COMD 3800 chapter 4/5 phonatory system
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
phonation
- a production of vibrating vocal folds
- aka voicing
structures of the phonatory system
- hyoid bone
- larynx
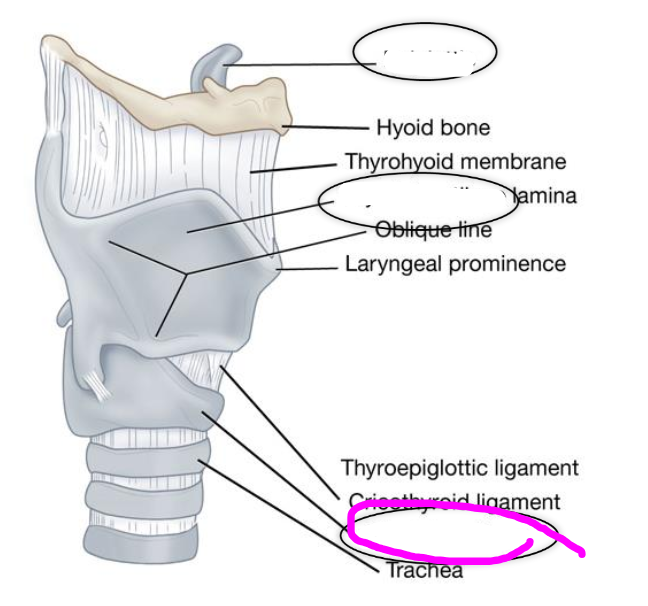
hyoid bone
- located @ level of C3
- very mobile
- does not connect to any other bone in the body
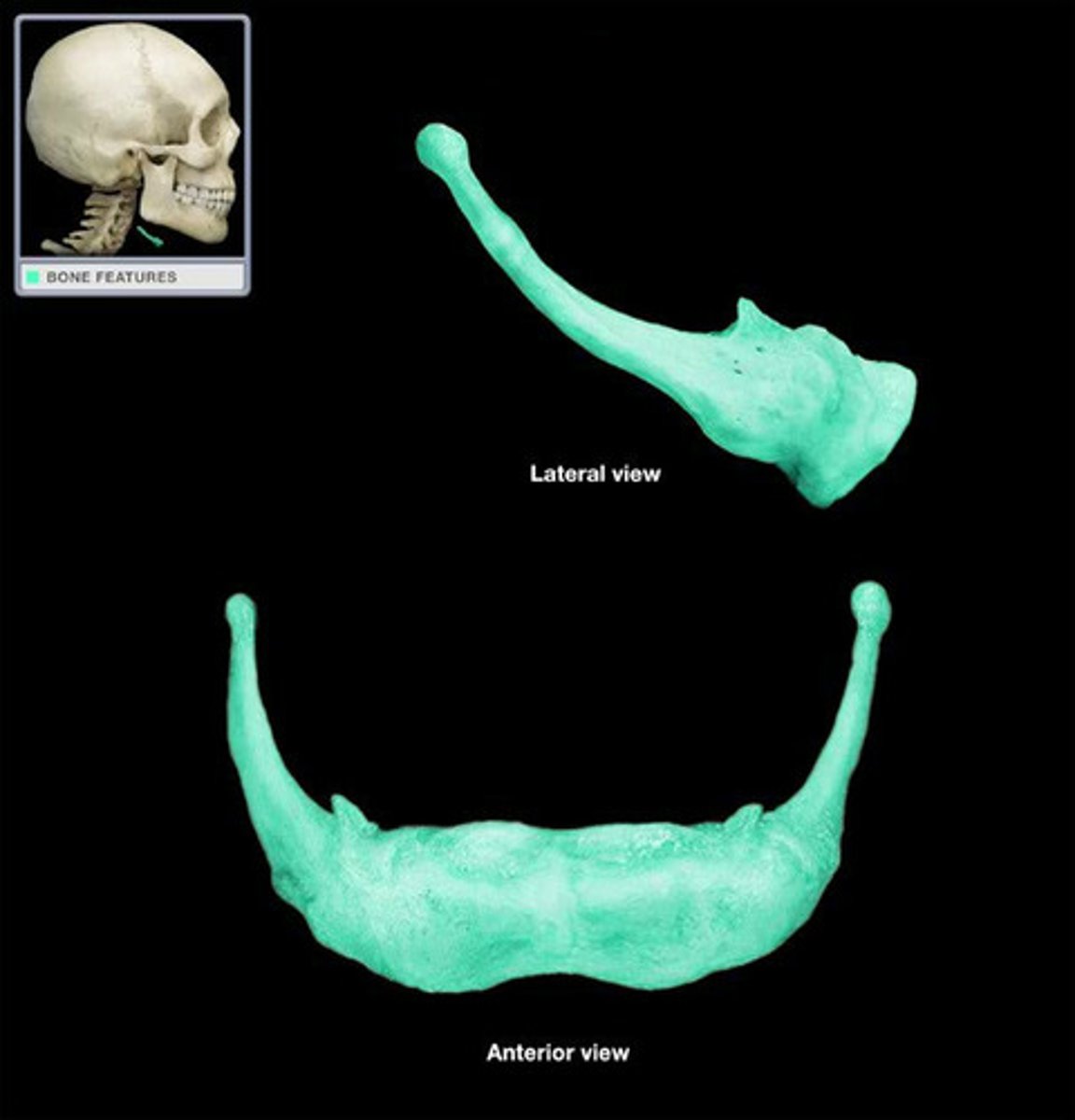
hyoid bone structure
- body (corpus)
- greater cornu
- lesser cornu
body/corpus (of the hyoid bone)
greater cornu (of the hyoid bone)
- articulates with the superior horns (cornu) of thyroid cartilage
lesser cornu (of the hyoid bone)
- cone shaped
- rise superiorly
larynx
- protects lower passageway from foreign materials
- can be used to hold air in lungs
- generates sound
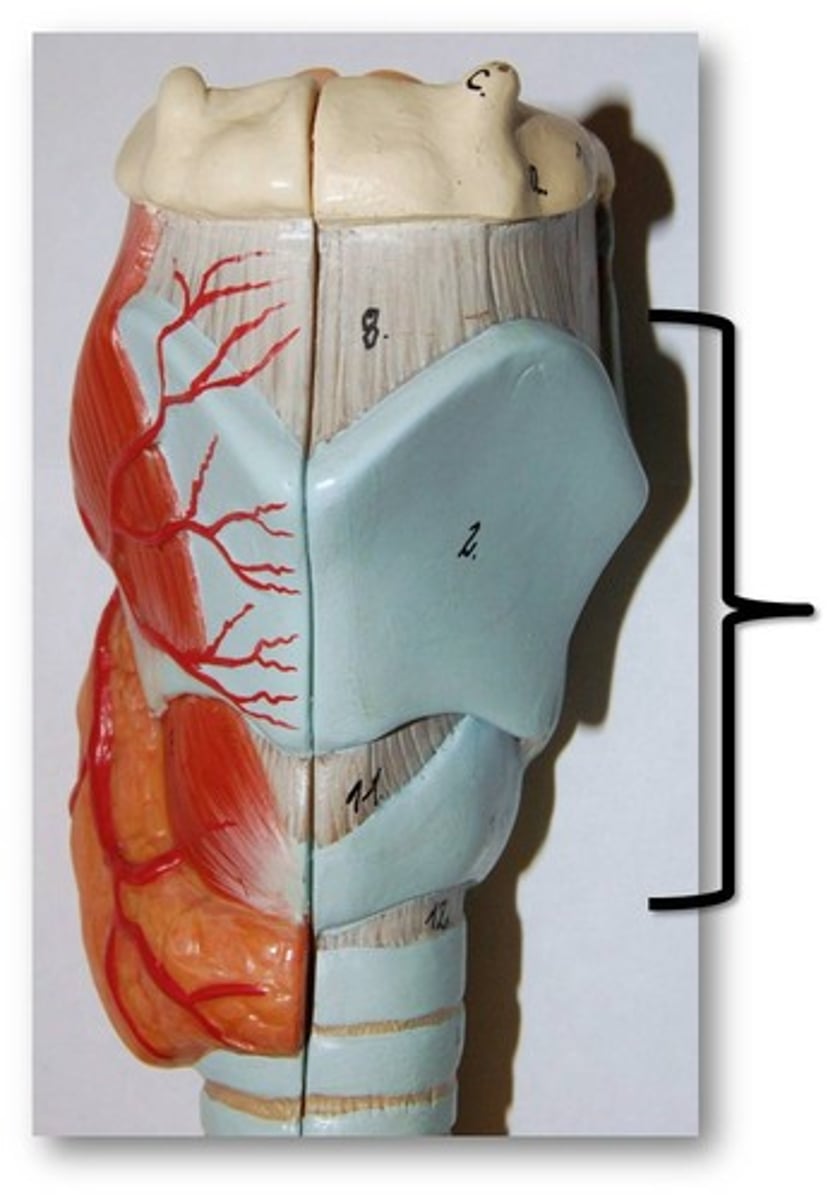
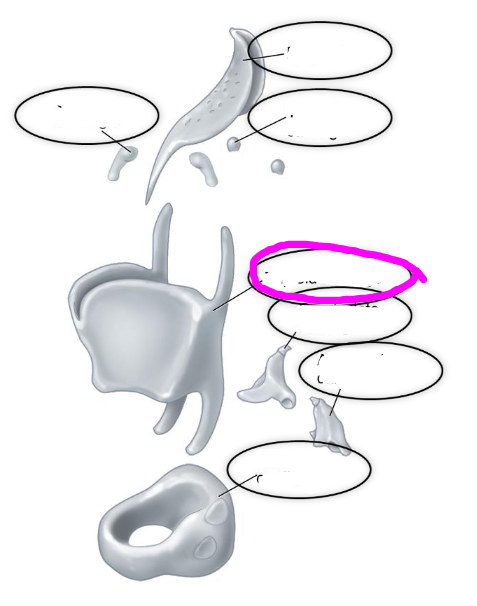
laryngeal cartilages
- thyroid cartilage
- cricoid cartilage
- arytenoid cartilage
- corniculate cartilage
- cuneiform cartilage
- epiglottic cartilage
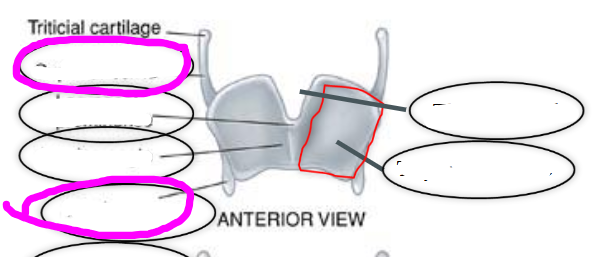
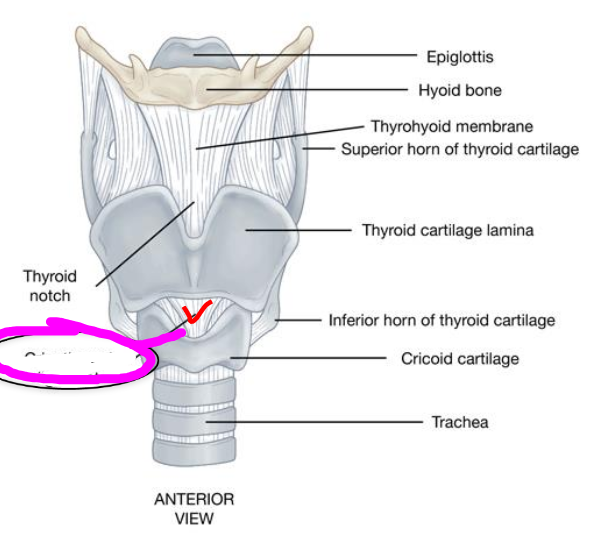
thyroid cartilage
- largest of the laryngeal cartilages
- articulates inferiorly with cricoid cartilage
thyroid laminae
aka quadrilateral plates
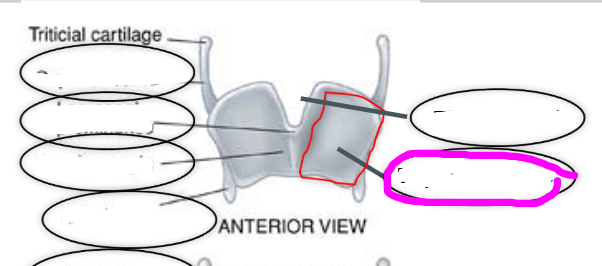
thyroid angle
point at which the two thyroid laminae come together
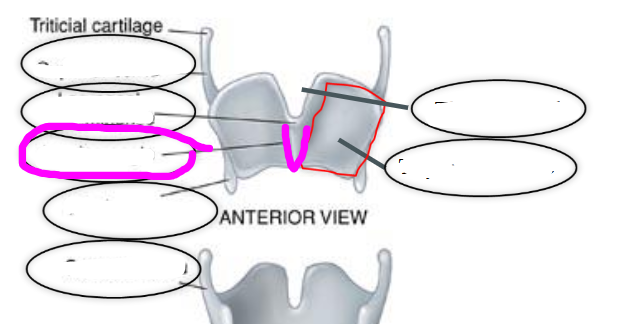
thyroid notch
- superior most point of thyroid angle
- adams apple
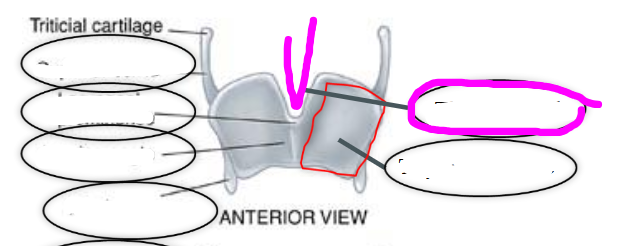
cornu (thyroid cartilage)
- located on the superior & posterior portion of the thyroid
- superior: points toward hyoid bone
- inferior: rests on cricoid cartilage
cricoid cartilage
- most inferior cartilage of the larynx
- unpaired, ring-shaped
arch (of cricoid cartilage)
- found on the cricoid cartilage
- low narrow portion in front
- provides clearance for the vocal folds
posterior quadrate lamina
- found on the cricoid cartilage
- wide and thick portion in back
- provides point of articulation for arytenoid cartilages
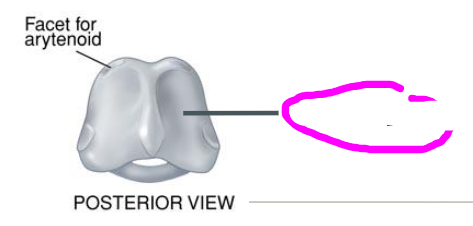
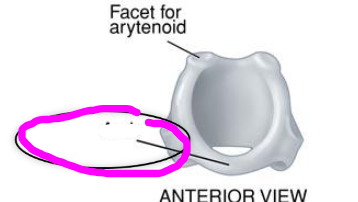
arytenoid cartilages
- located on superior surface of cricoid cartilage
