir Putin
privatization
transfers the ownership of state property into the hands of private investors (seen as a way to stimulate gains in economic efficiency by giving new private owners a powerful incentive - the reward of greater profits)
Deregulation
Removal of government restrictions concerning the conduct of a business.
Expropriation
Forced transfer of assets from a company to the government with compensation
1. Strawman - friedman doctrine, cultural relativism, the righteous moralist, the native immoralist
2. Utilitarian
3. Kantian
4. Rights Theories
5. Justice Theories
What are all the ethical approaches? 5
strawman approach
raised by scholars primarily to demonstrate that they offer inappropriate guidelines for ethical decision making in a multinational enterprise
SM - Friedman Doctrine
the only social responsibility of business is to increase profits, so long as the company stays within the rules of law
SM - cultural relativism
the belief that ethics are culturally determined and that firms should adopt the ethics of the cultures in which they operate
SM - Righteous Moralist
One who claims that a multinational's home-country standards of ethics are the appropriate ones for companies to follow in foreign countries
SM - Naive Immoralist
one who asserts that if a manager of a multinational sees that firms from other nations are not following ethical norms in a host nation, that manager should not either
Utilitarian Ethics
these hold that the moral worth of actions or practices is determined by their consequences
Kantian Ethics
the belief that people should be treated as ends and never as means to the ends of others
Rights Theories
a twentieth-century theory that recognizes that human beings have fundamental rights and privileges that transcend national boundaries and cultures
Justice Theories
focus on the attainment of a just distribution of economic goods and services
constant returns to specialization
The units of resources required to produce a good are assumed to remain constant no matter where one is on a country's production possibility frontier.
Dimishing returns
occurs when more units of resources are required to produce each additional unit
____ show that is is not feasible for a country to specialize to the degree suggest be the simple Ricardian model. ___ to specialization suggest that the gains from specialization are likely to be exhausted before specialization is complete.
Economies of Scale
cost advantages associated with large scale production
Mercantilism
an economic philosophy advocating that countries should simultaneously encourage exports and discourage imports
absolute advantage
a country has this in the production of a product when it is more efficient than any other country at producing it
comparative advantage
the ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another producer
Factor Endowment Theory
A theory that suggests that nations will develop comparative advantages based on their locally abundant factors. (advanced factors like communication infrastructure and sophisticated/skilled labor are most significant for competitive advantage)
new trade theory
The observed pattern of trade in the world economy may be due in part to the ability of firms in a given market to capture first-mover advantages.
import
bring (goods or services) into a country from abroad for sale.
export
A good or service produced in the home country and sold in another country.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Investment made by a foreign company in the economy of another country.
stock of FDI
the total accumulated value of foreign-owned assets at a given time
outflow of FDI
Flow of foreign direct investment out of a country
inflow of FDI
flow of FDI into a country
GDP (Global Domestic Product)
the total market value of all final goods and services produced annually in an economy
GNP (Gross National Product)
total dollar value of goods & services produced by a nation at home or away
GNI (Gross National Income)
The value of the output of goods and services produced in a country in a year, including money that leaves and enters the country
PPP (Purchasing Power Parity)
an adjustment made to the GNI to account for differences among countries in the cost of goods
(the buying power of income in a country)
Gini
A statistical formula that measures the amount of economic inequality within a country. "0" corresponds with perfect equality and "100" represents perfect inequality.
HDI (Human Development Index)
a measure of a country's standard of living, including health and education
Culture model
What model is this?
