Lattice Energy
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What is lattice energy?
The energy change when one mole of an ionic compound is formed from its gaseous ions under standard conditions
What is the enthalpy change for lattice energy?
Negative. Lattice energies are always exothermic, the more exothermic the stronger the ionic bond
Define enthalpy of formation
The enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is formed from the elements in their standard states under standard conditions
Define enthalpy of atomisation
The enthalpy when one mole of gaseous atoms are formed from the elements in their standard states under standard conditions
Give the equation for the standard enthalpy of atomisation of lithium and chlorine
Li(s) ——> Li(g)
½Cl2(g) ——> Cl(g)
What is the value of the enthalpy change for change of atomisation?
Positive/Endothermic because energy must be supplied to break bonds holding the atoms in the element together
Define enthalpy of first ionisation energy
The enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous atoms loses a mole of electrons to form one mole of unipositive ions.
It is endothermic
Give an equation for the first ionisation energy of Mg
Mg(g) ——> Mg+ + e-
Define the standard enthalpy change of first electron affinity
The enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous atoms gains one mole of electrons to form one mole of mononegative ions
Give the equation for the first electron affinity of Chlorine
Cl(g) + e- ——> Cl-(g)
Give the equation for the second electron affinity of oxygen
O-(g) + 2e- ——> O2-
What is the value of energy change for Standard enthalpy change of first electron affinity?
The first electron affinity is exothermic while the rest are endothermic
How can lattice energy be determined?
If the enthalpy change of formation and the enthalpy changes involved in changing elements from their standard states to gaseous ions is known
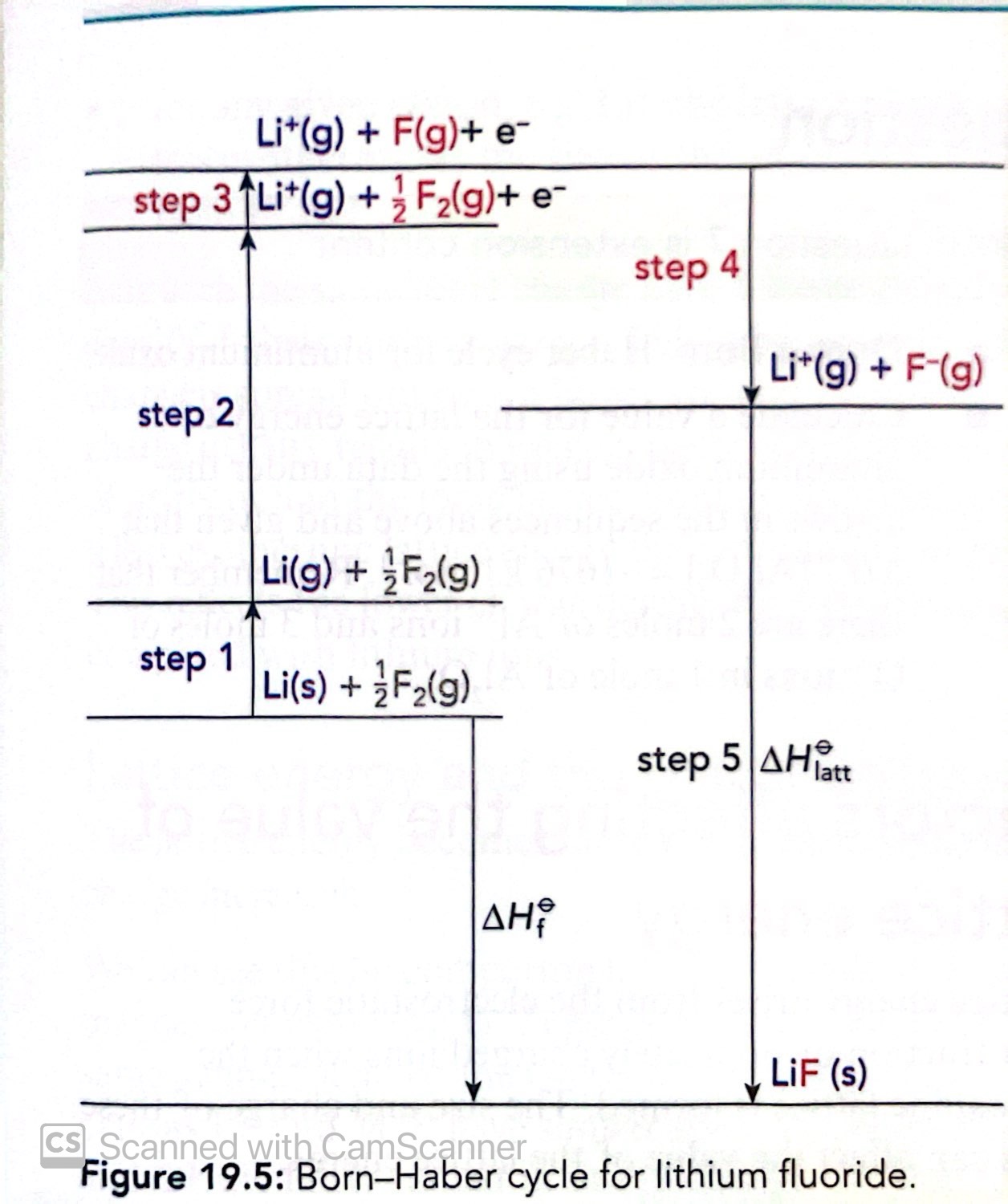
Give the formula that can be used to find lattice energy in a Born-Haber cycle
Enthalpy change of formation = Change of ionisation energy + atomisation + electron affinity + ionisation energy + lattice energy