- allows for rocking, gliding, rotating
- important for onset/offset of voicing
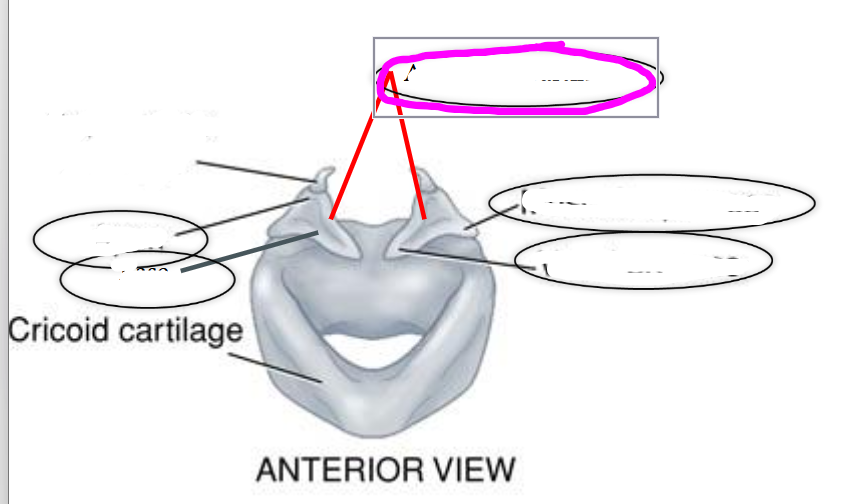
base (of arytenoid cartilage)
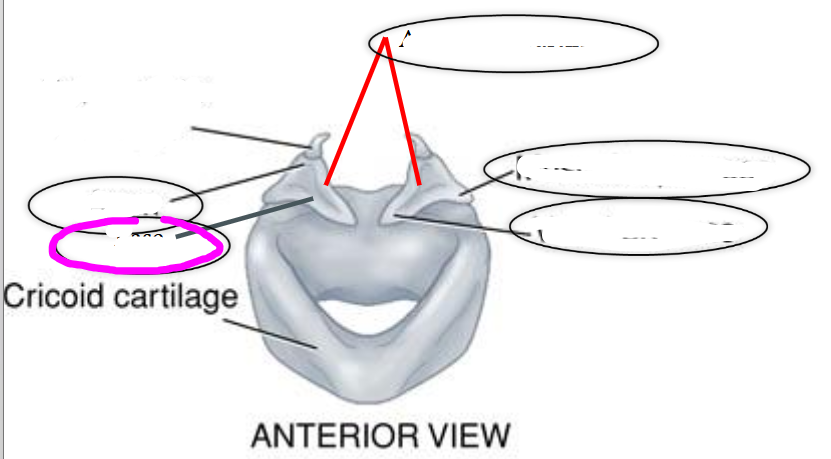
apex (of arytenoid cartilage)
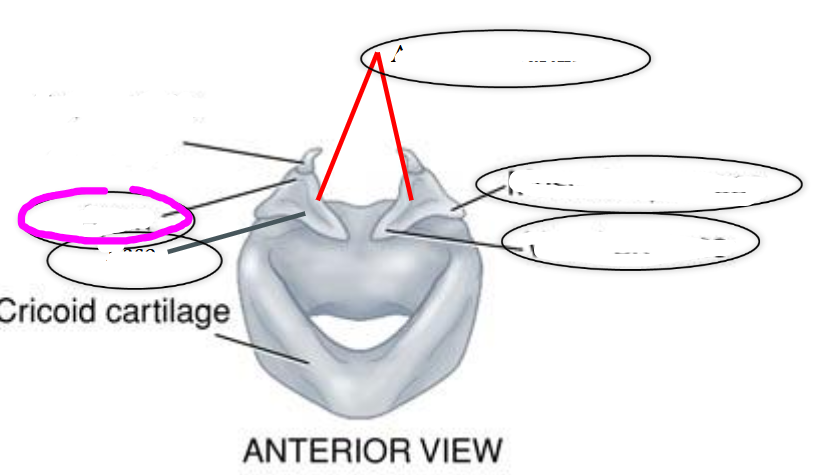
vocal process (of arytenoid cartilage)
- projects anteriorly toward the thyroid
- location of the vocal fold attachment
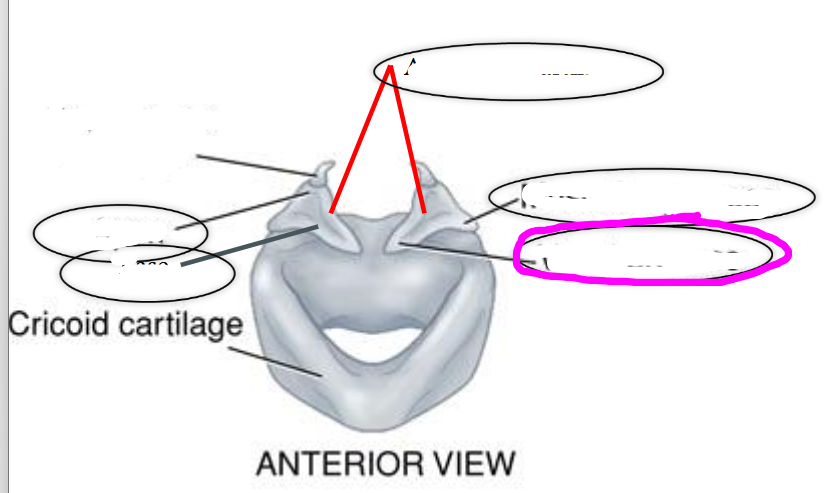
muscular process (of arytenoid cartilage)
- projects laterally on the arytenoid
- point of attachment for muscles that adduct & abduct the vocal folds
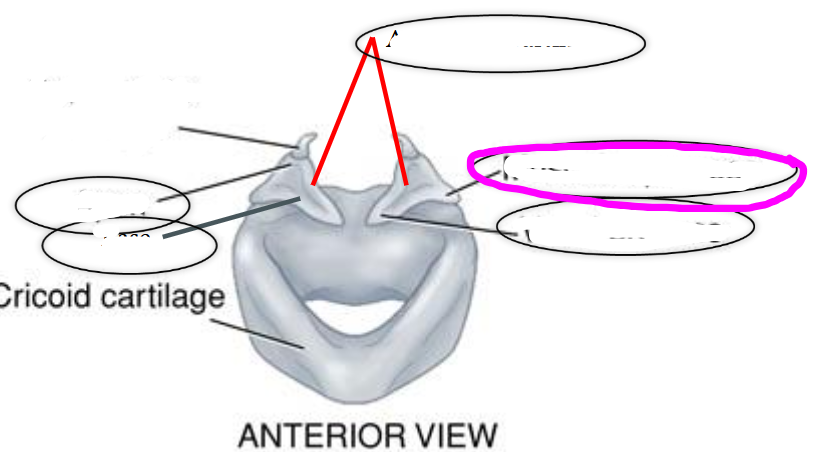
corniculate cartilage
- small horn shaped extension of arytenoids
- support aryepiglottic fold
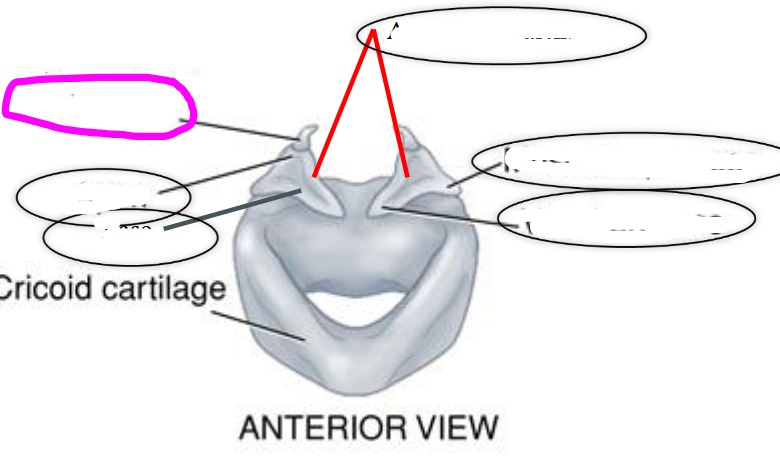
cuneiform cartilages
- small cartilages embedded within the aryepiglottic fold
- anterior to corniculate cartilages
- provide support for laryngeal covering
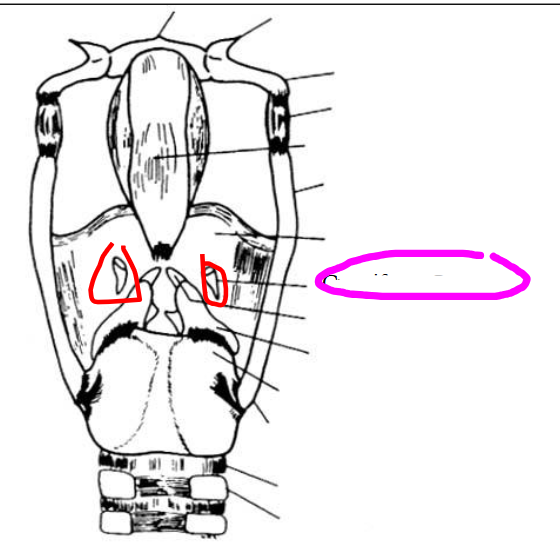
epiglottic cartilage (epiglottis)
- leaf like structure
- stem (petiolus) arises from the inner surface of the thyroid angle, just below notch
- protects airway by deflecting food & liquid from being swallowed
- surface of epiglottis is covered with a mucous membrane lining.
laryngeal joints
- cricothyroid joint
- cricoarytenoid joint
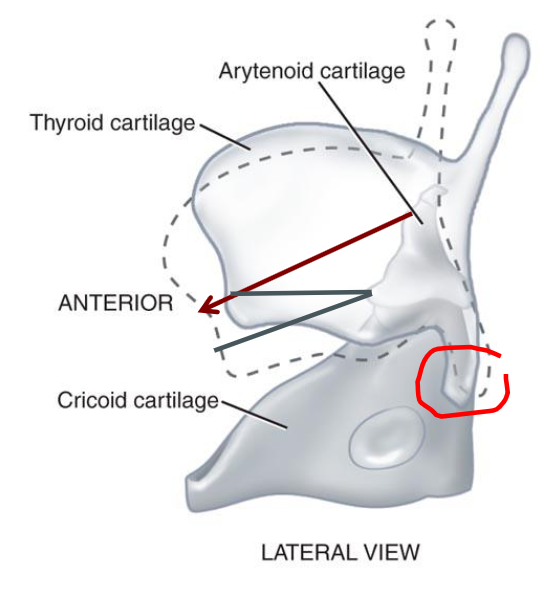
cricothyroid joint
- synovial (diarthrodial) joint that allows the thyroid to tilt downward. this stretches and tenses the vocal folds
- joint provides the major adjustment for change in vocal pitch
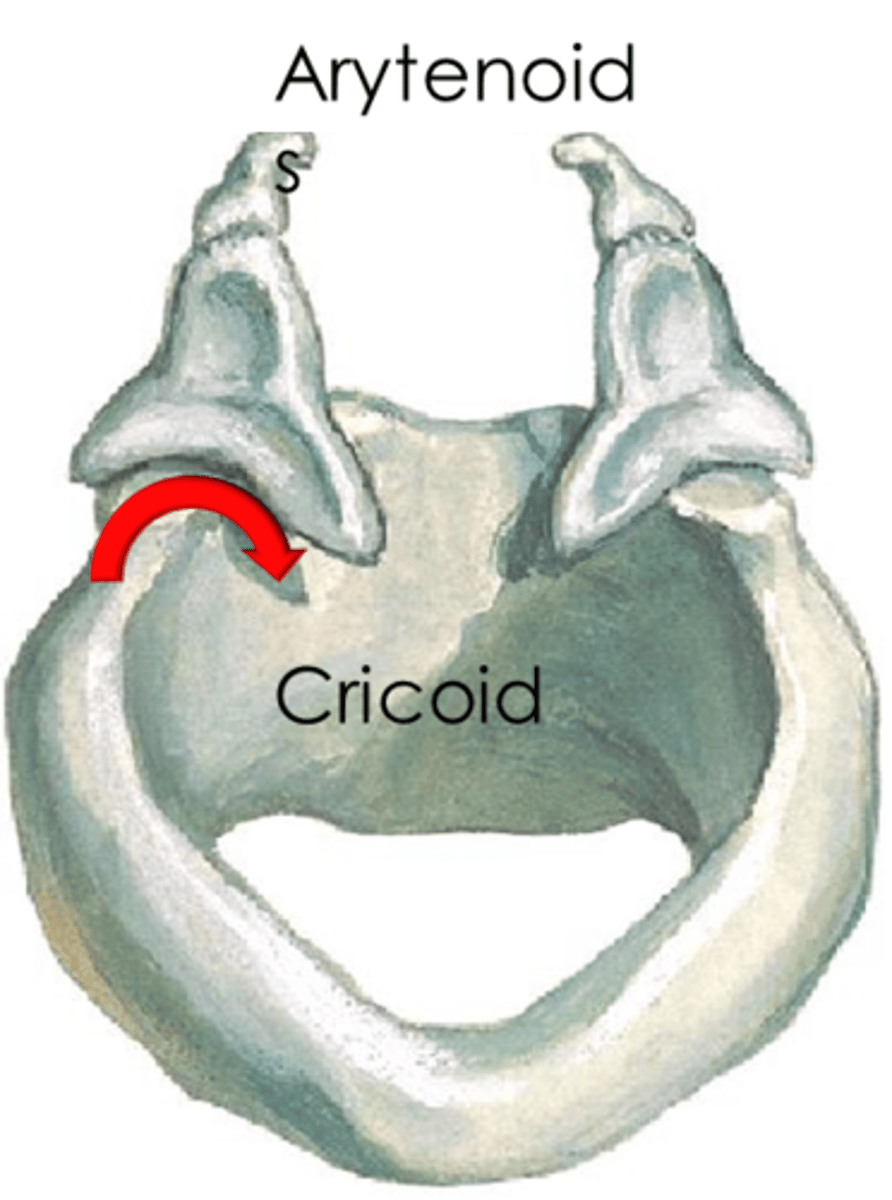
cricoarytenoid joint
- concave portion of arytenoids articulates with convex portion of cricoid lamina
- synovial joint (saddle joint) allows for rocking, gliding, and minimal rotation
- involved in adduction & abduction of vocal folds
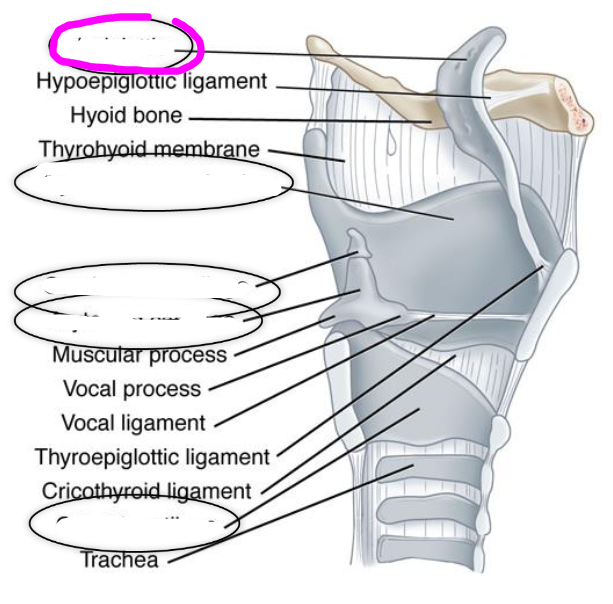
extrinsic laryngeal membranes and ligaments
- group of ligaments and membranes that connect the cartilage of the larynx to each other and to the hyoid bone and trachea
- thyrohyoid membrane
- hyoepiglottic ligament
- thryoepiglottic ligament
- criotracheal membrane
thyrohyoid membrane
connects the hyoid bone to the thyroid cartilage
