General pathology: Cell injury
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Apoptosis
Necrosis
A selective irreversible injury is known as ___ where as an unselective cell injury is known as ___?
Inadequate blood supply to organ or body part
Define Ischemia?
When there is membrane damage W/ lysosomal enzymes
At what point does ischemia become irreversible?
Decrease in mitochondrial function -> decrease in ATP -> Decrease in Na pump (more solutes in cell) -> water build up in cell/ swelling
What is the pathway of ischemic cell injury?
Intracellular acidosis decreases protein synthesis resulting cell membrane defects. This causes lysosomes to rupture and RNAase and DNAase are released digesting the inside of the cell
With hypoxia cells will start anaerobic metabolism, why does this lead to cell death and rupture?
Fiborus connective tissue (scar tissue)
If there is a large number of cells killed or unable to be generated what will form to compensate for the dead tissue?
Small area of dead tissue due to failure of blood suply
Define infarct?
Reversible in which water will move into the cell causing it to swell.
Hydronic degeneration is what?
Bovine papular stomatitis (due to parapoxvirus)
What is an example of hydronic degeneration?
hydronic degeneration
identify the vacuolar degeneration of the cow tongue?
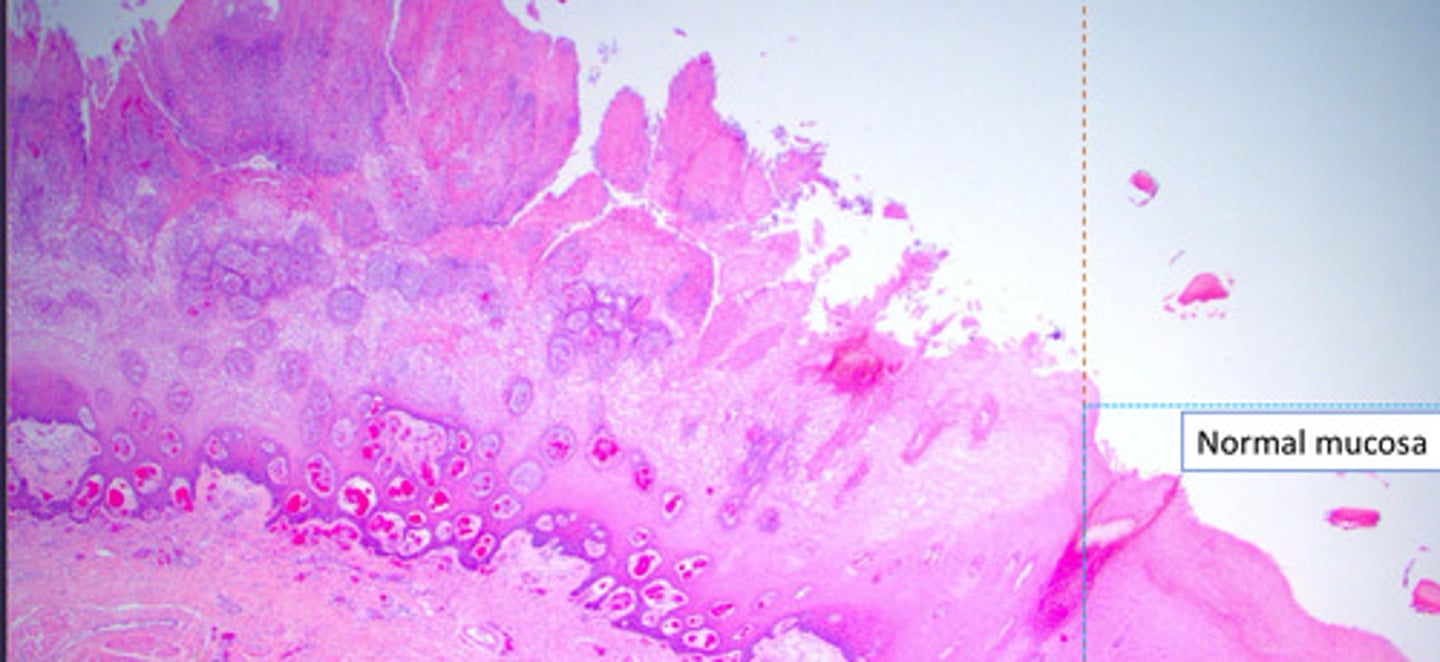
hydronic degeneration
identify the vacuolar degeneration of the of the oral cavity?
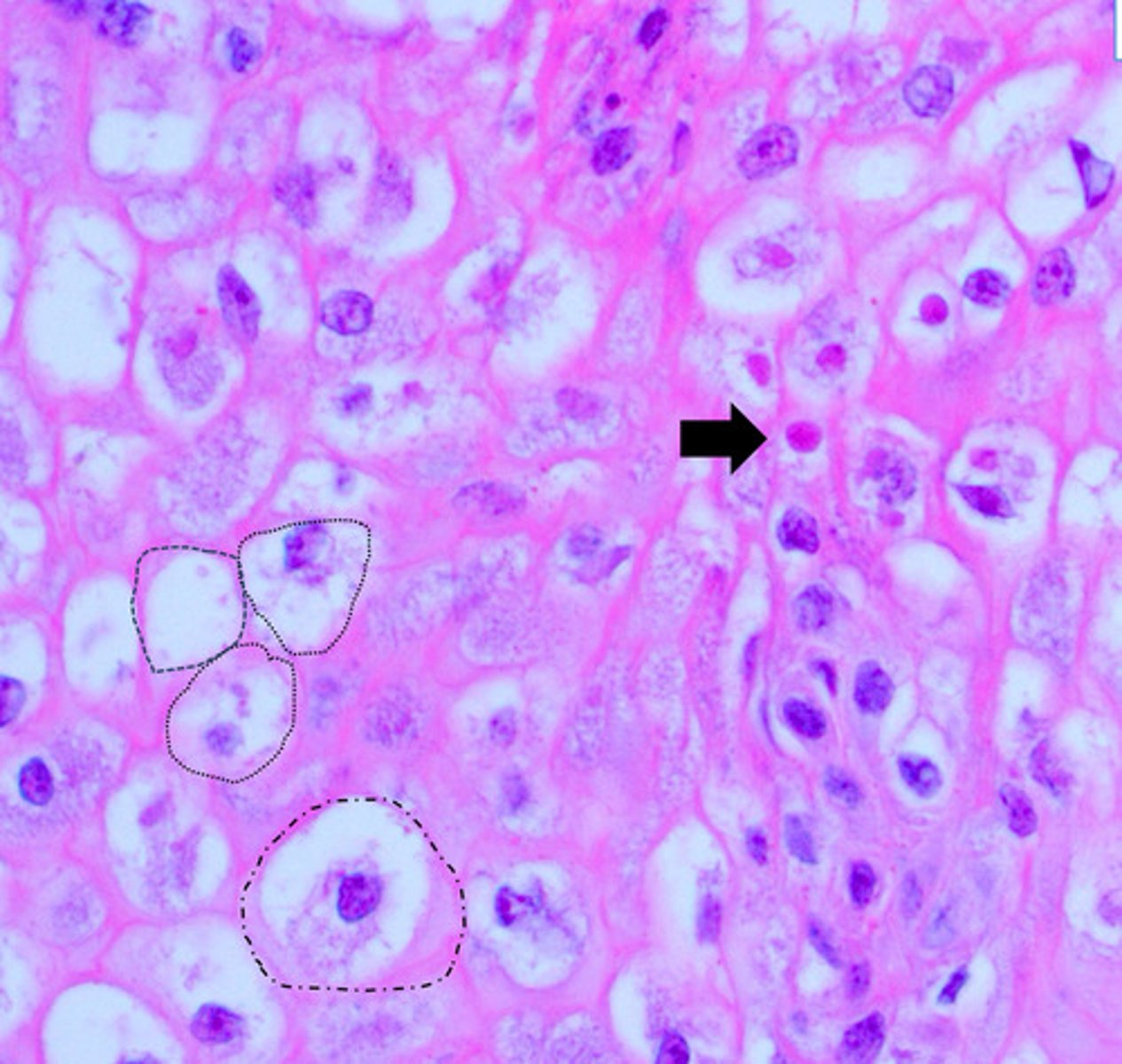
1. Excessive delivery of FFAs
2. Decreased oxidation/ use of FFAs
3. impaired synthesis of apoprotein
4. impaired formation of lipoproteins
5. impaired release of lipoproteins
What are the five causes of hepatic lipidosis?
