Pollution
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
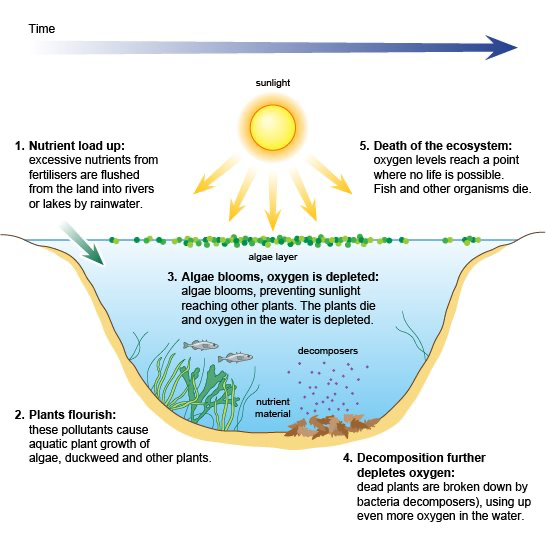
What is eutrophication?
Excessive nutrient enrichment of water, usually from nitrates and phosphates.
What nutrients favour algal growth leading to blooms?
Phosphates and nitrates.
What is an algal bloom?
A thick mass of algae on the water surface that blocks sunlight.
How does an algal bloom harm aquatic life?
It reduces dissolved oxygen and prevents photosynthesis in submerged plants.
What happens when submerged plants die in eutrophication?
Decomposition by bacteria consumes more oxygen, depleting supplies further.
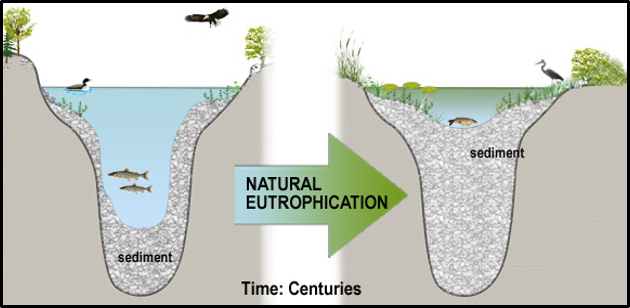
Can eutrophication occur naturally?
Yes, when water bodies dry gradually and nutrient-rich sediment accumulates.
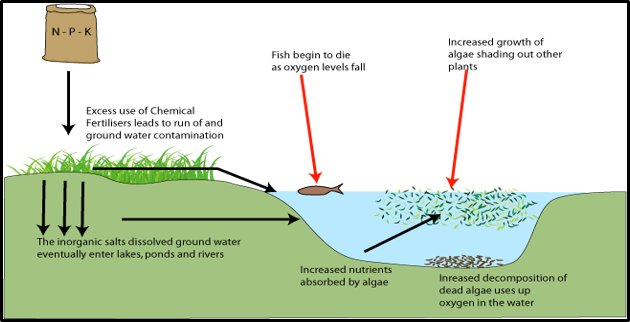
What is the main human cause of eutrophication?
Fertiliser leakage from agriculture introducing nitrogen and phosphates.
What does BOD stand for?
Biological Oxygen Demand.