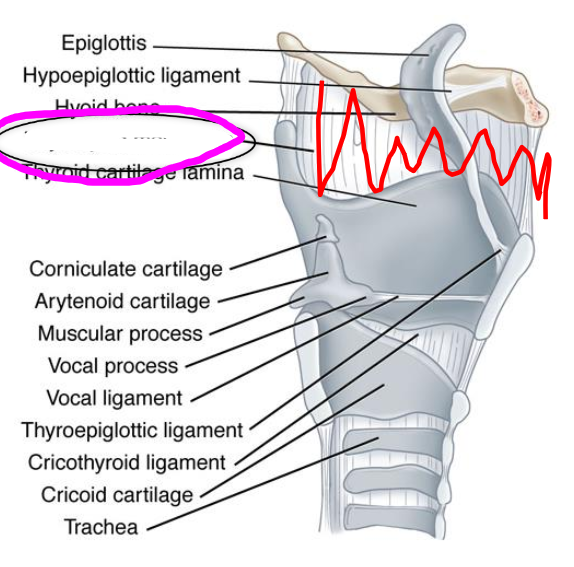
hyoepiglottic ligament
connects epiglottis to the hyoid bone
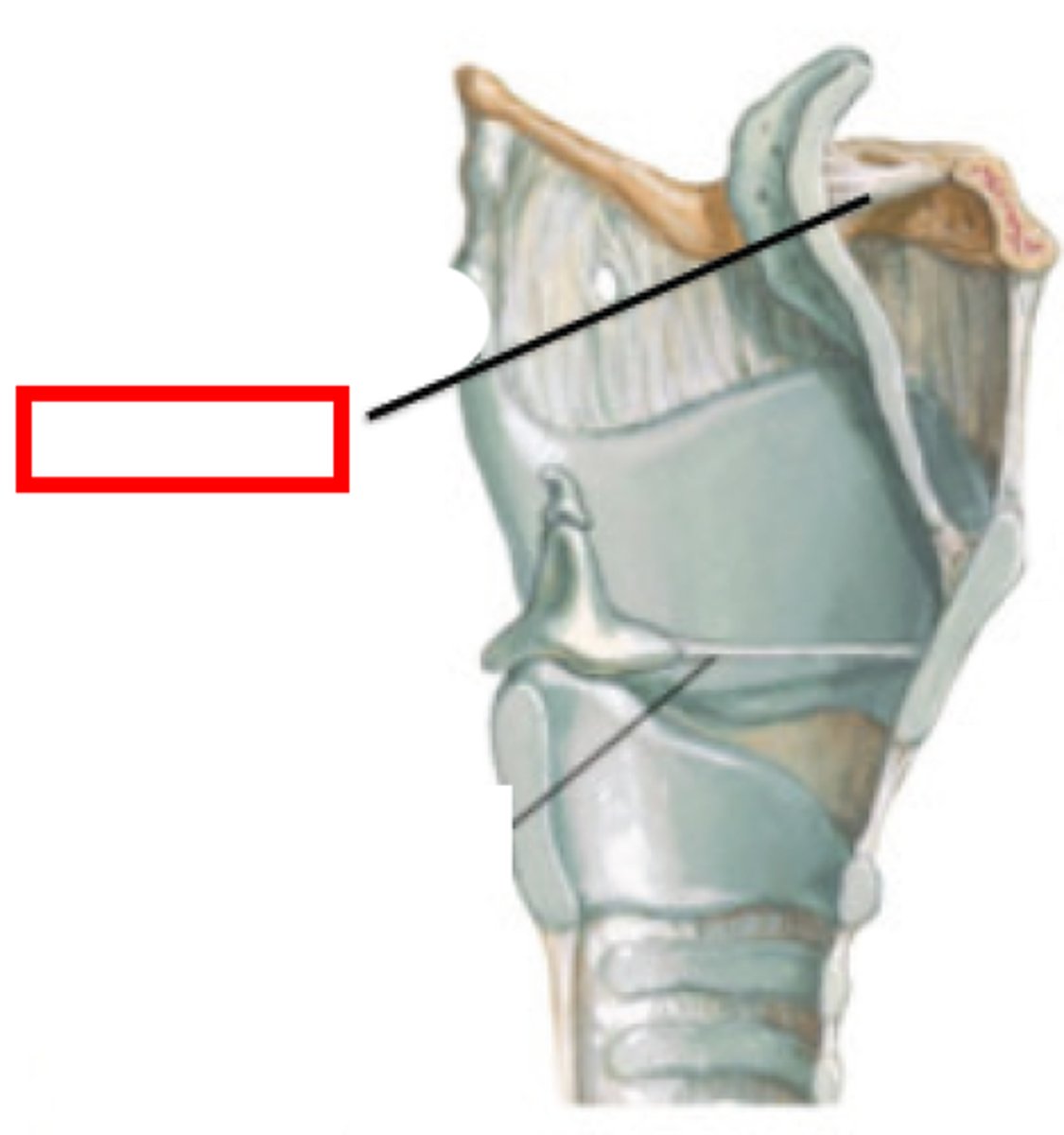
thyroepiglottic ligament
connects the epiglottis to the thyroid
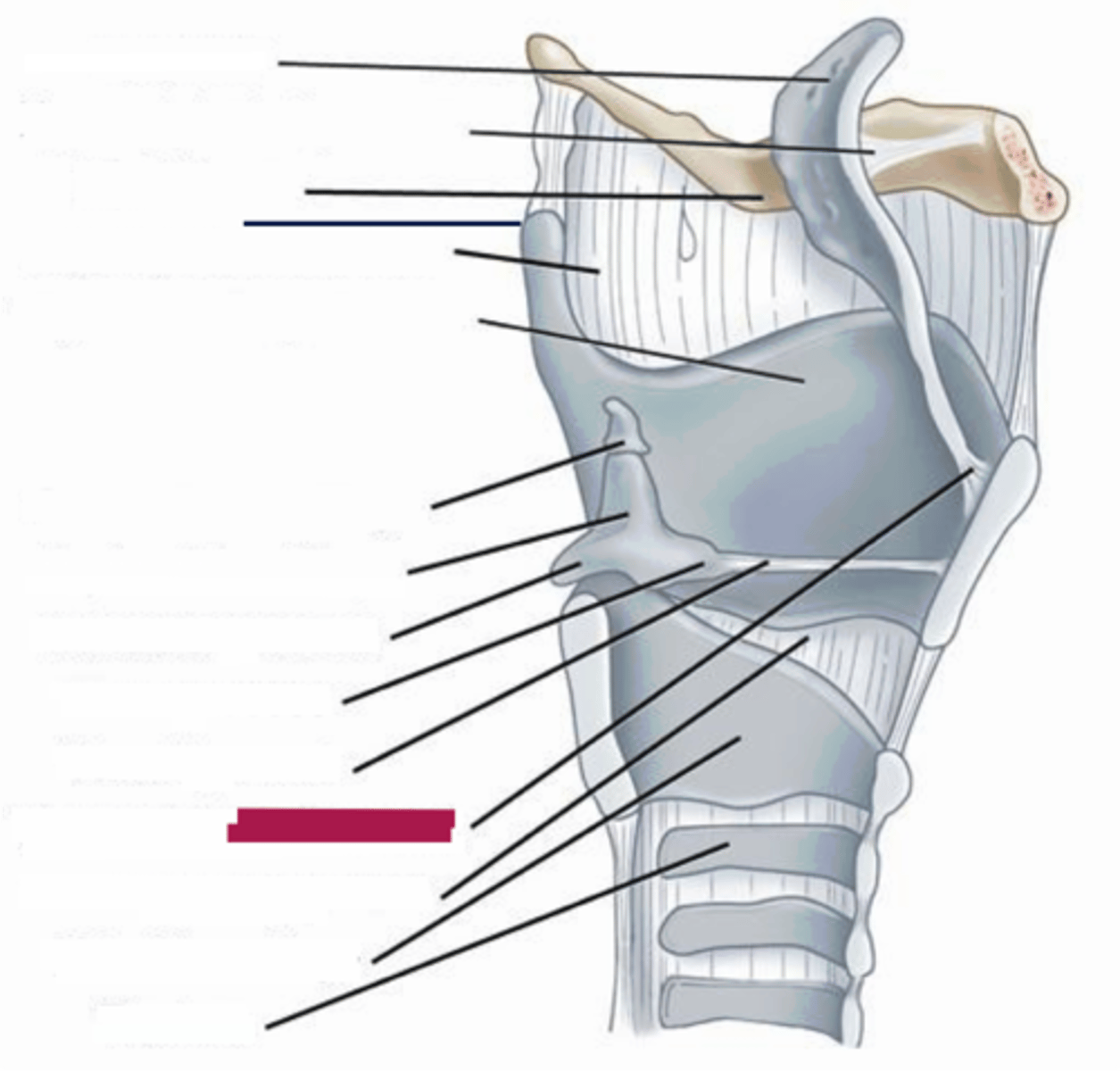
cricotracheal membrane
connects the cricoid cartilage to the first trachea ring
intrinsic laryngeal membranes and ligaments
- continuous sheet of connective tissue (elastic membrane)
quadrangular membranes (upper portion)
- aryepiglottic
- ventricular folds
conus elasticus (lower portion)
- vocal folds
- cricothyroid ligament
aryepiglottic folds
- part of the quadrangular membranes upper portion
- completely seal off the spaces in the laryngeal structure
- directs the airstream into the aditus and upward into the resonatory passageways
- first line of defense against foreign objects
- closes during swallowing and vomiting
--> prevents food/liquid from entering respiratory tract
ventricular folds
- part of the quadrangular membranes upper portion
- also known as false vocal folds
- pink and plump
- found between laryngeal vestibule and laryngeal ventricle
- contract -> meet at midline closing & sealing off the airway
- close during swallowing & during effortful activities (e.g. lifting heavy objects)
- during normal phonation, remain in quiet open position
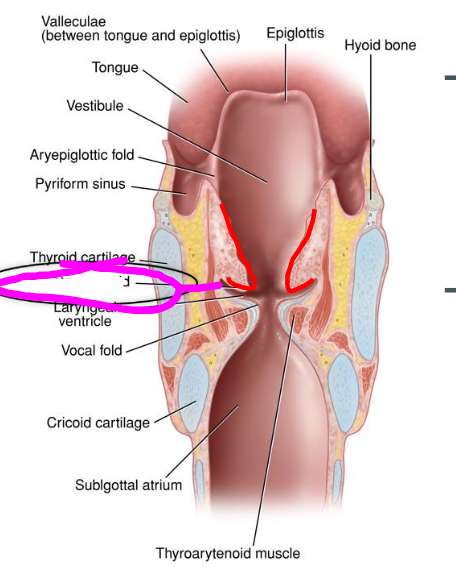
vocal folds
- part of the conus elastic lower portion
- white because of lack of vascular supply
- third line of defense in keeping foreign objects out of lungs
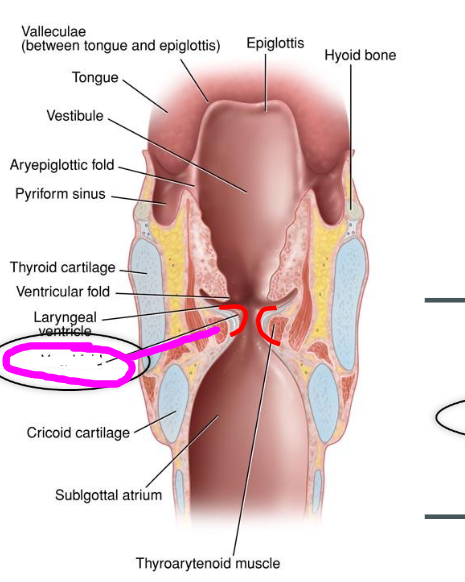
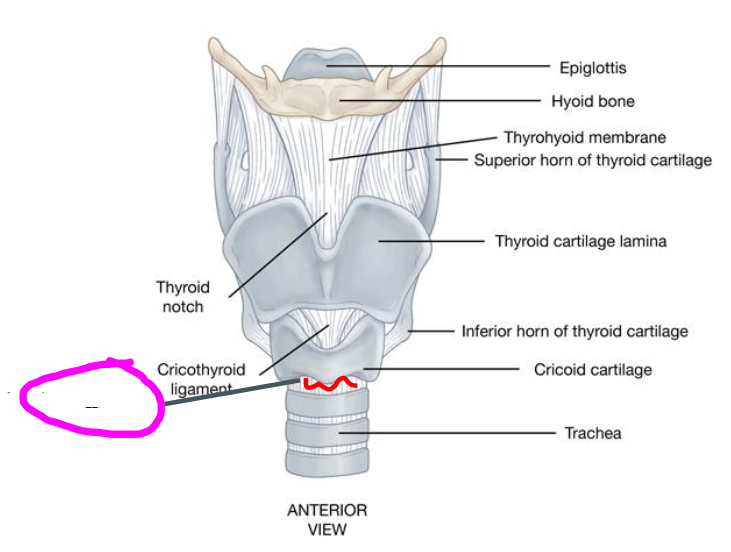
cricothyroid ligament
- part of the conus elastic lower portion
- connects the cricoid cartilage to the thyroid cartilage
cavities and spaces of the larynx
- laryngeal vestibule
- laryngeal ventricle
- inferior laryngeal ventricle (subglottal atrium)
- valleculae
- pyriform sinus
- glottis
laryngeal vestibule
- area in larynx above ventricular folds
- opening is called aditus
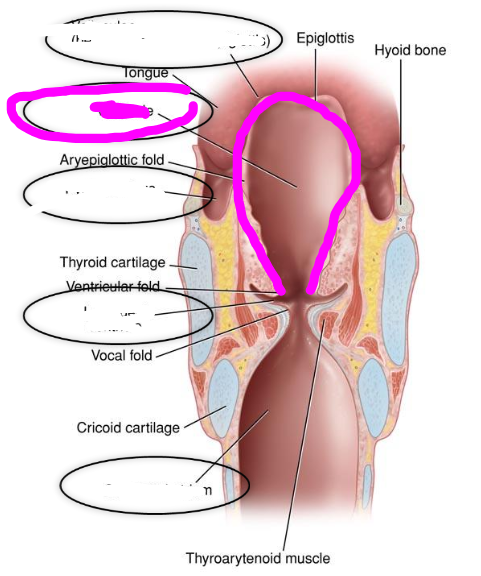
laryngeal ventricle
space between vocal folds and ventricular folds
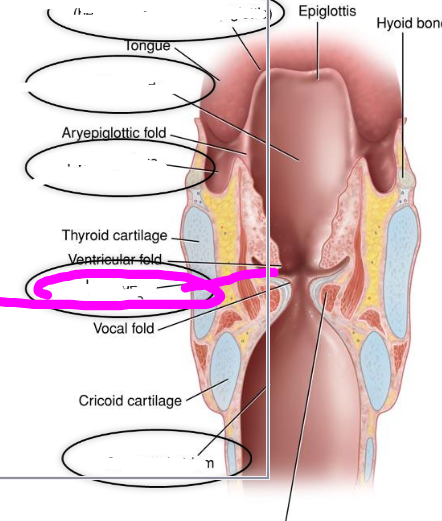
inferior laryngeal ventricle (subglottal atrium)
