Biology Final Exam
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
Cell Theory
idea that all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things, and new cells are produced from existing cells
Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann
Co-founder of cell theory
Homeostasis
A tendency to maintain balanced
Two types of reproduction
asexual and sexual
sexual reproduction
The fusion of sperm and egg touching
asexual reproduction
The fusion of sperm and egg not touching
heredity information
DNA carries and stores information
Community
multiple species in a certain area
Population
one species in a certain area
Evolution happens at a ____________ ____________
population level
Ecosystem
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.
Biome
A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms
atoms build
molecules
molecules build
cells
cells turn into
tissue
atom
Basic unit of matter
prokaryotes
No nucleus/ does not have membrane bound organelles
Eukaryote
Has a nucleus/ have membrane bound organelles (small organs)
How many electrons does a Chlorine valence shell have?
7 (2 in it's inner shell) (7 around it)
how to find atomic mass
protons + neutrons
isotope
different numbers of neutrons
cation of atoms
gain electrons
ation of atoms
lose electrons
carbohydrate molecule features
energy source
different structure of saccharides (sugars)
mono-saccharides, dia-saccharides, poly-saccharides
What is an example of mono-sacchardies?
glucose
What is an example of dia-sacchardies?
lactose, maltose, sucrose
What is an example of poly-sacchardies?
starch
Cellulose
A substance (made of sugars) that is common in the cell walls of many organisms
amyloplasts
breaks down sugars(starches)
What happens in Hydroplysis?
breaks down fats
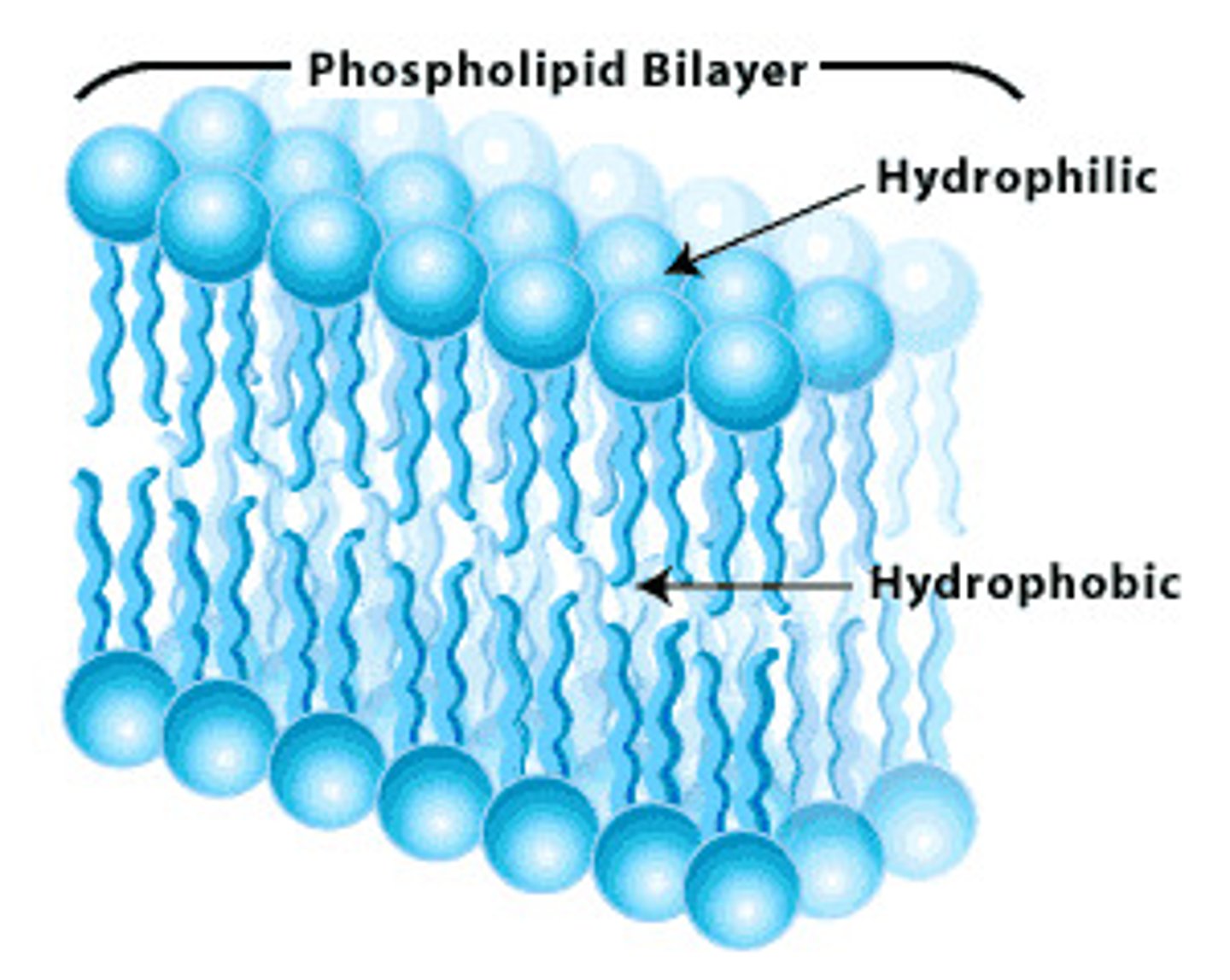
amphipathic (ampi- opposite end)
A molecule that has both a hydrophilic region and a hydrophobic region.
