Theory V - TEST #1
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
what 2 ions needed for nerve conduction
potassium +
sodium +
the nerve is ? in resting state
polarized
resting state is also called
resting potential
resting state occurs when there's a balance between
positive sodium ion on OUTSIDE
potassium ions on INSIDE
during depolarization the nerve membrane becomes
more permeable to sodium ion
inside of nerve is now +
after depolarization, the permeability of membrane to sodium
decreases as sodium pump actively transports sodium OUT of nerve cell
potassium diffuse and pumped INSIDE of cell
rapid sequence of changes is called
action potential
stimulus is
pain
when the resting potential of nerve membrane is disrupted by stimulus what occurs
depolarization
where is the impulse transmitted when depolarization occurs
along the nerve fiber by ion changes during depolarization
ion changes produce
local currents that flow along from depolarization of nerve to adjacent resting area
commonly accepted primary action of LA agents
reducing nerve membrane permeability to sodium ions
action potential never occurs when
sodium ions remain on outside of the nerve
impulse that arrives at blocked nerve is
unable to transmit to brain
not able to interpreted as pain/discomfort
LA agents
esters
amides
esters are
topical anesthetics
(benzocaine)
esters completely/incompletely in ?
completely hydrolyzed in BLOOD
esters excreted in
urine in SMALL amounts
amides are
biotransformation in liver
liver function of patient influences rate of biotransformation
amides are excreted in
urine
LA exertion in
kidneys (primary)
T/F : blood decreases as LA is injected
F
increased blood flow to injection site as LA agents dilate blood vessels
is there increased bleeding at the injection site?
YES due to increased blood flow to area