What order should be used when constructing Born-Haber cycles?
Atomise metal
Ionise metal
Atomise non-metal
Ionise non-metal
(For ionising metals ionisation energy should be used and for non-metals you use electron affinities)
Construct the Born-Haber cycle for Lithium Fluoride
Where does lattice energy arise from?
It arises from the electrostatic force of attraction of oppositely charged ions
It is a measure of strength of ionic bonds between cations and anions
What does the value of the enthalpy change of lattice energy mean?
The more exothermic the energy, the stronger the ionic bond and more stable a compound is
What factors affect lattice energy?
Size of ions
Charge of ions
Overall this called Charge Density
How does ion size affect lattice enrgy?
As the size of the ion increases, lattice energy becomes less exothermic and the compound becomes less stable
Why do larger ions have a lower charge density?
This is because the same charge is the same and is spread over a larger volume resulting in weaker electrostatic forces of attraction
How does charge on ions affect lattice energy?
As ionic charge increase so does lattice energy.
What is ion polarisation?
The distortion of the electron cloud of an anion by a neighbouring cation
The distortion is greatest when the cation is small and highly charged

What are the factors affecting polarisation?
The charge density of the cation
The ease which the anion can be polarised
What is polarising power?
The ability of a cation to attract the electron cloud of an anion and distort it
What factors can make an anion more likely to be polarised?
If the cation is small
If the cation has a charge of 2+ or 3+
If the anion is large
If the anion has a charge of 2- or 3-
What is polarisability?
The extent to which the electron cloud around an anion can be distorted by a cation
What is the trend in the thermostability of carbonates and nitrates down group 2?
Thermostablity increases
Why does thermostability increase down group 2?
Group 2 cations increase in ionic radius down the group, the smaller the ionic radius the better polarising power.
