Plant 2001 - slides
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Leaf arrangement is quite difficult to infer with deciduous species in the dead of winter because one would have to climb the tree and closely observe leaf scars.
This is false
complex tissue in plants that transports water upward
parenchyma
Name priority
the correct species name is the earliest published name
Criteria for valid publication
–Name must not have been previously used
–Taxon rank must be clearly specified
–A holotype must be designated
When do you use author citations?
On specimen labels and scientific papers.
Shoot
a stem with leaves
Primary roots
arise from radicle of the embryo
Secondary/lateral roots
branches of primary roots
Adventitious roots
arise from anywhere else (roots)
Pneumatophores
modified erect roots specialized for gas exchange (cypress knees)
Herbaceous aerial stems
little or no above ground woody tissue; above ground stems die at end of the growing season
Woody aerial stems
above ground stems exhibit secondary growth (diameter growth) and live for more than 1 growing season
A vascular tissue that conducts photosynthate (sucrose solution) throughout the plant is - transports dissolved sugars from source to sink
phloem
Tendril
coiled/claw like structure that grasps onto other plants and is used to climb
Spine
Sharp-pointed modified leaf or part of a leaf
Prickle
sharp-pointed structure developed from epidermal - randomly placed
Thorn
Sharp-pointed modified stem
Pith
central most tissue of stem
Elongation of a stem or root is a result of cell division at the
Apical meristem
Elongation growth is called
primary growth
Increase in girth/diameter of a stem or root is called
secondary growth
secondary growth results from
cell division at the lateral meristem
lenticel
Loosely packed pockets of periderm tissue that allow gas exchange with the atmosphere
Main function of xylem
mineral transport from soil to leaves
secondary xylem is referred to as
wood
Serotinous cone
A seed cone that is sealed with resin, opening only after heat from fire melts the resin
Accessory fruit
A fruit composed of the ovary plus flower parts external to the ovary
Monoecious
A plant that produces unisexual flowers with both staminate and pistillate flowers present on the same plant
Dioecious
unisexual flowers occur on separate plants, functionally making individual plants male or female
Aggregate fruit
A fruit derived from more than one pistil (usually many) of a single flower
Multiple fruit
A fruit derived from more than one flower
Palmately Compound
When leaflets of a compound leaf radiate from a central point
Pinnately compound
When leaflets are arranged along either side of a rachis
Loment
A modified legume that breaks into segments between each seed
Corolla
a collective term for all petals of a flower
Calyx
a collective term for all sepals of a flower.
Pollination
Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma
A plant’s branching pattern betrays its leaf arrangement since branches originate from axillary buds. Therefore, inferring leaf arrangement of a deciduous tree in the dormant season is a simple matter of surveying the crown and observing the branching arrangement.
False
According to the current rules, the first letter of a specific epithet must always be lowercase, even if that epithet commemorates a person or place.
True
Leaves in the lower part of a tree’s crown are typically thinner and broader than leaves in the upper part of a tree’s crown. This is because the lower crown leaves are in a diffuse light environment. These “shade leaves” usually look atypical, while “sun leaves” are more representative in shape for the species.
True
The genera Carya and Fraxinus are similar in having odd-pinnately compound leaves. However, they differ in leaf arrangement with Carya having alternate leaf arrangement and Fraxinus having opposite leaf arrangement.
True
Node
point of leaf attachment
Alternate leaf attachment
One leaf is found at node
Opposite leaf attachment
Two leaves are found at a node
Whorled leaf attachment
More than two leaves are found at a node
Samara
A dry, one seeded fruit with the pericarp extending as a wing for wind dispersal
Achene
A dry indehiscent fruit with one seed connected to the pericarp at one point
Mesic Site
A site which generally has adequate water supply (except during drought), that is usually not too wet nor too dry
Xeric Site
A site that has excessively well-drained soil (e.g. coarse sand) or supports thin soil closely underlain by rock
Stipules
paired appendages, technically part of the leaf, that subtend the petiole and blade. These features can be fused to each other or adnate to the petiole. When present, they can be persistent or caducous (fall off early in the season).
Drupe
A fleshy fruit with its pericarp differentiated into three layers, and with a single seed enclosed within a hard bony endocarp
Prunus
A genus that possess the drupe fruit type
Berry
fruit that is fleshy throughout, lacking a pit
Glabrous
smooth and lacks hair
Scabrous
Short stiff hairs giving a rough sandpaper-like texture
Inferring leaf arrangement of a deciduous tree during the dormant season requires one to obtain a twig from the tree’s crown and closely examine leaf scars on that twig. This task is not something one can easily do just by glancing up and visually surveying the crown.
False You can look at the branching pattern.
Any given tree of Taxodium distichum can be expected to produce both pollen cones and seed cones. Therefore, T. distichum is dioecious.
False, T. distichum is dioecious meaning a tree is either male or female- NOT both
Wetland delineation requires assessment of hydrology, wetland vegetation, and wetland soils features. For legal purposes, a site must have at least two of the three criteria met to be considered a wetland.
True
Which species among the choices below has persistent leaves with nodules along the leaf margins harboring a symbiotic bacterium?
A. Ligustrum lucidum
B. Ardisia crenata
C. Ilex cornuta
D. Platanus occidentalis
E. Persea palustris
Ardisia crenata
Which species among the choices below has leaves that are both persistent, and aromatic?
A. Ligustrum lucidum
B. Ilex cornuta
C. Persea palustris
D. Rubus trivialis
E. None of the choices above have BOTH persistent and aromatic leaves
None
This invasive exotic has persistent leaves and opposite leaf arrangement.