- portion below the true folds
- extends through to the trachea
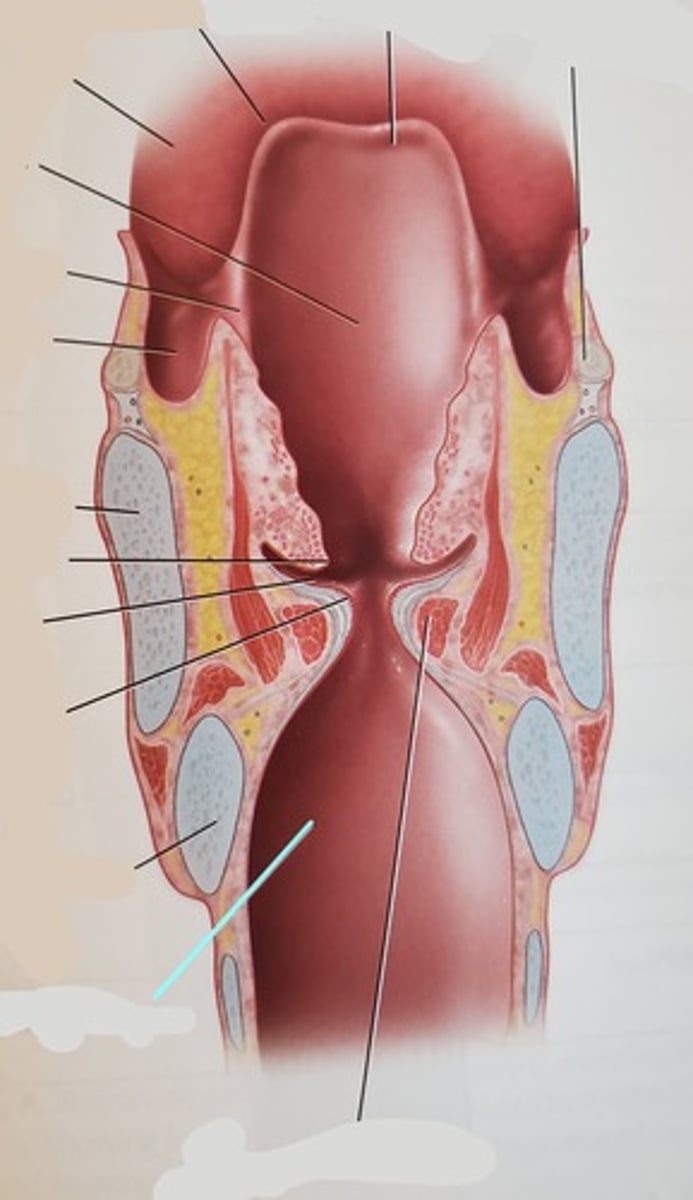
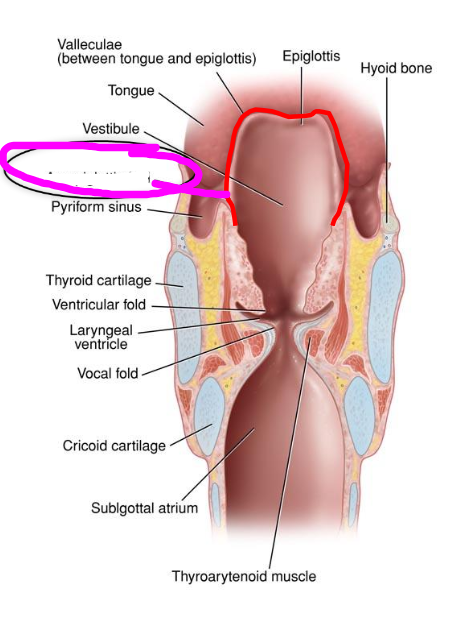
valleculae
- area between tongue root and epiglottis
- impaired swallow can cause food/liquid to pool in __, which increases risk of aspiration
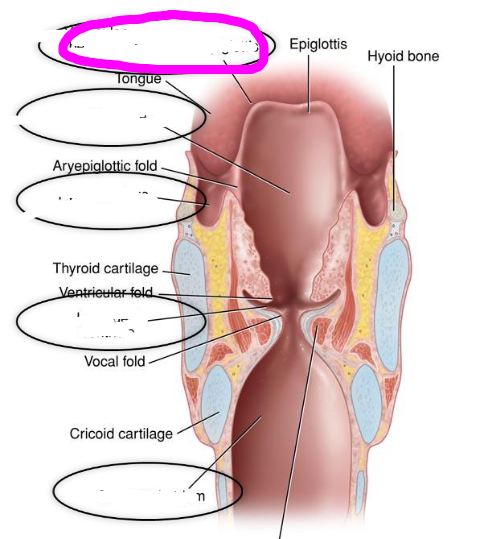
pyriform sinus
- between the lateral wall of thyroid cartilage and areypiglotic folds
- impaired swallow can cause food/liquid to pool in __, which increases risk for aspiration
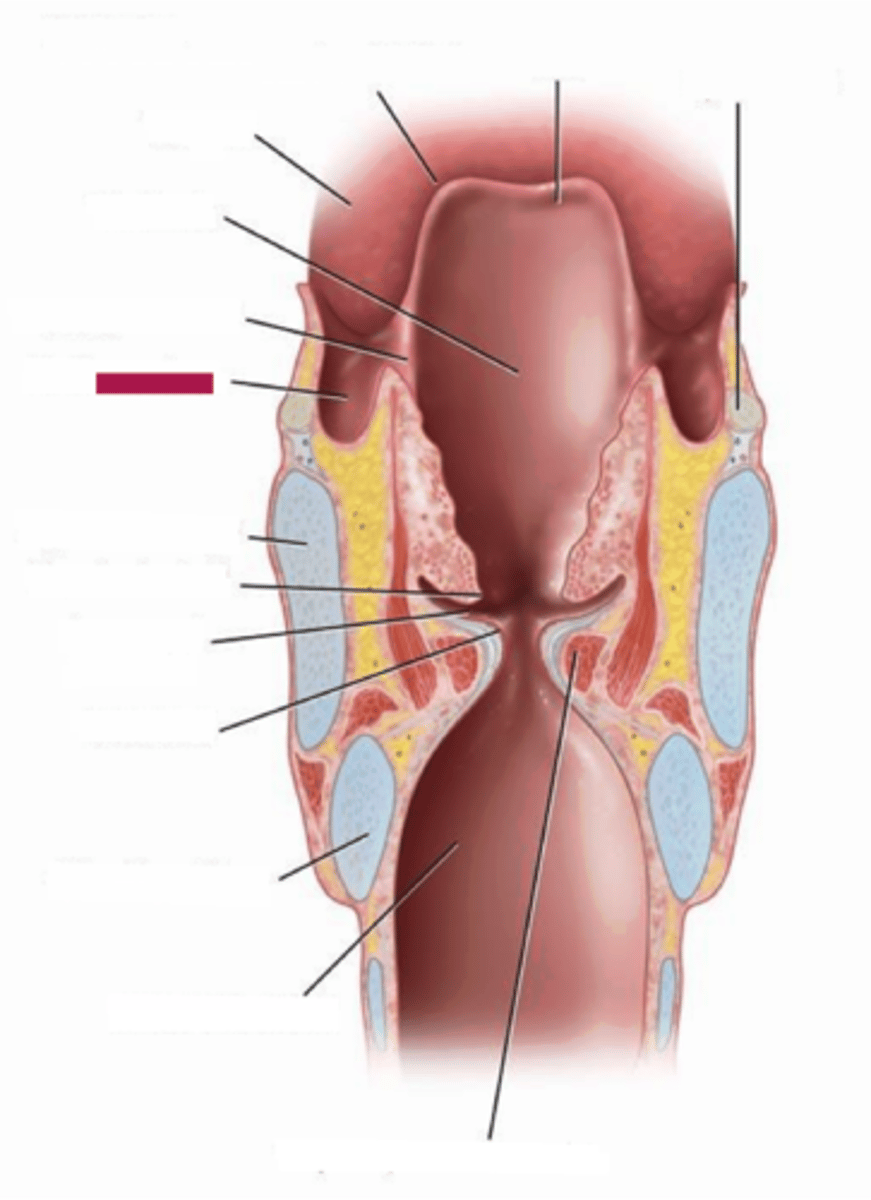
glottis
- opening between vocal folds
- triangular shape during quiet respiration
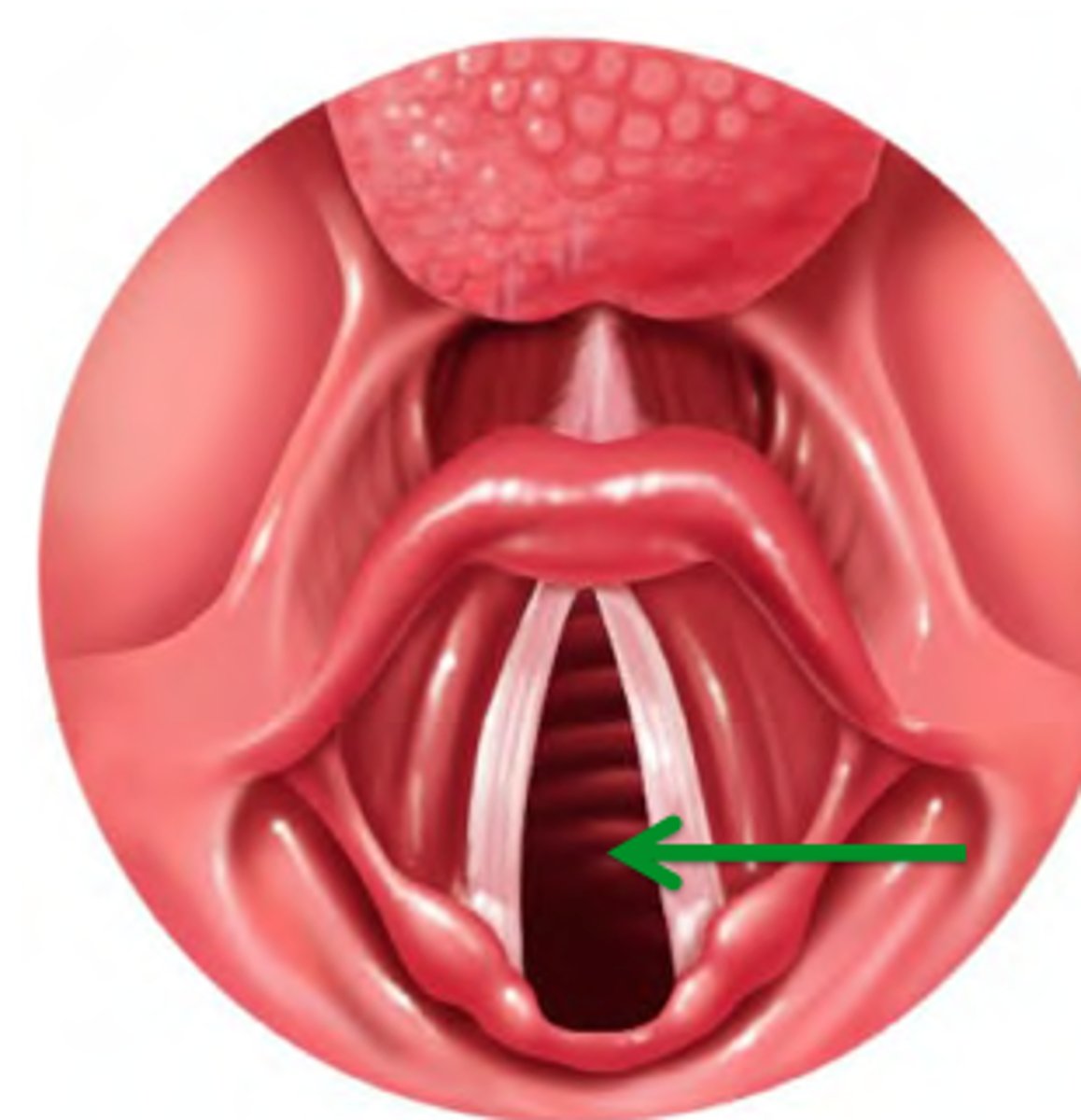
anterior commissure
the anterior most region of the glottis
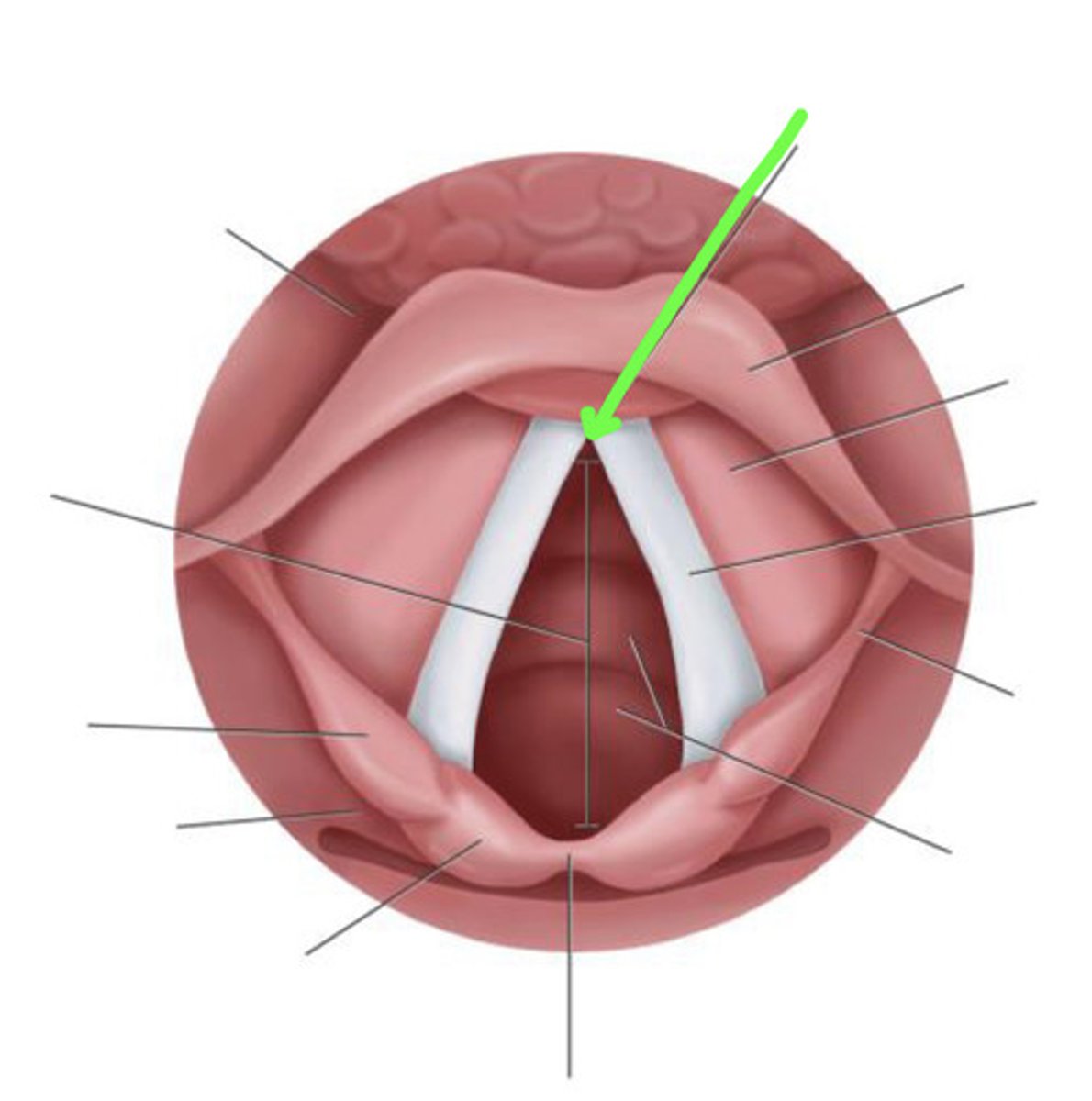
posterior commissure
the posterior most region
layers of the vocal folds
cover:
- epithelium
- superficial lamina propria (Reinke's space)
transition/vocal alignment:
- intermediate lamina propria
- deep lamina propria
body:
- thyroarytenoid
epithelium (of cover of vocal fold)
- part of the cover layers of the vocal folds
- mucosal covering of stratified squamous cells
- needs a thin layer of mucous lubrication for best oscillation
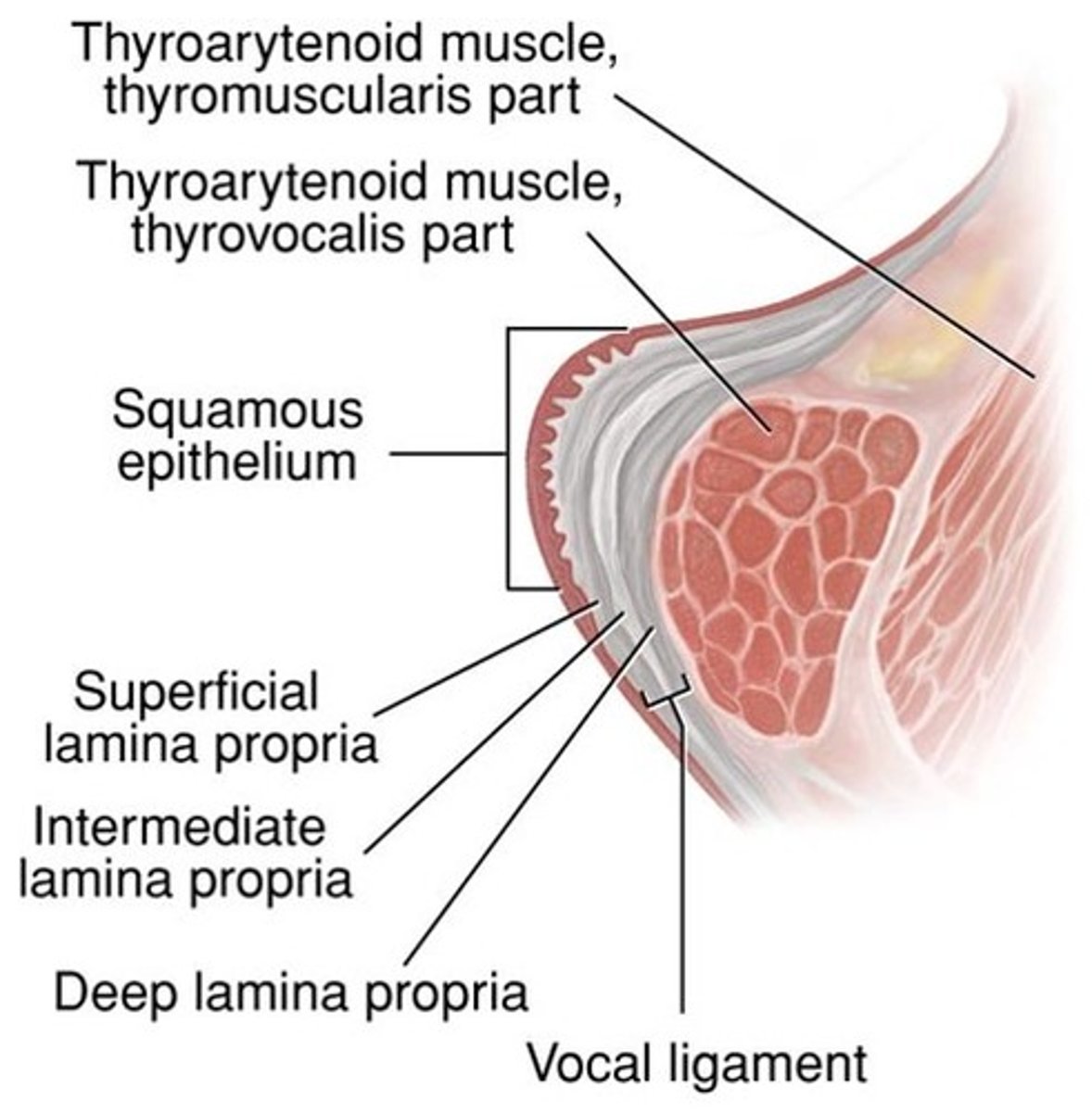
superficial lamina propria (Reinke's space)
- part of the cover layers of the vocal folds
- extracellular gelatin matrix
- helps cushion the vocal folds
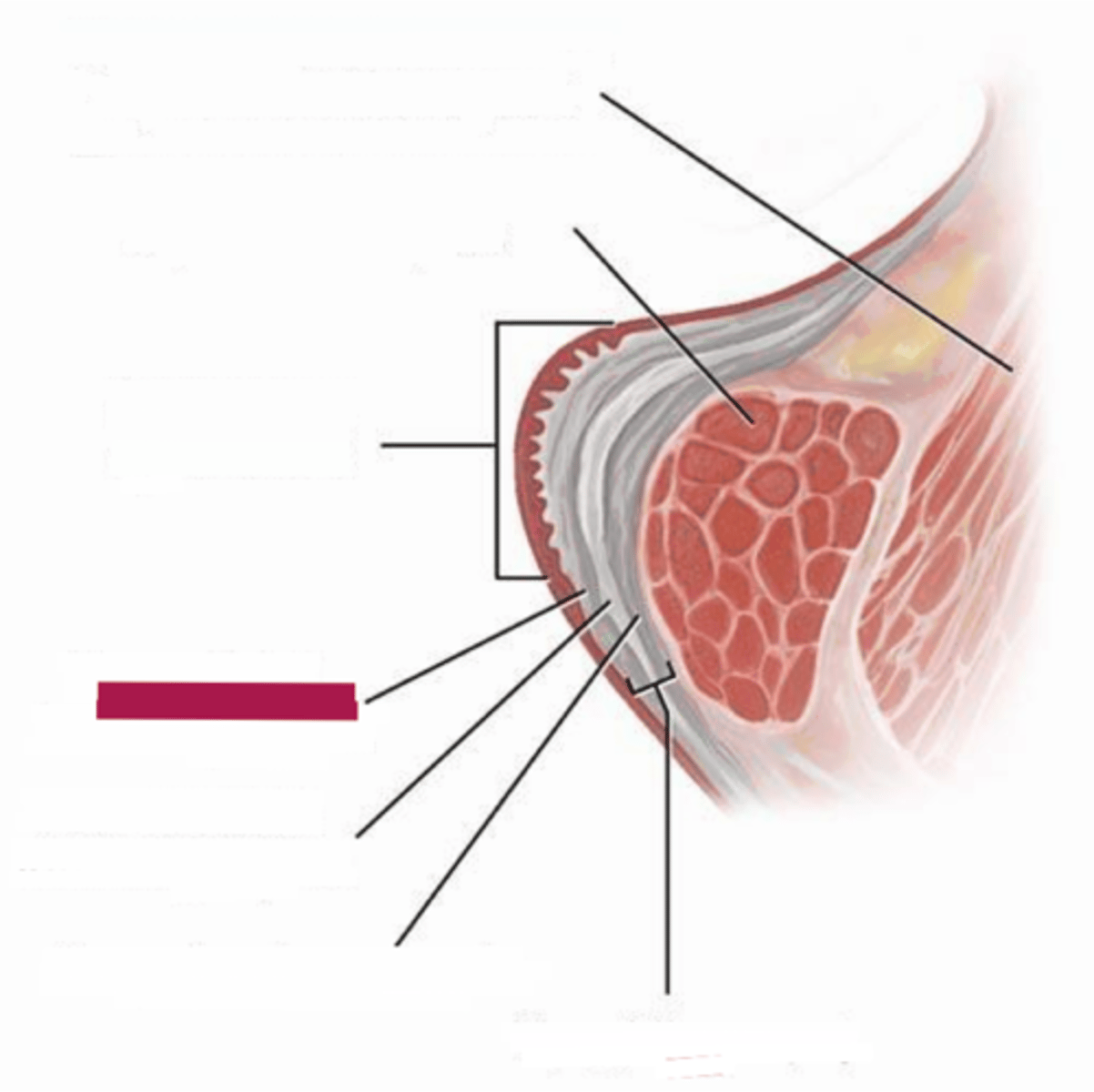
intermediate lamina propria
- part of the transition (vocal ligament) of the vocal folds
- compose of elastic fibers
- part of the vocal ligament

deep lamina propria
- part of the transition (vocal ligament) layers of the vocal folds
- collagen fibers
- supportive
- part of the vocal ligament
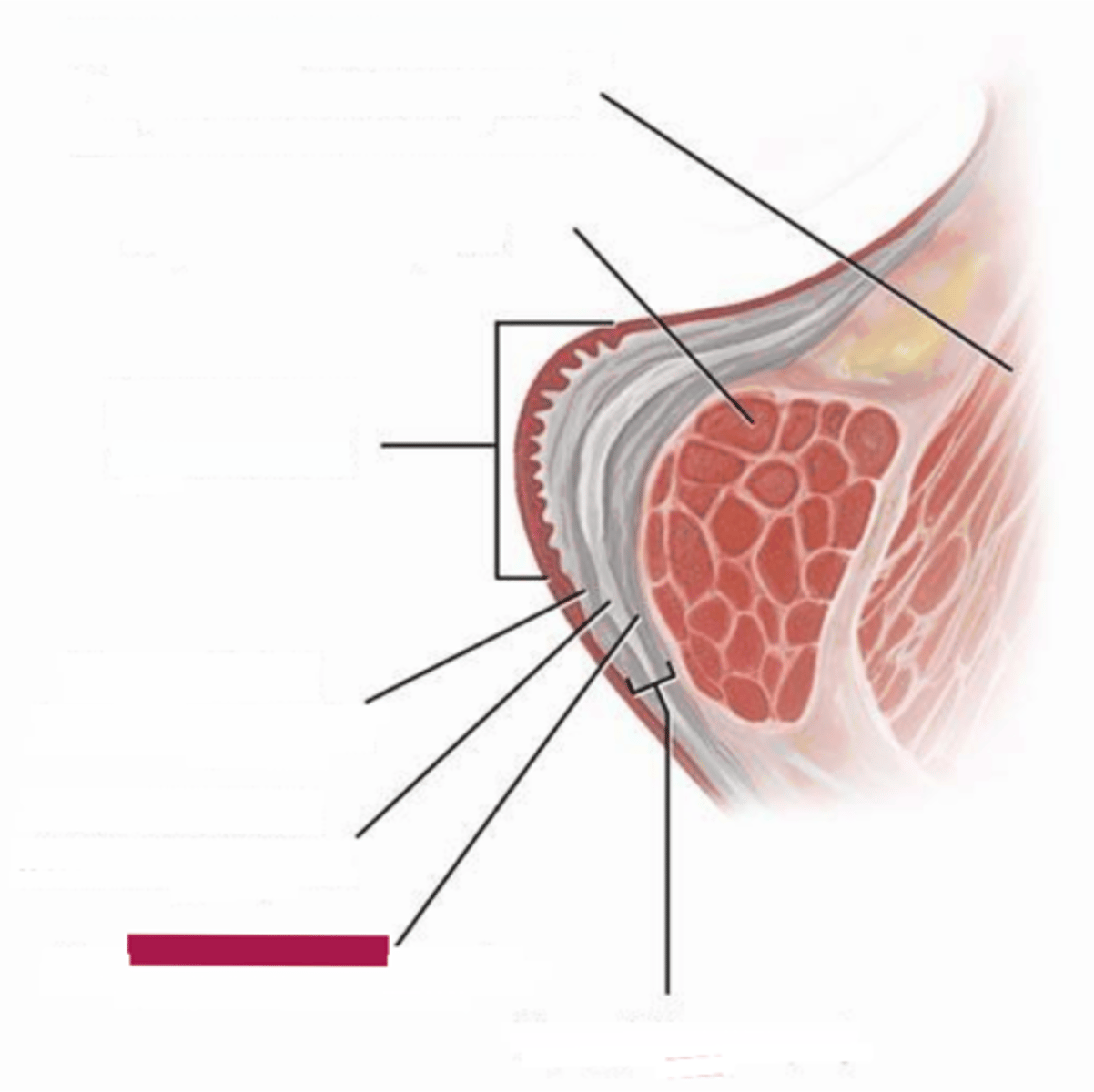
thyroarytenoid (of body of vocal fold)
- part of the body layers of the vocal folds
- thyrovocalis and thyromuscularis
- provides tone, stability, and mass
laryngeal musculature (function)
regulate valve openings and closing
- epiglottic value
- ventricular fold valve
- vocal fold valve
Provide movement of laryngeal cartilages for speech
intrinsic laryngeal muscles
