Organic Chemistry 1 ACS Questions Final Exam
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
sp, linear
Which is the correct hybridization state and geometry for the carbon atom in HCN?
sp, linear
sp2, trigonal planar
sp3, tetrahedral
None of the above
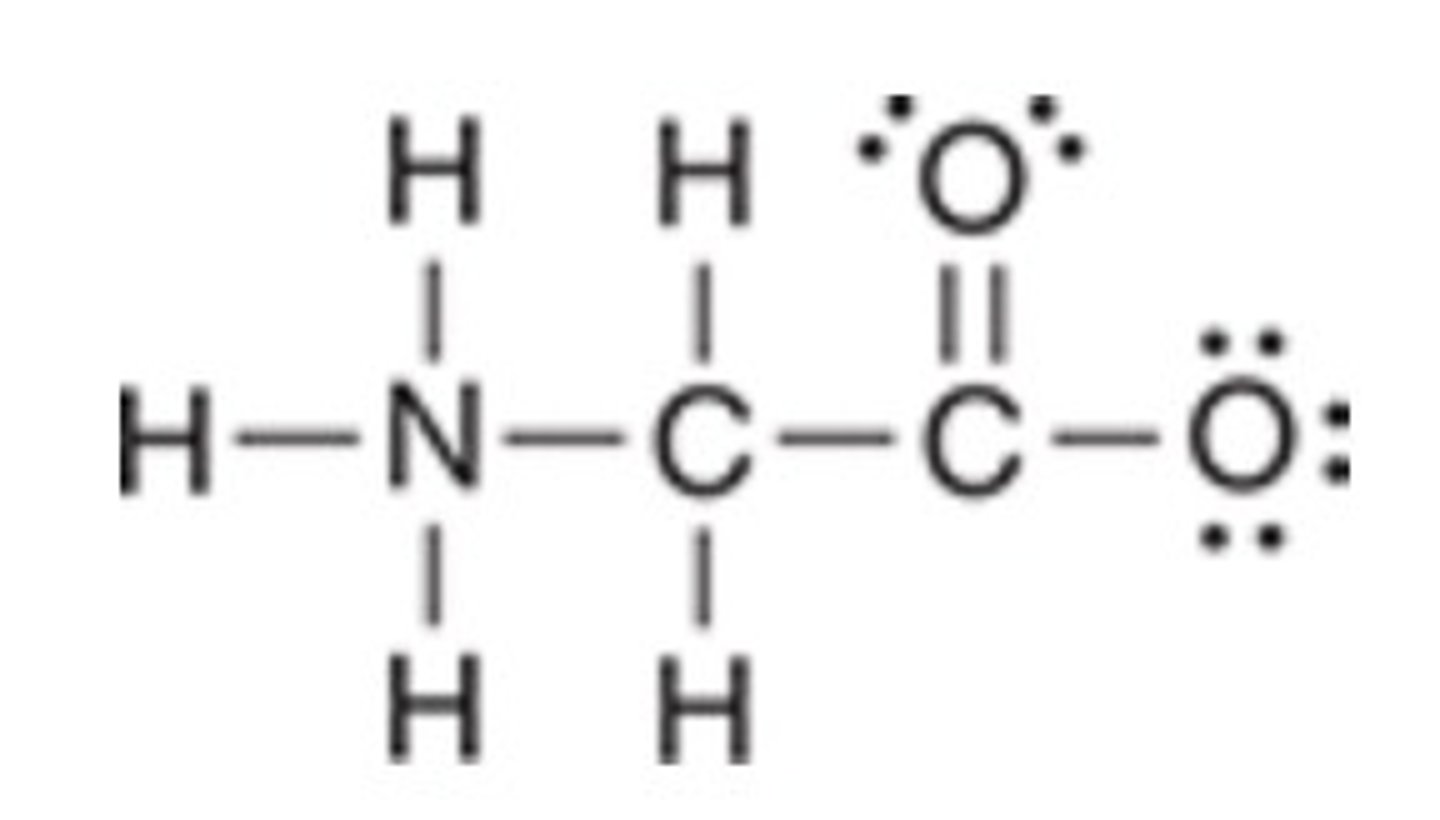
This structure has one positive charge and one negative charge.
The following structure has been drawn without formal charges. Which statement describes the missing formal charge(s)?
This structure has one positive charge and one negative charge.
This structure has one positive charge but no negative charges.
This structure has one negative charge but no positive charges.
This structure has no formal charges.
