econ - 2.1: demand
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credit https://www.econinja.net/microeconomics/2-1-demand/movements-and-shifts-on-the-demand-curve
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
define demand
the quantity of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase in a given period of time
what does the law of demand state?
the quantity demanded of a product will fall if price rises, and vice versa, ceteris paribus
what are the assumptions underlying the law of demand?
the income effect
the substitution effect
the law of diminishing marginal utility
what is the income effect?
as the price of a product falls, the real income of consumers increases, meaning they are able to buy more products at lower prices creating more demand.
what is the substitution effect?
as the price of a good or service falls, the product will become more attractive than more expensive substitute products, and customers will switch over (increasing demand)
what is the law of diminishing marginal utility?
as consumption of a good or service increases, the additional gain of consuming one more decreases, so consumers are only willing to pay lower prices
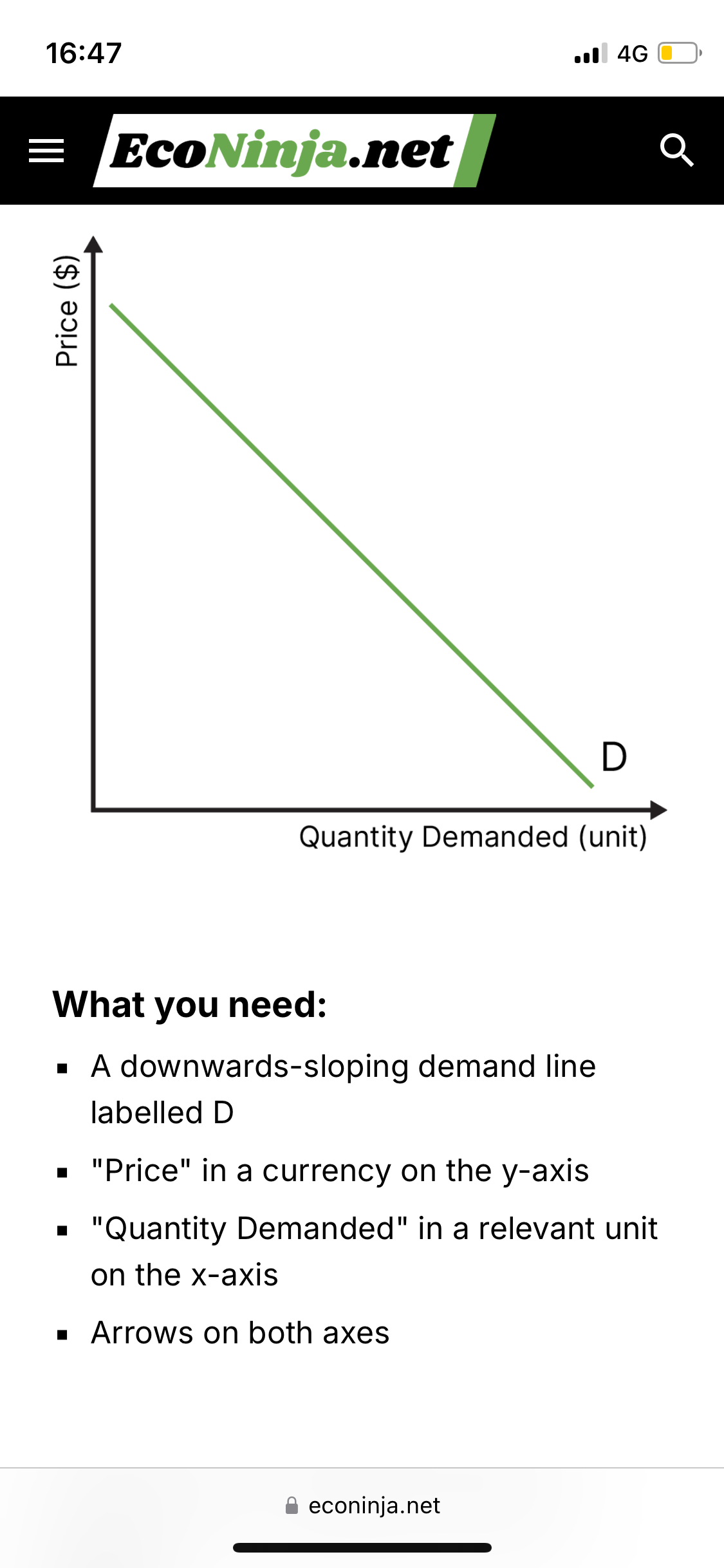
draw the basic demand curve
what is the market demand curve?
since a market is a place where transactions between buyers and sellers take place, the market demand curve is the sum of all individual demand for a product.
what are the five non-price determinants of demand?
income
tastes and preferences
future price expectations
number of consumers
prices of related goods
how does income affect demand?
higher levels of income = ability to buy more products
increases demand even when price stays the same
only the case for normal goods, not the case for inferior goods
how do future price expectations impact demand?
if a product is going to be worth lots in the future, many people will buy it now (and vice versa)
how does the number of consumers impact demand?
the more consumers there are in the market, the more demand there is
how do the prices of related goods impact demand?
complementary goods: goods that are jointly demanded (i.e. phones and phone cases) - when the price of one increases then the demand for the other decreases
substitute goods: goods that compete against on another (i.e. samsung and iphones) when the price for one increases, demand for the other increases
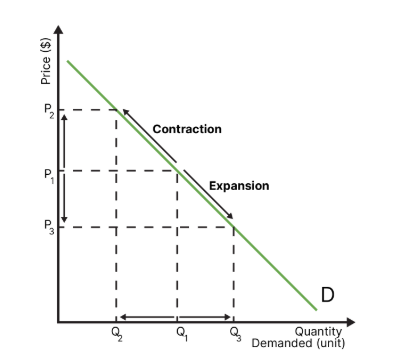
what are movements along the demand curve called and caused by?
called expansions or contractions, determined by price
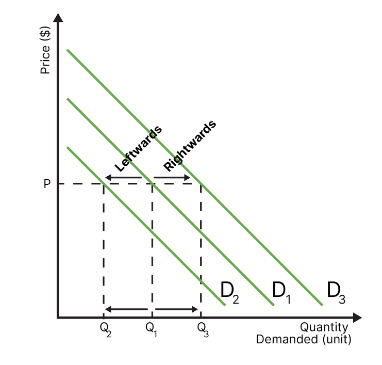
what are shifts of the demand curve called
called a leftward shift if demand decreases, and a rightward shift if demand increases. caused by one or multiple non-price determinants of demand.
draw the diagram for a contraction or expansion of demand
draw the diagram for a leftwards or rightwards shift of the demand curve