vasodilation is
relaxation of blood vessel wall
vasodilation results in
increased blood flow to injection site
What are vasoconstrictors?
pharmacologic agents that cause blood vessels to constrict
vasoconstrictors are identical or similar to ??
adrenalin (produced during sympathetic NS stimulation)
vasoconstrictors are referred to as
sympathomimetic
OR
adrenergic agents
does vasoconstrictors decrease or increase blood into injection site
DECREASE
does vasoconstrictors slow or fasten the LA absorption into blood stream
SLOW
do vasoconstrictors increase or decrease duration of LA action
INCREASES duration
do vasoconstrictors increase or decrease LA effectiveness
INCREASE
vasoconstrictors leads to
lower LA amounts in blood
epinephrine (vasoconstrictor) overdose can result from
CNS stimulation
vasoconstrictors concentrations often expressed as
RATIO
1 : 100,000
epinephrine available as
synthetic
epinephrine obtained from
adrenal medulla of ANIMALS
levonordefin (vasoconstrictor) concentration
greater than 1 : 20,000
vasoconstrictors contraindications
unstable angina
recent MI
recent coronary artery bypass
untreated / uncontrolled hypertension
untreated / uncontrolled congestive HF
determining appropriate LA to use
duration of action / half life
length of time LA is needed
need for pain control after
client health status
current medications
LA allergy
MRD is
max recommended dose
must consider ?? regarding MRDs
age
physical status
weight
pharmacokinetics is
study of action of drugs within body
pharmacokinetics process
absorption
distribution
metabolism
excretion
LA syringes types
reusable
disposable
problems a LA syringe can have
bent harpoon
disengagement of harpoon from rubber stopper
aspirating diffuculty
parts of reusable LA syringe
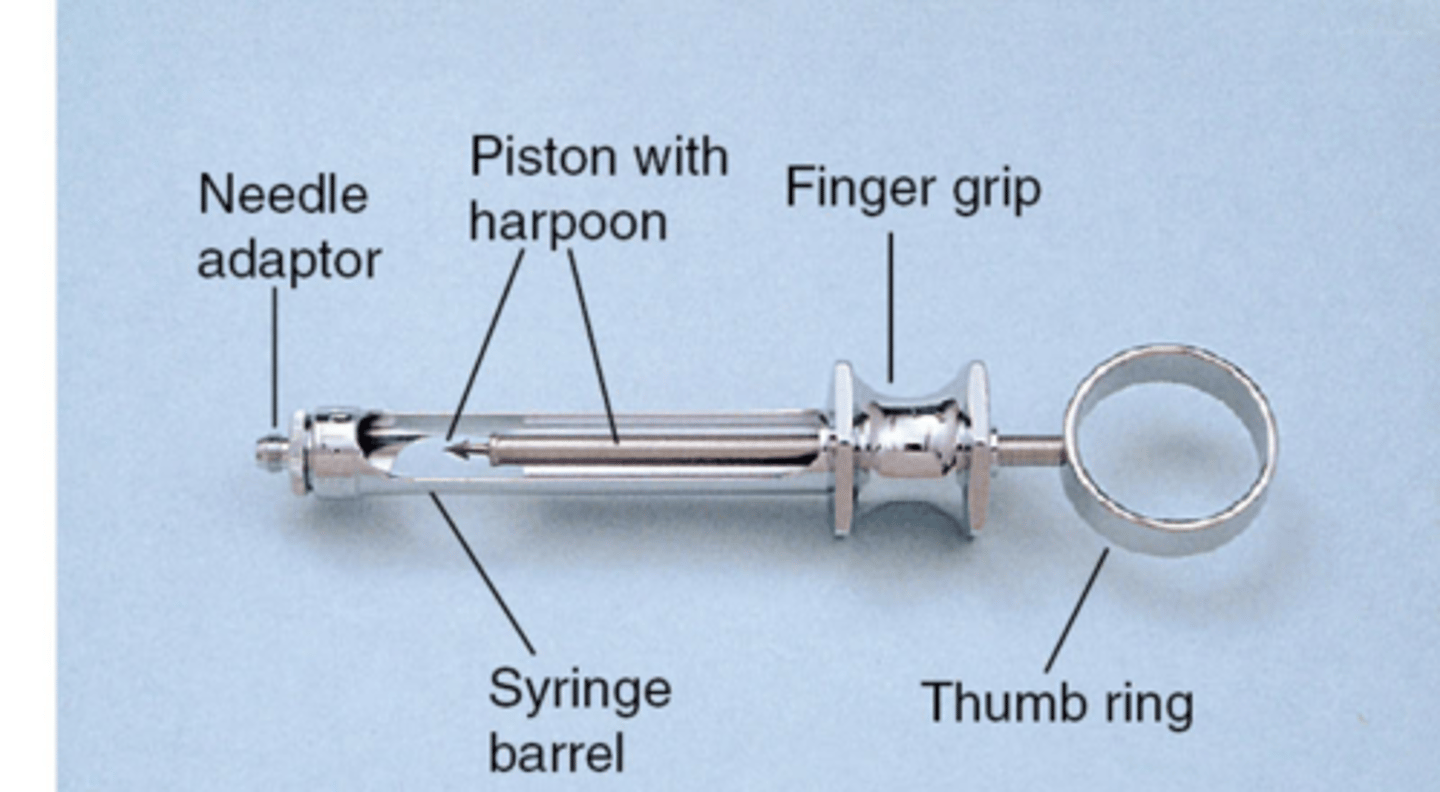
problems with the LA needle