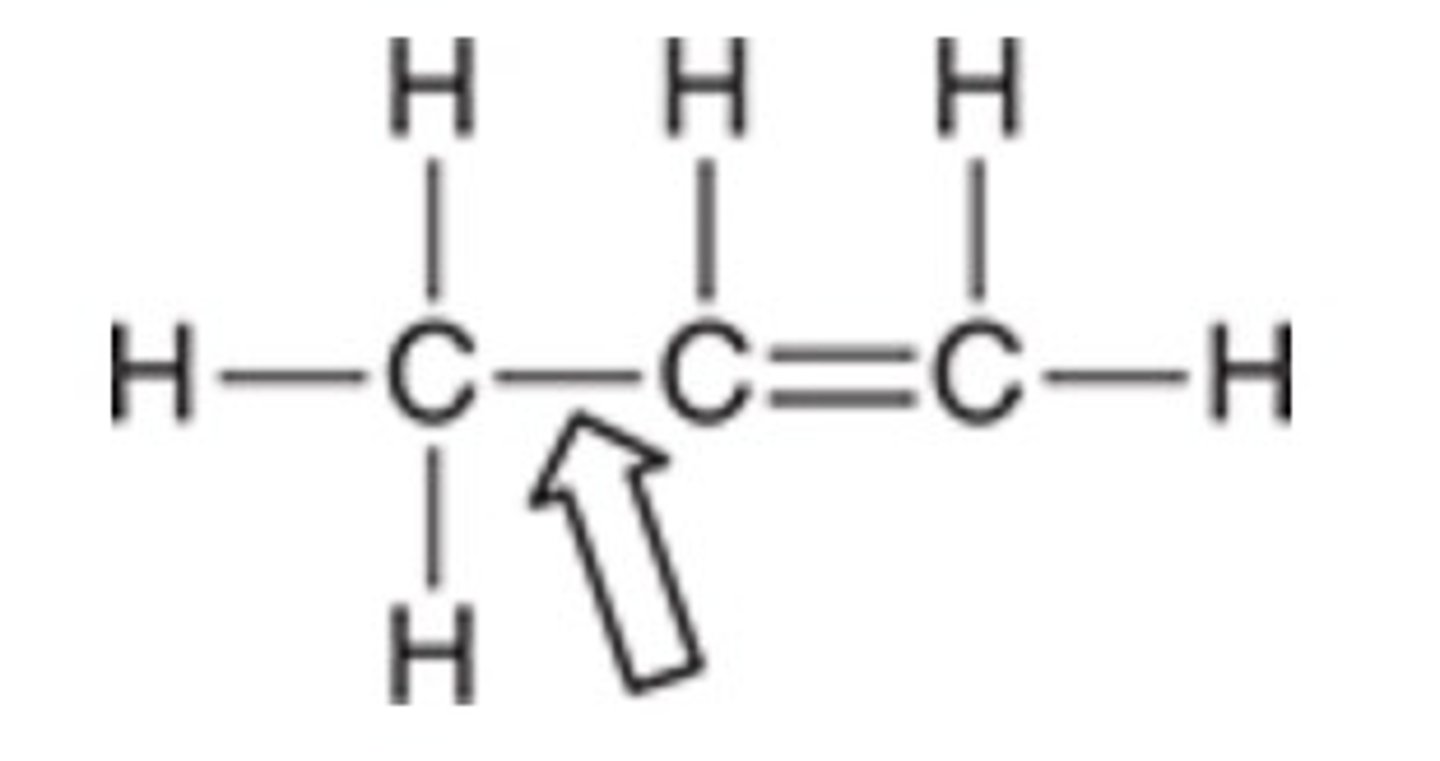
sp2-sp3
The indicated σ bond results from the overlap of which orbitals?
sp2-sp2
sp-sp3
sp-sp2
sp2-sp3
Trigonal planar
Of the following molecular geometries, which has the largest bond angle?