Levels of protein structure
1. Primary
2. Secondary
3. Tertiary
4. Quaternaryterm
Most simple level of protein structure
primary
Most complex level of protein structure
Quaternary
ATP
energy
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
synthesis lipids
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
synthesis proteins, ribosomes
What does the nucleoli make ?
RRNA (ribsomal RNA)
What are the folds in the mitochondria called?
cristae (folds itself so that it can gain more surface areas so that it can tact more energy into mitochondira)
Mitochondria
ATP (energy) production
3 Cell structures in plants
cell wall, large central vacuole, chloroplasts
Why is Down syndrome called trisomy 21?
has a extra chromosome
Trisomy 21
Carrying an extra copy of chromosome 21; also known as non-disjuction
Why didn't the chromosomes in Trisome 21 pull apart?
spindles would not pull them apart
fluid mosaic model
solubility in water (very fluid in water) -
It can get very big> hypotonic
It can get very small> hyperonic
integral protein
in the middle
peripheral proteins
to the side
Another name for integral protein?
Trans membrane proteins
main feature of plasma membrane
dealing with hydrophillic and hydrophobic (2 opposite ends)
active transport
Takes the most energy
Passive transport
Takes very little or no energy
Which transport goes with the concentration gradient ?
Passive transport
Which transport goes against the concentration gradient?
Active Transport
Phagocytosis (type of endocytosis)
bringing in solid (EX: bacteria cell)
Pinocytosis (type of endocytosis)
Bringing in liquids or oils
Ultimate source of energy for animals
Sun
Catabolic reactions (catabolism)
breaking down big molecules to make small things
Anabolic reactions (anabolism)
synthesis small things to make or build molecules
transfer of electrons
transfer of energy
Glycolysis
the breakdown of glucose (sugar) to pyruvate molecule
Autrophs
make their own food (EX: plants, algae, cyanobacteria)
Heterotroph
cannot make its own food (EX: animals, humans, fungus)
Stages of Mitosis
PMAT
Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
stages of meiosis
PMAT PMAT
Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I,
Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II
Which phase is in between mitosis and meiosis ?
Interphase
3 phases of interphase
G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase
Which inter phase copies and duplicates chromosomes?
S phase (make or build)
Haploid
having 1 chromosomes (23)
Diploid
having 2 sets of chromosomes (46)
If we had an organism that had 50 diploid chromosomes, how many haploids would we have?
25
Miosis produces what?
sperm, eggs, spores, polar bodies (All of the above)
dominant allele
always shows up 3 out of 4 (75%) in the organism when the allele is present.
recessive allele
always shows up 1 out of 4 in the organism when the allele is present.
Phenotype
the physical appearance of an organism
Genotype
the genetic appearance of an organism
loci
Location of a gene on a chromosome
Alleles
Different forms of a gene
Test Cross
monohybrid cross and dihybrid cross
monohybrid cross
involves one trait (shows up as 4 boxes)
dihybrid cross
involves two traits (shows up as 16 boxes)
linked genes
genes that are located on the same chromosome/allele and tend to be inherited together
Barr body
Inactivated X chromosome
What did Franklin do?
made X-ray diffraction photos of DNA
What does DNA polymerase do?
