17. Types of Reactions in Organic Chemistry
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
addition reaction
a chemical reaction in which two or more molecules react together to form a single molecule
addition reaction examples
ethene + hydrogen -> ethane, ethene + bromine -> 1,2-dibromoethane, ethene + chlorine -> 1,2-dichloroethane, ethene + hydrogen chloride -> chloroethane, ethene + water -> ethanol
addition reactions occur with…
alkenes
addition reaction change in geometry
planar -> tetrahedral
addition reaction change in saturation
unsaturated -> saturated
ethene + hydrogen -> ethane equation
C2H4 + H2 --[Ni]--> C2H6
what reagent and metal cataylst are used to synthesise ethane from ethene?
H2 and Ni
does benzene undergo addition reactions? why or why not?
benzene does not undergo addition reactions due to the stability of its delocalised electrons
mechanism of a reaction
the detailed step-by-step description of how the overall reaction occurs
ionic addition mechanism steps
polarisation, heterolytic fission, carbonium ion formation, ionic addition
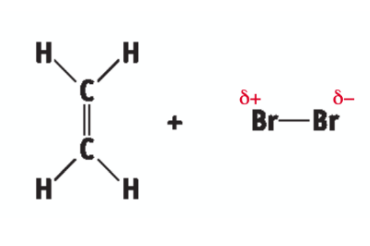
ionic addition: ethene and bromine - polarisation
Br2 molecule becomes polarised
ionic addition: ethene and bromine - heterolytic fission
two electrons end up on one atom to form two charged atoms

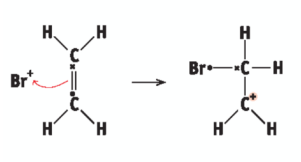
ionic addition: ethene and bromine - carbonium ion formation
Br+ ion attacks C=C bond for an electron and bonds with one C atom, the other C atom becomes + charged
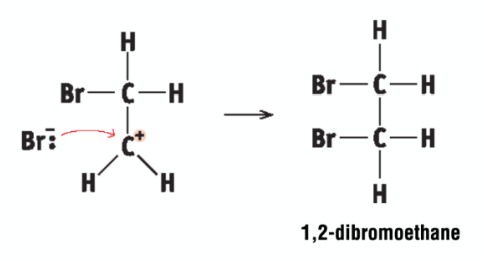
ionic addition: ethene and bromine - ionic addition
carbonium ion attacked by Br- ion to form 1,2-dibromoethane
what is 1,2-dibromoethane used for?
controlling moths in beehives
what is the supporting evidence for the ionic addition mechanism?
the products 1,2-dibromoethane, 1-bromo,2-chloroethane, and 2-bromoethanol when ethene reacts with bromine in water that contains sodium chloride proves that the intermediate of the reaction is a carbonium ion
ionic addition: ethene and chlorine - polarisation
Cl2 molecule becomes polarised
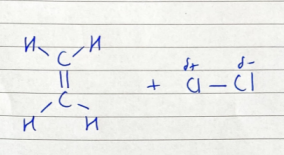
ionic addition: ethene and chlorine - heterolytic fission
two electrons end up on one atom to form two charged atoms

ionic addition: ethene and chlorine - carbonium ion formation
Cl+ ion attacks C=C bond for an electron and bonds with one C atom, the other C atom becomes + charged
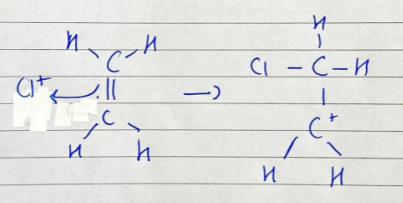
ionic addition: ethene and chlorine - ionic addition
carbonium ion attacked by Cl- to form 1,2-dichloroethane

ionic addition: ethene and hydrogen chloride - polarisation
polar HCl molecule becomes even more polarised

ionic addition: ethene and hydrogen chloride - heterolytic fission
two electrons end up on one atom and two charged atoms are formed
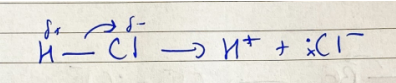
ionic addition: ethene and hydrogen chloride - carbonium ion formation
H+ ion attacks C=C bond for an electron and bonds with one C atom, the other C atom becomes + charged

ionic addition: ethene and hydrogen chloride - ionic addition
carbonium ion attacked by Cl- ion to form chloroethane
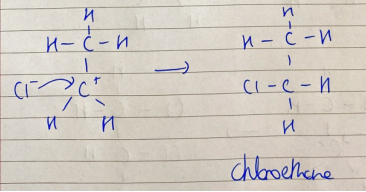
polymer
a large molecule made up of many identical repeating units called monomers
polymerisation is a type of…
addition reaction
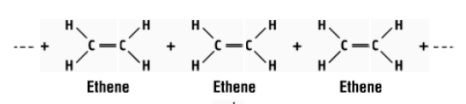
what reaction is this and what does it form?