Hepatic lipidosis
Identify the pathology?
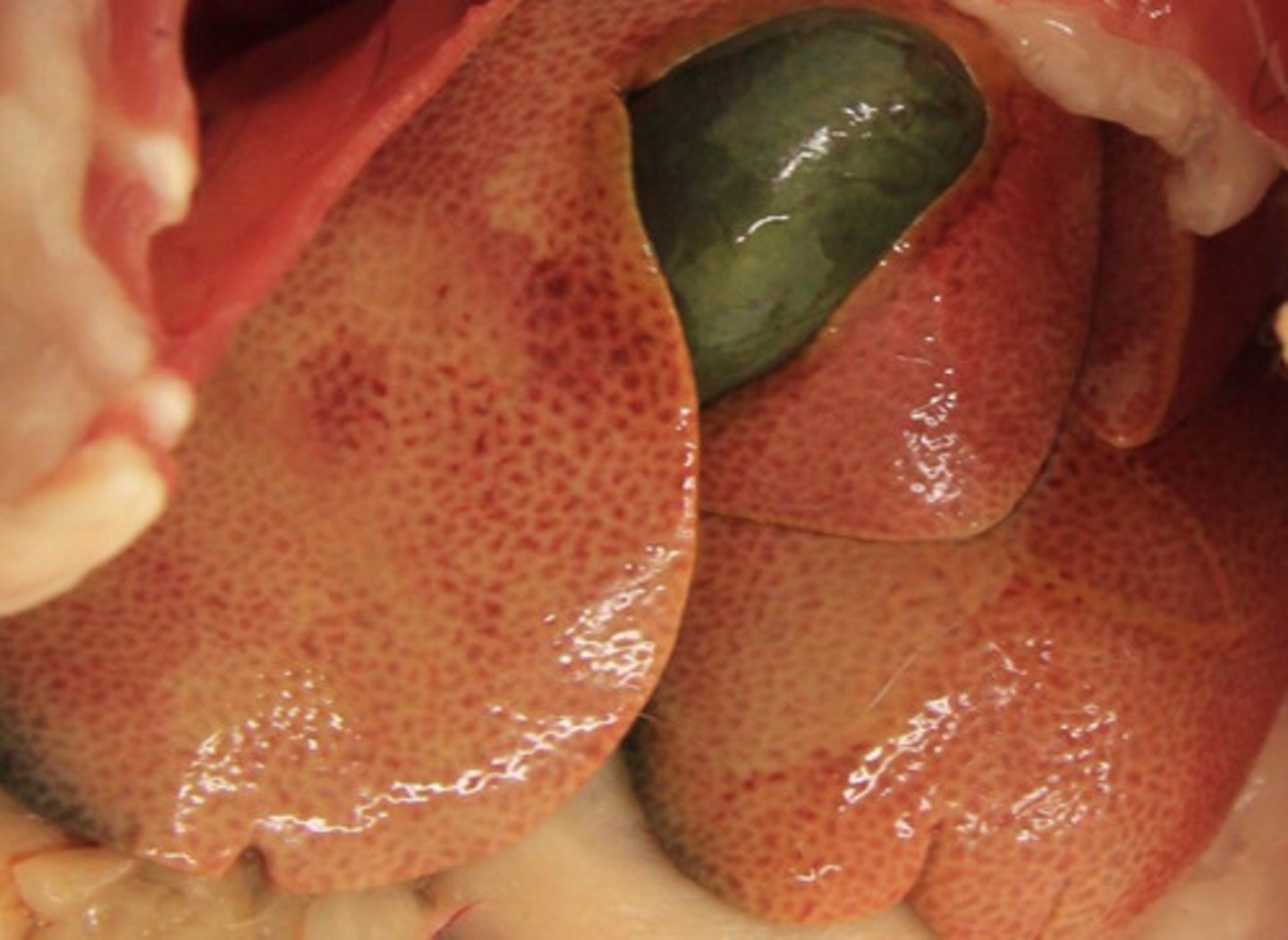
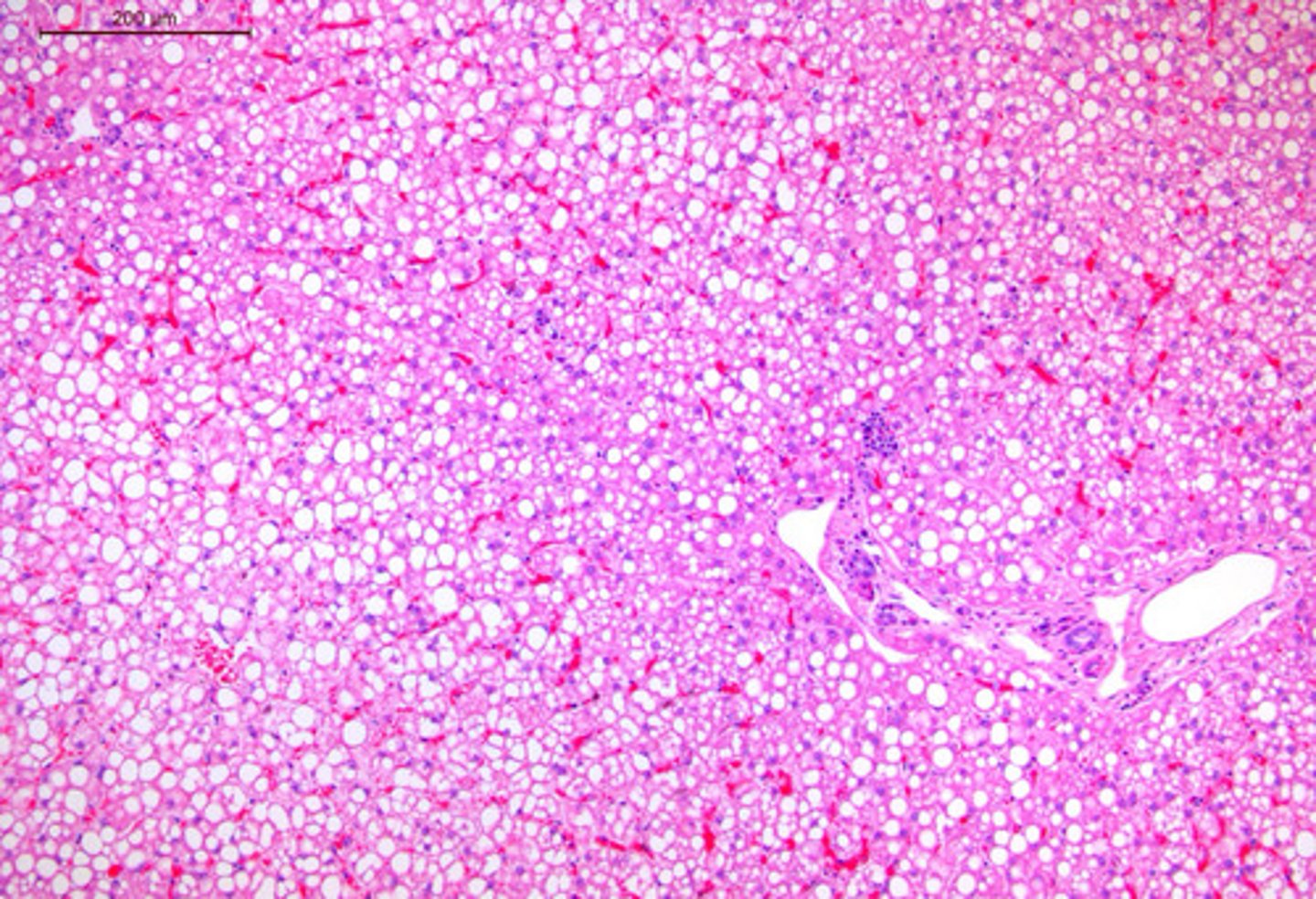
Hepatic lipidosis
Identify the microscopic pathology of the liver?
