9.1 Transport in the xylem of plants
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
1
New cards
xylem
specialised vascular tissue, composed of many cell types, that brings water to the leaves
2
New cards
transpiration
evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant
3
New cards
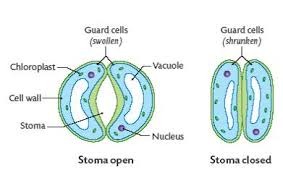
stomata
small openings in the leaf epidermis that allow gas exchange
4
New cards
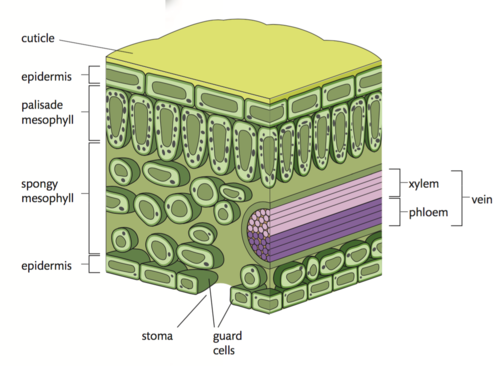
draw a plan diagram to show major structures of a generalised leaf
5
New cards
cuticle
layer protects the plant against
water loss and insect invasion
water loss and insect invasion
6
New cards
epidermis
the outermost layer (if cuticle not present) that protects the plant
7
New cards
vascular tissue
specialized tissue in plants that carries water and nutrients
8
New cards
phloem
specialized vascular tissue that carries the products of photosynthesis to the rest of the plant.
9
New cards
vascular bundles
veins that house both xylem and phloem vessels
10
New cards
palisade mesophyll
a densely packed region of cylindrical cells that occur in the upper portion of the leaf which contain large numbers of chloroplasts to carry out photosynthesis
11
New cards
spongy mesophyll
loosely packed cells with few chloroplasts and many air spaces which provide gas exchange surfaces
12
New cards
guard cells
specialised cells in epidermis that control the opening and closing of the stomata
13
New cards
transpiration stream
movement of water through a plant from the roots to the leaves as a result of the loss of water by evaporation from the surface of the leaves
14
New cards
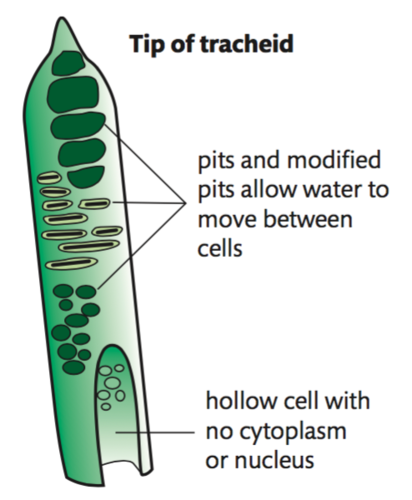
tracheids
components of xylem tissue;
dead cells that taper at the ends and connect to one another to form a continuous column
dead cells that taper at the ends and connect to one another to form a continuous column
15
New cards
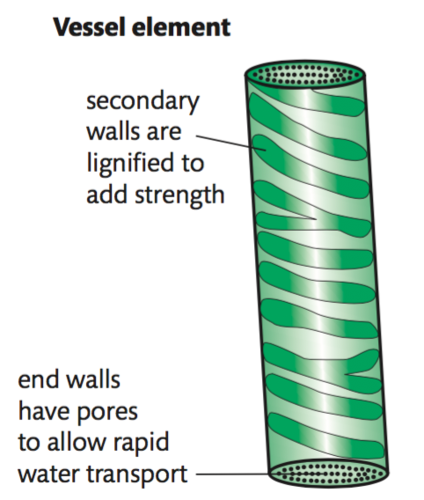
vessel elements
components of xylem tissue;
dead cells with thick, lignified walls. They are attached end to end to form continuous columns and have perforations, allowing water to move freely up the plant
dead cells with thick, lignified walls. They are attached end to end to form continuous columns and have perforations, allowing water to move freely up the plant
16
New cards
lignin
a complex organic compound that greatly strengthens
the cell walls of vascular plants (It also waterproofs plant parts and adds protection against pathogens)
the cell walls of vascular plants (It also waterproofs plant parts and adds protection against pathogens)
17
New cards
turgor pressure
pressure inside of a cell as a cell pushes itself against the cell wall
18
New cards
abscisic acid
A plant hormone that brings stomatal closing, among other effects
19
New cards
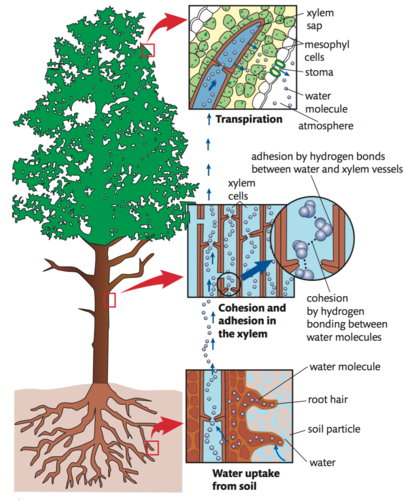
cohesion-tension theory
water is pulled up the xylem vessels by the cohesive force between the water molecules and the adhesion of the water molecules to the rigid vessel walls
20
New cards
root hairs
specialised epidermal structures that increase the surface area over which water and mineral ions can be absorbed
21
New cards
root cap
protects the apical meristem during primary growth of the root through the soil
22
New cards
apical meristem
group of undifferentiated cells that divide to produce increased length of stems and roots
23
New cards
lateral meristem
undifferentiated cells that occur in stem tissue and allow for growth in width.
24
New cards
fungal hyphae
fungal filaments that absorb minerals from the soil and exchange with sugars from the plant (mutualism)
25
New cards
mass flow
some minerals dissolved in water move into the roots as water moves into the outer root cells via osmosis
26
New cards
proton pump
used to transport mineral ions and solutes such as potassium ions, nitrogen-based ions, and even simple sugars
27
New cards
xerophytes
plants adapted to arid climates
28
New cards
Halophytes
plants adapted to grow in water with high levels of salinity
29
New cards
CAM plants
plants close their stomata during the day, collect CO2 at night, and store the CO2 in the form of acids until it is needed during the day for photosynthesis
30
New cards
C4 plants
a plant in which the Calvin cycle is preceded by reactions that incorporate CO2 into a four-carbon compound, the end product of which supplies CO2 for the Calvin cycle.
31
New cards
potometer
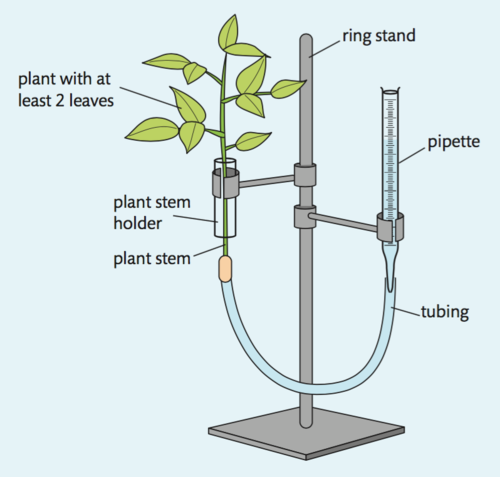
used to measure transpiration rates