Option A: Neurophysiology
1/50
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
nervous system process
sensor (eye, skin) → integration (brain, spinal cord) → effector (joints, muscles) in peripheral or central nervous system
Peripheral Nervous System
External nerves in muscles
Autonomic- self regulated action of organs and glands
Somatic- voluntary movements of skeletal muscles
Central Nervous System
Brain, spinal cord, links to other system
Neurons
cells of the brain that transmit electrical impulses
longest is in the whale
~86 billion in the body
dendrites vs axons
one is the projections from the cell that receive impulses from other neurones.
the other carries electrical impulses away from neurone to other neurones.
pre-synaptic terminal vs node of ranvier
place at the end of axon where electrical signal (action potential) is converted to a chemical signal (neurotransmitter).
allows ions to diffuse in and out of the neurone, sending signal jumping across gaps in the myelin sheath on the axon.
myelin sheath
myelination of nerve fibres allows for saltatory conduction
axon is coated in schwann (type of glial) cells
accelerates the saltatory conduction (travel) of electrical signals from node to node
no myelin = slow transmission = multiple sclerosis
sensor neurones
receptor cell, myelin sheath, axon, cell body.
receive information from muscle receptors.
relay neurones
dendrite, cell body, pre-synaptic terminal, cell body
pass electrical signals across body.
motor neurones
dendrite, myelin sheath, cell body, node of ranvier, into muscle
send instructions to muscles.
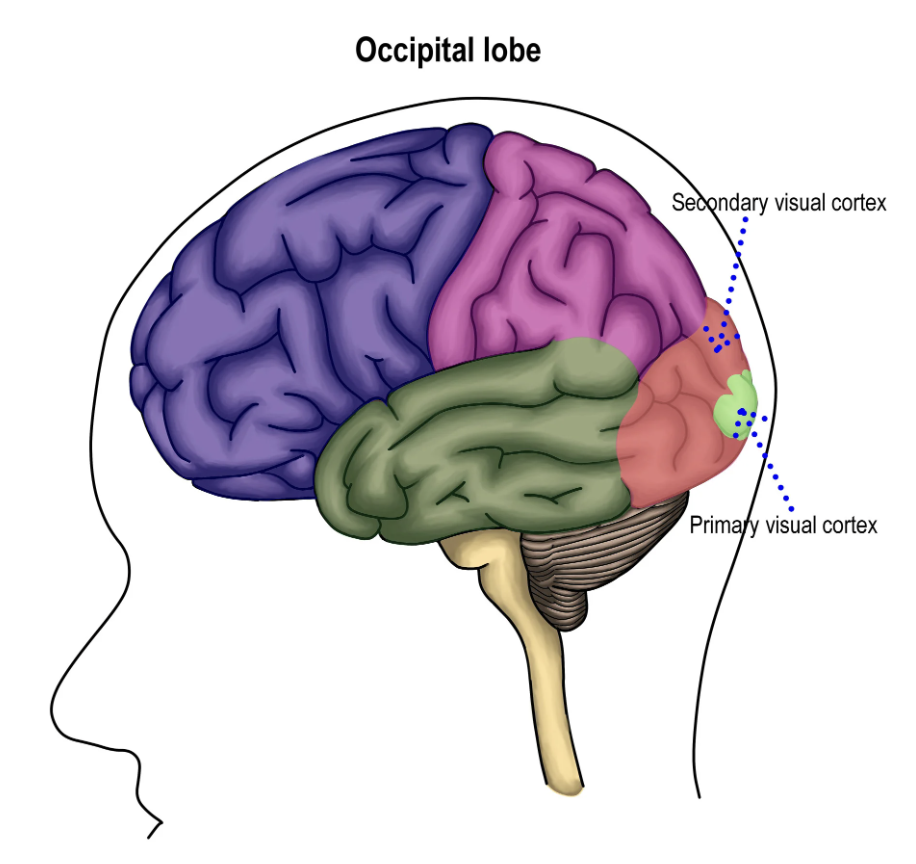
visual cortex
occipital lobe (hindbrain)
controls the reception, segmentation and integration of visual information
if damaged: loss of visual awareness, chronic blindness
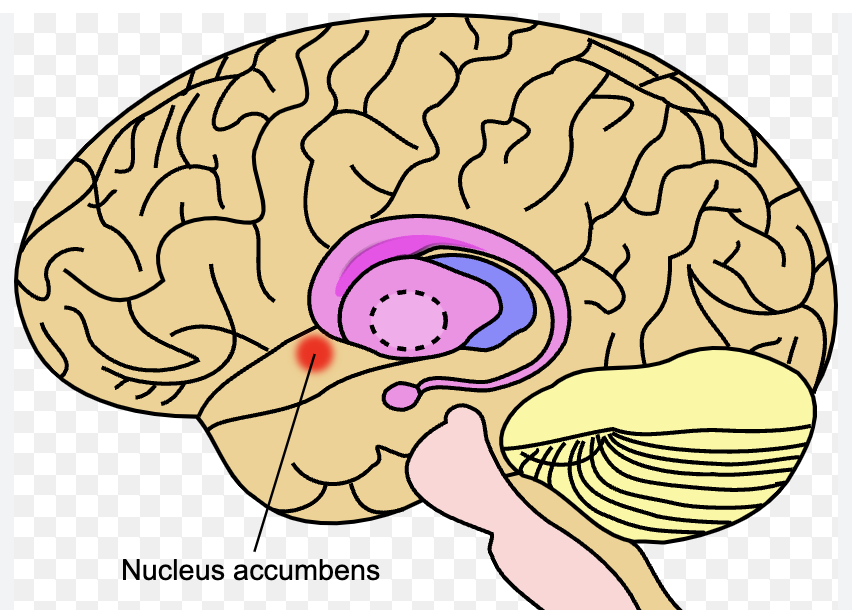
Nucleus accumbens
basal forebrain (one located in each hemisphere)
controls wakefulness by expressing dopamine- pleasure, reward, addiction
if damaged: less motivation, engagement, drive to achieve (similar results may occur after stopping antidepressants)
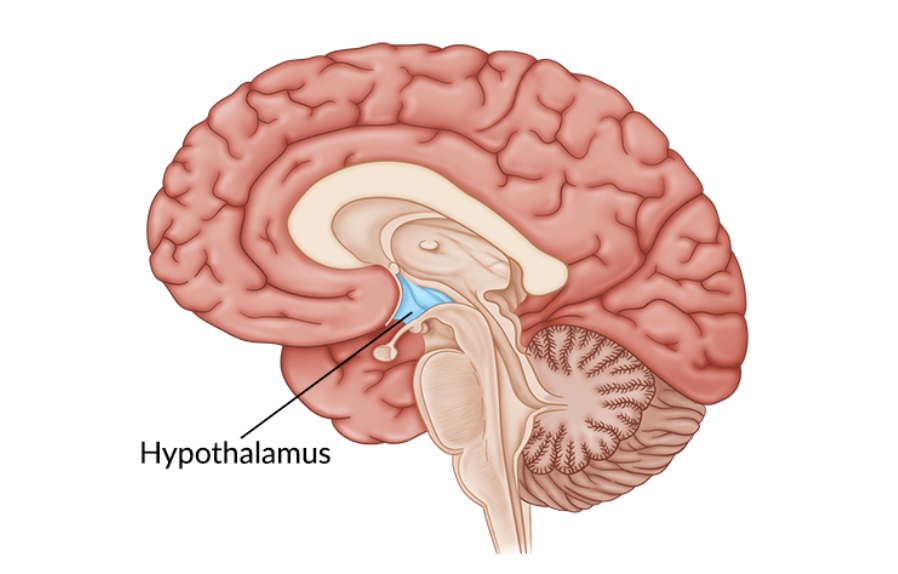
hypothalamus
ventral brain (above pituitary)
body temperature, hunger, thirst, mood, sex drive, blood pressure, sleep
if damaged: dysfunctional homeostasis, body temperature, growth, weight, emotion, sleep, water control
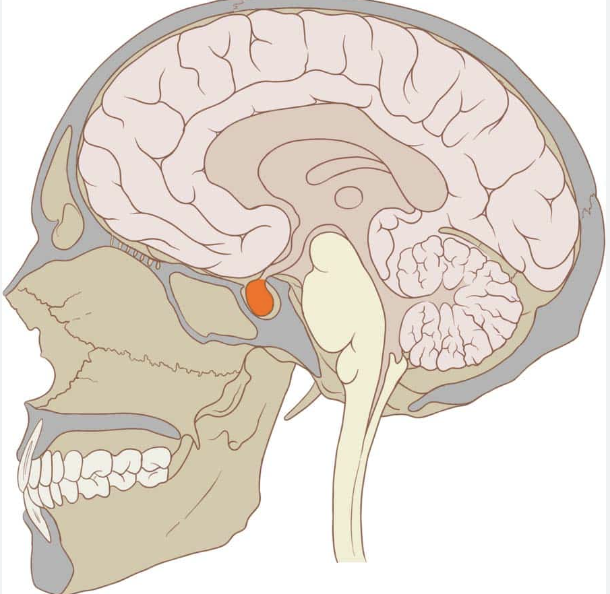
pituitary gland
base of brain behind nose bridge
controls growth, metabolism, reproduction, secretes hormones into bloodstream
if damaged: headaches, vision problems, nausea, fatigue, body composition change