Liver will be a firm pale tan-white w/ glycogen accumulation
Hepatic lipidosis is usually yellow and friable.
How is hepatolipidosis different from glycogen accumulation visually?
Excess glucocorticoids, DM, Hyperglycemia
What are the causes of glycogen accumulation in the liver?
Glycogen accumulation
What is the pathology represented by the yellow circle?
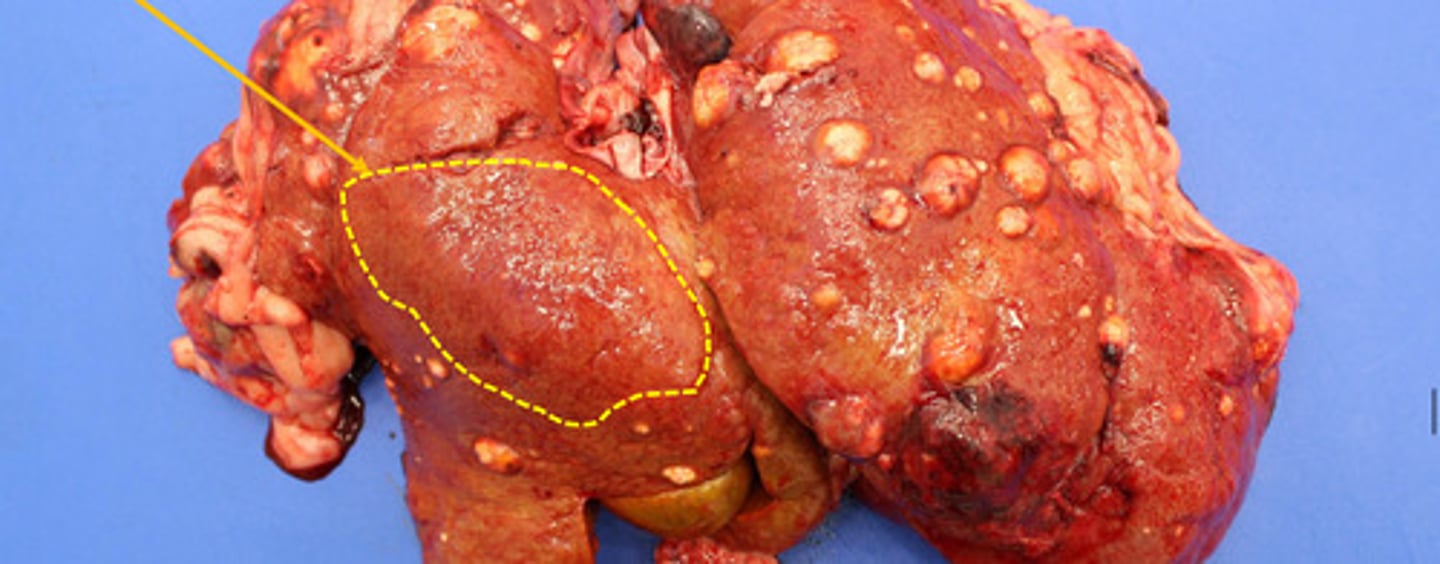
Glycogen accumulation
Identify the microscopic pathology of the liver?
Mis-folded proteins
lysosomal storage dz
Indigestible exogenous materials
What are some other forms of intracellular accumulation?
-hypoxic or ischemic inj
- Swelling and rupture of cell membrane causing inflammation and release of cellular content.
-Messy and pathological
What characteristics do we usually see with Necrosis?
Programed cell death in which cell shrinks due to physiological reasons
Cell membrane will stay intact forming apoptic bodies w/ no inflammation
What characteristics do we usually see w/ Apoptosis?
BAX and BAK proteins
In apoptosis intrinsic pathway a cell injury will occur stimulating what proteins to initiate the process?
BCL2, BCL-XL
What proteins regulate the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis?
cytochrom C which activates capases
What proteins do the mitochondria release to start the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis?
Fas and TNF receptor ligands.
What will trigger the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis?
9
8
The intrinsic pathway will use caspase __ and the extrinsic pathway will use caspase ___?
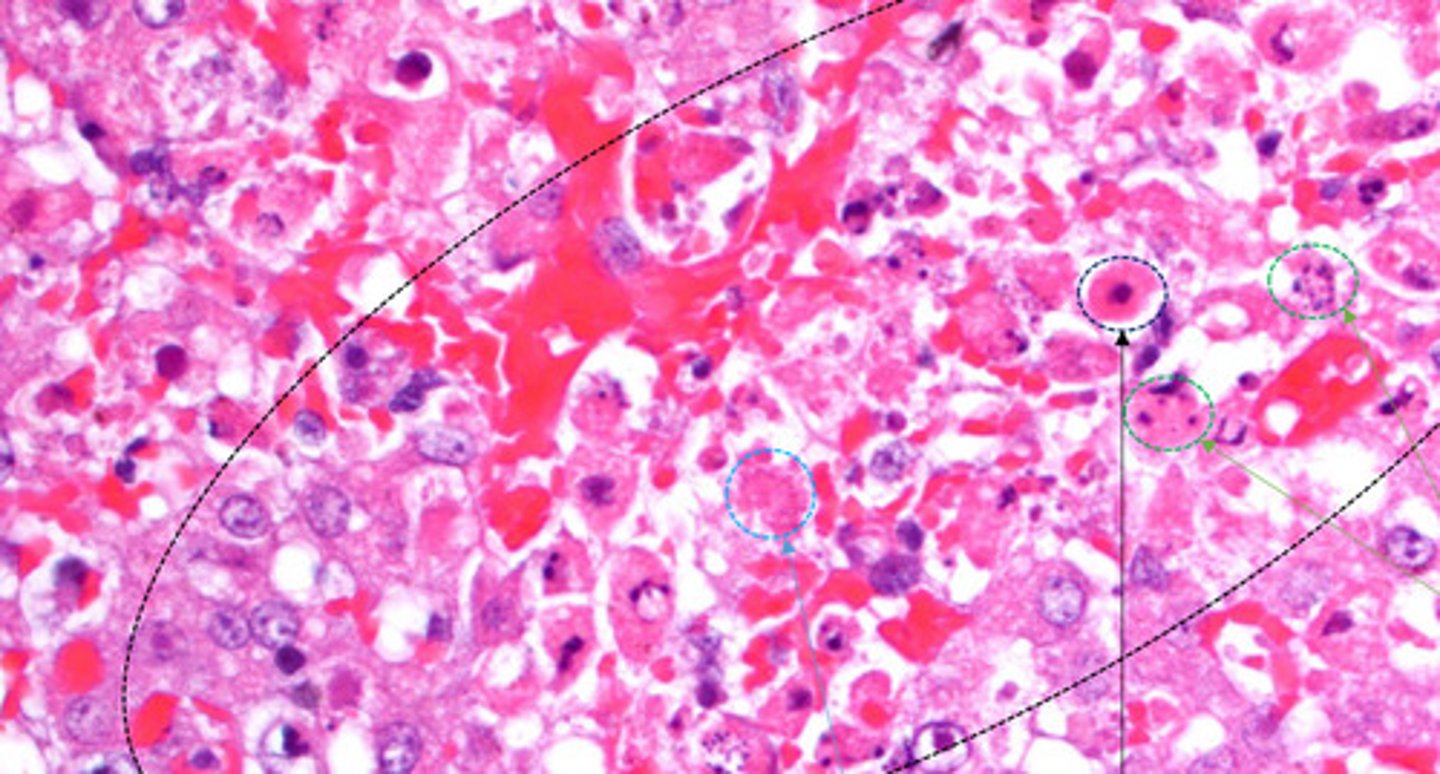
Irreversible condensation of chromatin in the nucleus
Define pyknosis?