pain on insertion
pain on withdrawal
needle stick exposure of clinician
needle break
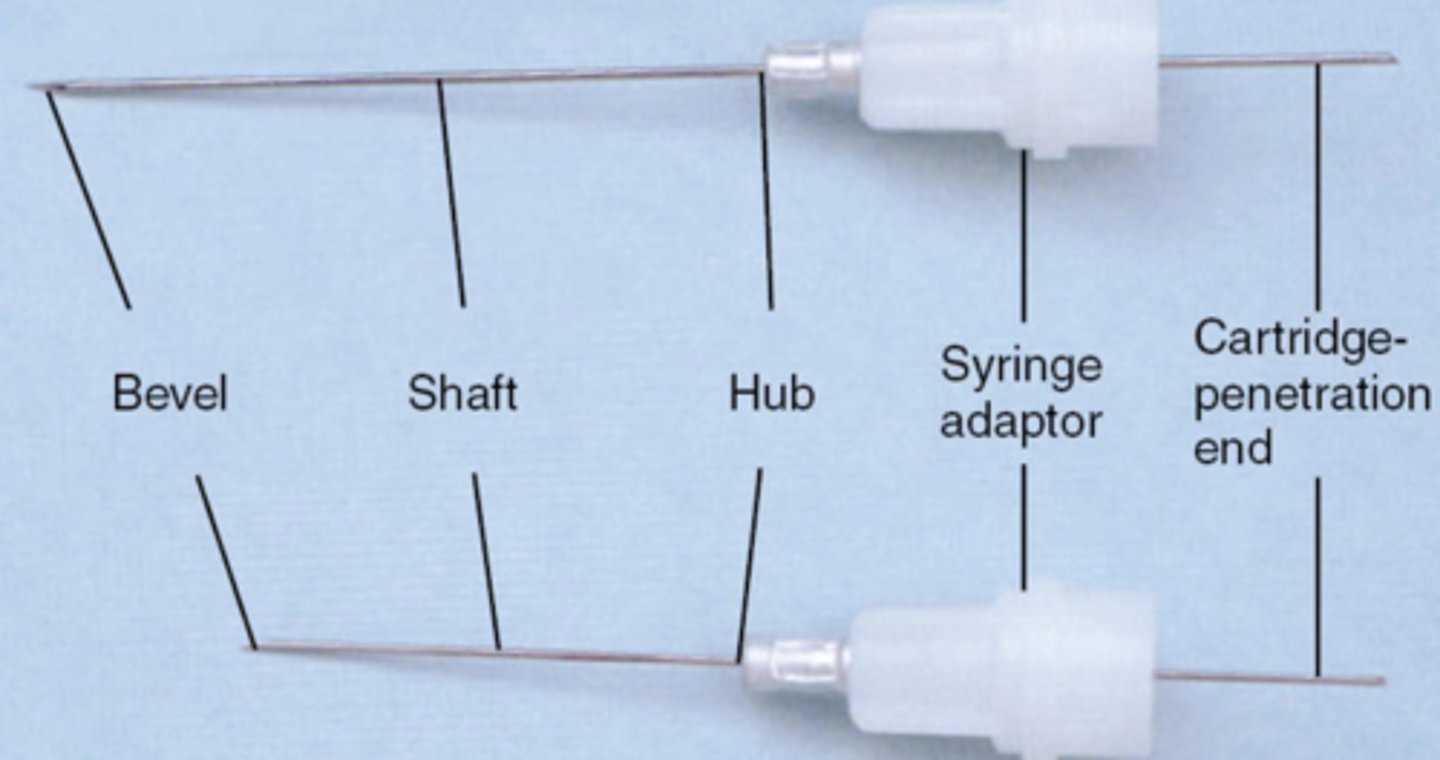
bevel of LA needle is
the very tip
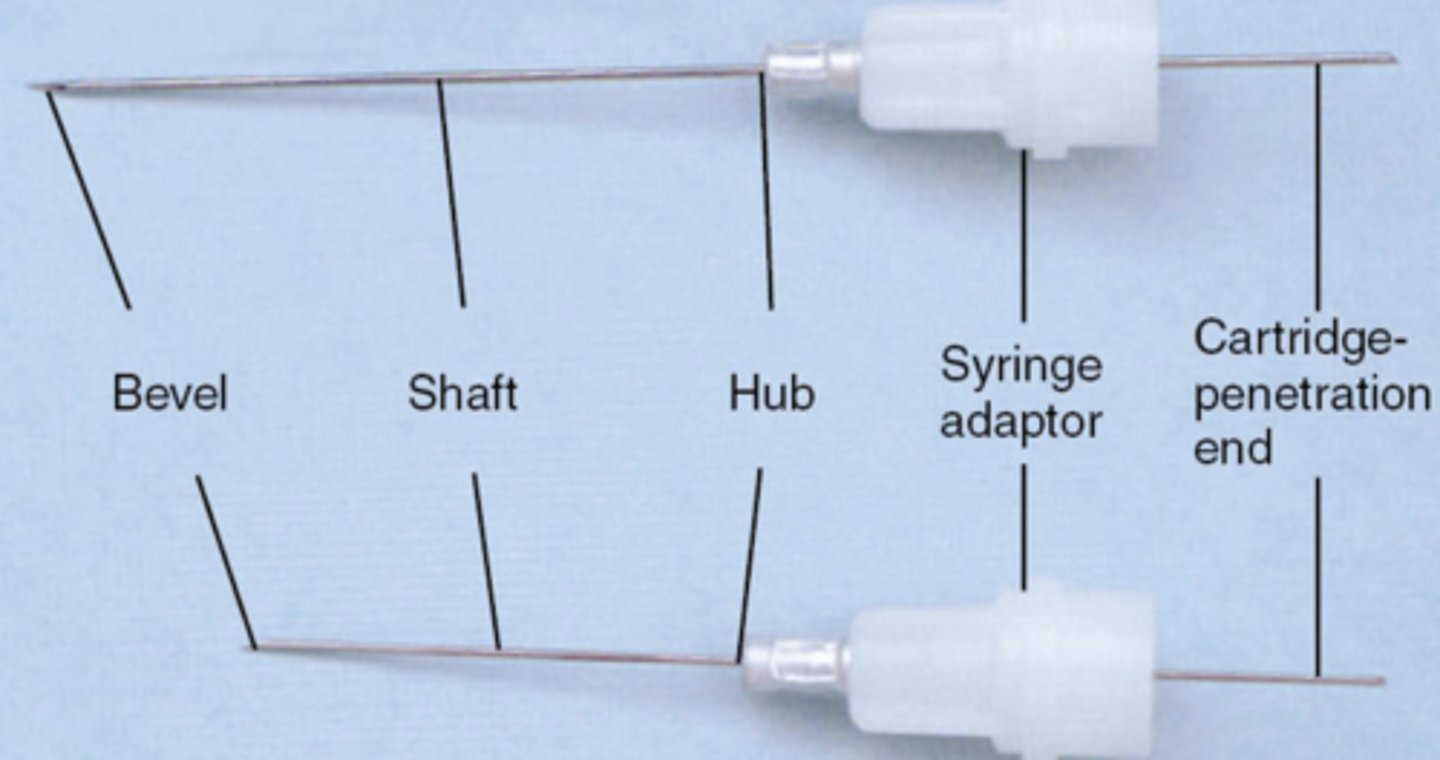
shaft of LA needle is
the middle part
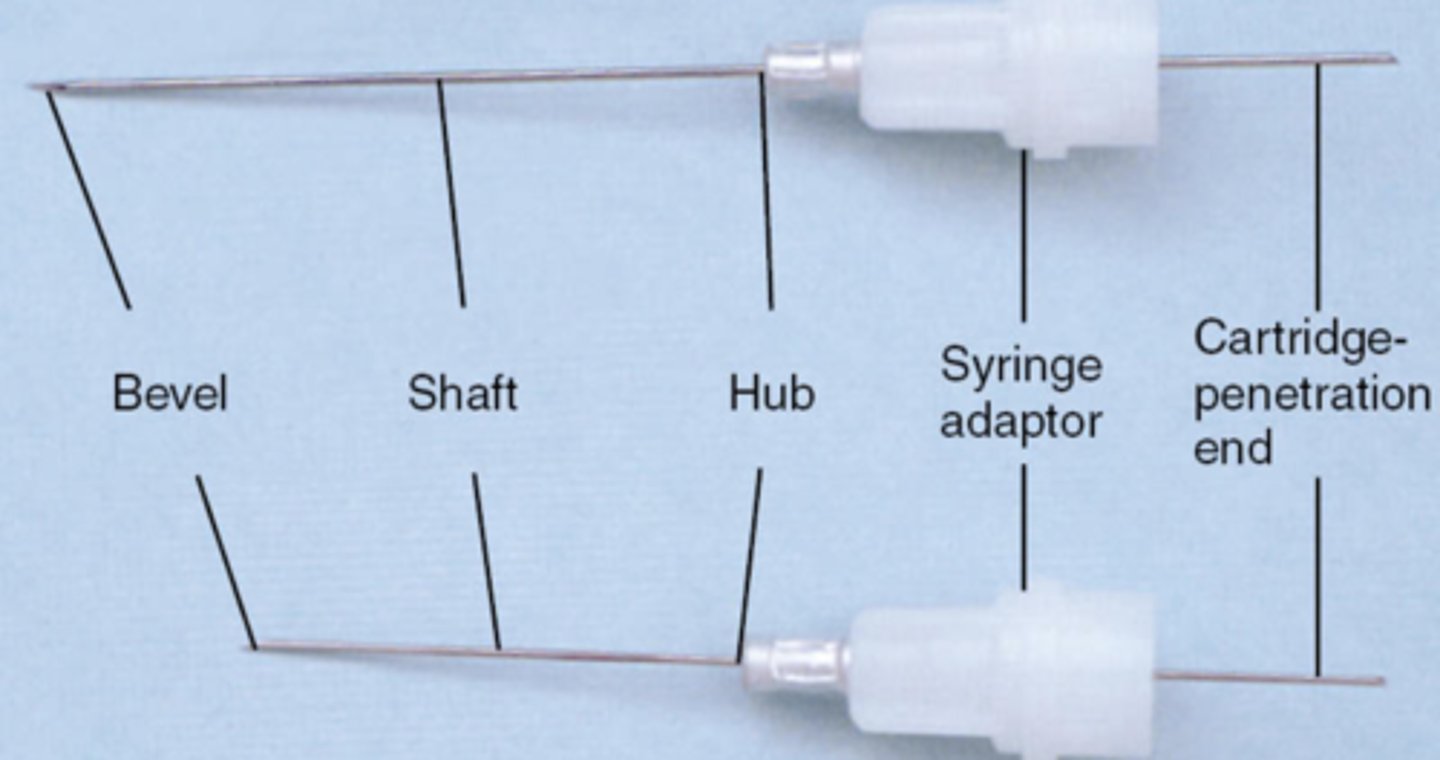
hub of LA needle is
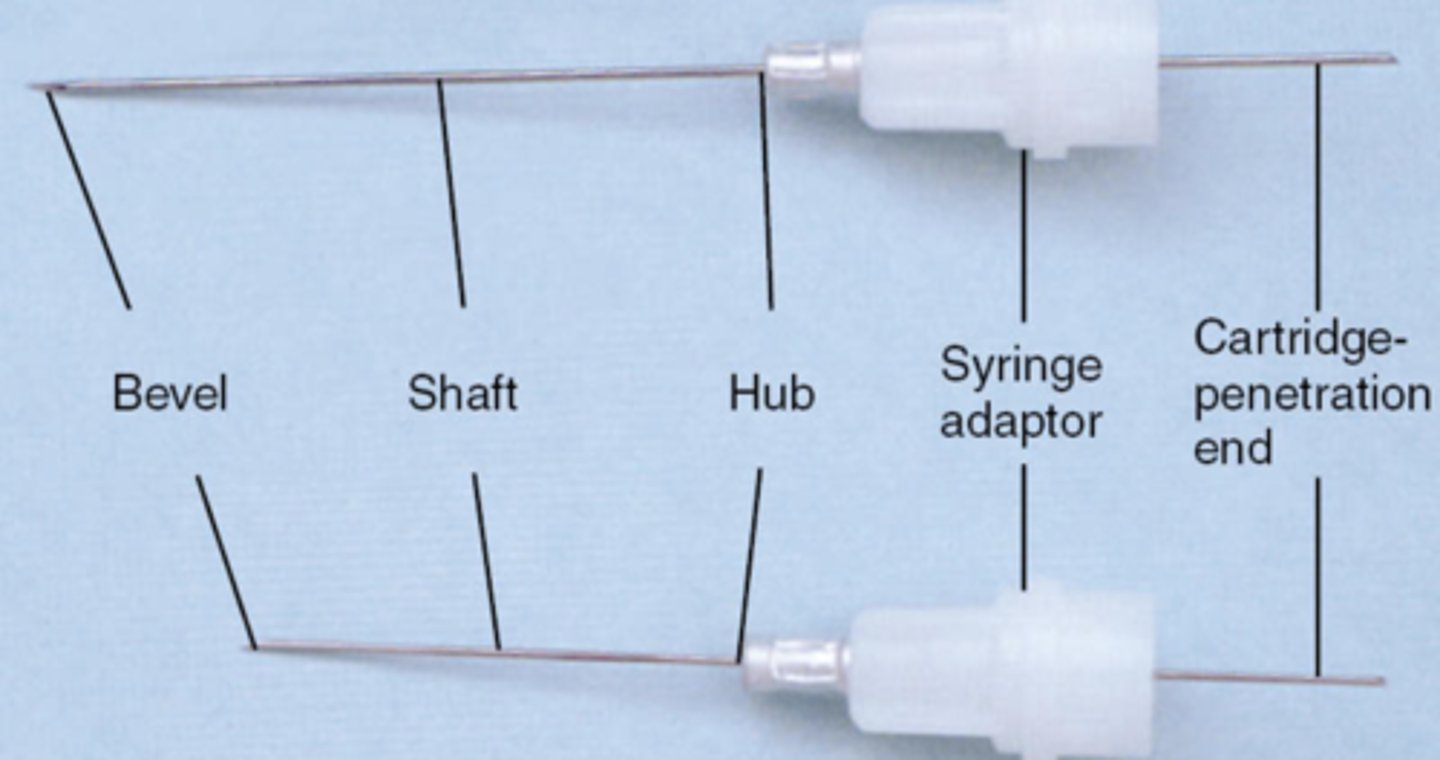
syringe adaptor is
attach the needle to the syringe
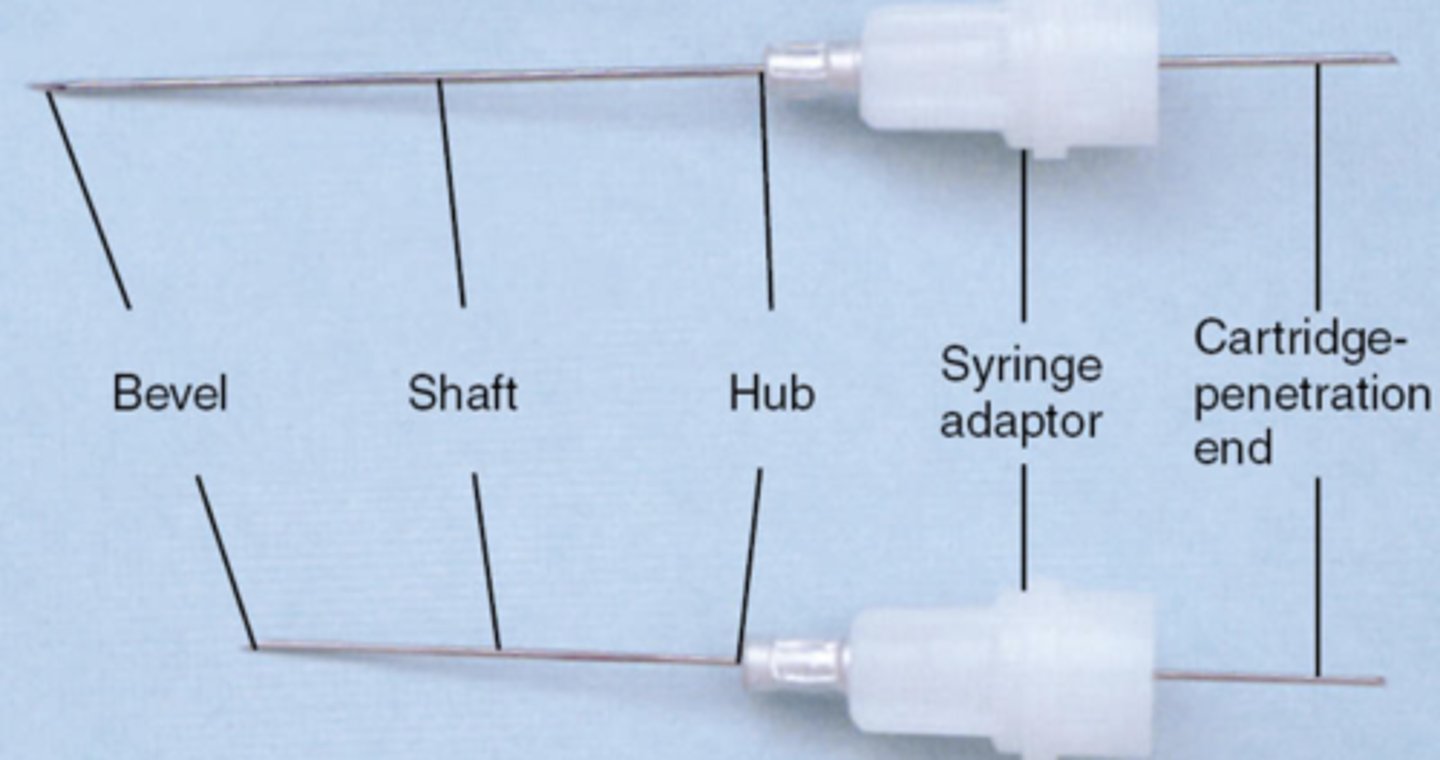
cartridge penetration end is
where the cartridge is penetrated
gauge is
diameter of lumen of needle
most common gauges
25
27
30
larger gauge advantages
ridged
stable
less deflection
less breakage
T/F the lower the gauge number is the smaller the diameter
FALSE
the HIGHER the gauge number is the smaller the diameter is
cartridge problems
bubble in cart
extruded stopper
corroded cap
rust on aluminum cap
leakage
burning
broken
armamentarium for LA procedure
syringes
needle
gauge