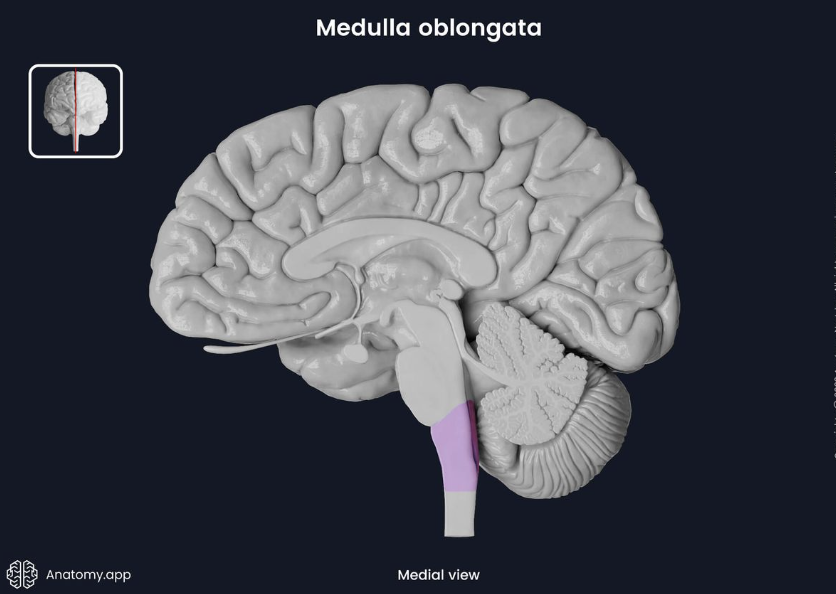
medulla oblongata
brain stem (connects brain and spinal cord)
controls heart, circulation, breathing, blood pressure
if damaged: respiratory failure, paralysis, loss of sensation
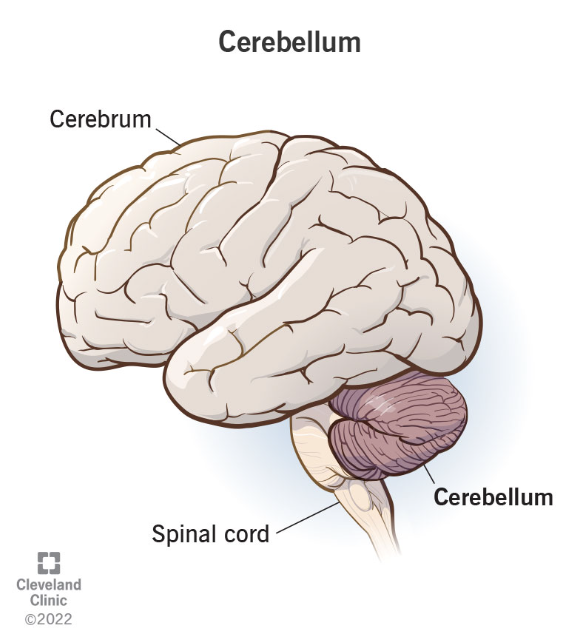
cerebellum
back of head, above/behind spinal cord
controls movement and balance, language, attention, eye movement
if damaged: loss of coordination, distance blind, tremors, staggering, no rapid alteration between stimuli
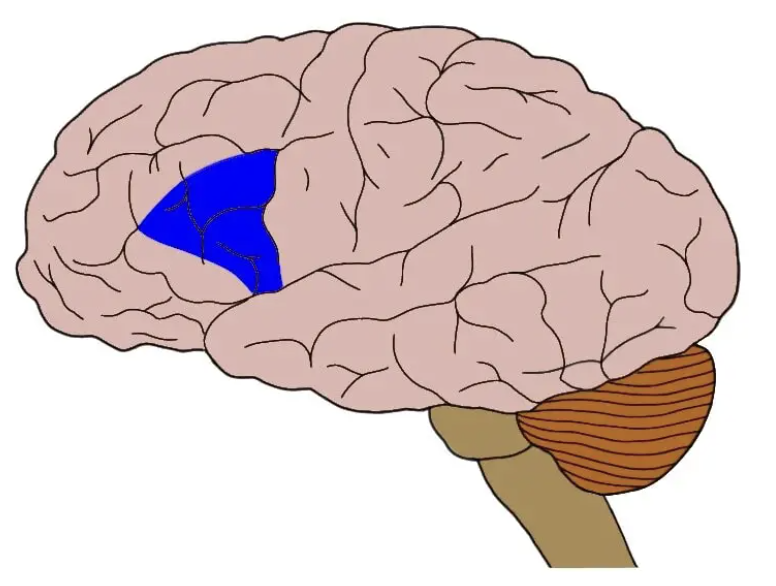
Broca’s area
posterior inferior frontal gyrus (front of brain)
controls speech, articulation, comprehension, sensorimotor learning
if damaged: breakdown between thoughts and language abilities
Ways to study the brain
Autopsy, dissection, removal of sections of animal brains, electrical stimulation of brains
Phineas Gage
Worker who had a tamping pole driven through his brain, resulting in the loss of his hippocampus. Subsequently more aggressive personality, loss of social inhibition.
Cerebral Cortex
The outermost layer of the brain, has two hemispheres → responsible for higher order functions
Human one is large with lots of folds- leads to high intelligence
left side processes for right side of the body, right side processes for the left side
corpus callosum connects the two hemispheres
Autonomic Nervous System
swallowing-
voluntary phase gets food from mouth to pharynx,
involuntary gets food from pharynx to stomach.
controlled by cerebral cortex, medulla oblongata
breathing-
a) timing of inspiration,
b) force of inspiration, voluntary expiration.
controlled by medulla oblongata
pupil reflex-
controlled by medulla oblongata.
muscles in the iris contract to dilate pupil and relax to constrict the pupil in response to light.
If eye doesn’t immediately respond to light, may indicate brain death
heart rate-
controlled by medulla oblongata. monitors blood pH
increases heart rate with the sympathetic system
decreases it with the parasympathetic system
animal models for neuroscience and their applications
drosophila- broad reaching, 4 chromosomes
zebrafish- transparent tissues
mus musculus- shares many human diseases
xenopus laevis (African clawed frog)- large eggs
caemorhabditis elegans (flatworm)- number of cells
used for ease of observation, simple systems and fewer ethical concerns.
embryogenesis
the process of making an embryo from a blastocyst.
Requires gastrulation- the differentiation of tissue into the endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm (three layers)
after gastrulation, neurulation can occur to create an embryo.