Pyramidal
Tetrahedral
Trigonal planar
Bent
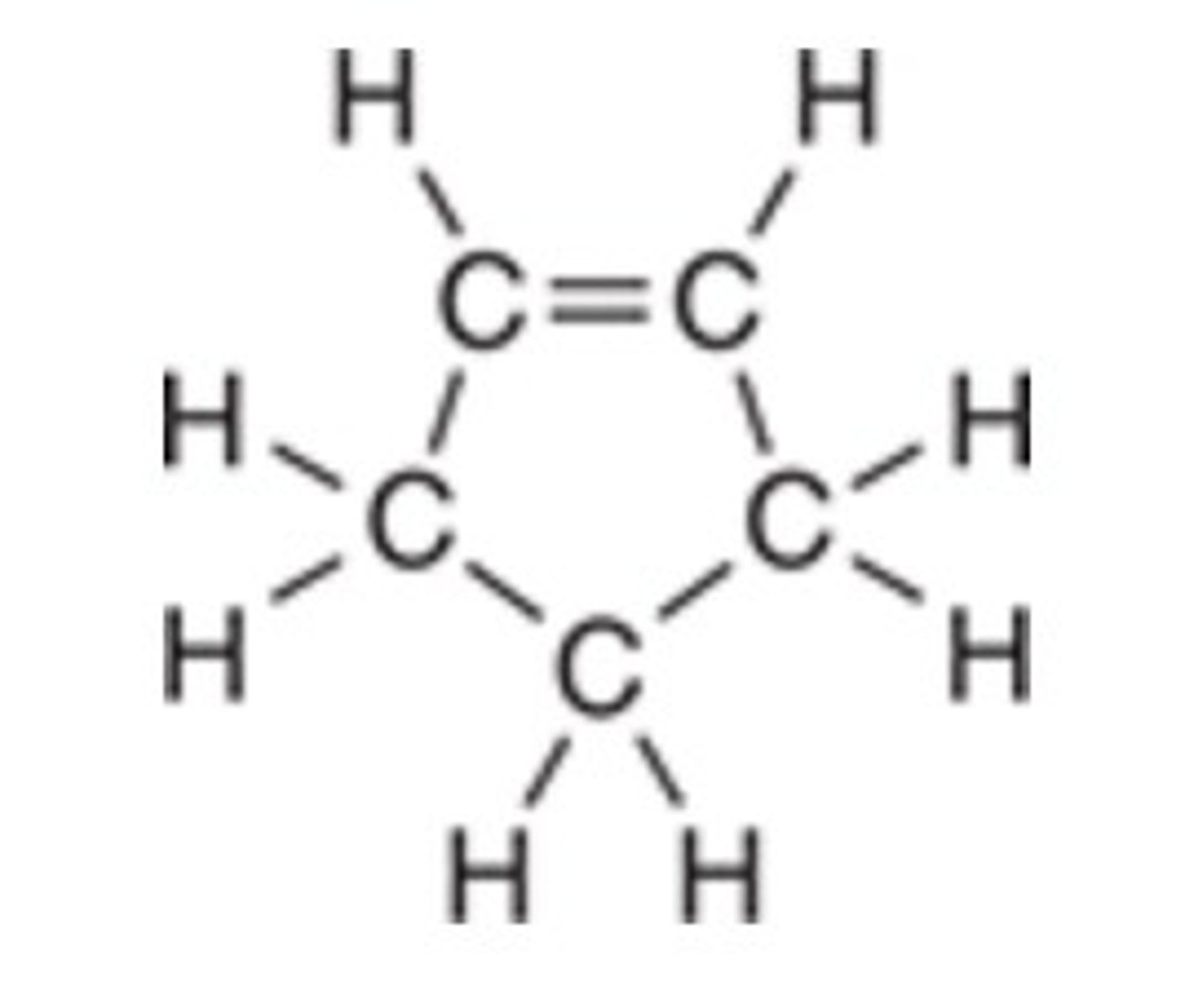
13
How many σ bonds are in the following compound?
8
9
13
14
Y, because the dipole moments do not fully cancel.