Fragmentation of nucleus
Define karyorrhexis?
Pale nucleus
Define Karyolysis?
Karyolsis.
After what stage do we usually see absence of a nucleus?
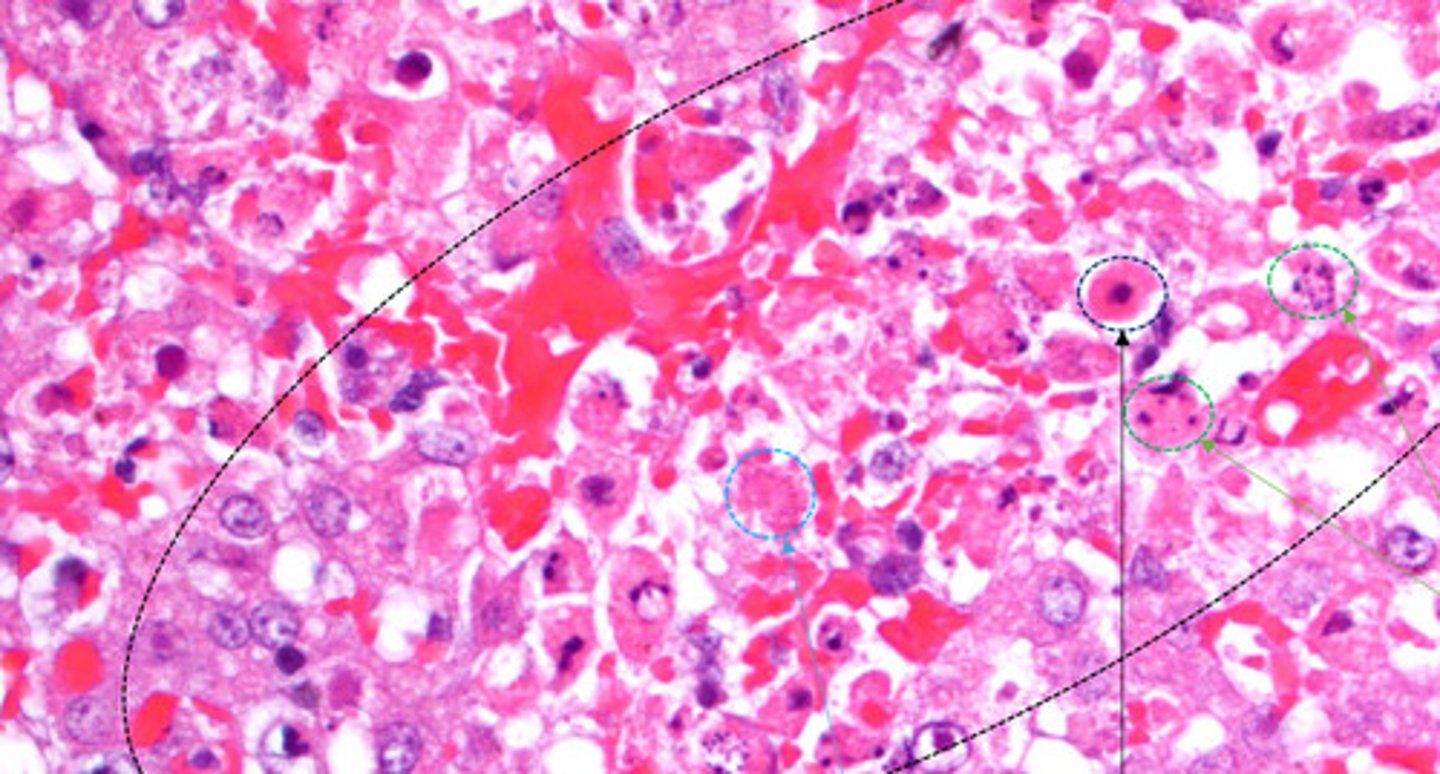
pyknosis
Identify the black circle?
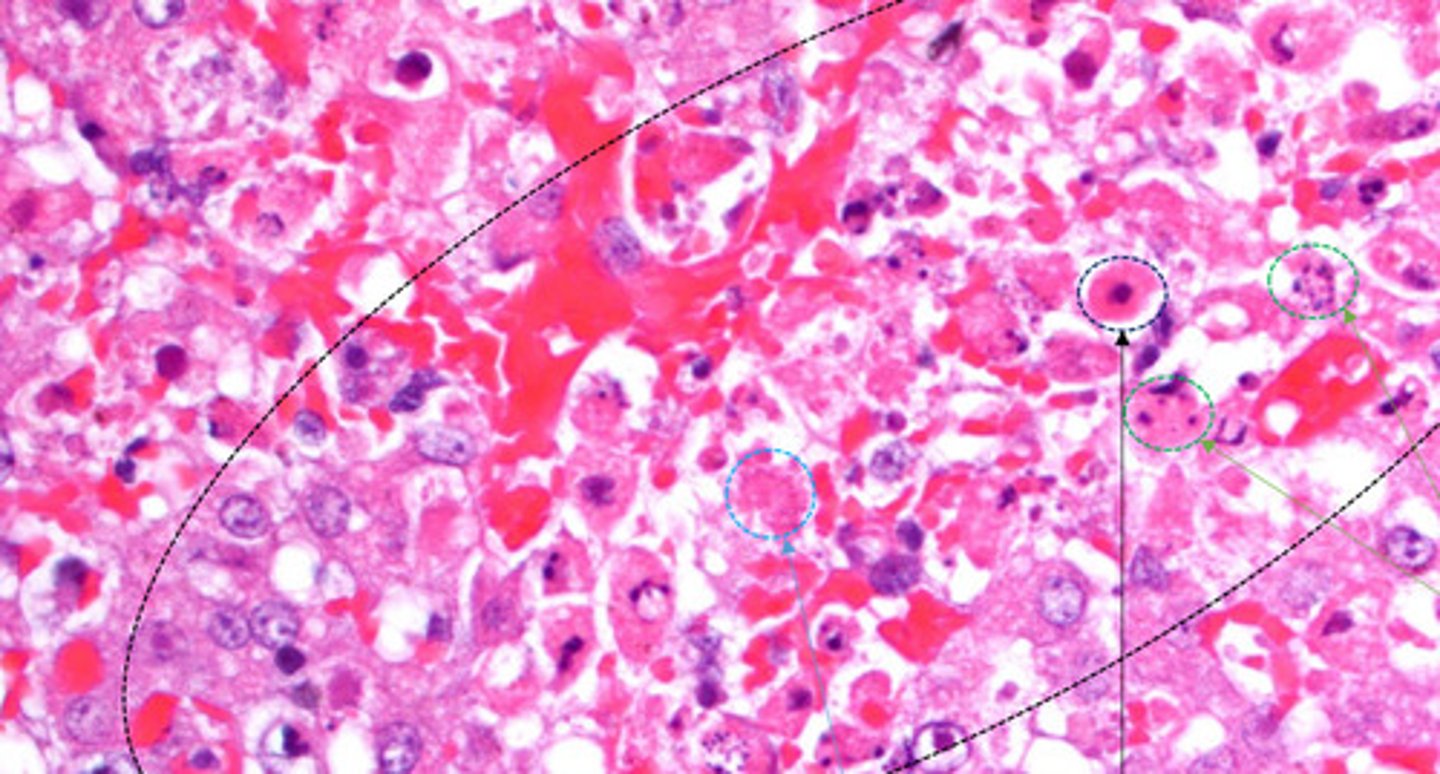
Karyorrhectic cells
Identify the green circle?