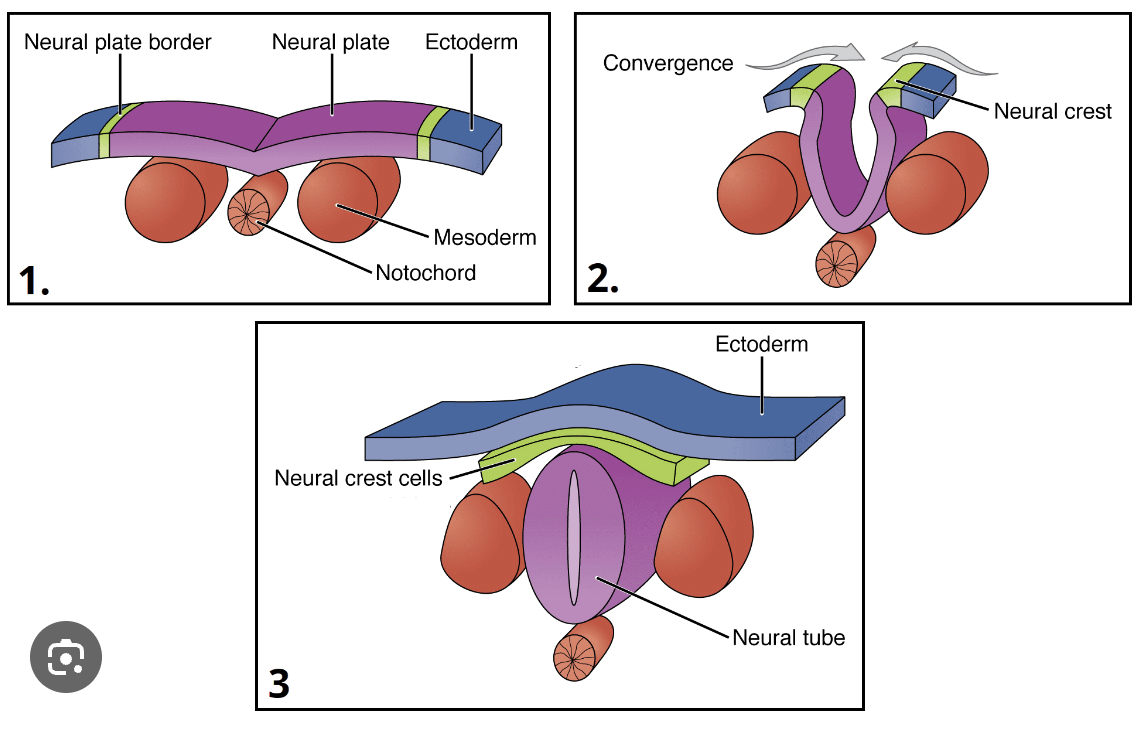
neurulation (as observed in xenopus)
ectoderm tissue differentiates to form neural plate and neural plate border- notochord derived from mesoderm tissue
neural plate folds inwards and downwards, notochord pushed downwards
neural tube closes to form neural crest, which will differentiate into peripheral nervous system
mesoderm differentiates into somites (which will become bones and muscles), neural tube forms spinal cord, notochord degenerates into spinal disks
the whole tube becomes the brain at one end and the spinal cord at the other
spina bifida
condition caused by an incomplete closure of the neural tube during neurulation. Leads to:
myelomenyocele- sac of fluid forms in gap, part of spinal cord exposed in sac
meningocele- sac of fluid but spinal cord not exposed
spina bifida occulta- gap in spine, no sac
embryonic brain development
neural tube elongates to form forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain.