The smallest radius has the highest covalent character so less energy is required to decompose while the least polarising member has the highest ionic character so more energy is required for decomposition
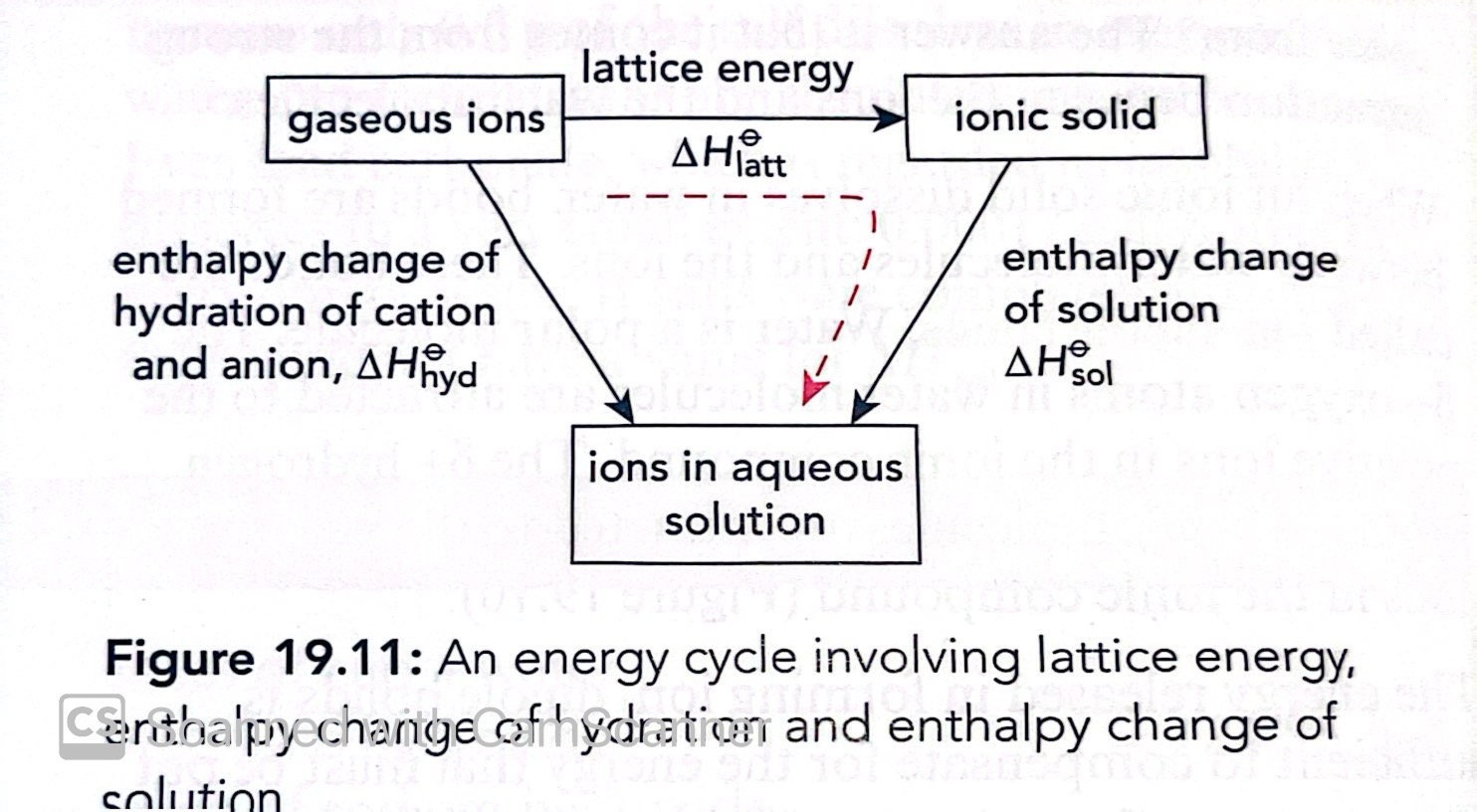
What is the enthalpy change of Solution?
The enthalpy change when a mole of ionic compound dissolves in a large volume of water to form a very dilute solution under standard conditions
What is the value of energy change for the enthalpy change of solution?
It can be either exothermic or endothermic
Between ionic compounds, the more negative the enthalpy change of solution the more soluble the salt
Compounds with high values are relatively insoluble
Give the equation for the enthalpy change of solution for NaCl
(aq) means a large volume of water
NaCl(s) + (aq) ——> NaCl(aq)
or
NaCl(s) + (aq) ——> Na+ + Cl-
Define enthalpy change of Hydration
The enthalpy change when one mole of a specified gaseous ion dissolves in a large volume of water to form a very dilute solution under standard conditions
What is the value of energy change for the enthalpy change of hydration?