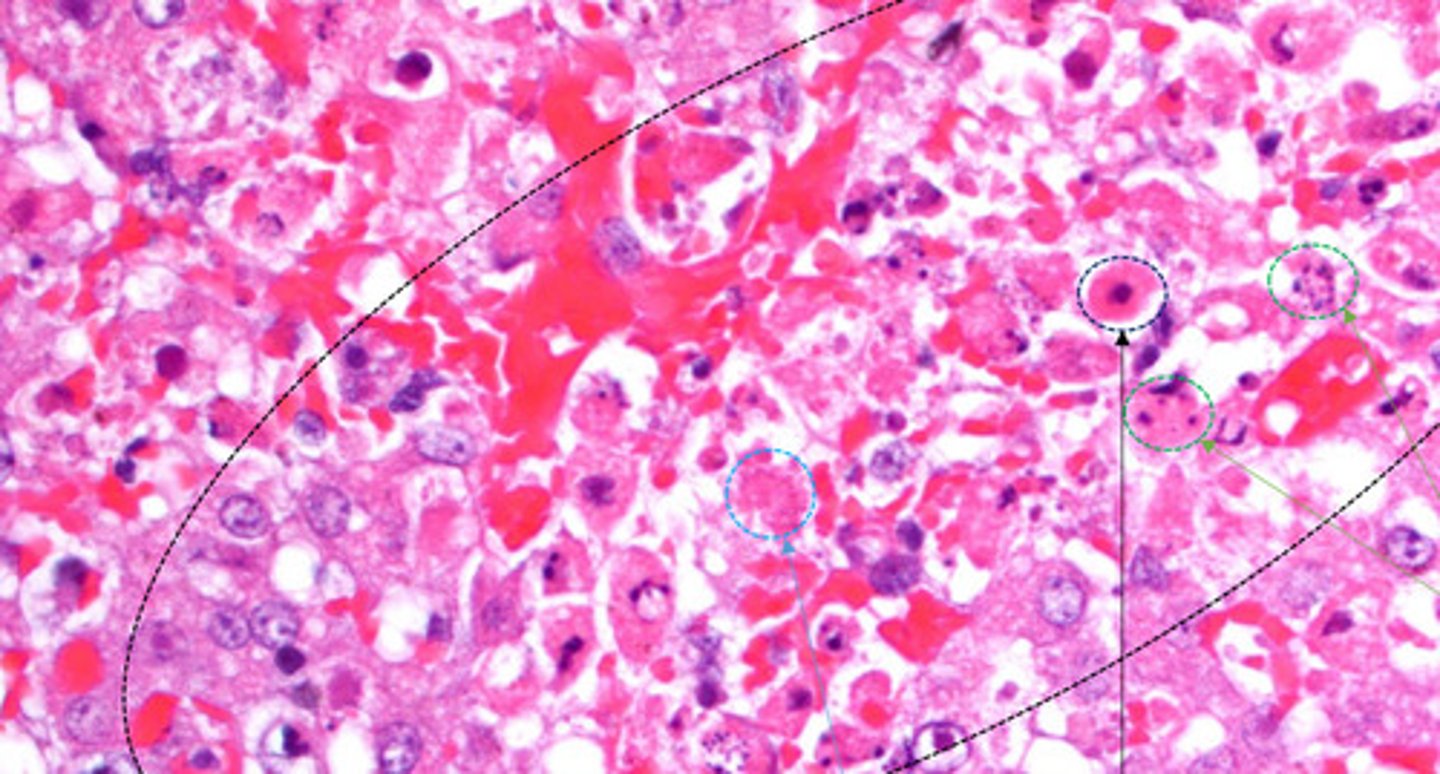
karyolytic cells
Identify the Blue circle?
Dense and rigid texture of dead cells (maintain their shape) (kidney, heart ect..)
Define Coagulative necrosis?
Complete enzymatic digestion of cells- melting away (Brain)
Define liquefactive necrosis?
Cheesy, coagulate granulomatous reaction (lung TB)
Define caseous necrosis?
Saponification (fatty acids w/ calcium) (pancreatitis)
Define Fat necrosis?
Necrosis due to ischemia of distal extremities
Define Gangrenous necrosis?
Clostridium perfringens
What can cause gas gangrenous necrosis?
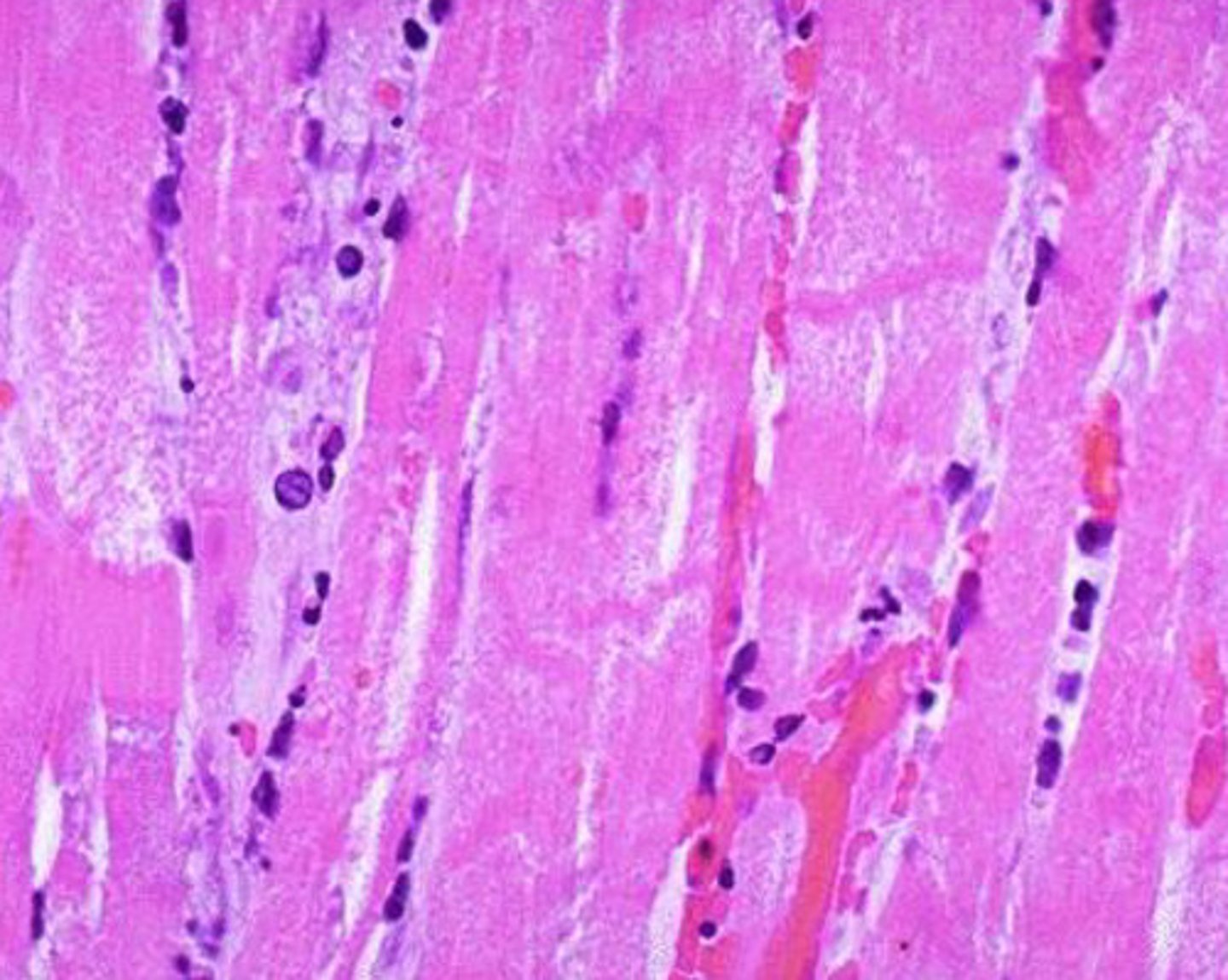
Coagulative necrosis of myocardial cells
What kind of necrosis is shown?