forebrain → (telencephalon → cerebrum) (diencephalon → thalamus)
midbrain → mesencephalon → brainstem
hindbrain → (melencephalon → pons + cerebellum) (myelencephalon → medulla oblongata)
development and migration of neurons
stem cells → progenitor cells → (neuron for signalling) (glial cell for support)
neural circuits- information networks connecting different types of neurons
glial cells- scaffolding network that direct immature neurons to their destinations (only 1/3 of immature neurons make it)
somal translocation- neuron forms an extension at the perimeter of its cell, and translocated its soma along this length
axon growth is directed by chemoattractants and chemorepellents
synaptic density
neuroplasticity- ability for the neurons to change their pathways over time
developing neurons form multiple synapses
neural pruning removes unused neuron connections
rerouting involves making new connections
peak neural pruning occurs between 2-4 years of age, and highest neural density is at 2 years old
sprouting allows the neurons to recover if one is damaged (eg if neuron A bonded to C is damaged, neuron B bonded to D will stretch to also bond to C)
for example, strokes may promote neural sprouting
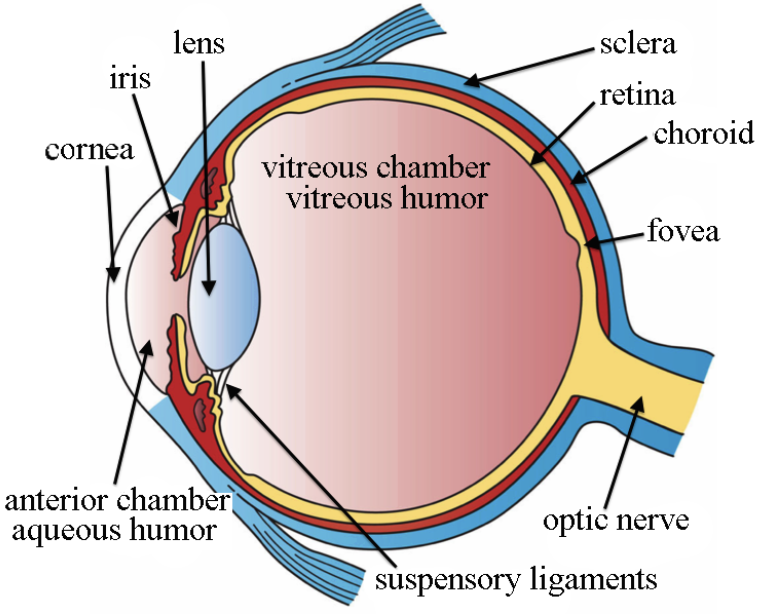
parts of the eye
lens- bends light to focus onto retina. flips/cones image, focus + clarity
cornea- protects from UV radiation, focuses light entry
eyelid- distributes tears, protects
fovea- high acuity vision, focus, blind spot
retina- light → images, photoreceptors
optic nerve- one way connection from eye to brain, from retina
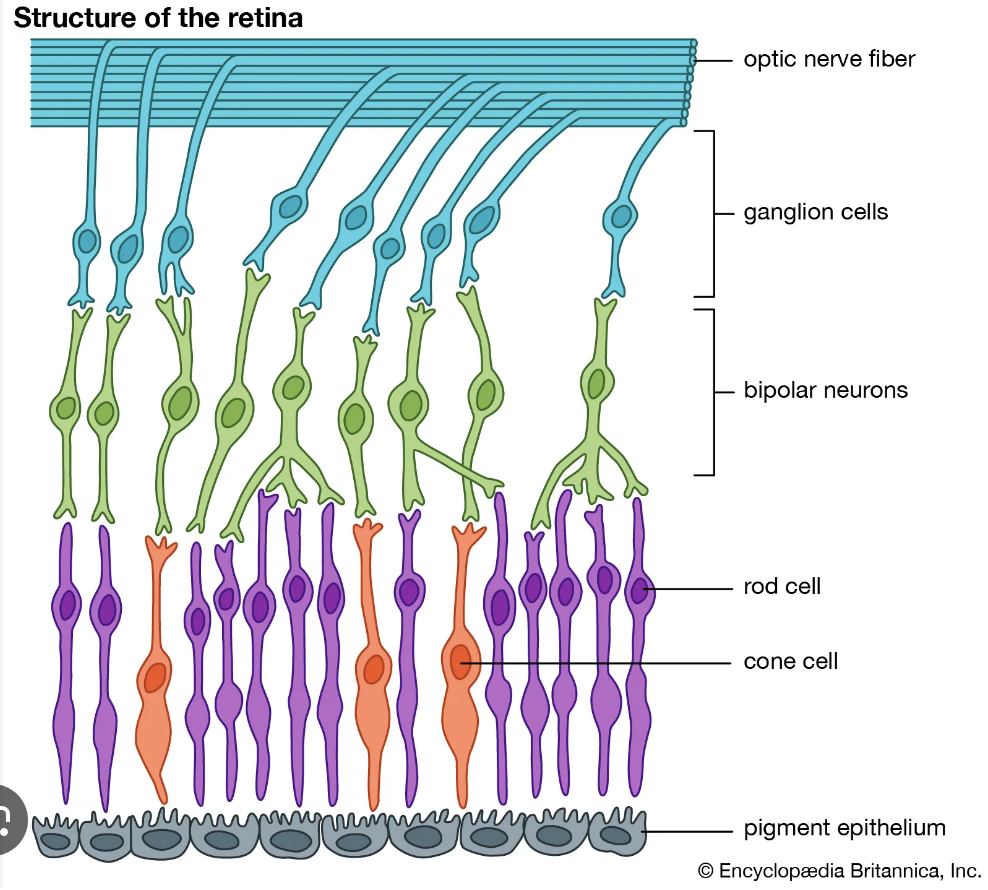
retina
light reflects off choroid, hits rods and cones
pigments in rods and cones break down, stimulating an action potential
synapses → photoreceptors → bipolar neurons → ganglia
ganglia carry impulse via optic nerve to occipital lobe in brain
rod cells
many found around periphery
dim light
low resolution (many rods 1 cell)
all wavelengths
achromatic b&w
one type- all contain rhodopsin