A. Ilex cornuta
B. Ardisia crenata
C. Persea palustris
D. Ligustrum lucidum
E. Sabal minor
Ligustrum lucidum
26) Which species among the choices below is armed, and has palmately compound leaves?
A. Gleditsia triacanthos
B. Ilex cornuta
C. Rubus trivialis
D. Sabal minor
E. None of the species above are BOTH armed and have palmately compound leaves
None have both
Quercus texana and Quercus pagoda have similar leaf shapes, with acute lobes bearing bristle tips. However, these two red oak species can easily be distinguished by several traits. Which statement below most accurately communicates differences between these two oaks?
A. Q. texana is a hydrophyte with leaves largely glabrous beneath, while Q. pagoda is a mesophyte with leaf undersurfaces densely hairy throughout. Undersurfaces of Q. pagoda leaves are notably paler than the upper surface, while there is little difference in color between lower and upper leaf surfaces in Q. texana.
B. Q. texana is a mesophyte with leaves densely pubescent beneath (hairs stellate), while Q. pagoda is a hydrophyte with leaves mostly glabrous beneath. Also, Q. texana leaf undersurfaces are much paler than the upper surface, while both Q. pagoda leaf surfaces are similar in color/tone.
C. Q. texana and Q. pagoda actually occupy the same habitat/niche and typically occur right next to each other, so ecology is of no help in separating the species. One must rely on morphology with Q. texana leaves being largely glabrous beneath, and Q. pagoda having densely pubescent leaf undersurfaces (hairs stellate). Also, Q. pagoda leaves are “two-toned”, with the lower surface being much paler than the upper surface. Leaf undersurfaces in Q. texana are not markedly different in color/tone than upper leaf surfaces.
A.
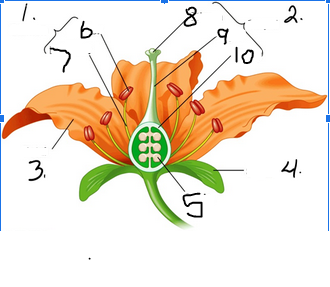
What is number 1
Stamen
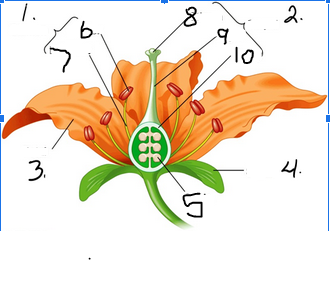
What is number 2
Pistil
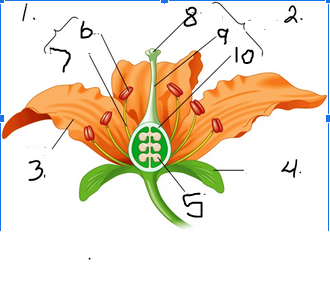
What is number 3
Petal
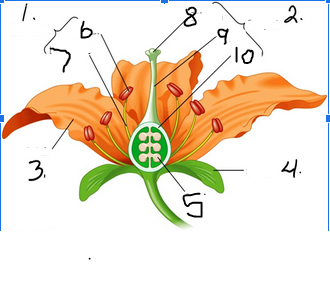
What is number 4
Sepal
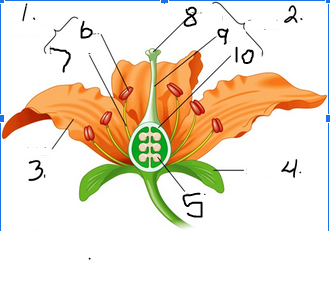
What is number 5
Ovule
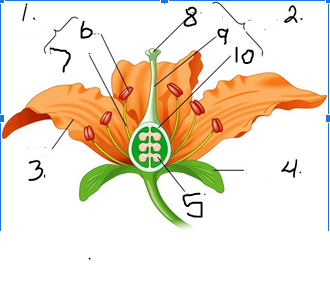
What is number 6
Anther
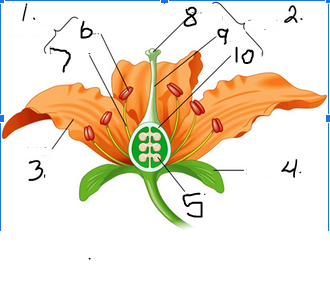
What is number 7
Filament
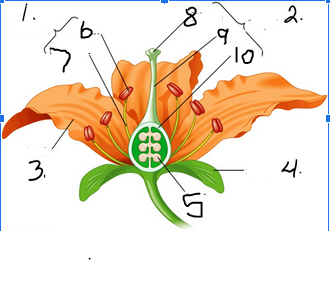
What is number 8
Stigma
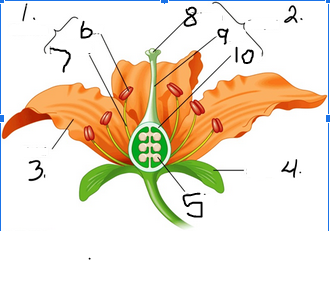
What is number 9
Style
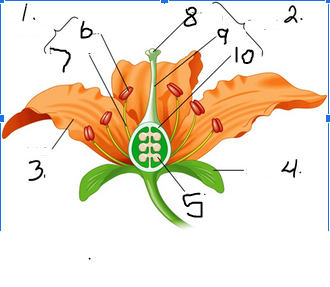
What is number 10
Ovary
Pedicel
the stalk of an individual flower in an inflorescence

Dicot
Flower parts in multiples on 4-5
Monocot
flower parts in multiple of 3
Perianth
Corolla and Calyx
Androecium
All stamens
Gymnoecium
all pistils
Peduncle
the stalk of an entire inflorescence
Inflorecense
Dehisent
tissues of the pericarp break open, freeing the seeds
Indehisent
seeds remain in the fruit after the fruit has been shed from the parent plant