cartridge
additional armamentarium for LA procedure
gauze
topical anesthetic
applicator sticks
haemostat / cotton pliers
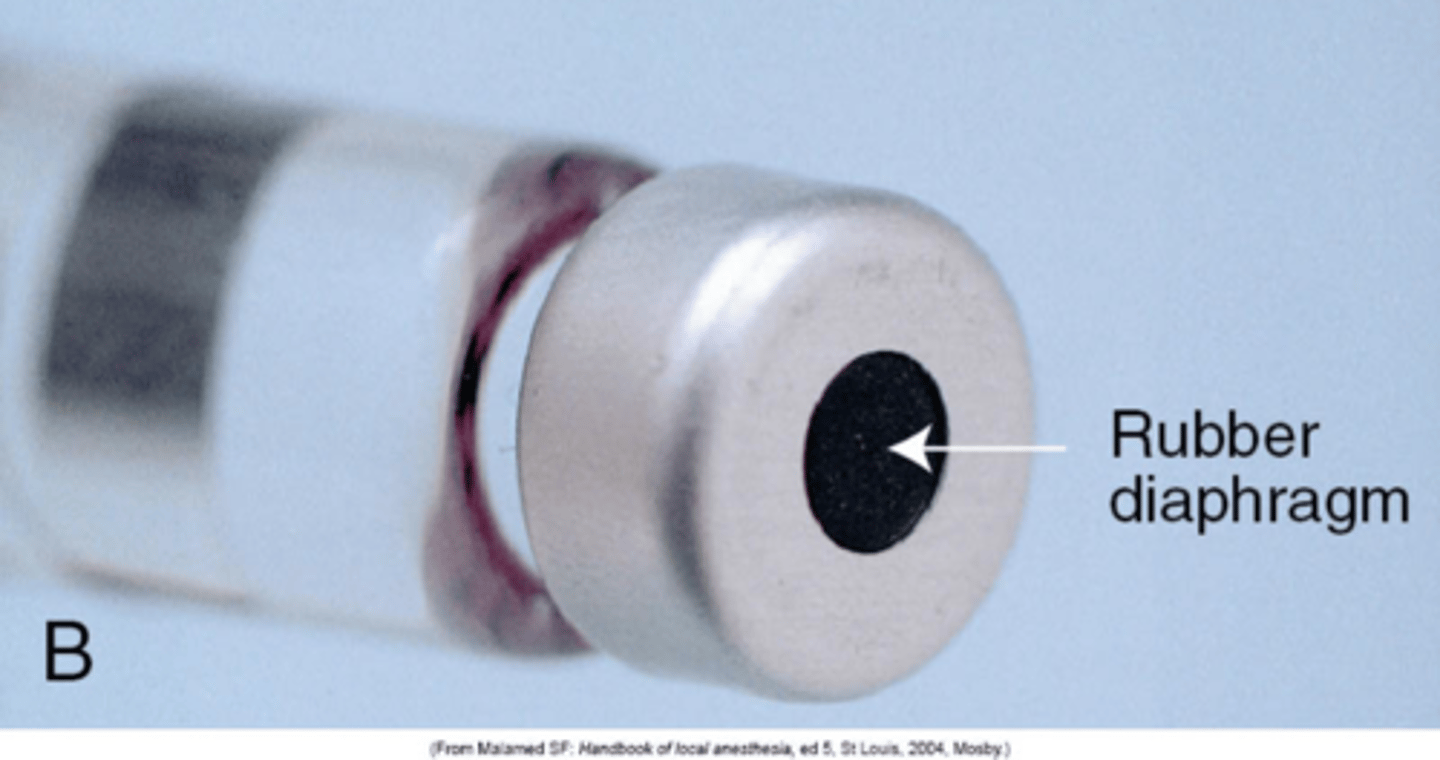
parts of cartridge
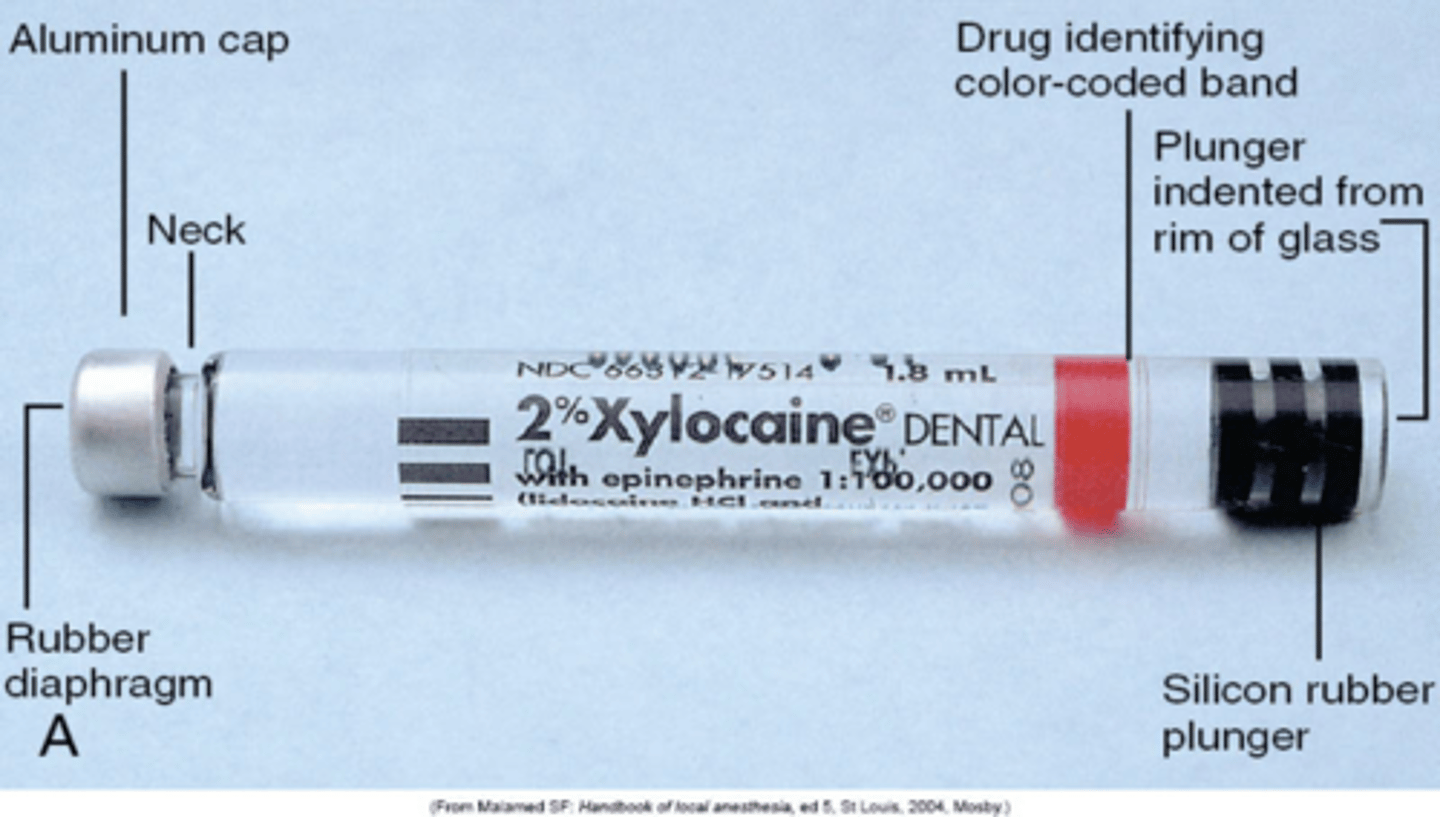
rubber diaphragm is
bottom of cart
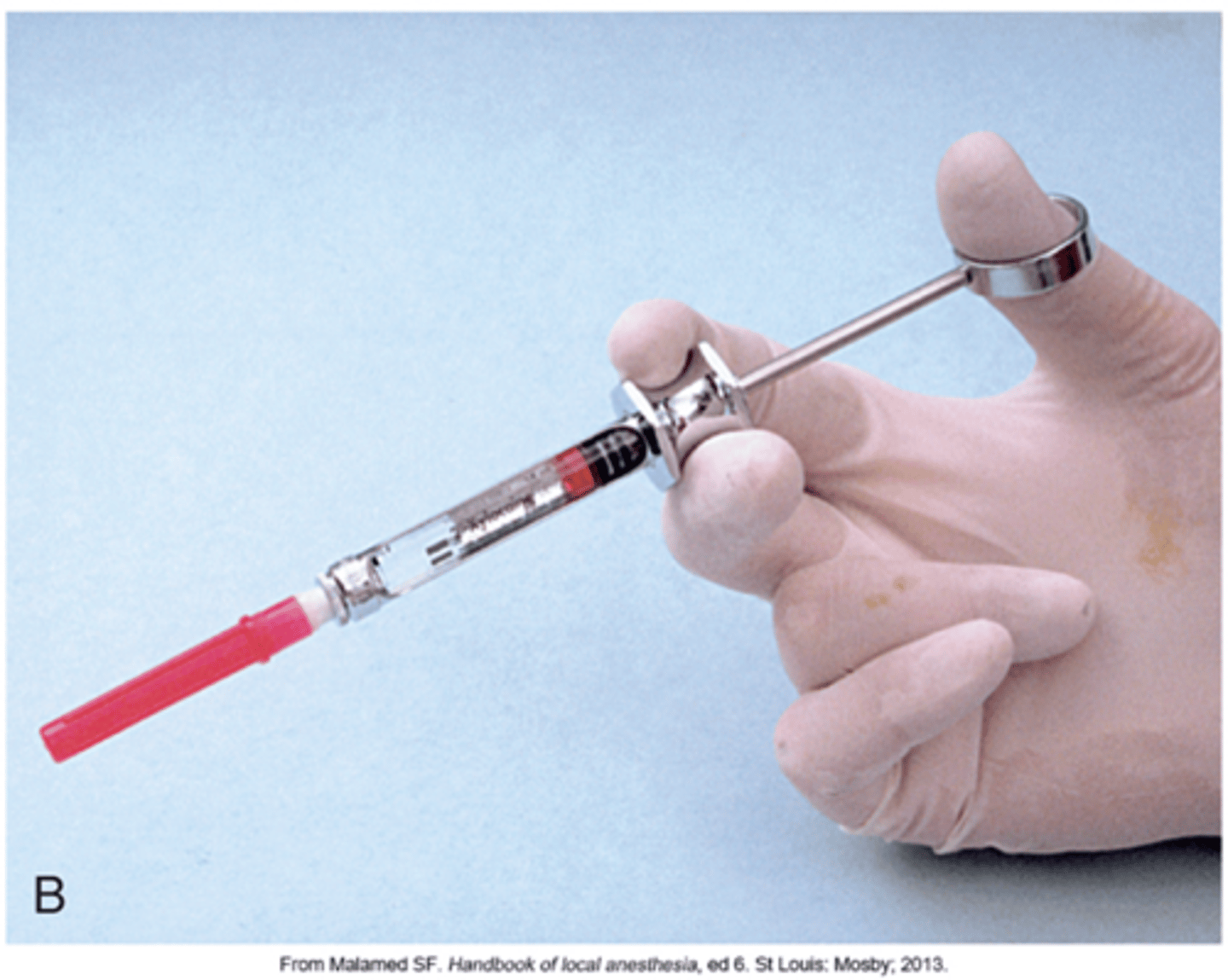
what is the best clinician ergonomics for LA injection
PALM UP
= better control
topical anesthesia provides
temporary numbing on nerve endings on oral mucosa
topical anesthesia supplied as
ointments
liquids
sprays
patches
supraperiosteal are also called
field block
supraperiosteal incorrectly referred to as
infiltration
supraperiosteal injections involve
depositing anaesthetic near APEX OF SINGLE TOOTH
supraperiosteal injection are
not as successful
supraperiosteal injections are more effective on
mand anteror teeth
supraperiosteal injections commonly done on
max
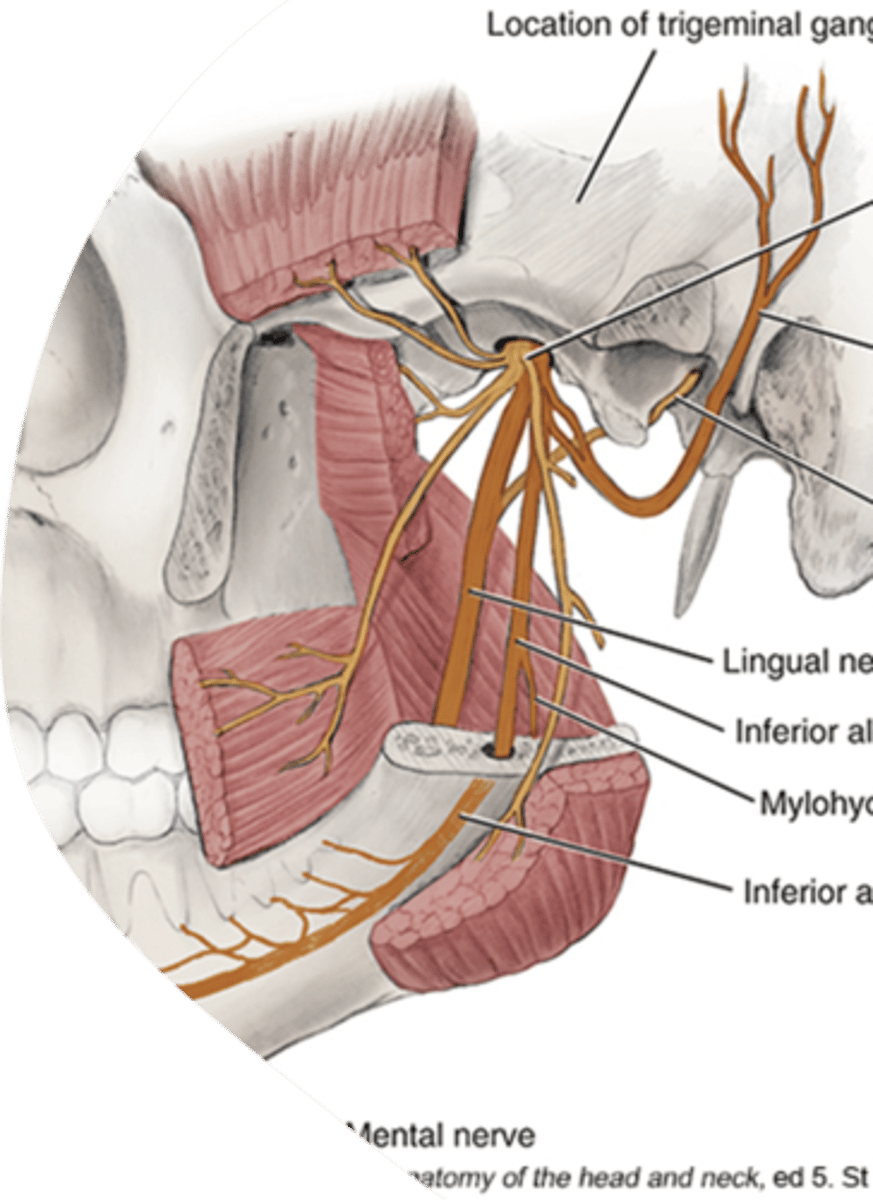