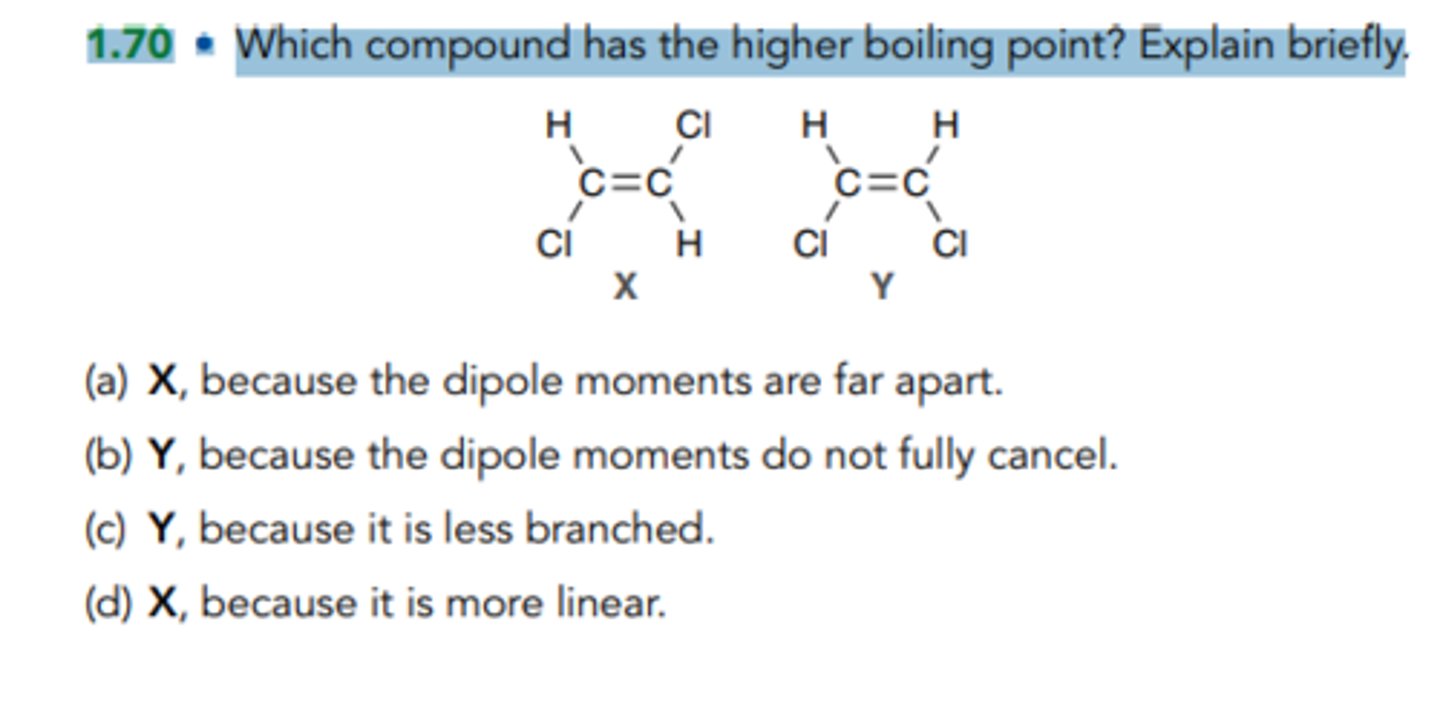
Which compound has the higher boiling point? Explain briefly.
X, because the dipole moments are far apart.
Y, because the dipole moments do not fully cancel.
Y, because it is less branched.
X, because it is more linear.
6
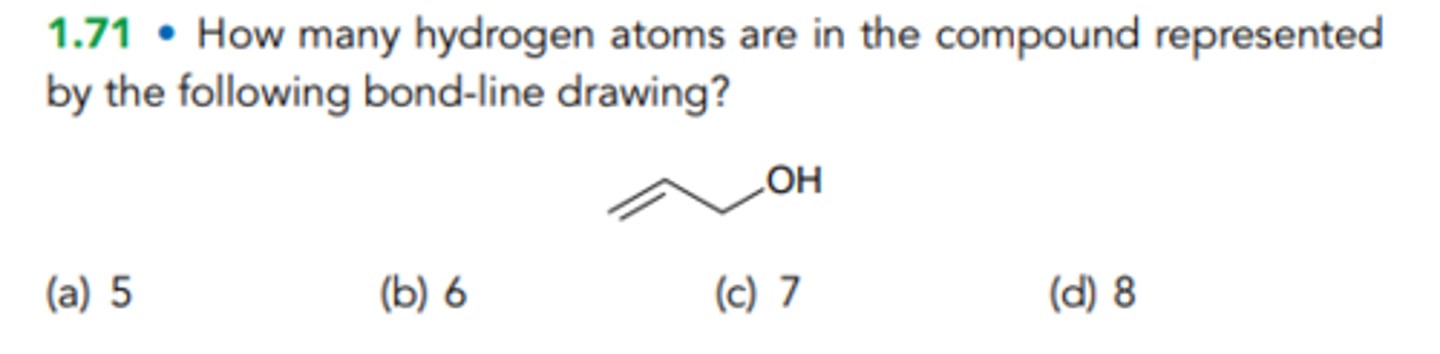
How many hydrogen atoms are in the compound represented by the following bond-line drawing?