polymerisation of ethene to form polythene
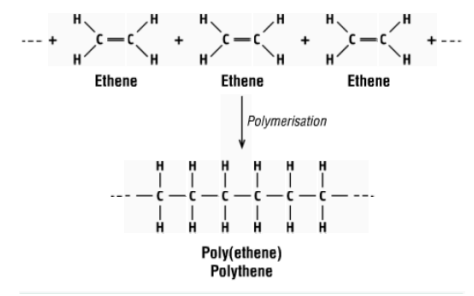
what is the monomer and polymer in this reaction?
monomer - ethene, polymer - polythene
polyethene uses
plastic bags, lunchboxes
what reaction is this and what does it form?
polymerisation of propene to form polypropene
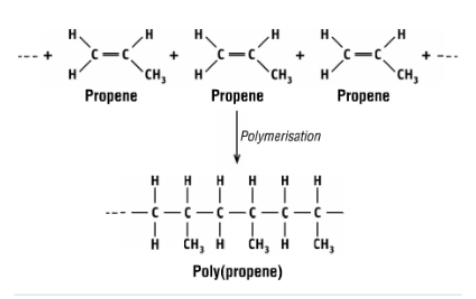
what is the monomer and polymer in this reaction?
monomer - propene, polymer - polypropene
polypropene uses
plastic jugs, luggage
examples of synthetic products of the petrochemical industry
cosmetics, plastics, detergents, solvents, paints
when drawing the repeating unit of a polymer…
do not draw end atoms, but leave the end bonds empty with dots to represent that it stretches on
elimination reaction
a chemical reaction in which a small molecule is removed from a larger molecule to leave a double bond in the larger molecule
dehydration reaction
elimination reaction in which water is removed
elimination reaction example
dehydrating ethanol to produce ethene
substitution reaction
a chemical reaction in which an atom or group of atoms in a molecule is replaced by another atom or group of atoms
substitution reaction example
halogenation of alkanes in the presence of UV light, methane + chlorine → chloromethane + hydrogen chloride
free radical
any atom or group of atoms with an unpaired electron
monochlorination of methane - initiation
Cl2 molecule broken down into two Cl free radicals in the presence of UV (homolytic fission)
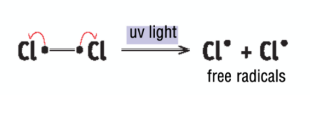
monochlorination of methane - propagation
a Cl atom attacks a methane molecule to form hydrogen chloride and a methyl free radical
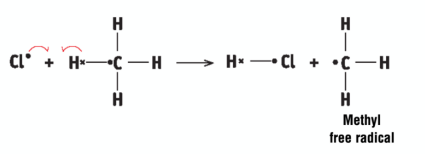
monochlorination of methane - propagation (part 2 electric boogaloo)
a methyl free radical attacks a Cl molecule to form chloromethane and a Cl atom, a chain reaction occurs
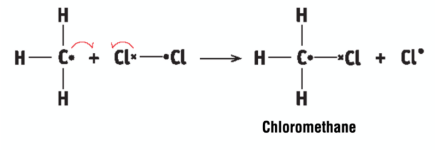
chain reaction
a reaction that continues on and on because a product from one step of the reaction is a reactant for another step of the reaction
monochlorination of methane - termination
Cl2, chloromethane, and ethane are formed to stop the chain reaction

what is the supporting evidence for the free radical substitution reaction?