It is always exothermic
It is more exothermic for ions with the same charge by smaller ionic radius and same radii but larger charge
Give an equation for the enthalpy change of hydration of Na
Na+(g) + (aq) ——> Na+
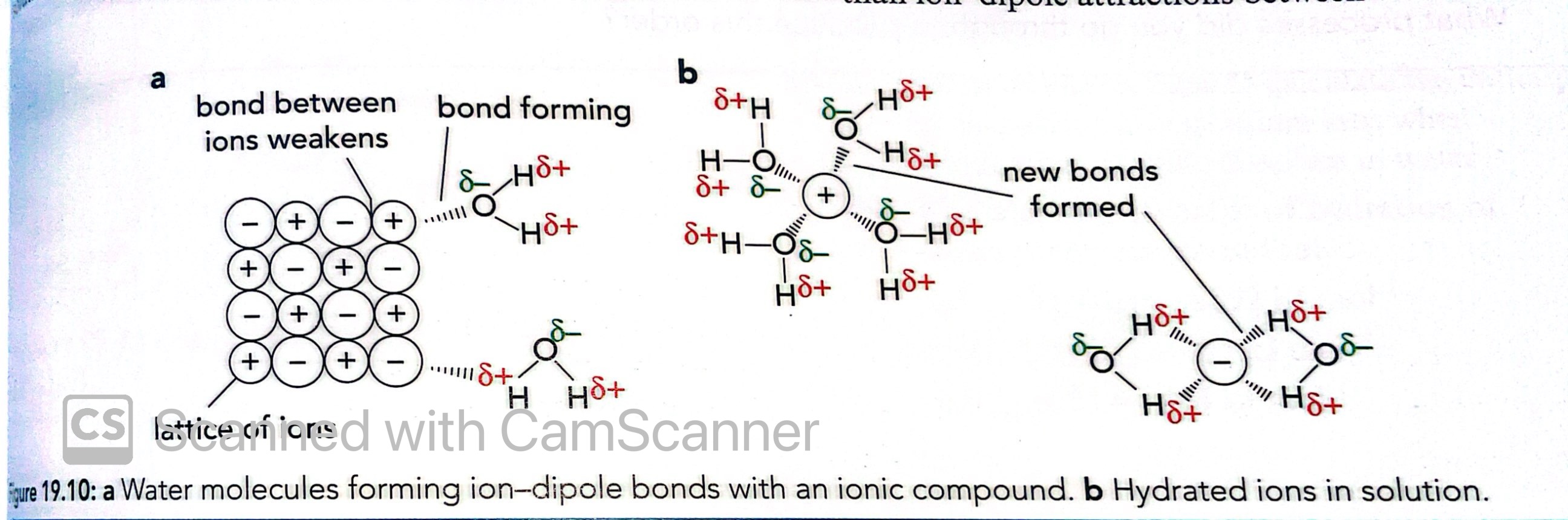
What are ion-dipole bonds?
The bond formed between an ion and a polar compound
How does water form ion-dipole bonds with an ionic compound?
Water molecules are attracted to the compound and begin to attach to the lattice
This weakens the bonds in the lattice and they begin to break and new ones are formed
Hydrated ions in solution remain
What equation can be used in a Hess cycle to calculate enthalpy changes in solution?
Enthalpy change of hydration= Lattice energy + enthalpy change of solution
What is trend in solubility of group 2 sulfates down the group?
Solubility decreases
Enthalpy change of hydration decreases down the group, explain why?
Smaller ions have greater enthalpy change of hydration because the change depends on the size of the cation while the anion remains unchanged
What happens to lattice energy in terms of solubility of group 2 sulphates?
Lattice energy decreases down the group and is inversely proportional to the sum of radii of both ions.
The sulphate ion is much larger than the cations so it contributes to the reduction