5
6
7
8
D) 9 5
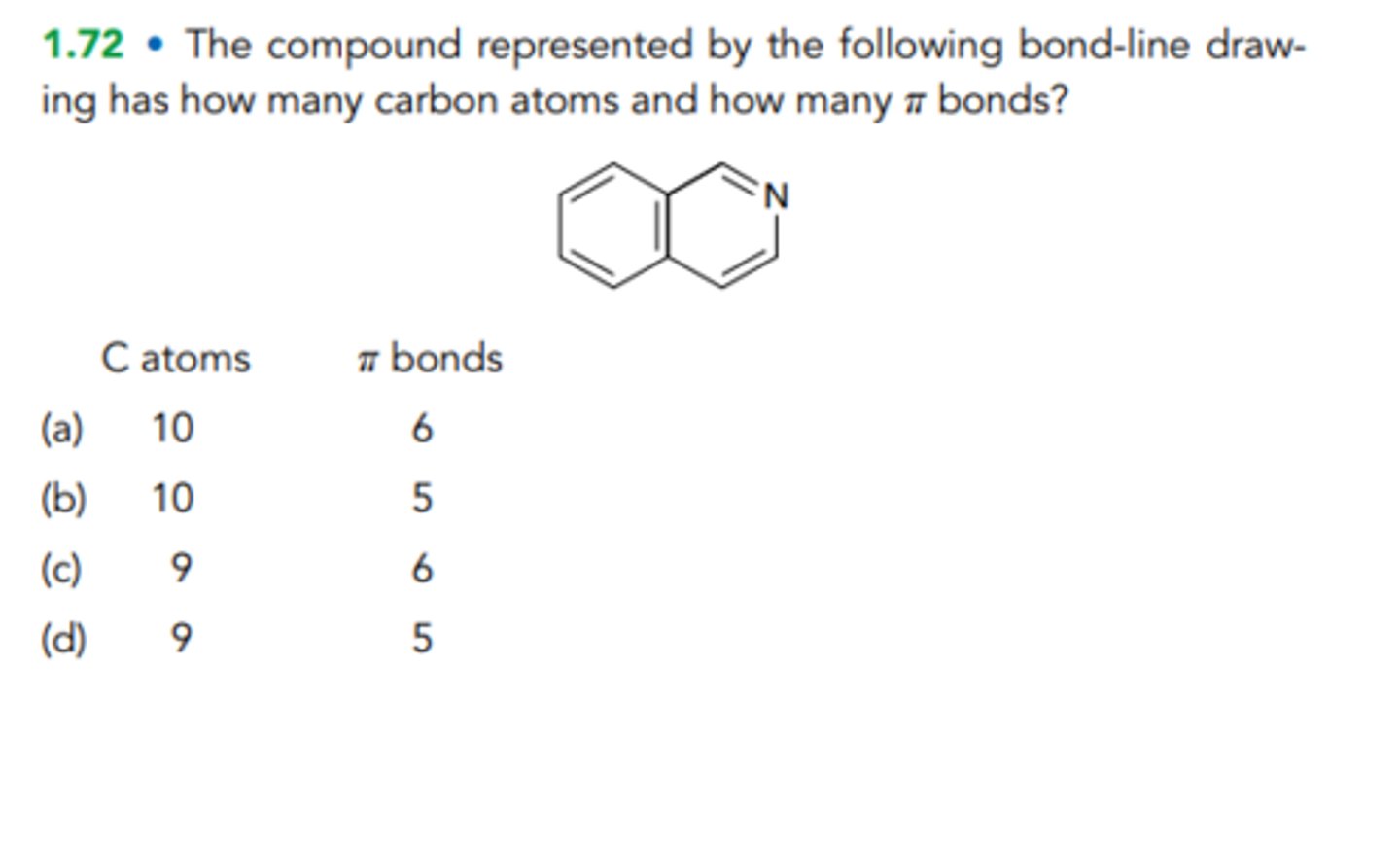
The compound represented by the following bond-line drawing has how many carbon atoms and how many π bonds?