inferior alveolar nerve block abbreviation
IA
IA needle gauge + length
25-27 gauge
IA operator position
8:00-9:00
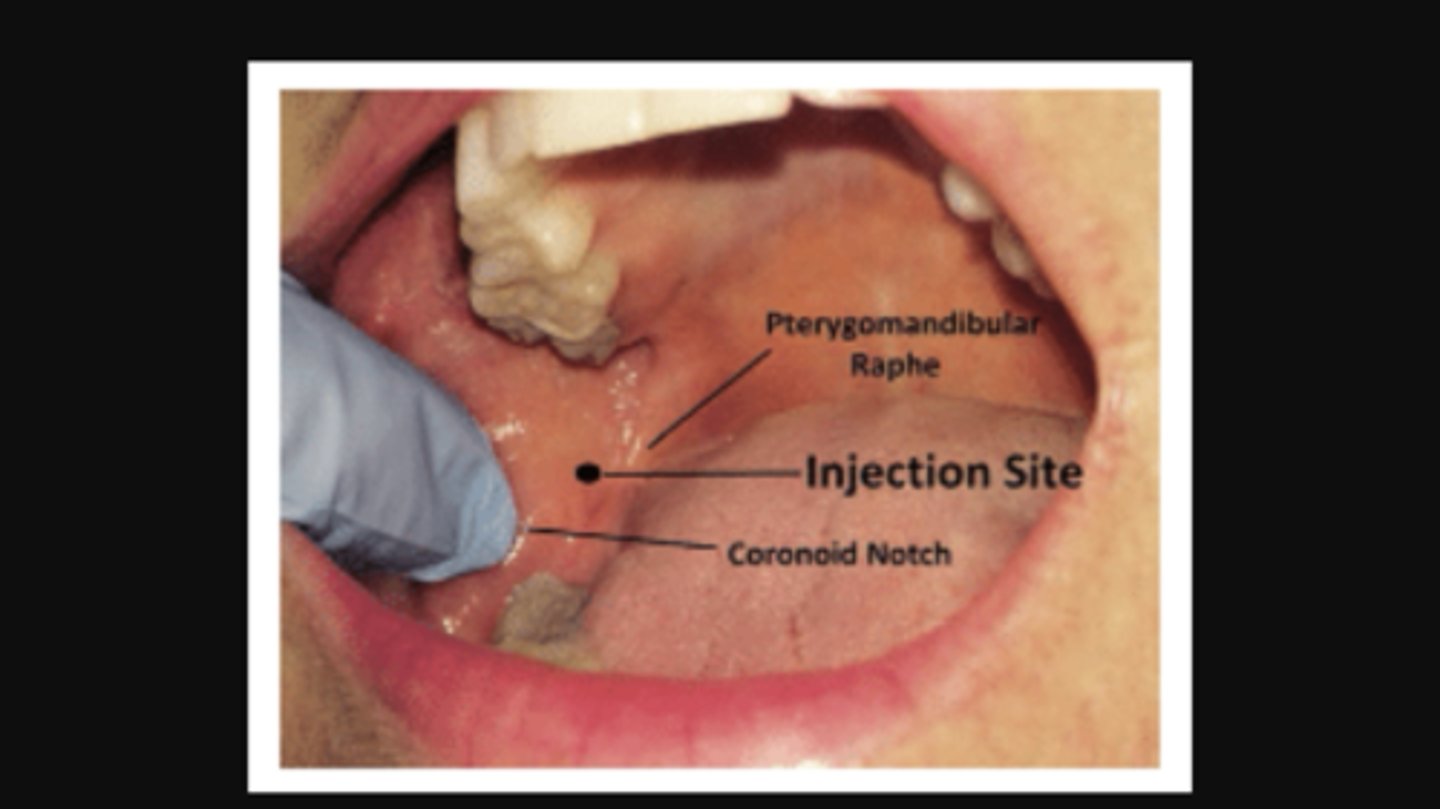
IA penetration site
middle of pterygonmandibular triangle
6-10 mm above mand occlusal plane
IA landmarks
anterior board of ramus
coronoid notch
mand foramen
pterygomandibular rapie
IA penetration depth
20-25 mm
two thirds - 3 quarters of needle
IA amount of anesthetic deposited
0.9 - 1.8 ml
1/2 - 1 cartlidge
IA length of time to deposit the LA
60 - 90 seconds
IA anesthesia recommended on
mand teeth
facial soft tissue anterior to mand 1st molar
T/F : IA is an uncommon injection
FALSE
common
IA failure rate
20-25
due to technique
IA anesthetizes nerves ;
inferior alveolair
incisive
mental
lingual
IA complications
LINGUAL SHOCK
lingual shock symptom
momentary
unavoidable
T/F : depositing small amounts of solution will prevent lingual shock
FALSE
target area for IA