cone cells
few found around centre
bright light
high resolution (1 cone 1 cell)
red, green, blue only
colour vision
3x different iodopsin pigments
visual processing
optic chiasm- part of brain where optic nerves cross over
optic nerve- connects eyes to brain
visual field- portion of spaace in which objects are visible
contralateral processing- each side of brain controls oppisite
stereoscopic vision- register 3d visually
red green colour blindness
sex linked on the x chromosome
mother needs to be at least a carrier, father needs to be colour blind for the child to be colour blind
a problem with cones in the retina (responsible for colour recognition)
how is sound perceived in the human ear?
sound vibrations → chemical neurotransmitter
eardrum is moved by sound waves
eardrum causes movement of bones (incus, malleus) of the inner year- amplify sound by 20x on oval window
causes movement of fluid in cochlear
hair cells act as mechanoreceptors- sense movement, release a chemical neurotransmitter
carried one way up auditory nerve to brain
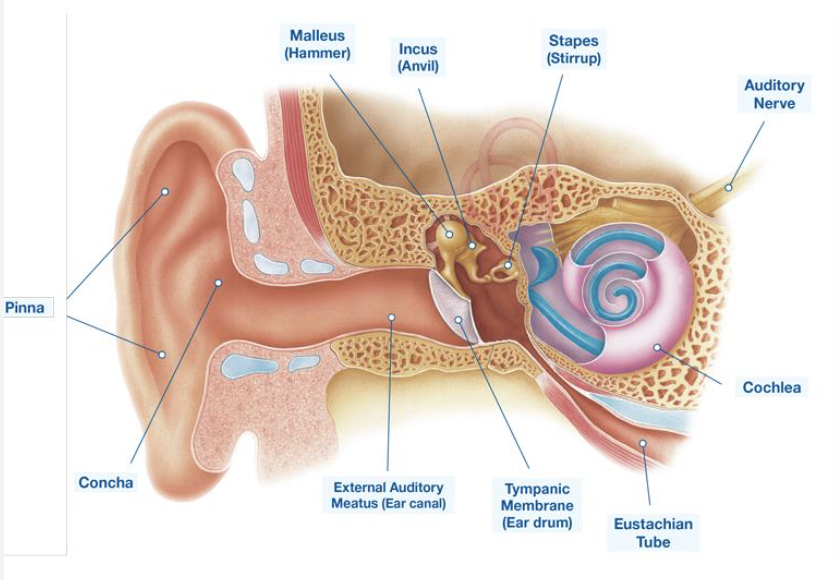
structure of the ear
eardrum vibrates movement
bones vibrate against drum
hair cells in cochlear generate neurotransmitter as sound passes over them
cochlear implant
needed if auditory nerve is healthy, but hair cells are damaged or lost
sound → external mic → external supercomputer turns sound into digital information → sent to implanted device → sends electrical signal to electrode in cochlear → information goes up auditory nerve (bypasses hair cells)
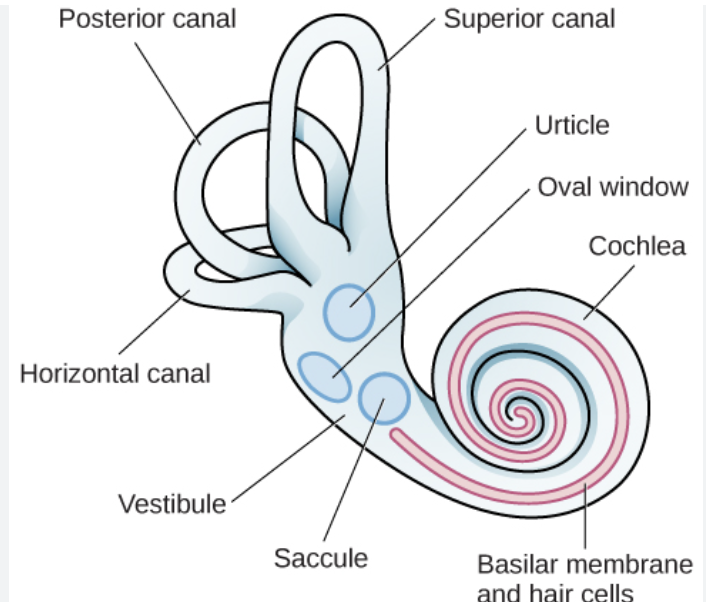
vestibular system
controls balance
located in the ear
posterior canal- left right tilt recognition
superior canal- up/down tilt
horizontal canal- shake head “no”
head movement “sloshes” appropriate canal, movement detected by hair cells in cupula (wide base of each canal), transmitted into vestibular nerve so brain may deduce head movements, maintain balance
olfactory system
controls sense of smell