C atoms
π bonds
(a)
10 6
(b)
10 5
(c)
9 6
(d)
9 5
C
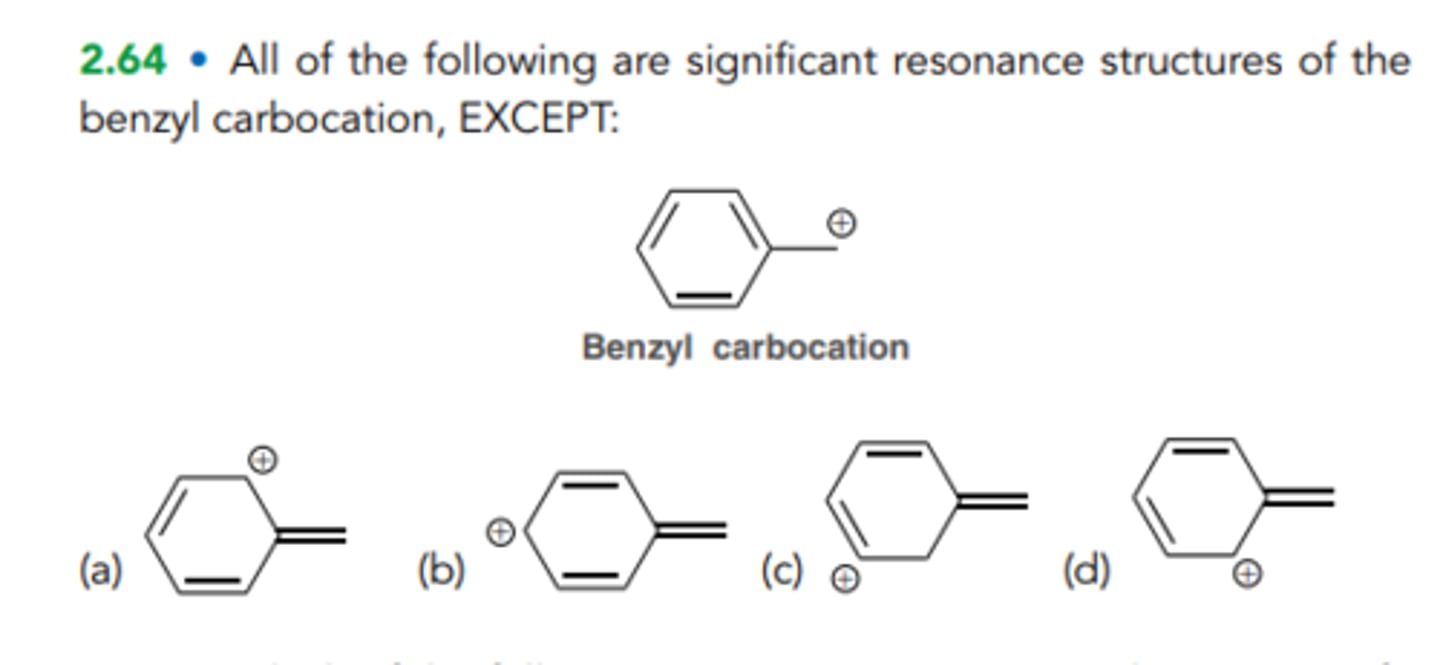
All of the following are significant resonance structures of the benzyl carbocation, EXCEPT:
A
Which of the following resonance structures is the most significant contributor to the resonance hybrid?
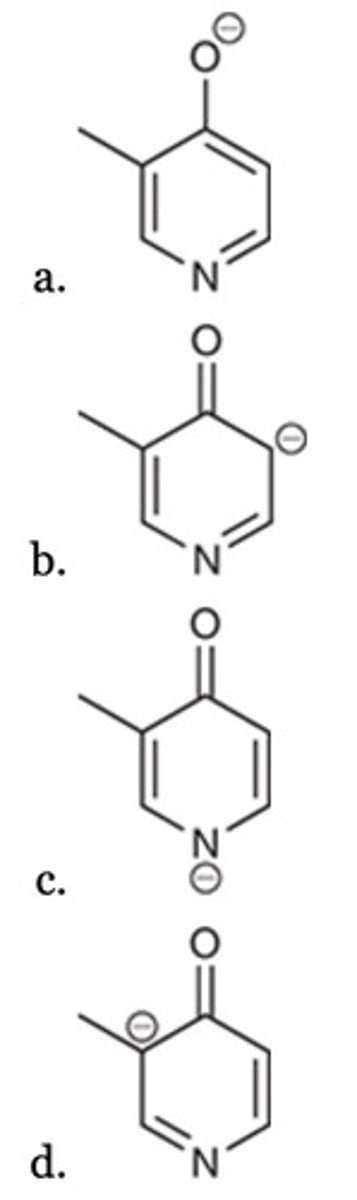
D
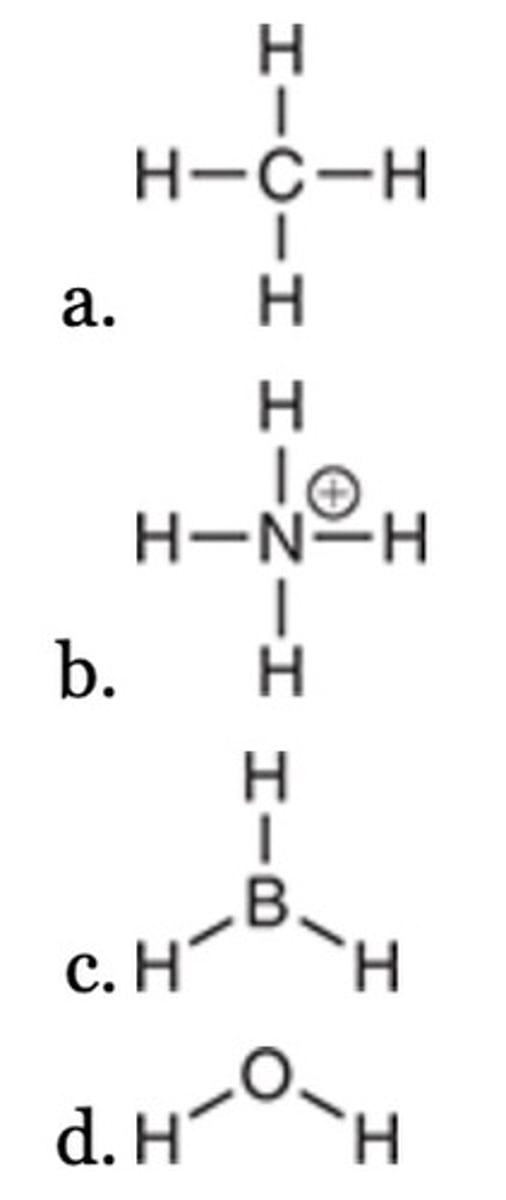
Which of the following structures exhibits an sp3-hybridized nitrogen atom?
