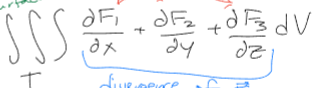Triple Integrals
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Volume
∫∫∫SdV
Average Value
1/V * ∫∫∫Sf(x,y,z) dV
Mass of solid with density
∫∫∫Sδ(x,y,z) dV
centroid of a solid
xA = (∫∫∫S x dV) / V; repeat for y and z
Center of Mass with density
xM = (∫∫∫S xδ(x,y,z) dV) / M
Moment of Inertia
relationship between angular acceleration and torque; mass/velocity * ∫∫∫(distance to axis)² dV
triple integrals geometrically
“adding up” a function over every point in a solid
Volume of a Solid bounds
outside integral → constant; middle bounds → only include remaining variable; inside integral → can include two other variables
how do you find bounds (upper/lower)?
plug in point with the two variable coordinates (not the variable you’re finding the bounds for) that is inside the intersection
Flux Integral
integral of a vector field over a surface; flow of a vector field through a surface calculated by F * N
Spiral/Helix parameterization
<cost, sint, 0.1t>
Line parameterization
<2-t, 1+3t, 4t> = <2, 1, 0> + t <-1, 3, 4>
Torus/Donut parameterization
<(b+acos(s))cost, (b + cos(s))sint, asin(s)>
Cylinder parameterization
<cost, sint, s>
Describe surfaces
use parametric equation with 2 variables; partial derivatives get tangent vectors; cross-product of two partial derivatives get normal vector; calculate surface area by double integrating normal vector’s length
normal vector of r(u,v)
ru(u,v) x rv(u,v)
Surface area equation
∫∫∫D l ru(u,v) x rv(u,v) l dudv
Flux of a vector field F through a parameterized surface r(u,v)
∫∫DF * N dA; dot product of vector field and normal vector of parameterized surface
Calculate Flux Process
1- parameterize; 2- plug parameterization into vector field; 3- calculate N = ru x rv; 4- dot product of 2 & 3; 5- integrate (double)
Divergence Theorem
If T is a solid bounded inside the closed surface S, to calculate the flux of a vector field through S, then
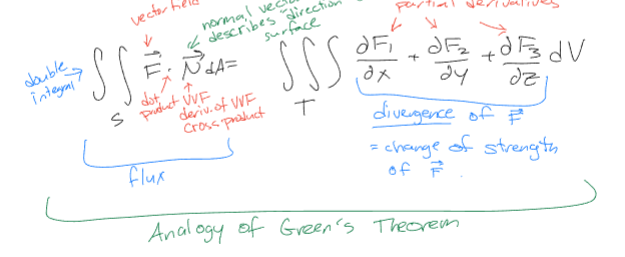
Divergence Theorem Equation
∫∫∫T dF1/dx + dF2/dy + dF3/dz dV