above mand foramen
pytergomandibular space mimics
tear drop
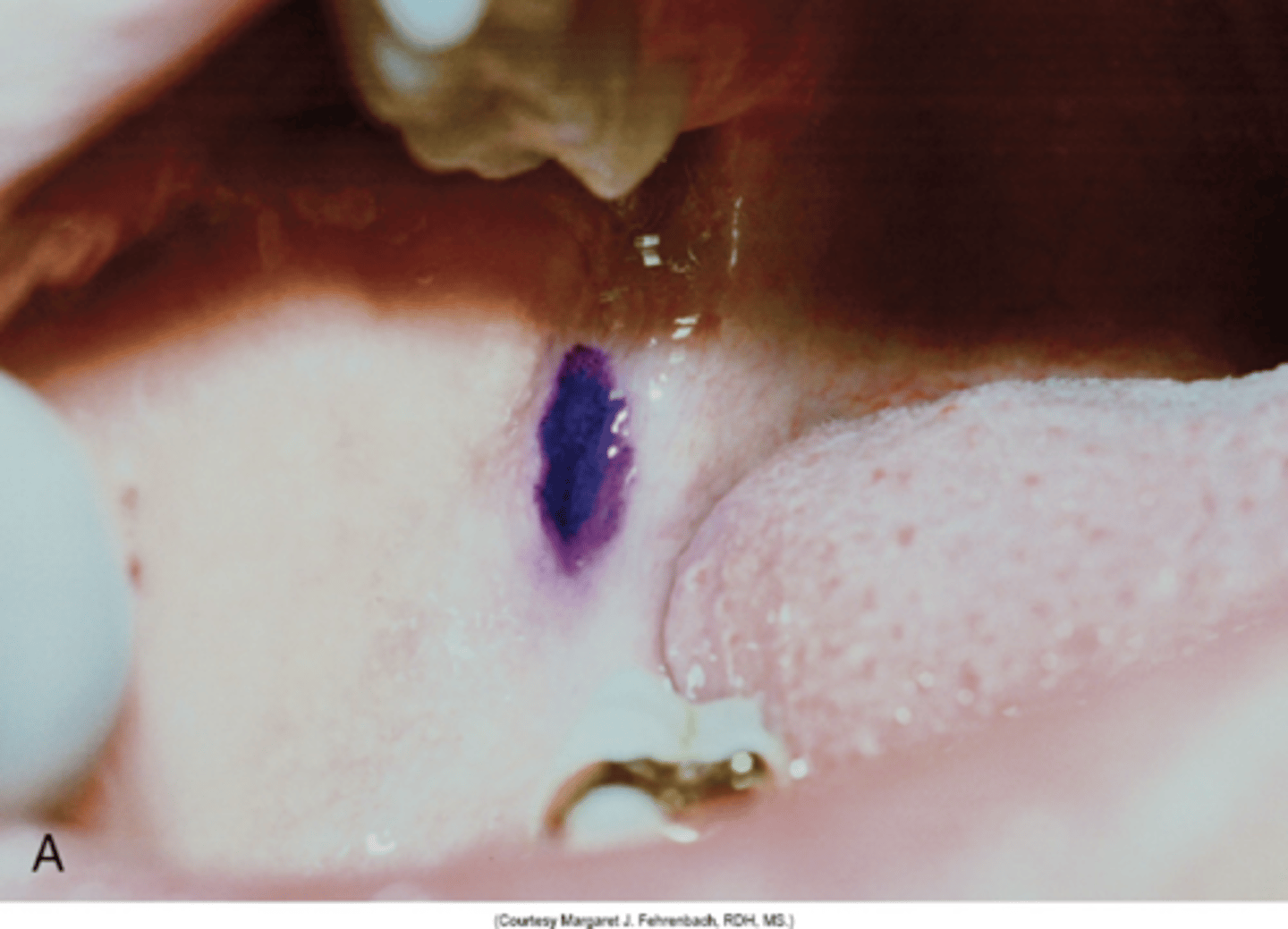
how to locate pytergomandibular space
place thumbs / index finger on greatest depression of anterior border of ramus
pterygomandibular located
6-10 mm above occlusal plane
T/F bilateral IA should be done
FALSE
should be avoided (it causes anesthesia of entire tongue)
IA trouble shooting
no bone contact (tip too posterior)
buccal nerve block abbreviation
B
B needle gauge + length
25-27 gauge
B injection operator position
8:00-9:00
B injection penetration site
buccal vestibule
distal + buccal to most distal molar at height of occlusal plane
B injection landmarks
mandibular molars
buccal vestibule
mucobuccal fold
B injection penetration depth
1-4 mm
often only BEVEL is inserted
B injection amount of anesthetic deposited is
0.3 - 0.45
1/8th - 1/4th of cart
B injection length of time to deposit
10-20 sec