Ch: 18 Endocrine System
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
contrast the endocrine and nervous system
the nervous system initiates a fast and rapid response. the endocrine system initiates a slow, but lasting response.
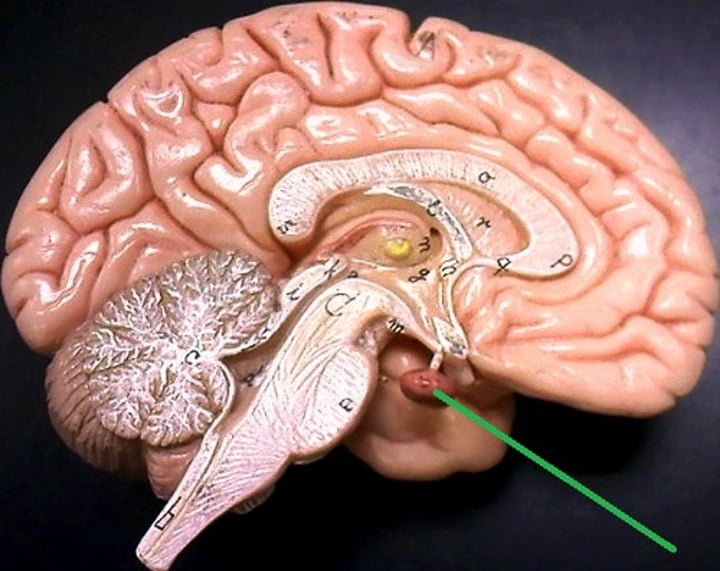
what gland is known as the hypophysis?
the pituitary gland
which one is more prominent positive or negative feedback mechanisms?
negative feedback
releasing hormones of the hypothalamus targets the anterior OR posterior pituitary?
ANTERIOR
what is melatonin secreted by?
the pineal gland
function of antidiuretic hormone (pituitary secreted)?
Promotes reabsorption of water from the kidney tubules and vasoconstriction
function of TSH hormone (pituitary secreted)?
Stimulates production and secretion of thyroid hormones
function of prolactin hormone (pituitary secreted)?
Stimulates milk production
function of oxytocin hormone (pituitary secreted)?
stimulates milk secretion
function of ACTH hormone (pituitary secreted)?
Increases secretion of cortisol from the adrenal cortex
tropic
releasing; stimulates other glands to release hormones
function of LH hormone (pituitary secreted)?
Stimulates testosterone production
function of FSH hormone (pituitary secreted)?
stimulate sperm production
function of Lipotropin hormone (pituitary secreted)?
increases lipid production