- have both origin and insertion within the larynx
- make fine adjustments to the vocal mechanism
adductors
- lateral cricoarytenoid
- transverse arytenoid
- oblique arytenoid
abductors
- posterior cricoarytenoid
tensors
- cricothyroid
- thyrovocalis
relaxers
- thyromuscularis
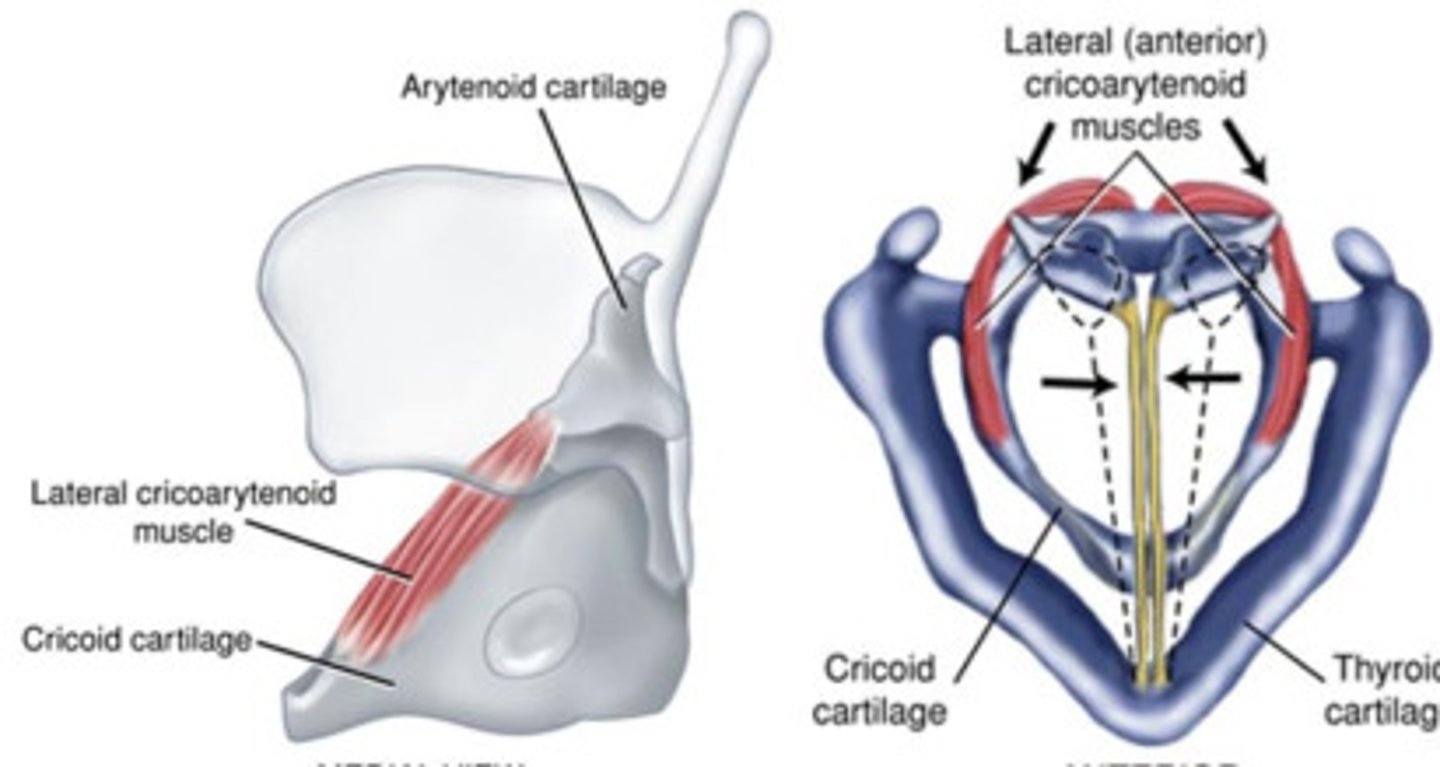
lateral cricoarytenoid
- adductor of intrinsic laryngeal muscles
- adducts (brings together) the vocal folds
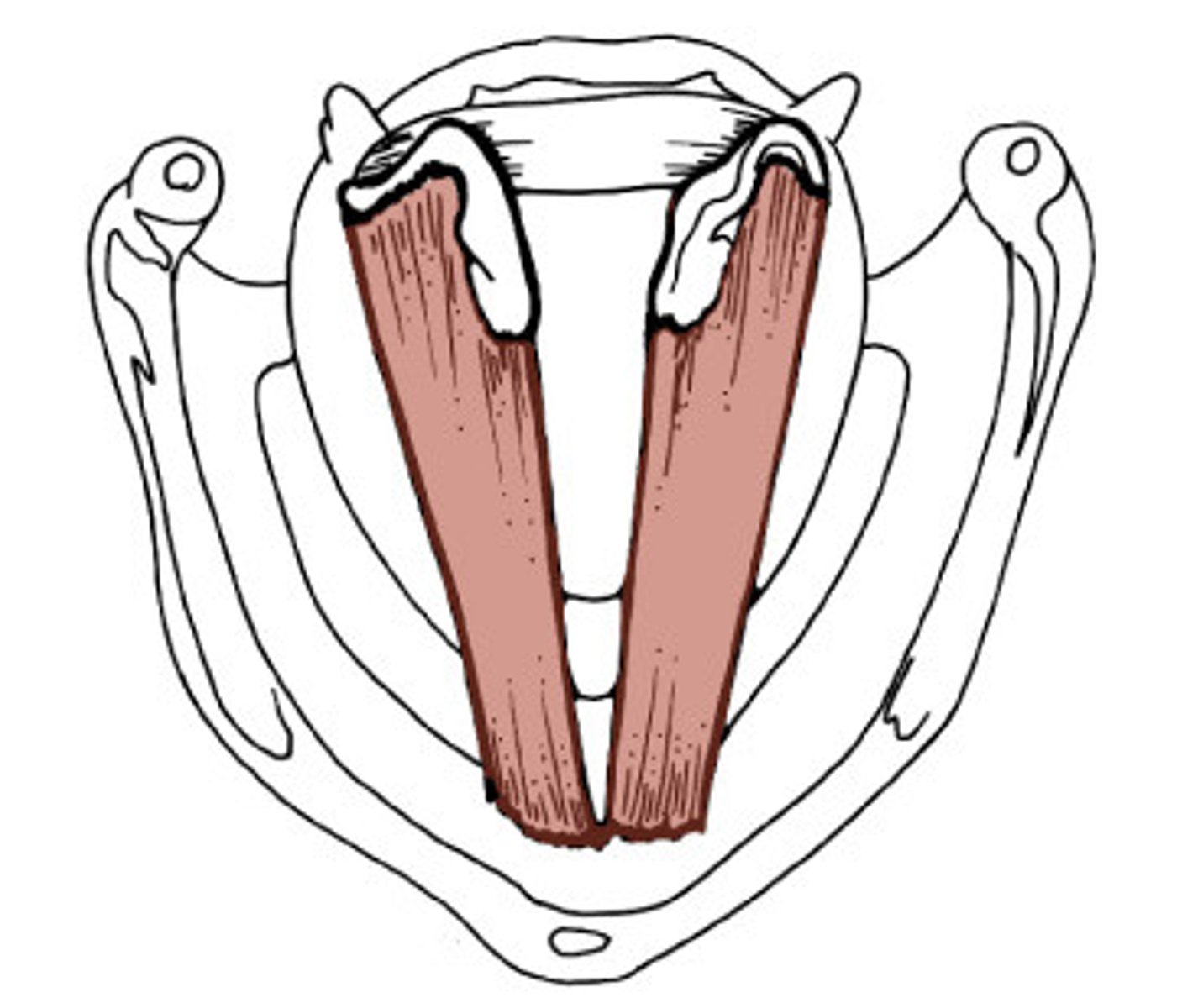
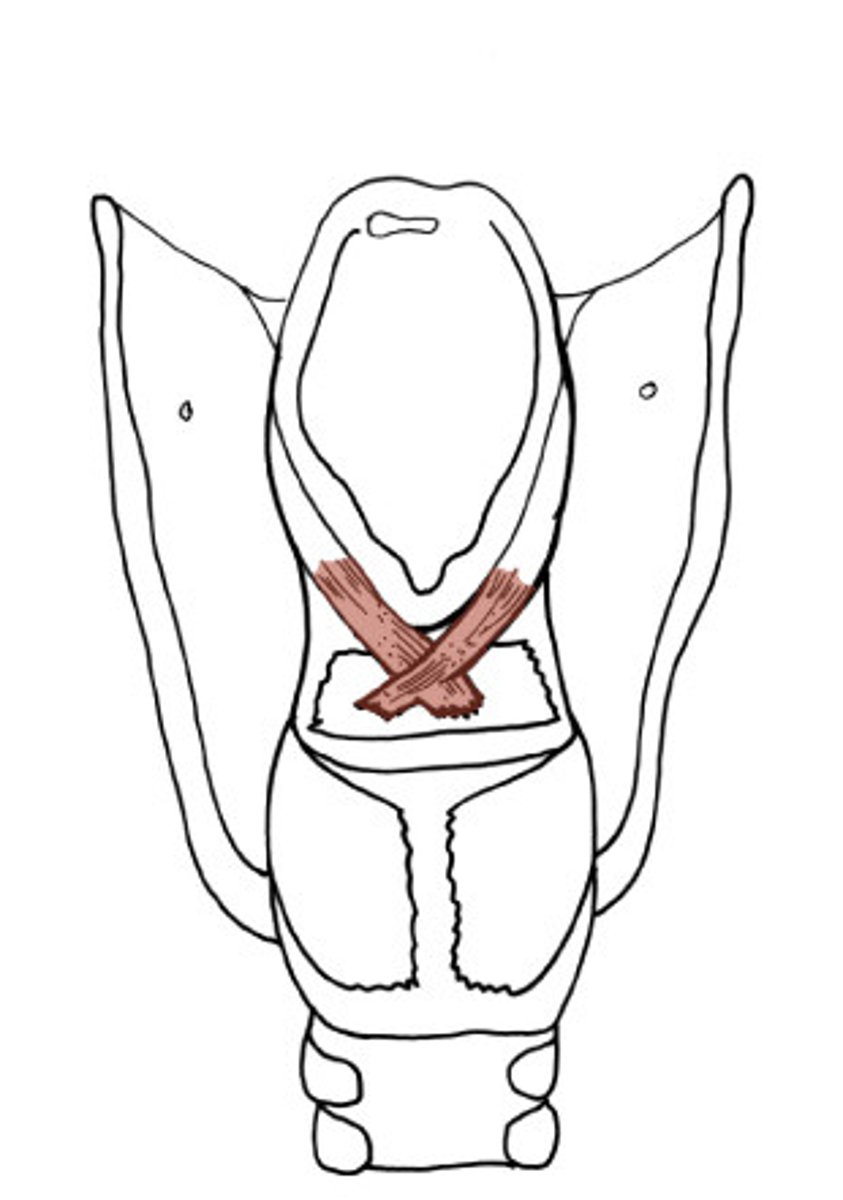
transverse arytenoid
- adductor of intrinsic laryngeal muscles
- specifically, only unpaired intrinsic muscle of ___
- adducts (brings together) the vocal folds
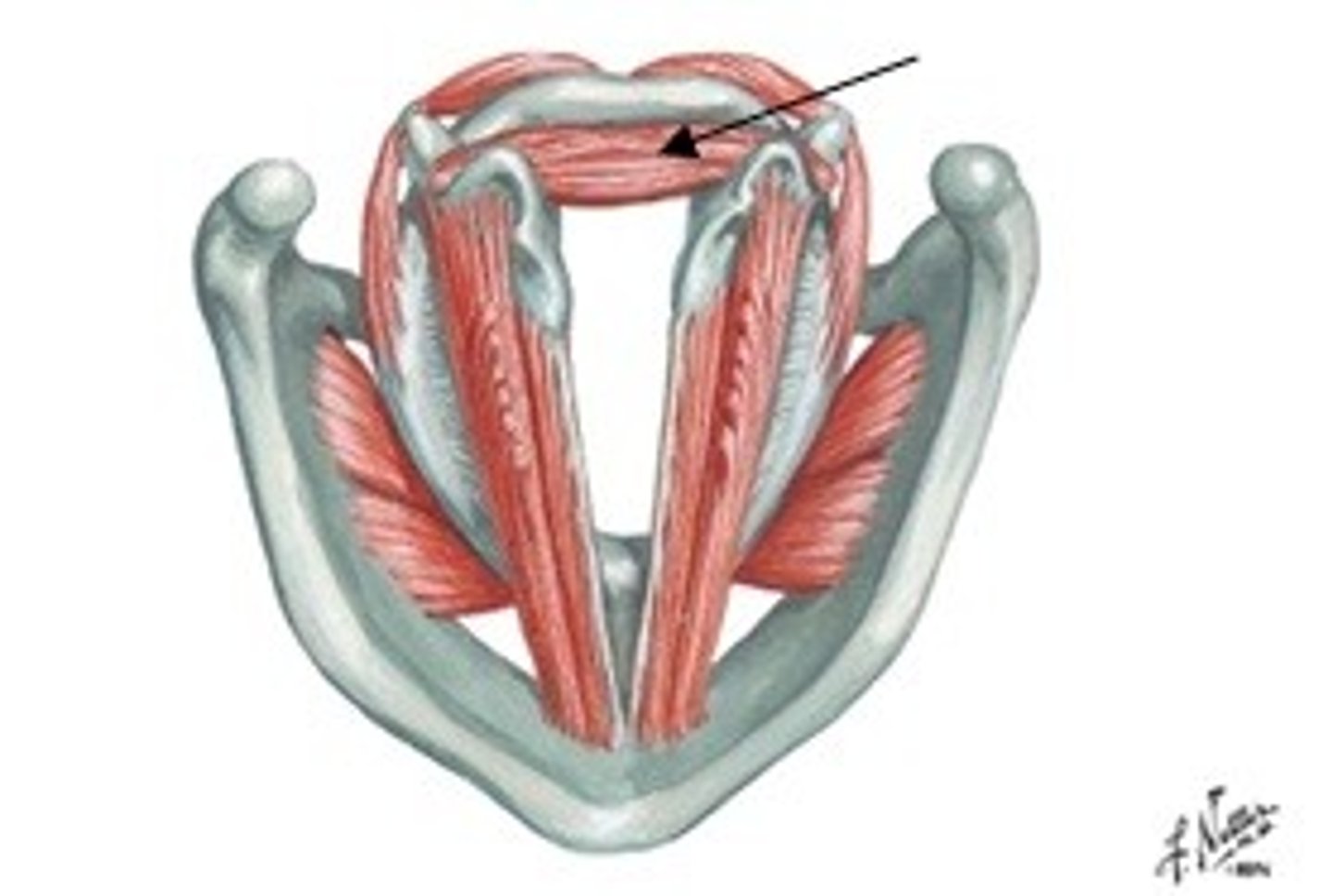
oblique arytenoid
- adductor of intrinsic laryngeal muscles
- adducts the vocal folds (how tightly they are pressed against each other), rocks arytenoid and vocal folds down and inward
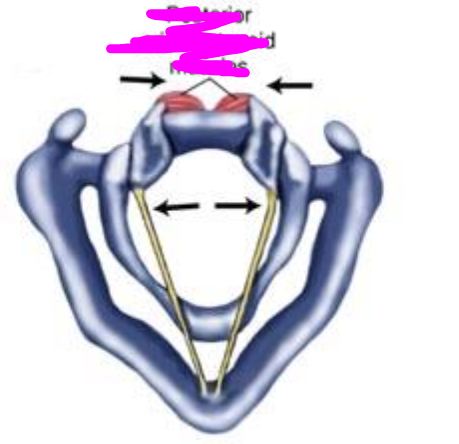
posterior cricoarytenoid
- abductor of intrinsic laryngeal muscles
- abducts vocal folds
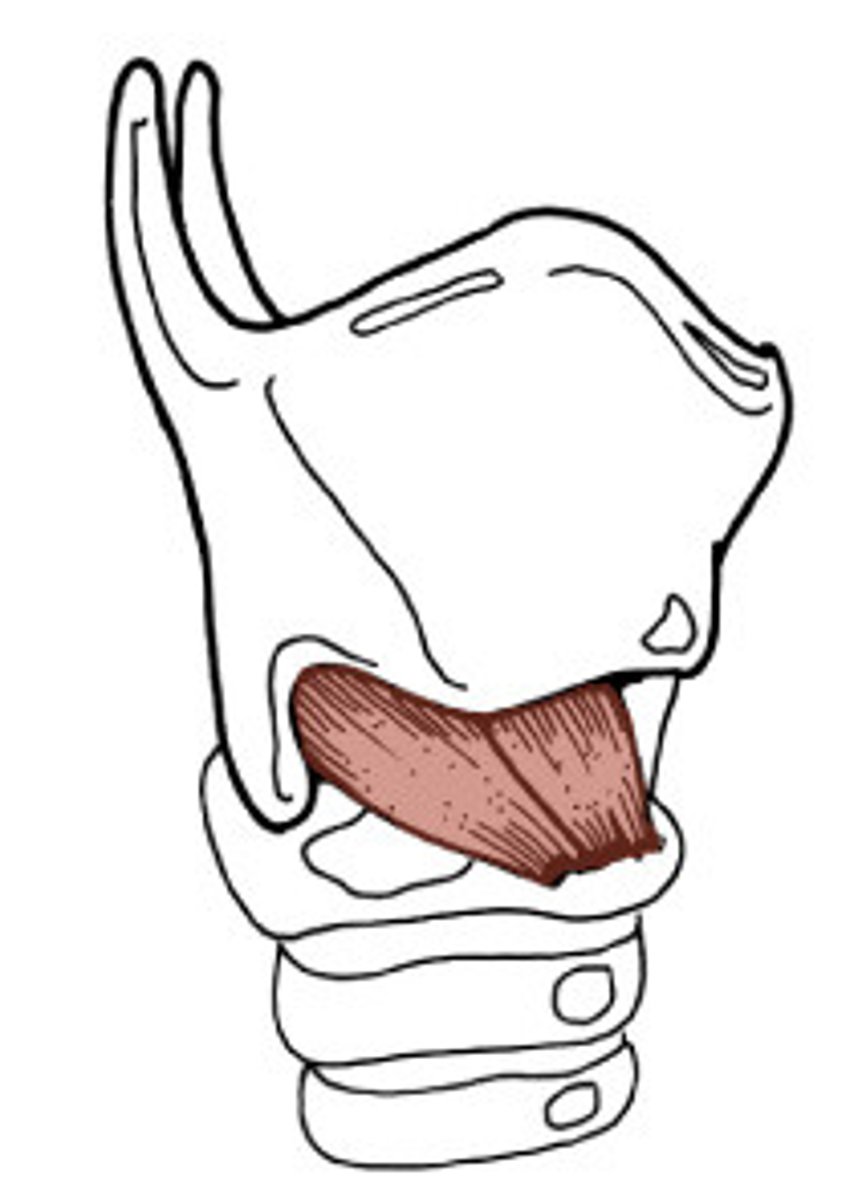
cricothyroid muscle
- tensor of intrinsic laryngeal muscles
- primary tensor of the vocal folds
- responsible for laryngeal adjustments associated with pitch change
- pars recta
- pars oblique
pars recta (of cricothyroid)
- rotates thyroid cartilage downward
vertical part
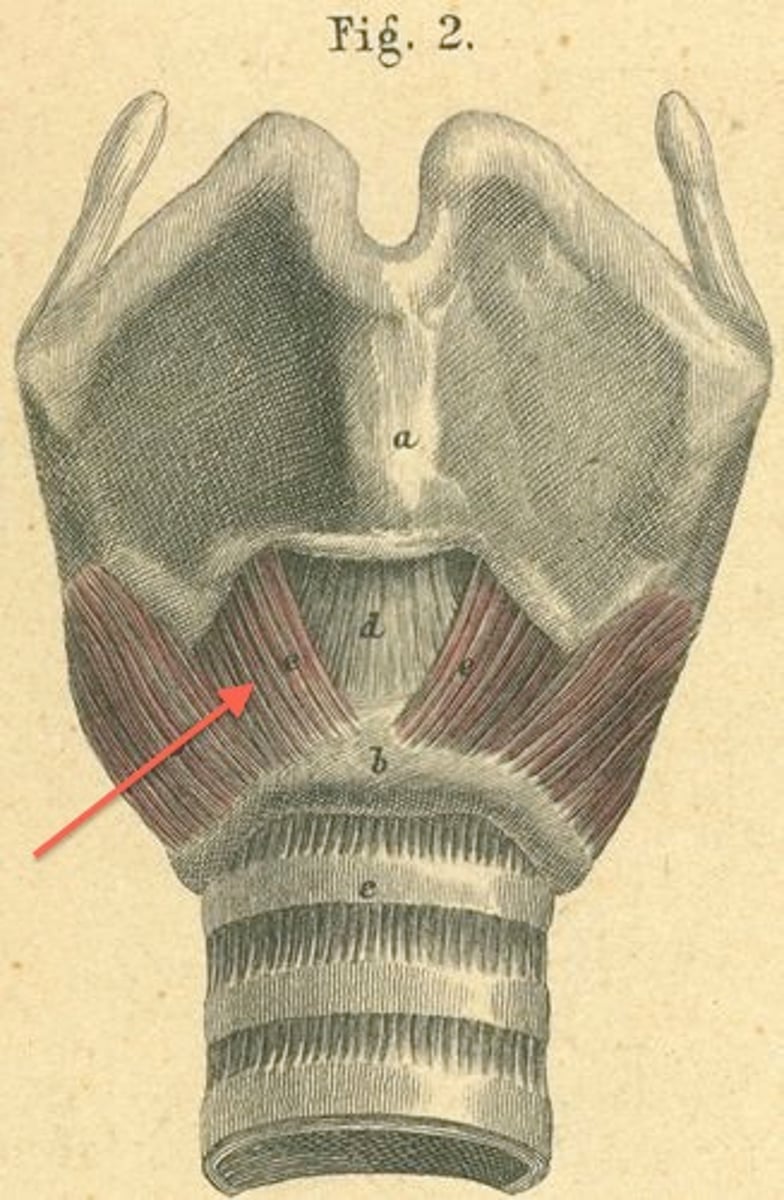
pars oblique (of cricothyroid)
- rotates thyroid cartilage downward
- stretches vocal folds
oblique part
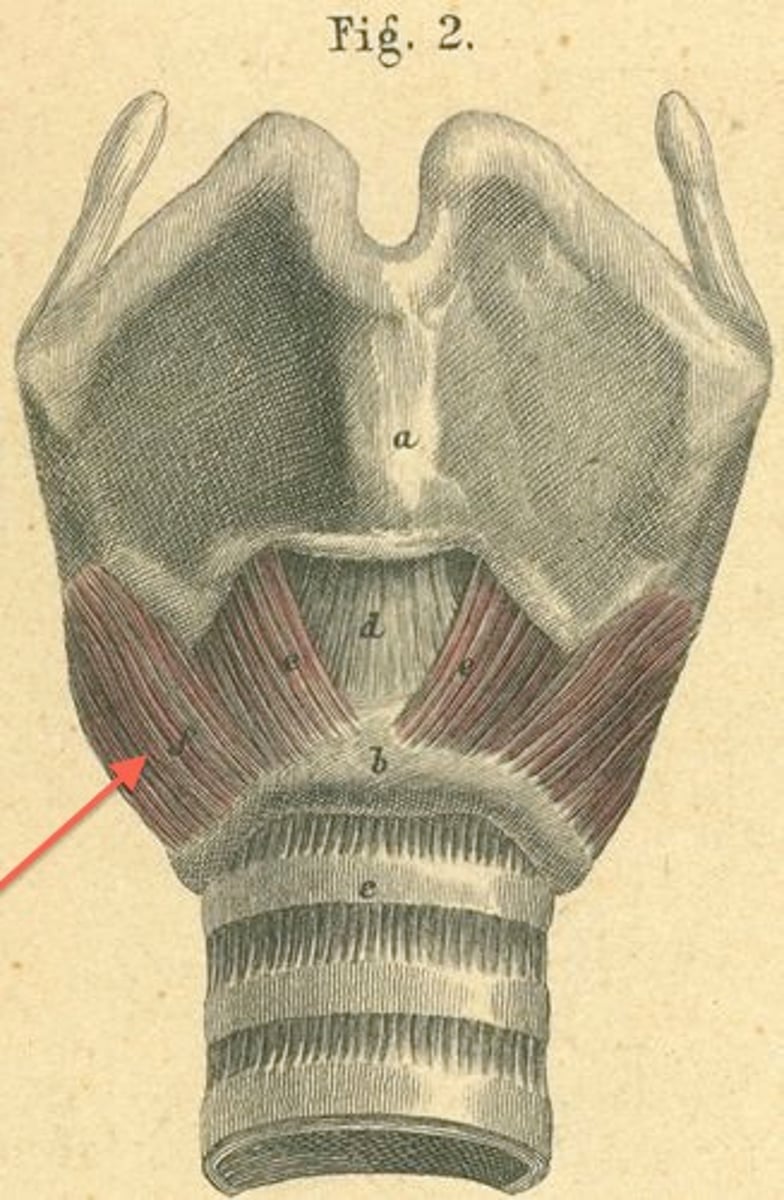
thyrovocalis
- tensor of intrinsic laryngeal muscles
- body of the vocal folds
- part of thyroarytenoid
- tenses vocal folds
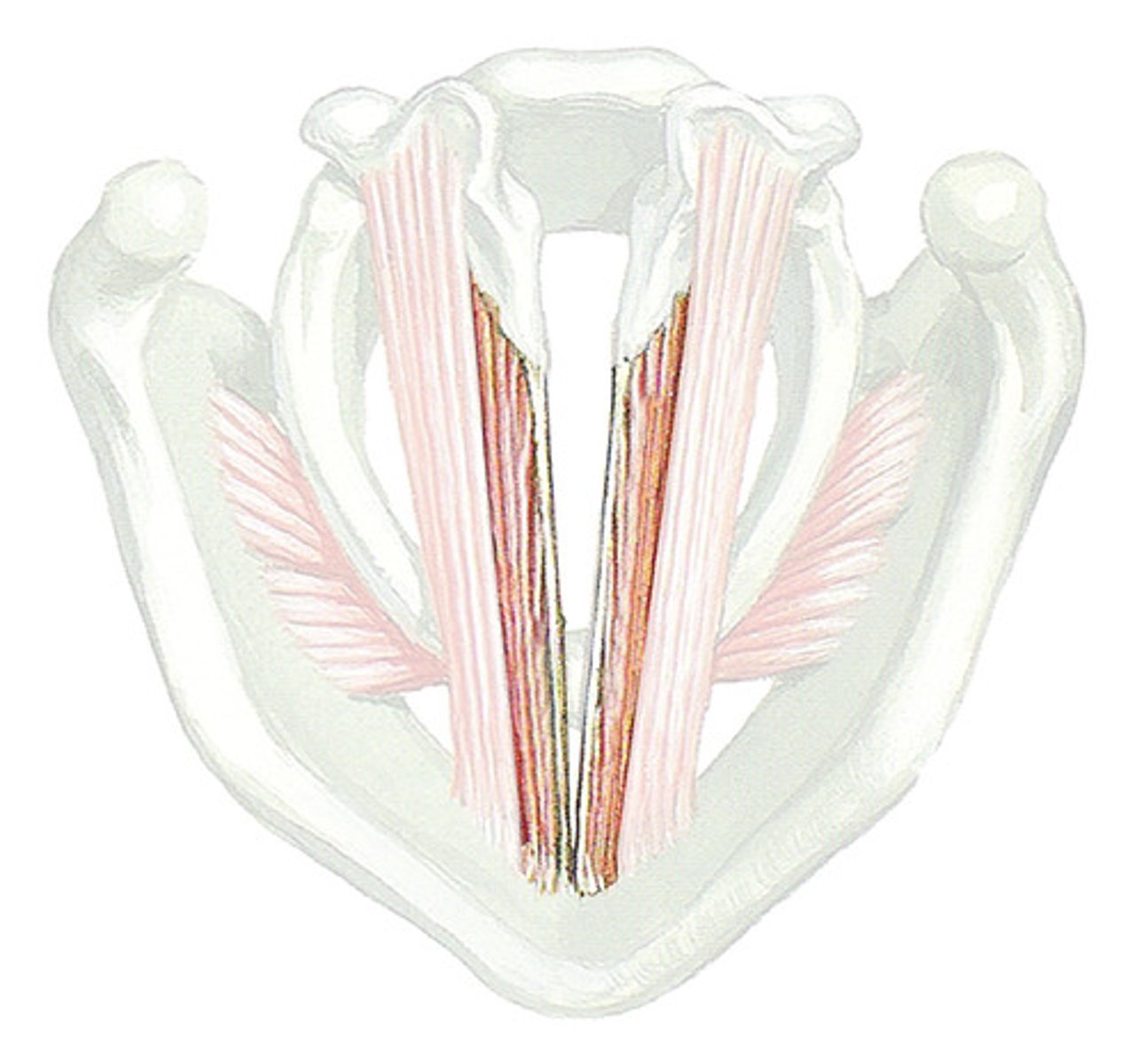
thyromuscularis
- relaxer of intrinsic laryngeal muscles
- part of the thyroarytenoid
- shorten and relax vocal folds
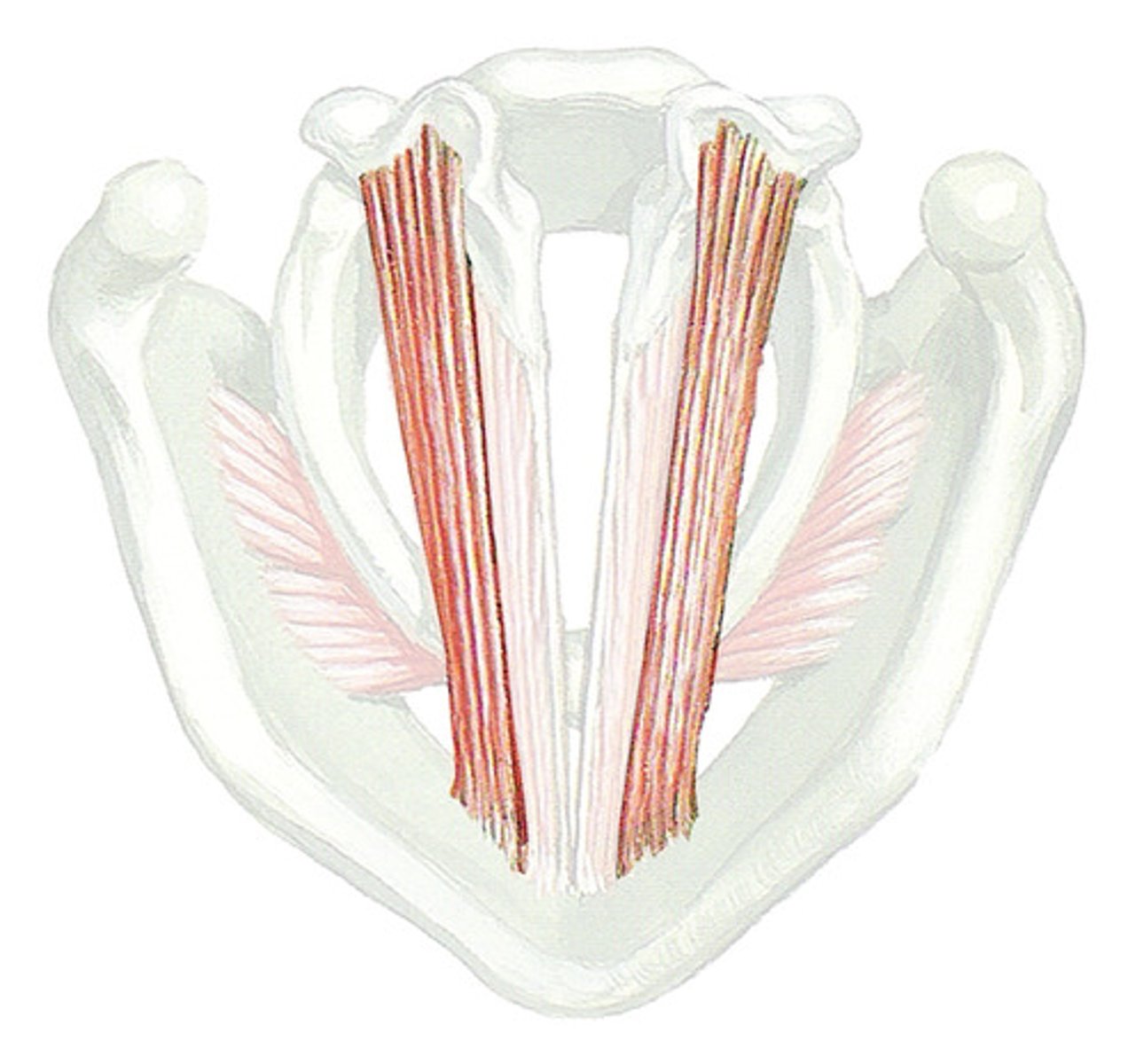
extrinsic muscles of the laryngeal musculature
- forms a network that surrounds the larynx and anchors it in position within the neck
- makes major adjustment to larynx, elevating and depressing
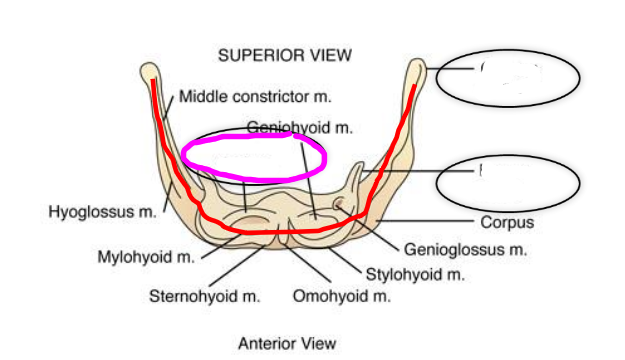
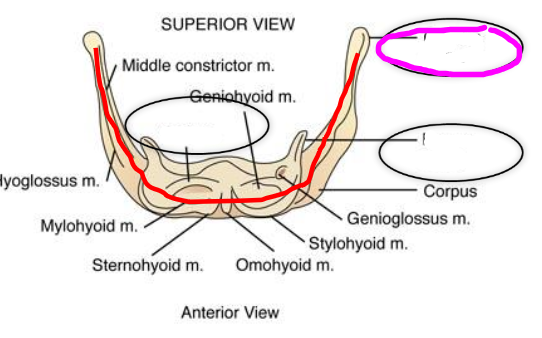
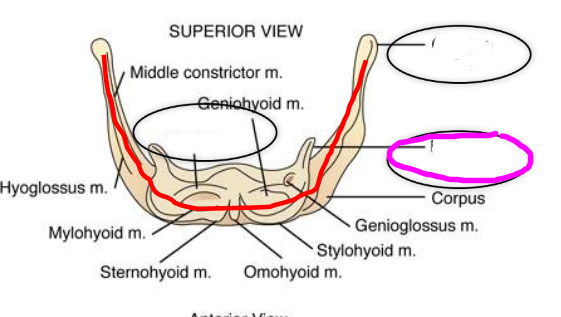