Coagulative necrosis of the kidney
What kind of necrosis is shown?

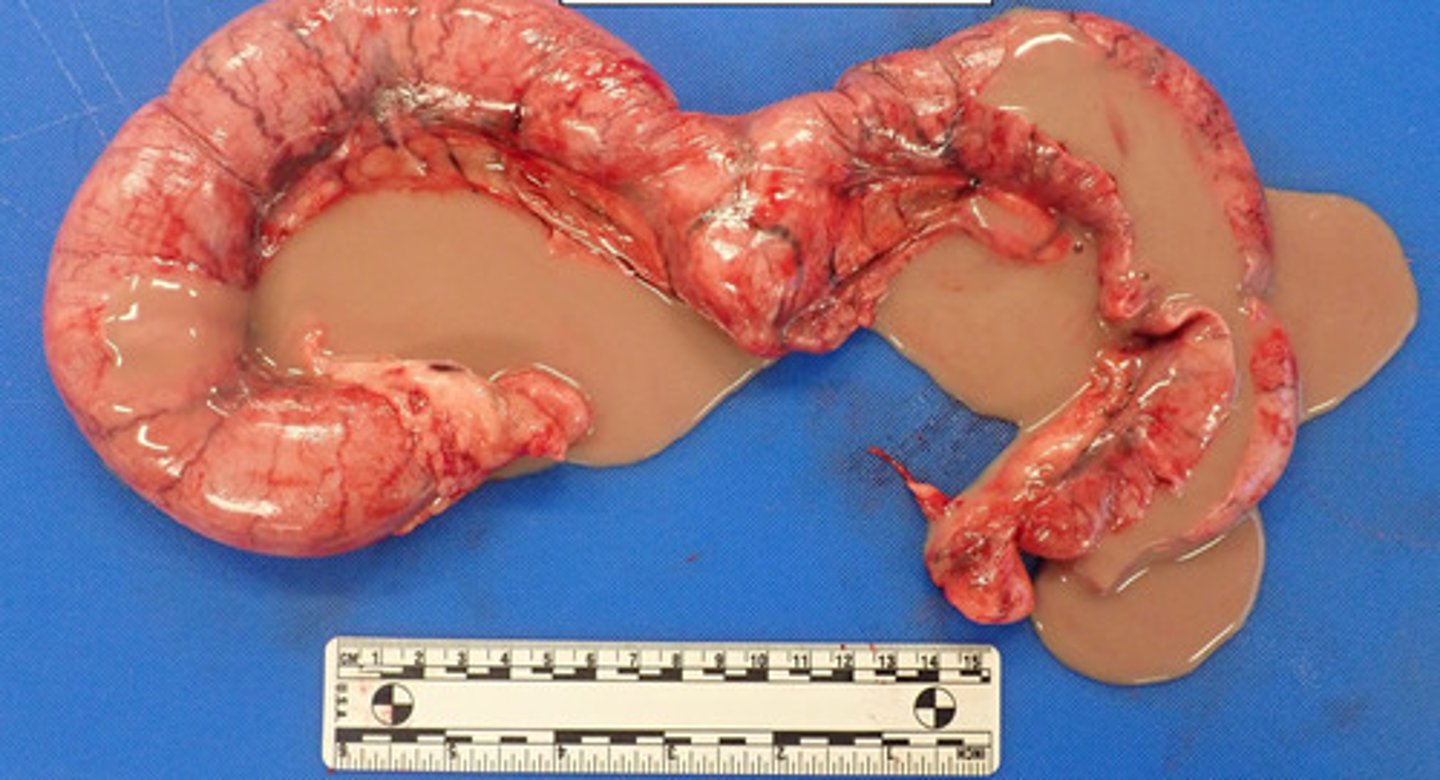
Suppurative (Liquefactive necrosis of the uterus)
What kind of necrosis is shown?
Liquefactive necrosis of the brain histo
What kind of necrosis is shown?