function of Vasopressin hormone (pituitary secreted)?
blood vessel constriction
The only 2 hormones released by the POSTERIOR pituitary gland are:
ADH and oxytocin
which hormone increases gene expression and thus promotes tissue growth throughout the body?
GH (growth hormone)
what is the pituitary gland controlled by?
the hypothalamus
what gland is this (found on either side of trachea)
thyroid gland
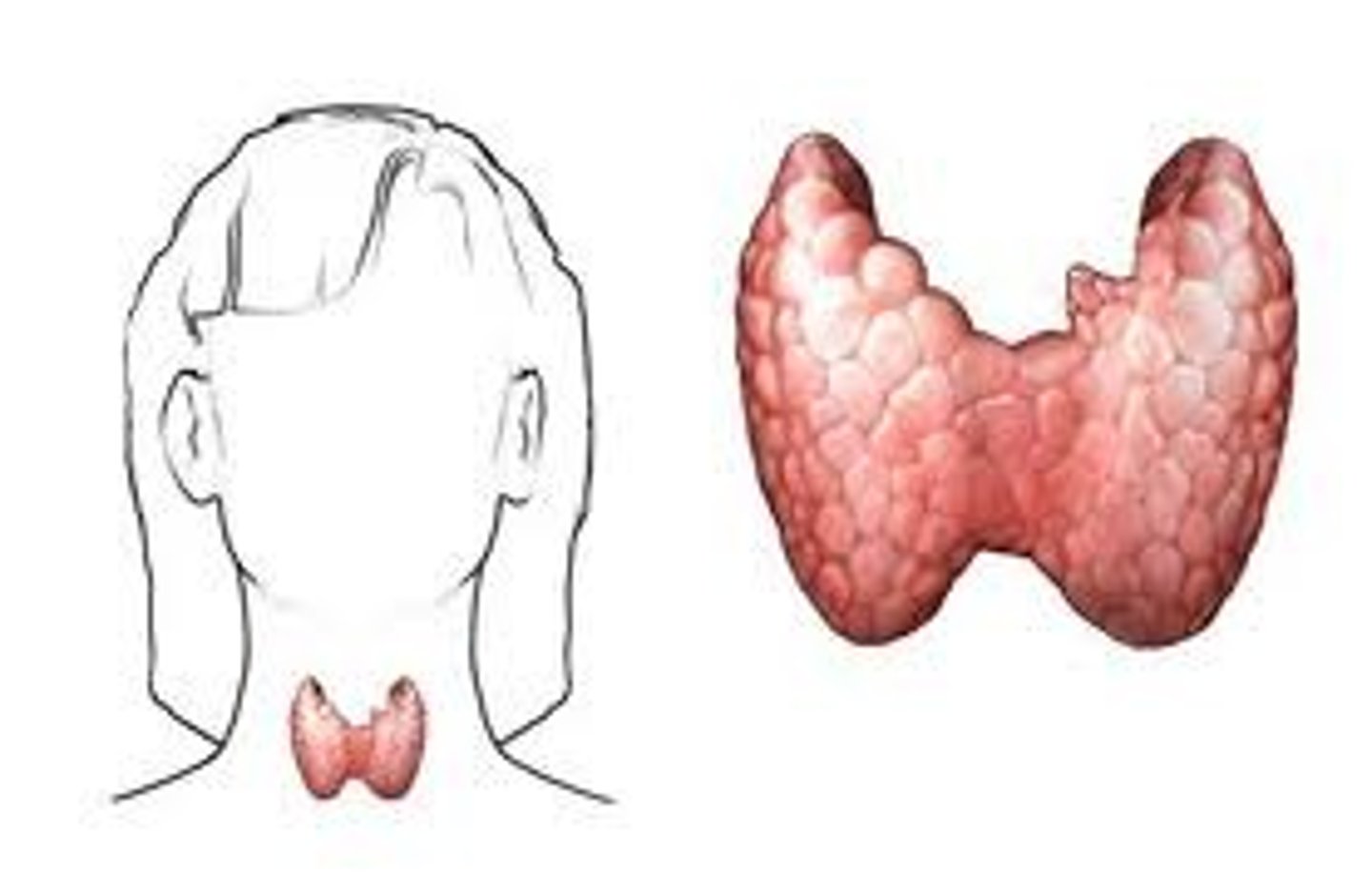
What is T4?
Tetraiodothyronine or thyroxine
function of calcitonin or C cells (thyroid secreted)
decrease calcium levels in blood by decreasing osteoclast activity (less bone breaking activity)
function of parathyroid hormone
increases bone reabsorption and calcium absorption in the intestines
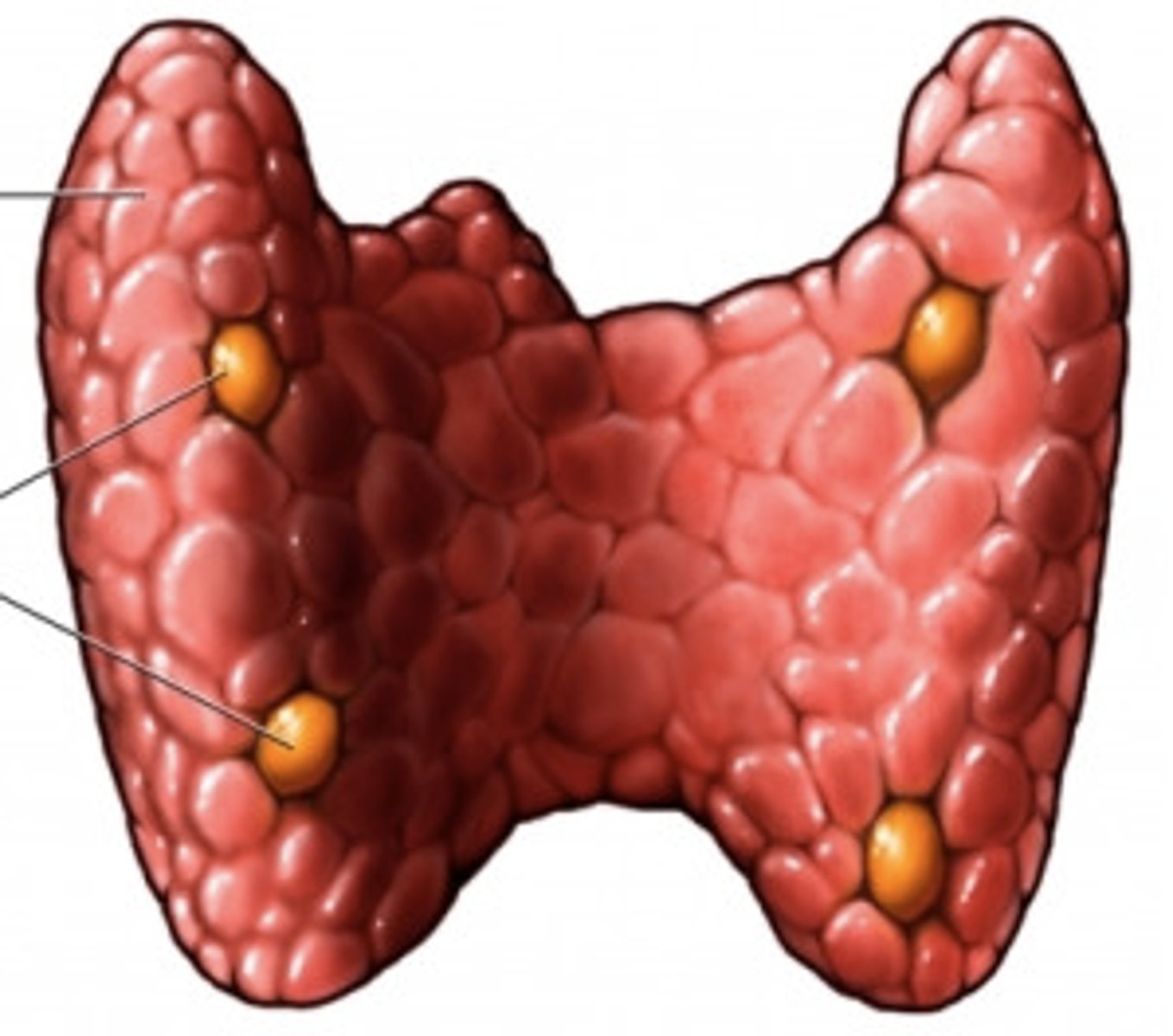
what gland is this?
parathyroid gland
function of Mineralocorticoids?
sodium and potassium balance
target tissues of PTH?
kidneys, intestines, bone
when is aldosterone secreted?
when potassium levels increase OR BP decreases
function of calcitonin
increases osteoblast activity for the rebuilding of bone. It decreases calcium in the blood.
function of aldosterone?
stimulate kidneys to retain sodium and excrete potassium = when sodium and potassium low = MORE aldosterone
function of insulin?
targets the liver, skeletal muscle, and adipose tissue, resulting in glucose uptake into those tissues
stimulates cells to absorb and store or metabolize amino acids and glucose
increased glucose intake + convert glucose -> glycogen
what does hyperglycemia do to insulin secretion?
stimulates it + elevated blood glucose levels
what tissue does insulin target?
most cells (skeletal, fat, liver // Mostly all except nervous)
what hormones stimulates cells to absorb and store or metabolize amino acids and glucose?
estrogen + progesterone
main difference between insulin and glucagon?
insulin = (-) blood sugar levels //takes glucose from blood -> muscles, liver, other cells
glucagon = (+) blood sugar levels // takes GLYCOGEN from liver, skeletal muscle -> blood
what are paracrine chemical messengers?
Chemicals released from one cell that diffuse short distances and influence the activity of another cell type
what are autocrine chemical messengers?
A chemical produced by a cell which influences that cell (same cell type)
function of glucagon?
- break down glycogen
-increase blood sugar levels
- increase gluconeogenesis
explain differences between type 1 AND type 2 diabetes
still needed to make flash cards for this
what is gestational diabetes?
diabetes developed during pregnancy, comes and go with pregnancy, influenced by genetics
ACTUAL TEST QUESTION: when blood sugar levels decrease.........
insulin secretion decreases
glucagon secretion increases