Hyoid and Laryngeal Elevators
- digastricus
- stylohyoid muscle
- mylohyoid muscle
- geniohyoid muscle
- genioglossus muscle
- hyoglossus muscle
Hyoid and Laryngeal Depressors
- sternohyoid muscle
- omohyoid muscle
- sternothyroid muscle
- throhyoid muscle
digastricus
- extrinsic muscle, Hyoid and Laryngeal Elevators
- anterior: elevates hyoid anteriorly
- posterior: elevates hyoid bone posteriorly
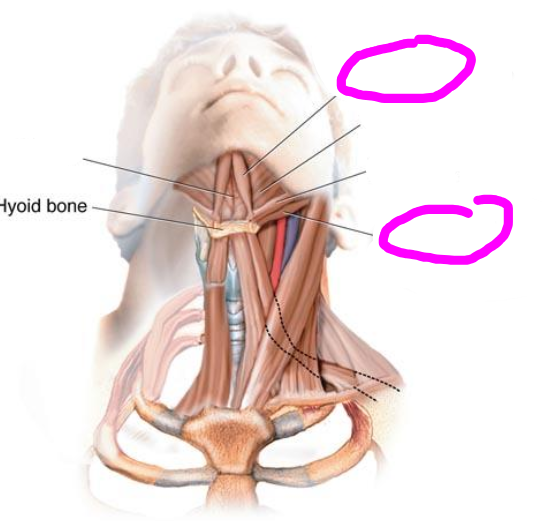
stylohyoid muscle
- extrinsic muscle, Hyoid and Laryngeal Elevators
- elevates hyoid posteriorly
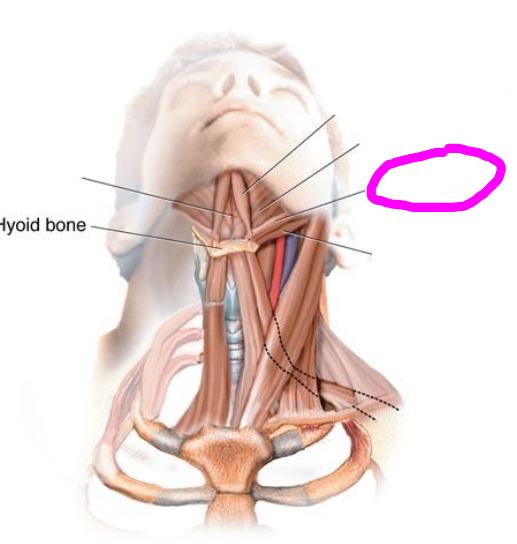
mylohyoid muscle
- extrinsic muscle, Hyoid and Laryngeal Elevators
- makes up the floor of the oral cavity
- elevates the hyoid anteriorly
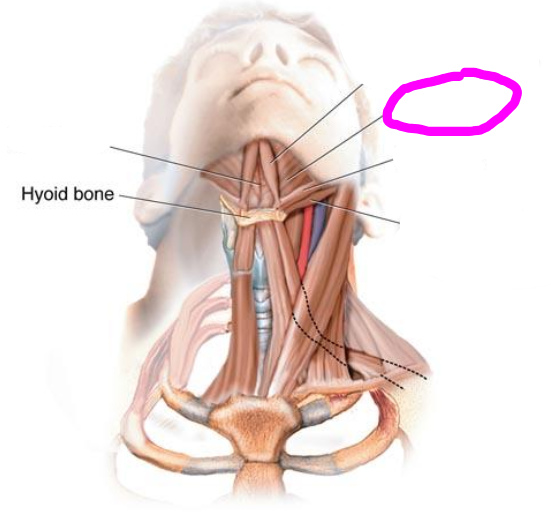
geniohyoid muscle
- extrinsic muscle, Hyoid and Laryngeal Elevators
- elevates hyoid anteriorly
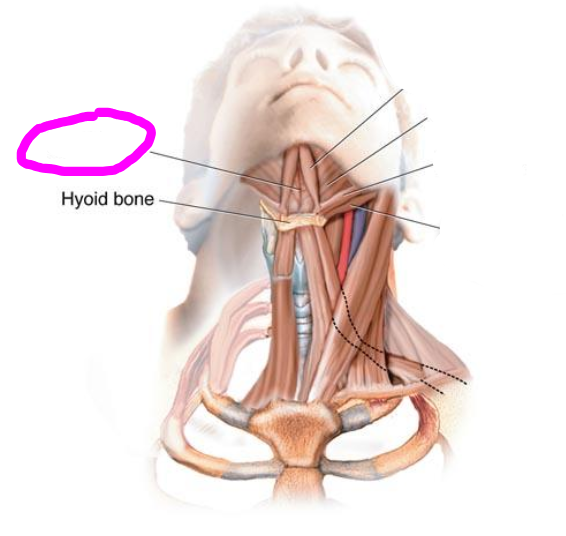
genioglossus muscle
- extrinsic muscle, Hyoid and Laryngeal Elevators
- forms the primary muscle of the tongue
- elevates hyoid
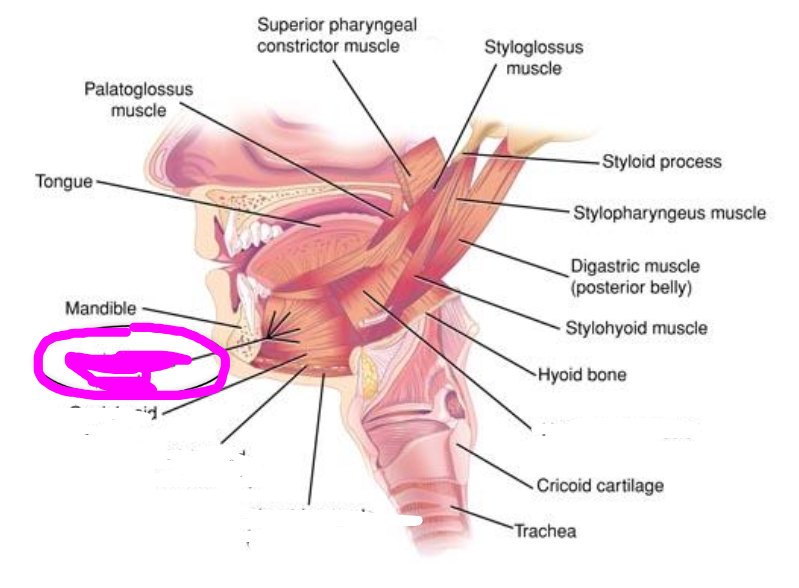
hyoglossus muscle
- extrinsic muscle, Hyoid and Laryngeal Elevators
- elevates hyoid and depresses tongue
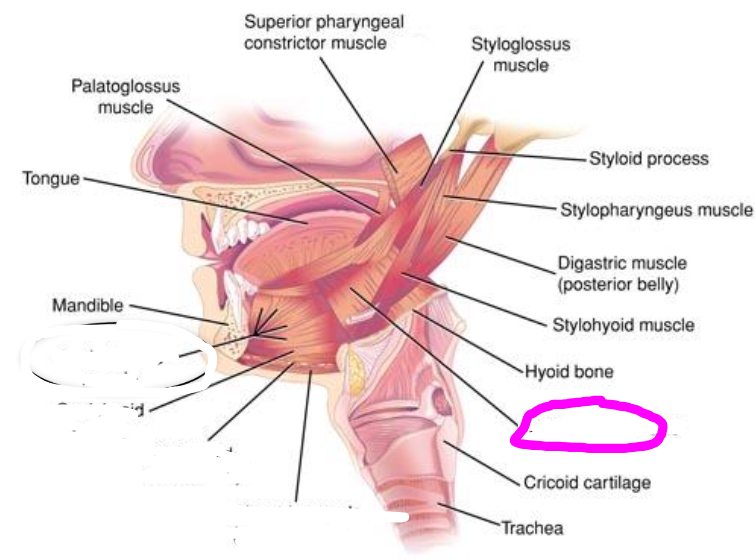
sternohyoid muscle
- extrinsic muscle, Hyoid and Laryngeal depressors
- depresses hyoid
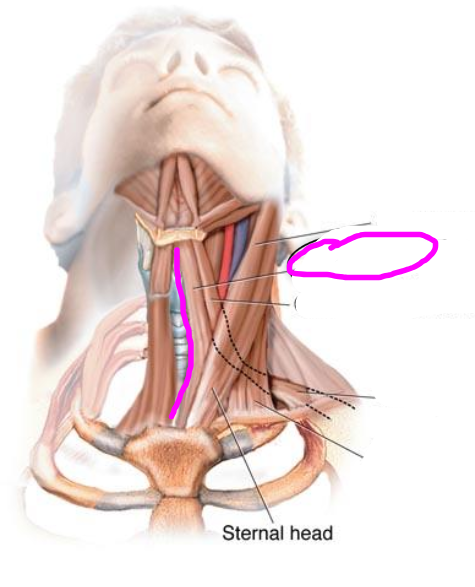
omohyoid muscle
- extrinsic muscle, Hyoid and Laryngeal depressors
- superior and inferior
- depresses hyoid
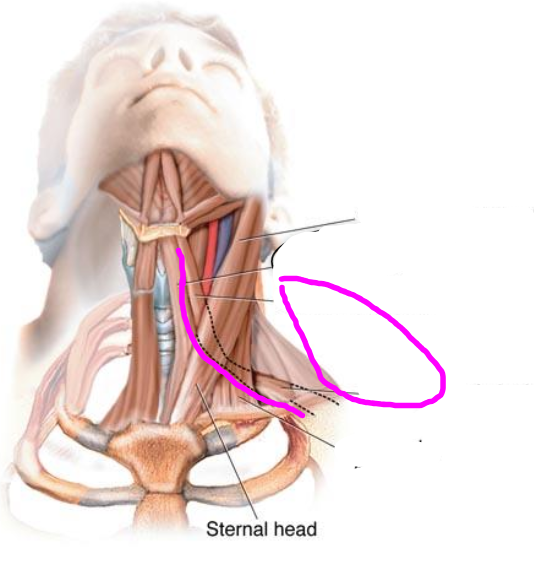
sternothyroid muscle
- extrinsic muscle, Hyoid and Laryngeal depressors
- assist with producing high and low pitch
- helps make fine adjustments to vocal folds
- depresses thyroid cartilage
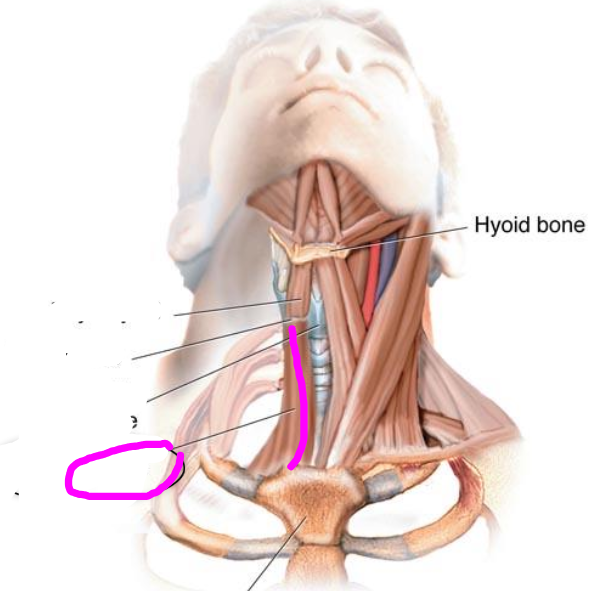
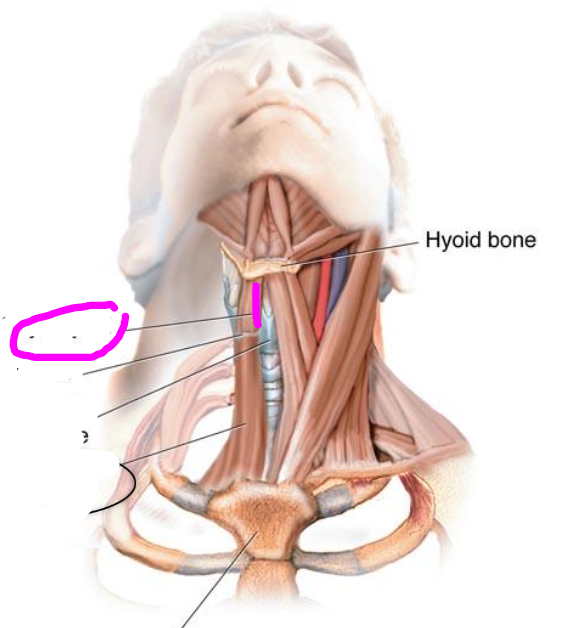
thyrohyoid muscle
- extrinsic muscle, Hyoid and Laryngeal depressors
- depresses hyoid or elevates larynx
vocal fold vibration
NOT the product of repeated adduction and abduction of the vocal folds
instead, myoelastic-aerodynamic theory of phonation
Myoelastic
• Elasticity: Returns to original shape after being displaced
(Vocal folds: muscles covered by delicate membranes. This soft tissue allows them to move when sufficient force is exerted.)