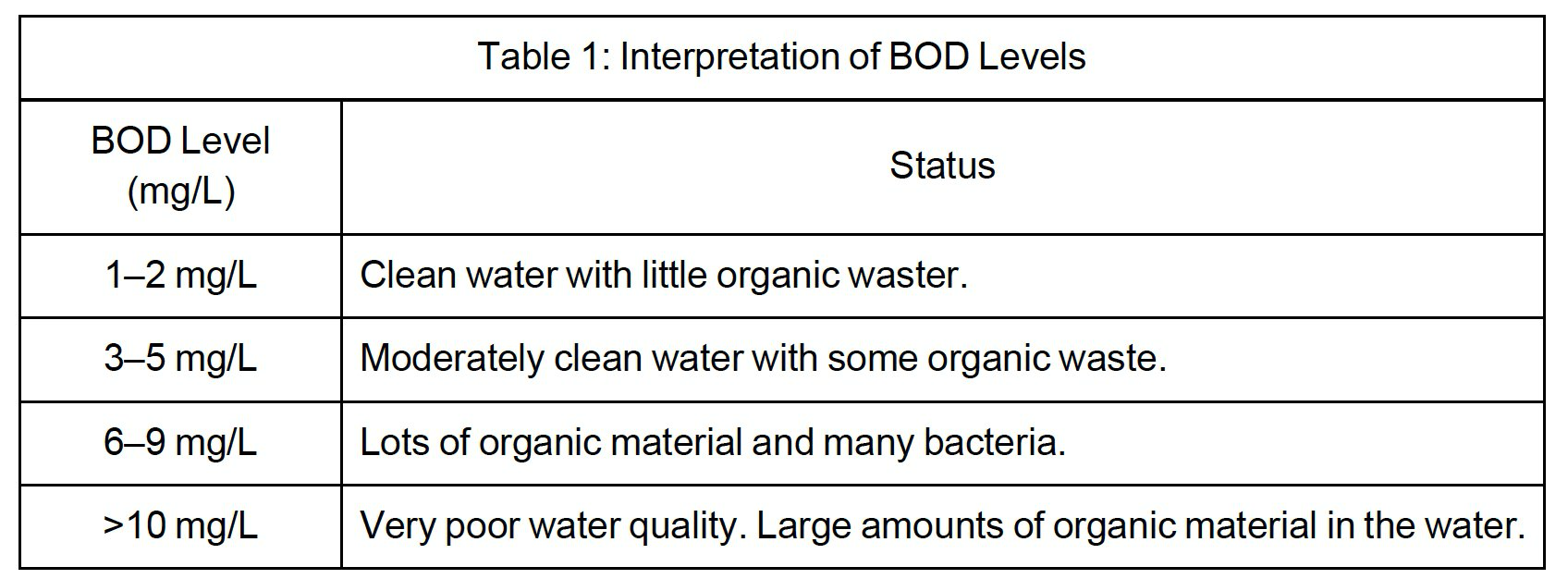
What does BOD measure?
The amount of dissolved oxygen required to break down organic material in water.
How is BOD an indirect measure of pollution?
Organic pollution increases respiration, using more oxygen, raising BOD.
Summarise the steps to measure BOD.
1) Measure initial dissolved oxygen, 2) Incubate water in dark at 20°C for 5 days, 3) Measure oxygen again, 4) BOD = difference.
Why is the water kept in the dark during BOD measurement?
To prevent photosynthesis from replenishing oxygen.
What types of waters typically show high BOD levels?
Shallow, slow-moving waters like ponds and wetlands.
What is bioaccumulation?
The buildup of toxins in body tissues during an organism’s life.
Why do bioaccumulated toxins persist in animals?
They are often fat-soluble and cannot be excreted.
What is biomagnification?
Increase in toxin concentration at successive trophic levels in a food chain.
Why do predators have higher toxin concentrations than prey?
They consume more contaminated organisms, compounding the toxins.
Name a pollutant found widely in fish and shellfish.
Mercury.
Why should large fish be eaten less often?
They accumulate higher, potentially harmful levels of mercury.
What is DDT and why was it banned?
An agricultural insecticide that accumulates in fat tissues through food chains
Why are plastics such a persistent pollutant in nature?
They are non-biodegradable.
What are macroplastics?
Large, visible pieces of plastic more than 5 mm in size.
What are microplastics?
Tiny pieces of plastic debris less than 5 mm in size.
How do microplastics enter food chains?
They and their contaminants bioaccumulate in organisms and magnify up trophic levels.
How do predators experience effects of plastic pollution?
They accumulate higher concentrations due to biomagnification.
What is the trend of macro- and microplastic abundance?
They are steadily increasing in oceans worldwide.