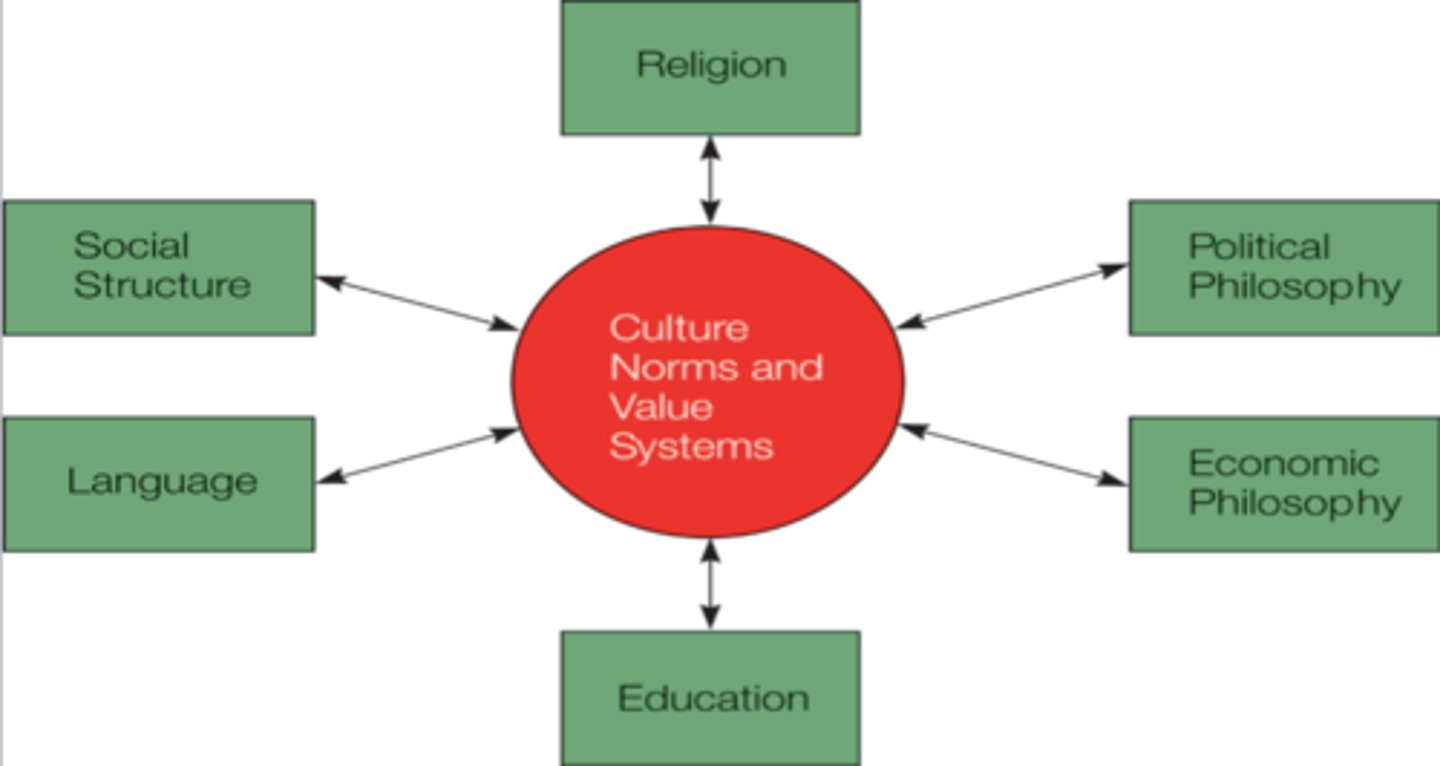
religion
political philosophy
economic philosophy
education
language
social structure
What are the branches on the culture model?
the ethics model
what model is this?
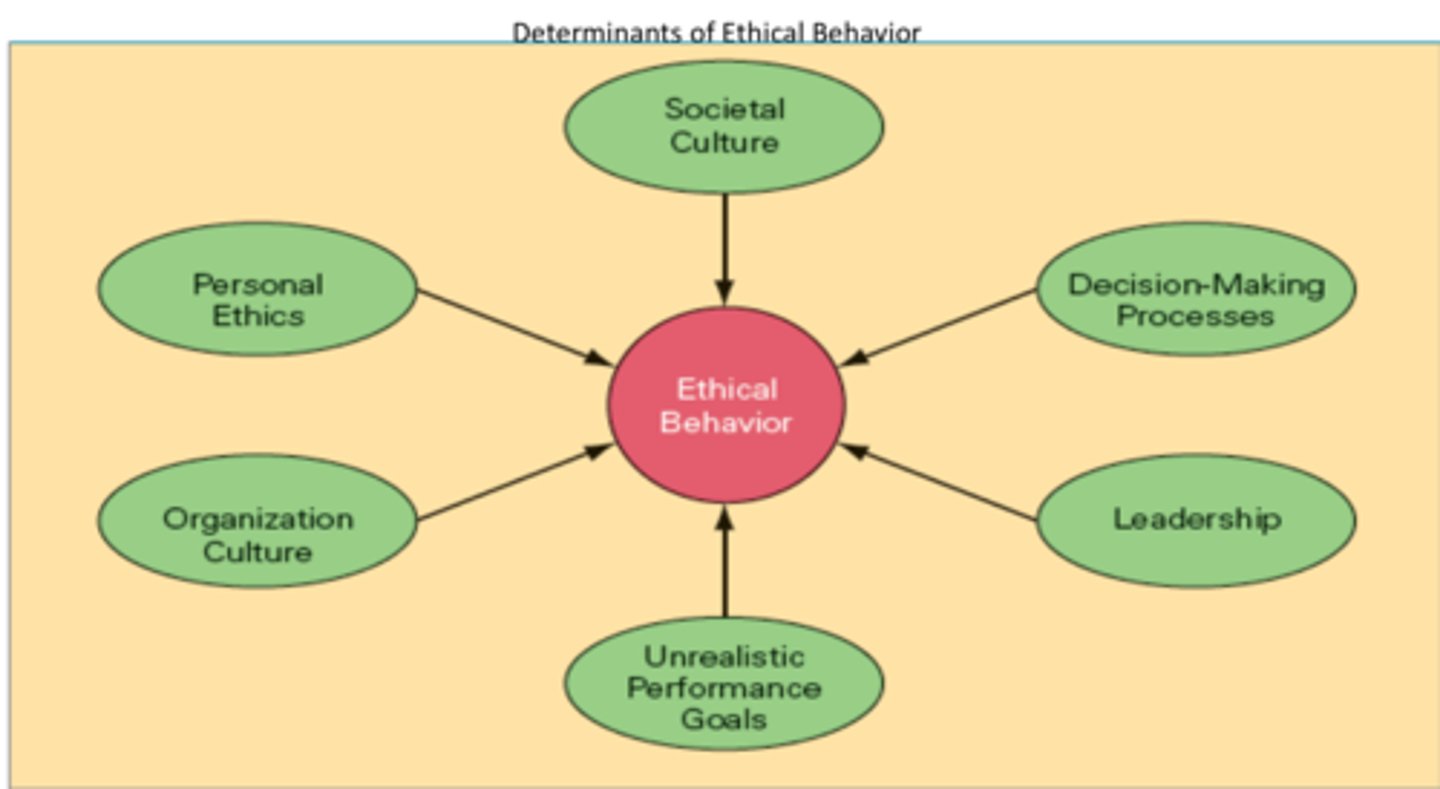
societal culture
decision making processes
leadership
unrealistic performance goals
organizational culture
personal ethics
what are the branches of the ethical model?
World Bank and International Monetary Fund
These two institutions were created in 1944 by 44 nations that met at Bretton Woods, New Hampshire
The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade
International treaty that committed signatories to lowering barriers to the free flow of goods across national borders and led to the WTO
Declining Trade and Investment Barriers ( + technological trade )
What are two macro factors that underline the trend toward greater globalization?
united nations
the goal of this institution is to preserve peace through international cooperation and collective security
G20
this institution comprises the finance ministers and central bank governors of the largest economies in the world, plus representatives form the European Union and the European Central Bank.
it has declined
How has the share of the U.S. world output changes since the 1960s?
brings the world together and we are able to gain more money through trade
Argument for Globalization
some people take advantage of other countries wage rate. they will pay Americans $9 an hour, but the majority of their workers are in Honduras making $0.50 an hour.
Argument against Globalization
Saudi Arabia
The opening case of chapter 2, "National Differences in Political, Economic, and Legal Systems" focuses on transformation in _____
democracy --> <---totalitarianism
Complete the missing end of this political dimension:
common law
a system of law based on precedent, tradition, and customs
treat the convention's rules as a part of it's law
When a country adopts the United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods, it signals to the other adopters that it will:
property rights
the legal rights over the use to which a resource is put and over the use made of any income that may be derived from that resource
private action