receptor cells in epithelium of nose
contain cilia (little hairs)
membrane contains odorant receptor molecules
only volatile substances (capable of readily changing state of matter) bind to receptor molecules
different receptor proteins specific to different chemicals
innate behavior
inherited from parents, develops independently from environment
reflexes
kinesis
taxis
fixed action patterns
reflexes
involuntary, rapid response to stimulus detected by receptor
stimulus → receptor → sensory neuron → motor neuron (bypass brain) → effector muscle → response
= a reflex arc eg pain reflex to withdraw body part
kinesis
change in rate of activity in response to environmental stimulus
taxis
change in movement in response to an environmental stimulus → towards or away
fixed action patterns
pattern goes to completion even if stimulus is removed- involuntary
learned behaviour
based on experience and dependent on environment
non associative learning
habituation- getting used to a stimulus
sensitisation- more of a response to a repeated stimulus
associative learning- imprinting
phase sensitive learning- occurs at a particular life stage
independent of behavioural consequences- automatic
filial (for parents) or sexual (partner)
associative learning- observation
watching and copying others’ behaviour after seeing results
associative learning- classical (reflex) conditioning
unconditioned stimulus- leads to unconditioned automatic response
unconditioned response- automatic to a stimulus eg salivation for food
neutral stimulus- at first elicits no response
conditioned stimulus- may eventually trigger a conditioned response
conditioned response- must be learned by pairing a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus
learning to associate something with an action
Pavlov’s dog
paired the unconditioned stimulus/response of a dog salivating for food with the neutral stimulus of a bell. eventually the conditioned response of salivating when the bell is heard.
operant conditioning