the reaction will happen even if UV light is only used for a very short period since it causes a chain reaction, trace quantities of ethane/butane are found which could only be formed from two free radicals, these reactions are sped up by the addition of a known souce of free radicals (tetramethyl lead for methane, tetraethyl lead for ethane)
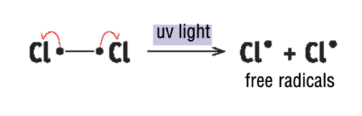
monochlorination of ethane - initiation
a Cl2 molecule is broken down into two Cl free radicals in the presence of UV light
chlorination of ethane - propagation
a Cl atom attacks an ethane molecule to form hydrogen chloride and an ethyl free radical
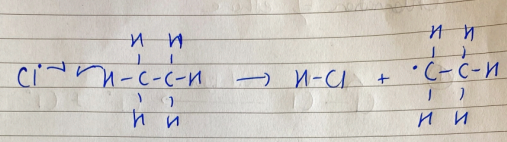
chlorination of ethane - propagation (part 2 electric boogaloo)
an ethyl free radical attacks a Cl molecule to form chloroethane and a Cl atom, a chain reaction occurs
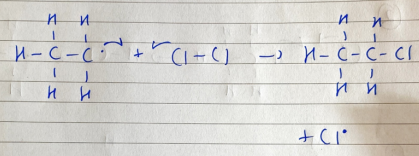
chlorination of ethane - termination
Cl2, chloroethane, and butane are formed to stop the chain reaction
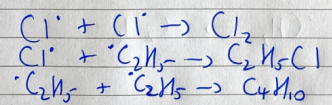
fully halogenated alkanes are used in…
fire extinguishers
why are fully halogenated alkanes often used in fire extinguishers?
they are not very combustible
why is esterification a substitution reaction?
the OH of the carboxylic acid is replaced by the O and alkyl group of the alcohol
what is the reverse of esterification?
hydrolysis
hydrolysis
the chemical decomposition of a substance by water
base hydrolysis of esters is called
saponification
redox reaction
a chemical reaction in which there is a transfer of electrons from one chemical species to another
primary alcohols are oxidised to…
aldehydes, then to carboxylic acids
what reagent is used to synthesise an aldehyde/carboxylic acid from a primary alcohol?
acidified KMnO4
secondary alcohols are oxidised to…
ketones
ketones are…
difficult to oxidise
aldehydes and ketones can be reduced to…
alcohols
name the reagent and transition metal catalyst used to reduce aldehydes/ketones to alcohols
hydrogen and nickel (H2/Ni)
carboxylic acids can be reduced back to…
aldehydes and alcohols
what reagent and metal catalyst is used to reduce carboxylic acids back to aldehydes and alcohols?
hydrogen and nickel catalyst (H2/Ni)
write a balanced equation that shows that alcohol can act as an acid
C2H5OH + Na —> C2H5O-Na+ + ½H2
why can alcohols act as an acid?
the polarity of the OH bond makes it easier for the H atom to break off as an H+ ion
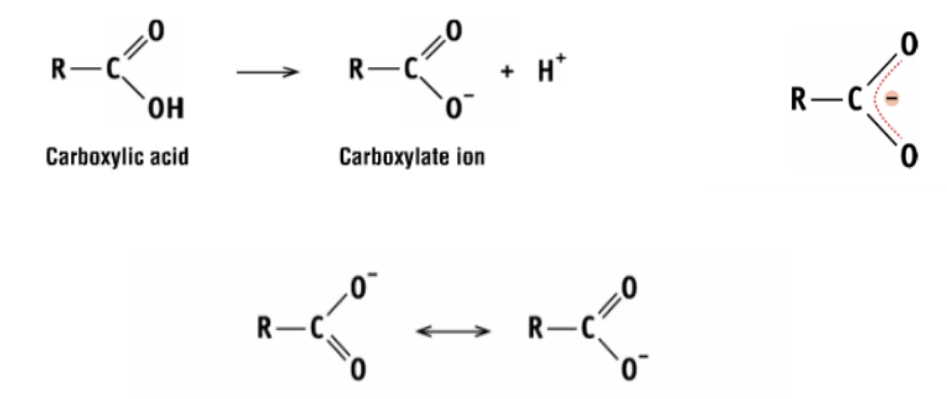
why can carboxylic acids act as an acid?