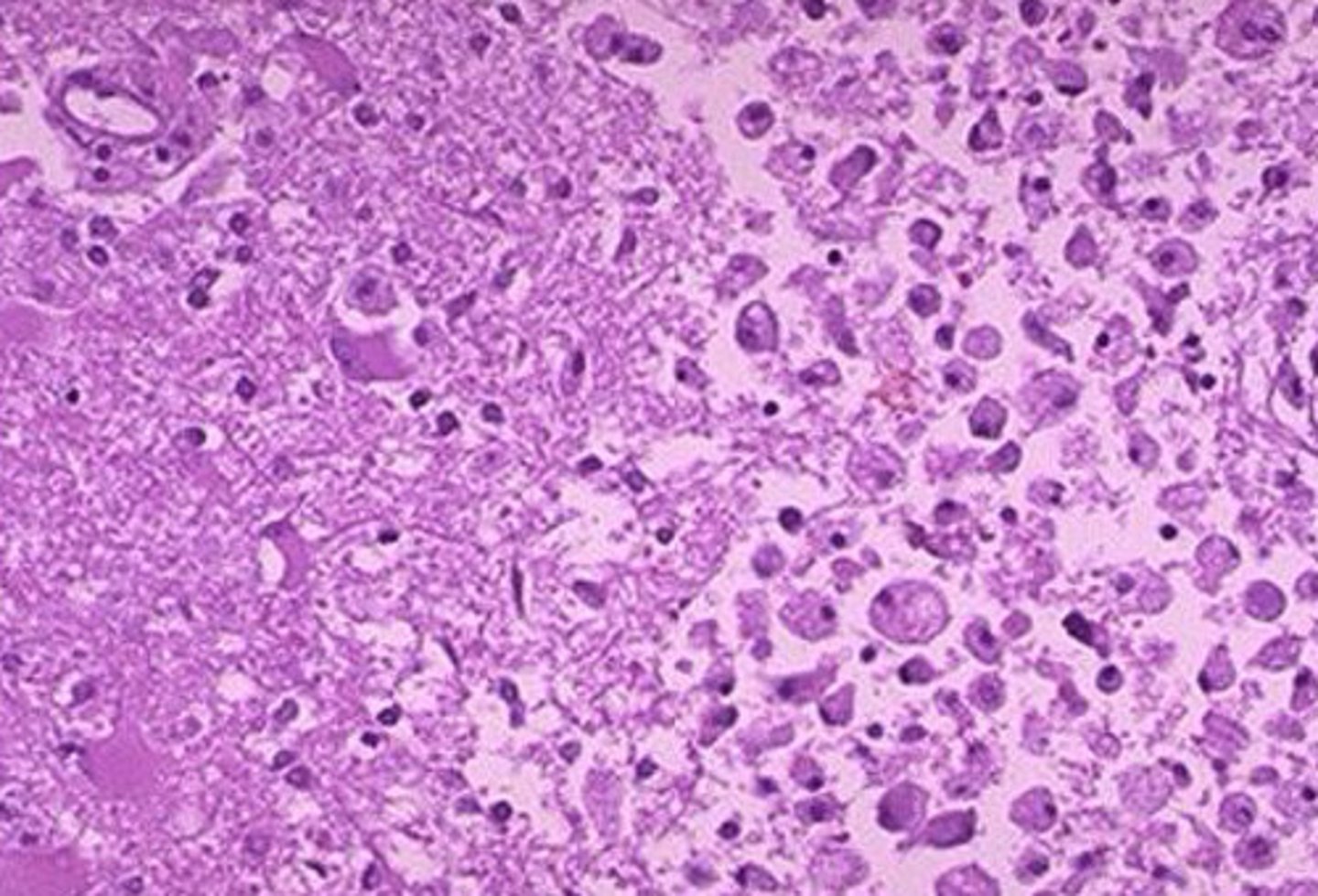
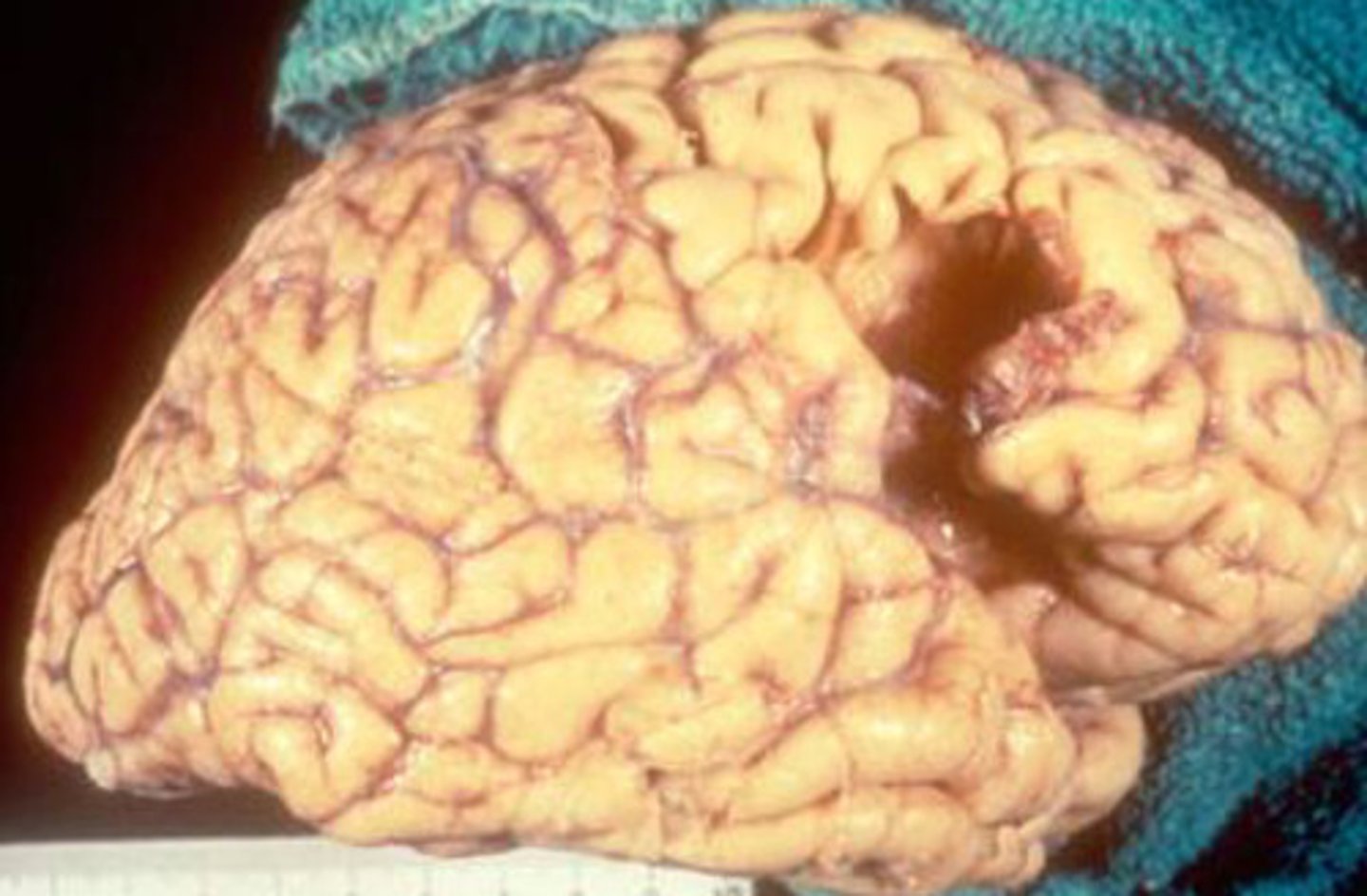
Liquefactive necrosis of the brain
What kind of necrosis is shown?
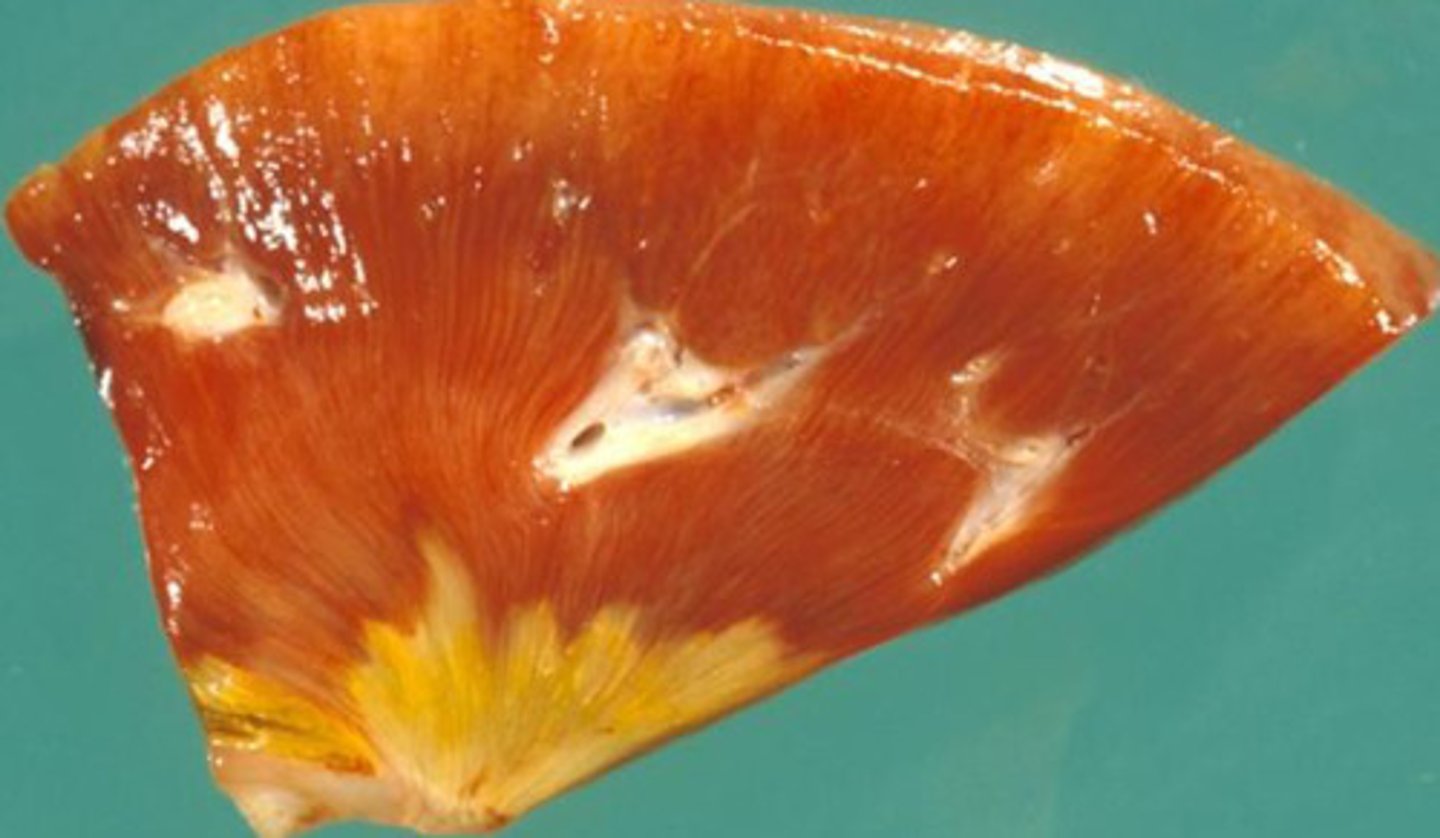
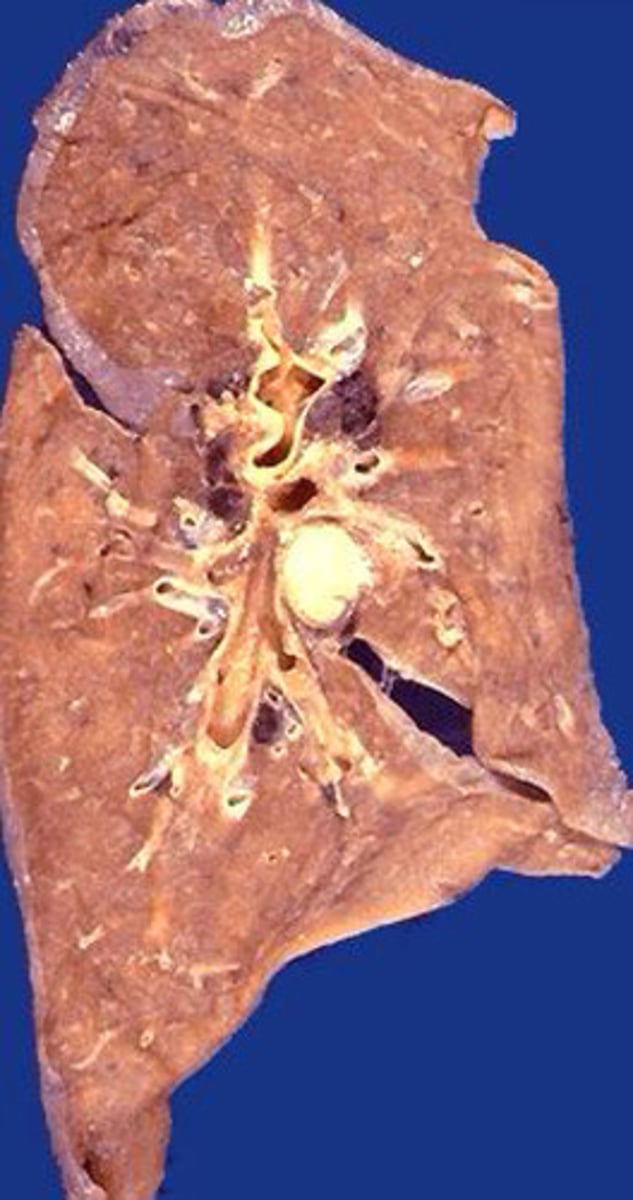
Caceous necrosis of the lung