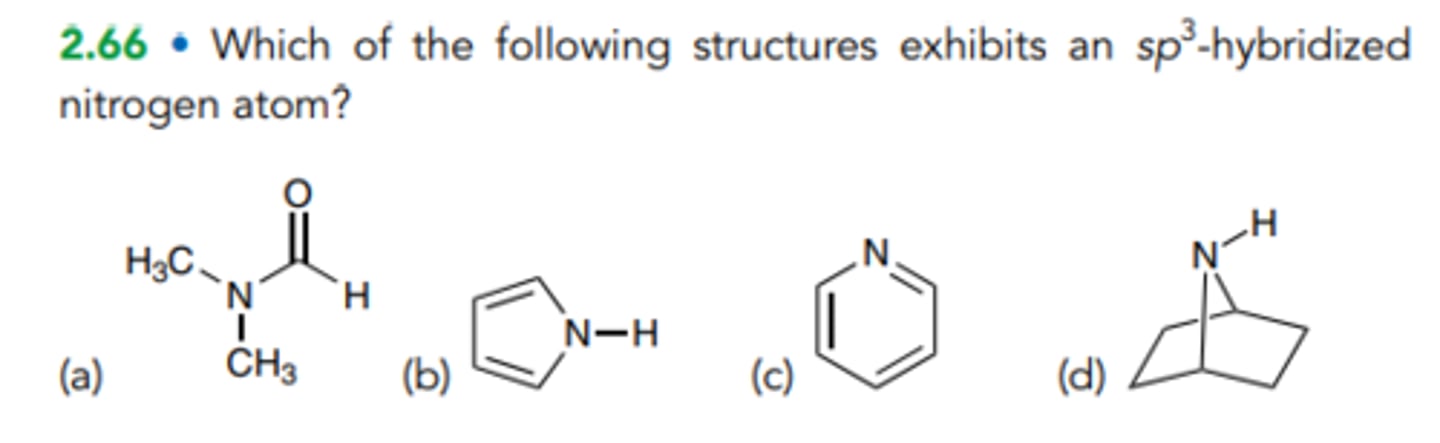
C
Which is a bond-line drawing of (CH3)2CHCH2OC(CH3)3?