the theft, piracy, blackmail, and the like by private individuals or groups
the payment of speed, grease, or facilitating payments.
The U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act allows...
trademark
Designs and names, often officially registered, by which merchants or manufacturers designate and differentiate their products
WIPO (World Intellectual Property Organization)
An international organization whose members sign treaties to agree to protect intellectual property
pensions and retirement age
from the opening case of chapter 3, a central problem in brazil's economic recovery has been ___
it has maintained high protections of domestic companies
from the opening case of chapter 3, what has been Brazil's approach to trade barriers (prior to 2016)?
Shadow Economy
another name for the black market or economy
UN
Which institution adopted Amartya Sen's work?
it doesn't consider cost of living
Why is GNI per person misleading?
black economy
an unreported sector of the primary economic system in which transactions are handled in cash only
life expectancy at birth, educational attainment, and the sufficiency of average incomes to meet basic needs of life
What are the three measures considered in HDI (human development index)?
market economy and strong property rights
What is required for innovation and entrepreneurship to grow in a country?
OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development)
promotes policies that improve economic and social well-being of people around the world
UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization)
based on the idea of establishing peach through moral and intellectual collaboration
innovation and entrepreneurship
What are the engines of economic growth?
benfits, cost, risks
What contributes to overall attractiveness? (three things in the country attractiveness model)
business ethics
accepted principles of right or wrong governing the conduct of business people
the sullivan principles
widely accepted business practices that suggest a company may operate within an unethical system if (1) it acts ethically and (2) it actively promotes social change toward ethical behavior
employment practices
human rights
enviormental regualtions
corruption
moral obligation of multinational corp.