• Stiffness: Strength of material that restores it to original shape
• Inertia: a body in motion tends to stay in motion
Aerodynamic
• Bernoulli's Principle
o ↑velocity of airflow @ point of constriction
o ↓ air pressure perpendicular to flow
laryngeal function
o Attack
adduct vocal folds to initiate phonation
o Sustain Phonation
maintain laryngeal posture, ongoing airflow maintains the vibration
o Termination
abduct vocal folds to stop phonation
frequency
- rate of vibration of an object
- measured in cycles per second (hertz-Hz)
pitch
- perception of sound's frequency
- vibration rate related to vocal fold's
1. thickness (mass),
2. length, and
3. elasticity (tension)
higher pitch
- the faster the vibration (the higher the frequency) the higher the sound will be perceived
- contraction of cricothyroid muscles lengthens vocal folds and thins medial edge
lower pitch
- the slower the vibration (the lower the frequency) the lower the sound will be perceived
- the contraction of thyromuscularis:
brings thyroid cartilage and arytenoids closer together
& shortens vocal fold length, making them more massive and less tense
amplitude
- amount of displacement of an object from its rest position
- measured in decibels (dB)
loudness
perception of the sound's amplitude
Increase:
o ↑ amplitude ↑ loudness
o ↑ medial compression of vocal folds:
---Vocal folds press together more tightly
---Vocal folds press together for a longer period of time
normal voice quality
Maximum frequency range
• voice is flexible in pitch during conversation
Minimum-maximum amplitude
• voice is able to vary loudness
Maximum phonation time
• Measured by the longest period of time that an
individual can sustain a vowel on one breath
--Adults: 15 - 25 seconds
--Children: at least 10
• Coordinated air flow with vocal fold adduction
Minimal additive noise
• Minimal breathiness or roughness
dysphonia
- generic term for any voice that sounds deviant in terms of quality, pitch, or loudness
- breathiness
- rough/hoarse voice
(abnormal voice qualities)
breathiness
- vocal folds dont close completely during each vibratory cycle
