topic 8 - space physics (flashcards)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
how does a star begin to form?
at the start of a star’s life, a nebula is formed
what is a nebula?
cloud of dust and gas particles which is present in the galaxy
what type of reactions take place at the start of a star’s life cycle as dust and gas are drawn together?
fusion reactions
what factor determines the type of life cycle of a star undergoes?
the size of the star
what phases does a star go through?
protostar
main sequence star
describe what happens at the protostar phase
the gas and dust particles are drawn together by gravity ; the kinetic energy gained leads to thermonuclear fusion reactions, starting the main phase
→gravity is the attractive force that causes these fusion reactions
what happens when fusion reactions occur in the protostar?
Energy gets released in the core of the protostar, causing it to get warmer. The core becomes hot & bright, creating a star
Using the generated heat from the reactions, hydrogen nuclei fuse to form helium nuclei. The reactions give out much more energy, allowing more helium nuclei to be formed.
During fusion, the force of gravity and force of pressure balance each other out so the star is at equilibrium → main sequence star
how does a star remain stable for many years?
There are two forces that balance each other out as they act on the star:
force of gravity - attracts particles towards centre of the star
force of pressure - pushes particles out
how does a star last for a long time?
there is a large supply of hydrogen in the universe, which ensures the star has enough fuel to last for a while.
describe what happens at the main sequence star phase
small hydrogen and helium atoms are fused together, forming larger atoms, from helium to carbon to iron
from this point, stars will evolve according to its size
what happens when a star runs out of gas to fuse with?
it is no longer in equilibrium, so it collapses
describe the death of a small star
RED GIANT - when almost all of the hydrogen has been used, the star will expand (sun will engulf nearest planets)
WHITE DWARF - the matter making up most of the red dwarf is distributed to the surroundings. The remainder collapses as hot, dense mass, which will cool & fade from sight (BLACK DWARF)
describe the death of a massive star
SUPER RED GIANT - similar to red giant, but bigger with a much denser core (e.g. Betelgeuse)
star rapidly collapses in a supernova explosion. The intense heat and pressure will cause further fusion to create the heaviest naturally-occurring elements and distribute them throughout the universe → a neutron star or black hole may remain
what is a neutron star?
a very small, extremely dense, rapidly-spinning object that may remain after a supernova
how is a black hole formed?
the largest stars will leave behind a black hole.
these are formed since the heaviest stars, having such a strong gravitational pull, can trap anything going near it, including protons (particle of light), which cannot escape
how are planets formed from the debris left over from the collapse of a star?
gravitational attraction brings particles together, but there is not enough energy to start new fusion reactions
define centripetal force
any force which acts towards the center of its orbit
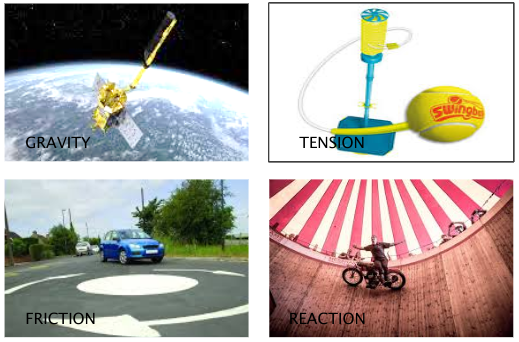
what forces are most like to act as a centripetal force?
GRAVITY - used on astronomical scale (refer to planet’s/star’s gravity)
TENSION - when a string/cord connects the object to the centre of the circle
FRICTION - caused by contact with a surface beneath the object
REACTION - caused by contact with a surface around the edge of the circle
centripetal acceleration
the object is always accelerating: even though its speed is constant, the velocity constantly changes, since the direction is always changing
what affects centripetal force?
proportional to the mass of the object
proportional to the object’s velocity squared
inversely proportionate to the radius of orbit
so, f = mv2 / r
what is a satellite?
an object that has orbit
what are the two types of orbit?
GEOSTATIONARY - satellite orbits the earth, always fixed above the equator
orbits every 24hrs - orbits with earth’s rotation
orbit radius approx. 6x earth’s radius
only enough room in space for approx. 400 of these satellites
CIRCUMPOLAR - satellite orbits the earth, passing the North and South poles
orbits every 1.5 to 3hrs
orbits just a few hundred km above earth
can be many more polar orbitting satellites - possible to have 5 in view at any one time
uses of satellites
GEOSTATIONARY:
communication - TV, radio, telephone
GPS & satellite navigation
CIRCUMPOLAR:
detailed weather forecasting
land surveys - studies of land usage & mapping
astronomy
military - espionage (spying)
examples of naturally occurring satellites
moon is a natural satellite of earth
earth is a natural satellite of sun
what is the Big Bang?
it is the most commonly accepted explanation for the origin of the universe:
Edward Hubble made the hypothesis that, due to the way stars & galaxies are moving away from us, the universe must’ve started from a giant outpouring of matter from a central dense point.
what is the doppler effect?
if a wave source is moving relative to an observer, there will be a change in the observed wavelength and frequency
when source moves away from observer, the observed wavelength increases & frequency decreases
when source moves towards observer, the observed wavelength decreases & frequency increases
what is the red shift?
an observed increase in the wavelength of light from distant galaxies
Light appears red shifted from galaxies which are moving away from earth
The change with distance of each galaxy’s speed is evidence of an expanding universe
for two distant galaxies at different distances, the one with the smaller red shift is moving slower. The further away a galaxy is from us, the faster it is moving away from us
what is recessional velocity?
the further away a galaxy is, the faster it is moving away from us.
the relationship between recessional velocity and distance indicates that the universe is expanding as time increases
what is CMB radiation?
Cosmic Microwave Background radiation
it is the cooled remnant of the Big Bang that fills the entire universe. radiation that started life as gamma rays but was stretched to occupy the waveband equivalent to microwaves by the Universe expanding
evidence for the Big Bang
CMB (Cosmic Microwave Background) radiation is observable in every direction in the universe
there is clear proportionality between recessional velocity and distance for galaxies distant from earth
→ both clear evidence for an expanding universe