What are 5 areas where the most ethic issues happen in companies?
tragedy of the commons
a parable that illustrates why common resources are used more than is desirable from the standpoint of society as a whole
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
the idea that business people should consider the social consequences of economic actions when making business decisions and that there should be a resumption in favor of decisions that have both good economic and social consequences
moral courage
the will to stand up for what is right, regardless of personal cost (walk away from profit, because its unethical)
The Product Life Cycle Theory
a theory helps to explain that production becomes more international as the product matures.
Hecksher-Ohlin
Who is best known for factor endowments?
Porter's Diamond of Competitive Advantage
This is what?
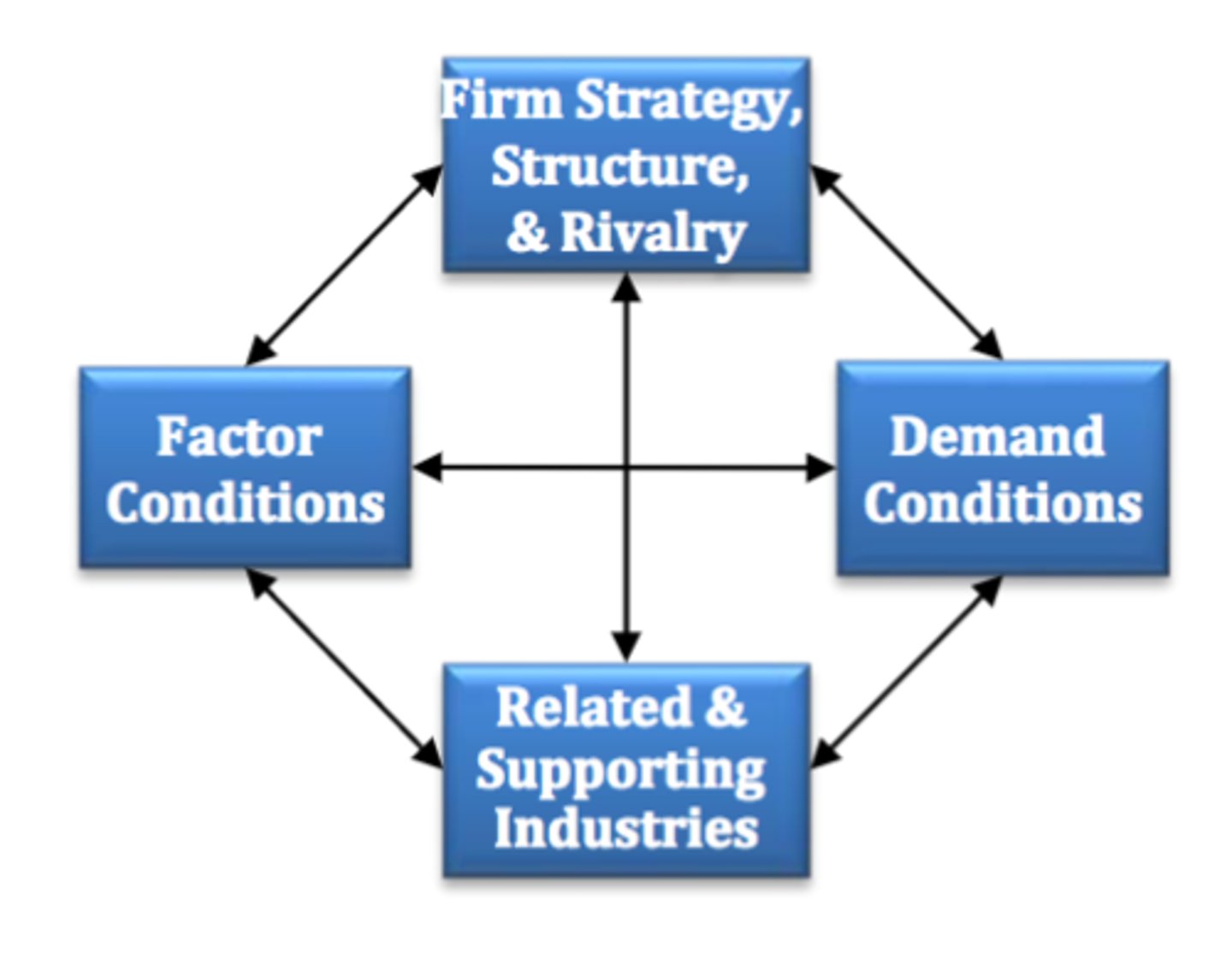
Factor conditions
Demand conditions
Related and supporting industries
Firm strategy, structure, and rivalry
What are the areas of Porter's Diamond of Competitive Advantage?
tariff
tax levied on imports
specific tariff
tariff levied as a fixed charge for each unit of good imported
ad valorem tariff
a tariff levied as a proportion of the value of an imported good
subsidy
A government payment that supports a business or market
import quota
a direct restriction on the quantity of a good that can be imported into a country
tariff rate quota
lower tariff rates applied to imports within the quota than those over the quota