- air leakage at the glottis creates a friction noise
- breathy noise is measured at the higher frequencies
(dysphonia)
rough/hoarse voice
- excessive vocal fold closure during phonation
- vocal folds vibrate in a less periodic cycle
- rough/hoarse noice is measured at the lower frequencies
(dysphoina)
laryngitis
- inflammation of the vocal folds
- caused by excessive use of the voice, infections, inhaled irritants, or reflux
(vocal fold disorders)
vocal nodules
- noncancerous growths on the vocal cords, similar to a callus
- most often caused by vocal abuse
(vocal fold disorders)
vocal polyps
soft noncancerous growth similar to a blister
(vocal fold disorders)
vocal fold paralysis
- one or both vocal folds doesn't open or close
- caused by injury, problems in surgery, stroke, cancer, neurological disorders
(vocal fold disorders)
relaxed whisper (facilitative and aversive activities of the vocal folds)
- less stressful to vocal folds
- more open and softer
forced whisper (facilitative and aversive activities of the vocal folds)
- strong funneled air stream
- stiffened folds
- turbulence just above glottis
yawning (facilitative and aversive activities of the vocal folds)
facilitates relaxation of vocal tract musculature
coughing (facilitative and aversive activities of the vocal folds)
- airway protection
- encourage adduction of vocal folds
- prolonged __ abusive to vocal folds
throat clearing (facilitative and aversive activities of the vocal folds)
- vocal folds grate on each other
- can help remove irritants
- entire larynx goes into stressful movements
- encourage very soft & breathy clearing
- loud or frequent = abusive to vocal folds
laughing (facilitative and aversive activities of the vocal folds)
- laryngeal musculature are reflexively relaxed
- can help generate efficient vocal physiology in therapy
- can cause excessive laryngeal pressure & stress if done too loudly or excessively
crying (facilitative and aversive activities of the vocal folds)
- open relaxed cry: enriched resonance between the vocal folds and the supraglottic resonating spaces
- tight, loud, or excessive crying: laryngeal and supraglottic musculature are tensed