Enzymes zips/bonds the nucleotides together to form the double helix
leading strand
in front
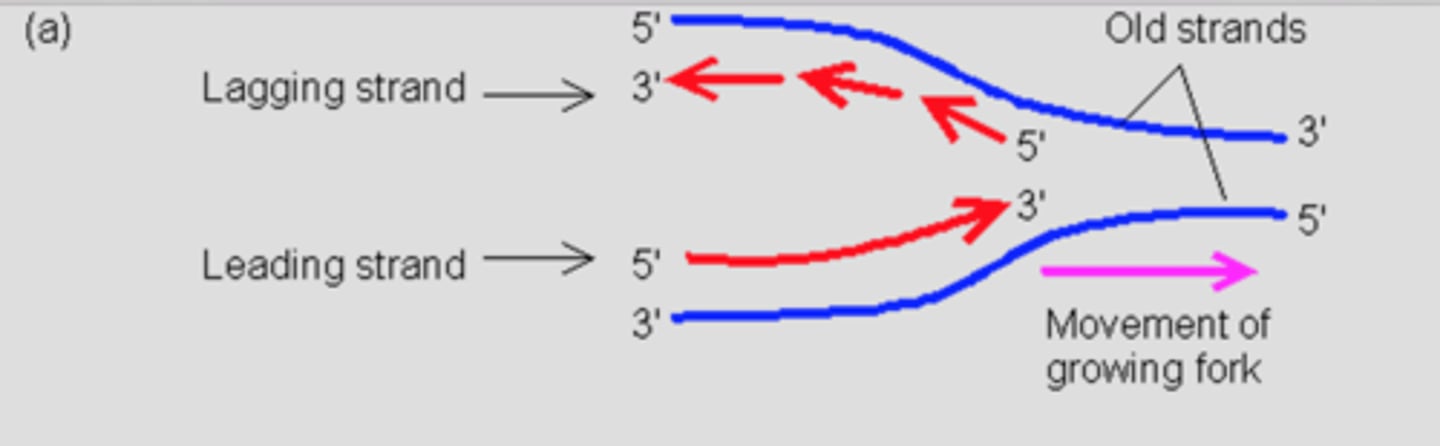
lagging strand
behind
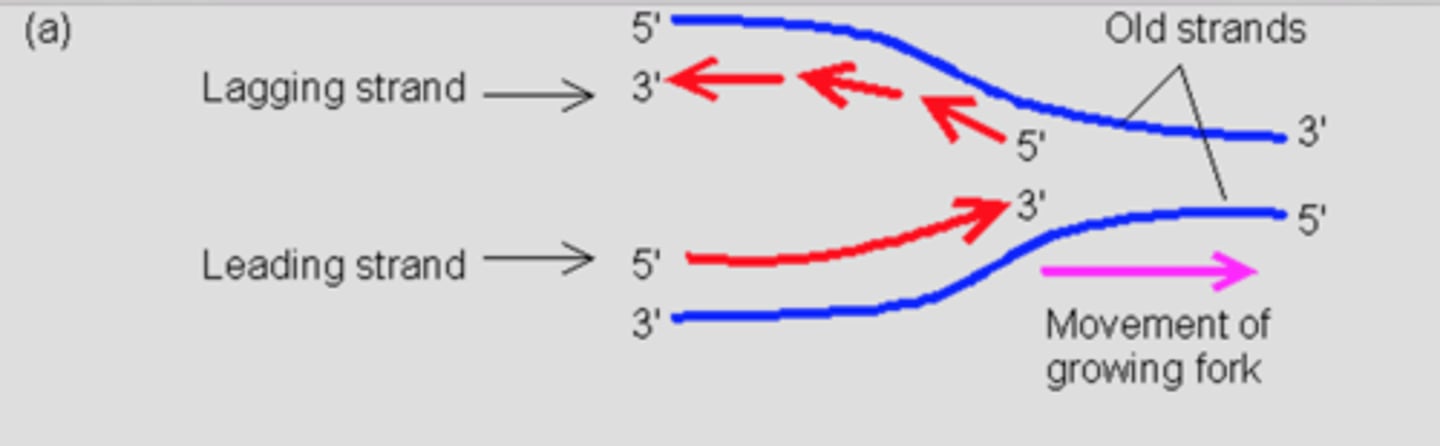
DNA is known to be parallel or anti-parallel? and Why?
Anti-parallel, because they are going in two opposite directions
What bonds anti-parallel DNA?
complementary bases (A>T)(G>C)
What's the purpose of replication fork?
DNA helicase unwinds resulting DNA to split and the replication takes place
Telomeres
the ends of a chromosome
Human Genome project
help map out genetic code
Hypertonic
Causes a cell to shrink (EX: salt, sugar)
Hypotonic
Causes a cell to shrink (EX: water)
Isotonic
Causes a cell to swell
Enzymes
speeds up chemical reactions and lowers the activation
What process makes genetic diversity? Miosis or Mitosis ?
Miosis produces genetic diversity
Which phase did crossing-over happen?
prophase 1
How many X and Y does kinefelter syndrome have?
2 X and 1 Y (XXY) happens to male