What kind of necrosis is shown?
Fat necrosis of the pancreas
What kind of necrosis is shown?
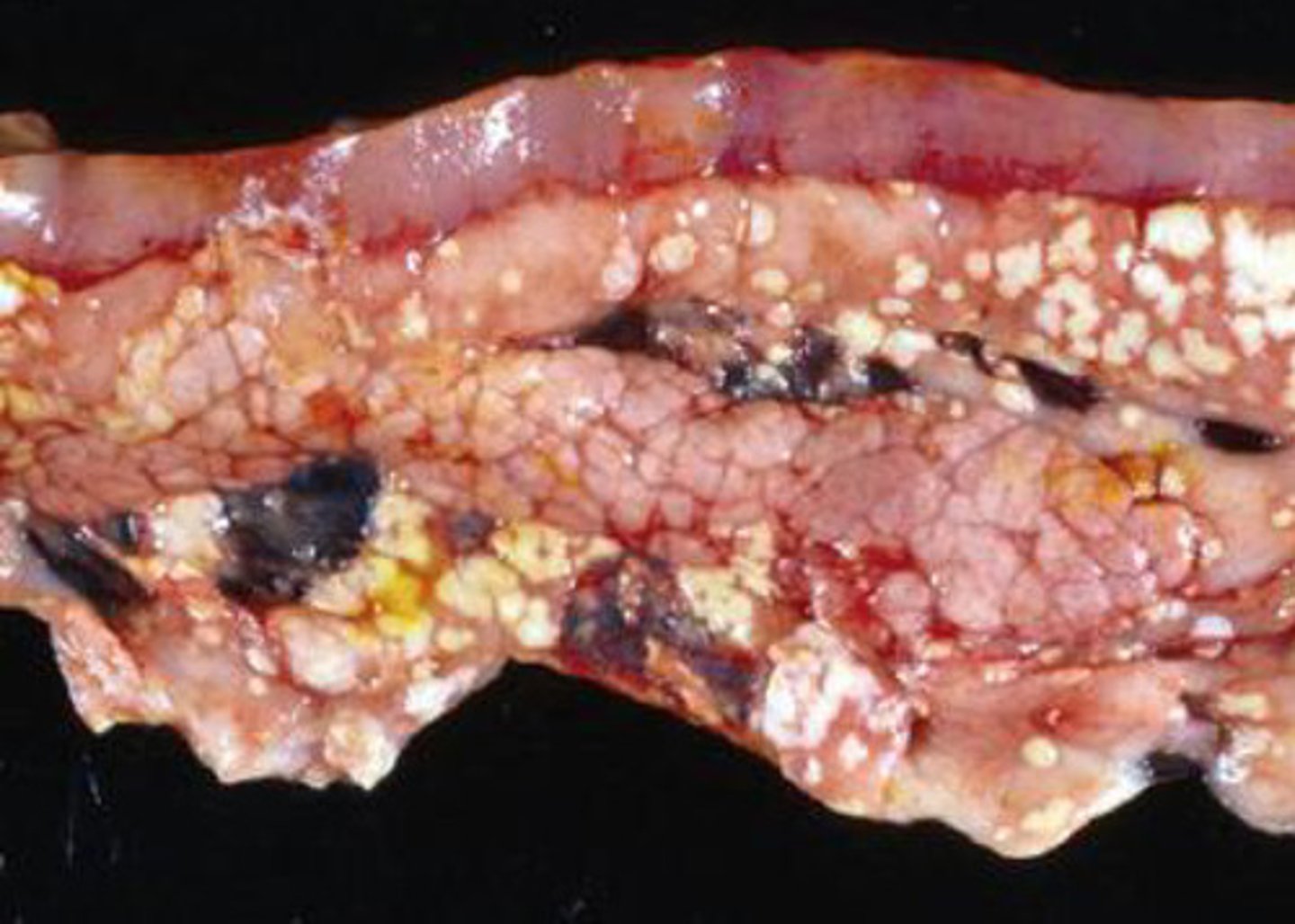
Fat necrosis of the pancreas
What kind of necrosis is shown?

Cytoplasm,,
Collagin
Fibrin
RBC
Protein
Eosin will stain what pink?