the inductive effect and the stability of the carboxylate ion
draw a diagram to show the acidic nature of carboxylic acids and explain
the two carbon-oxygen bonds are equal length. the carboxylate ion is so stable it makes the carboxylic acid want to lose its proton
organic synthesis
the process of making organic compounds from simpler starting materials
useful products of organic synthesis
aspirin, penicillin, PVC
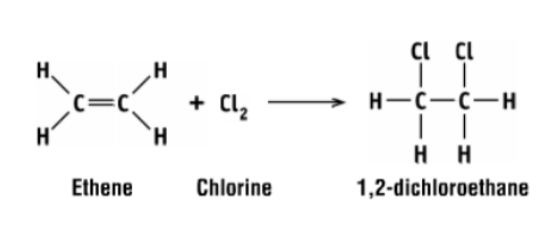
synthesis of PVC from ethene step 1
ethene reacts with chlorine to form 1,2-dichloroethane (first intermediate)
synthesis of PVC from ethene step 2
1,2-dichloroethane is subjected to thermal cracking which removes HCl to form chloroethene (second intermediate)
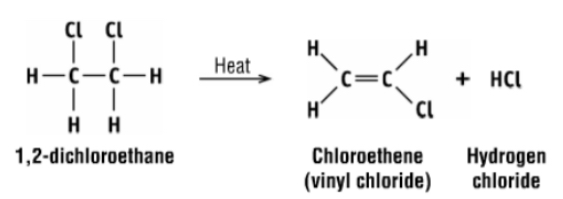
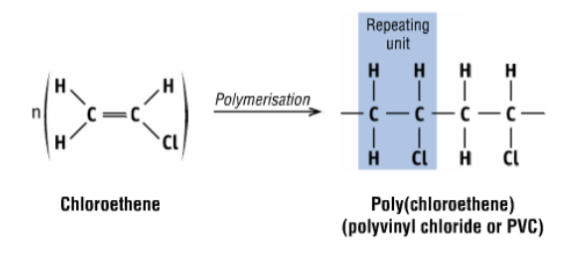
synthesis of PVC from ethene step 3
chloroethene is polymerised to poly(chloroethene) which is also called polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
what is the principle of the separation of the components in a mixture using any type of chromatography?
the principle on which all chromatographic separation techniques are based is that separation of a mixture of components occurs as a result of selective adsorbance of the components of the mixture on a stationary phase while carried by a mobile phase
paper chromatography phases
mobile - water, stationary - paper
gas chromatography phases
mobile - gas, stationary - non-volatile liquid spread on an inert solid
gas chromatography processes
injection, transport of the sample along the column, separation in the column, detection
high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) phases
mobile - solvent, stationary - very fine particles of silica
HPLC processes
injection, transport of the sample along the column, separation in the column, detection
gas chromatography uses
measure levels of alcohol in blood
HPLC uses
measure levels of alcohol in blood
infrared spectrometry principal
the principal of infrared spectrometry is that organic compounds absorb IR radiation of certain frequencies
what does infrared spectrometry do?
identifies organic compounds
infrared spectrometry processes
IR radiation is passed through the sample, IR radiation of a certain fixed frequency is absorbed, an absorption spectrum is obtained and can be used to identify the compound
ultraviolet spectrometry principle
the principle of ultraviolet absorption spectrometry is that absorbance is directly proportional to concentration
what does ultraviolet spectrometry do?
identifies concentration of an organic compound
ultraviolet spectrometry processes
a solution of the substance being analysed is placed between a source of UV light and a detector, the detector measures the intensity of light reaching it, a UV absorption spectrum is obtained and can be used to identify the concentration of the compound