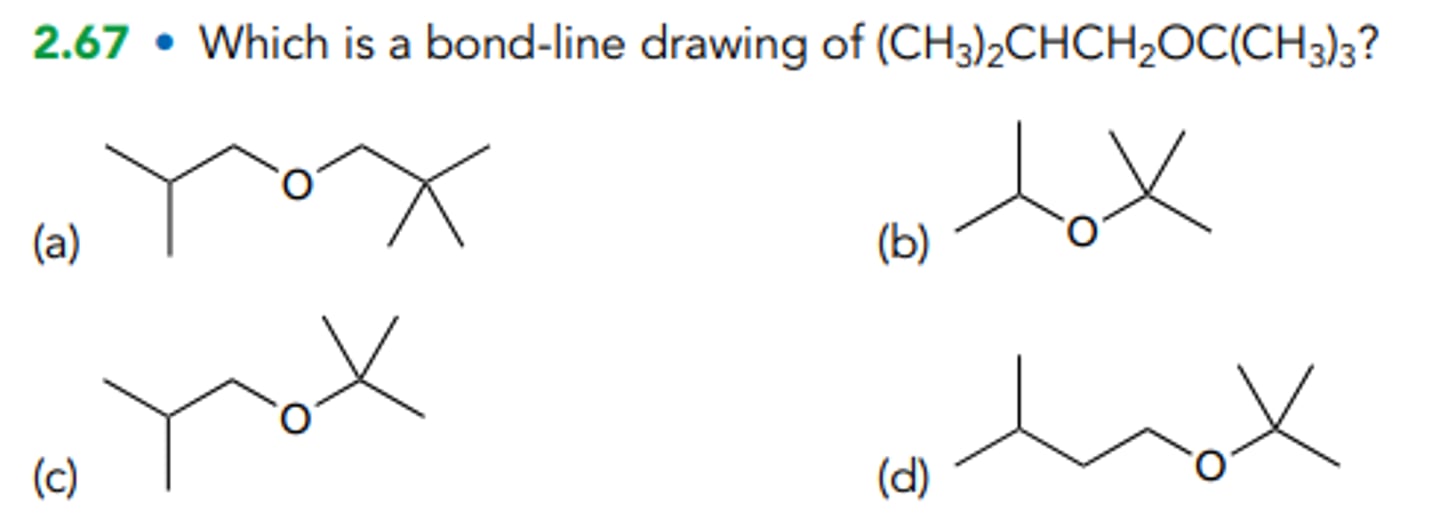
C
Which of the following has the correct curved arrow(s) placement to show resonance for the given allylic carbocation?
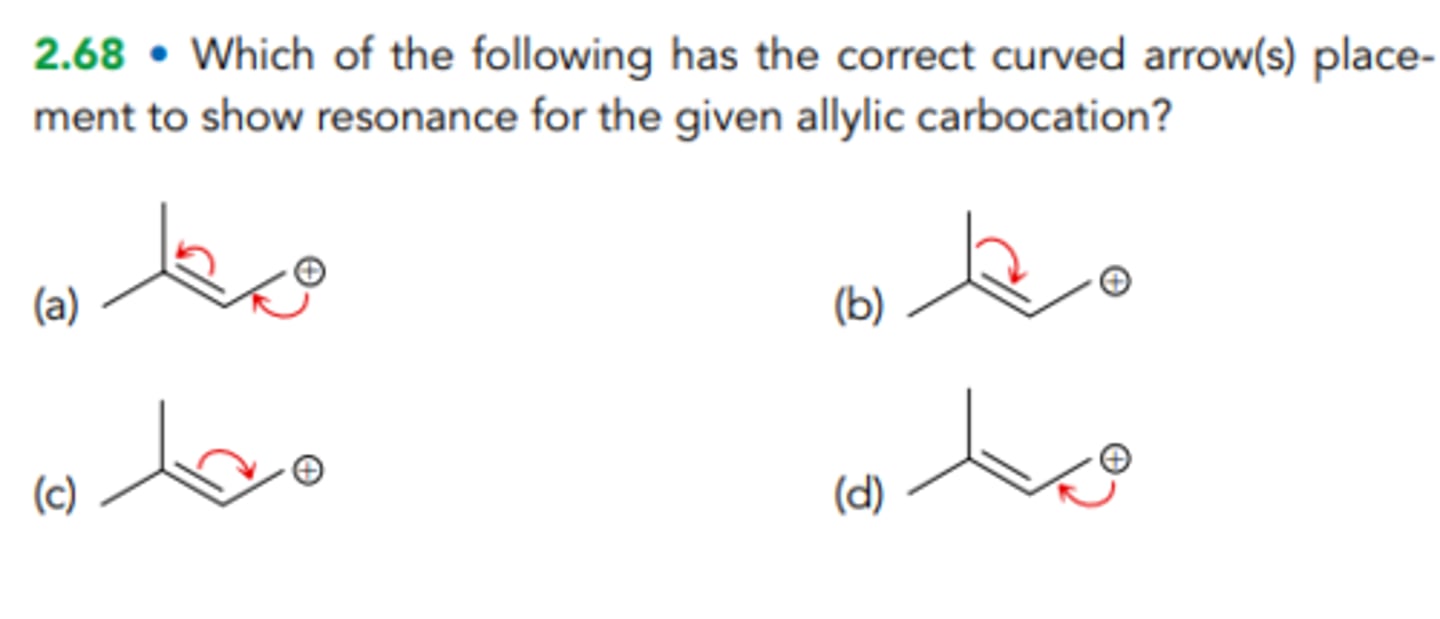
A
Which of the following anions is resonance delocalized?
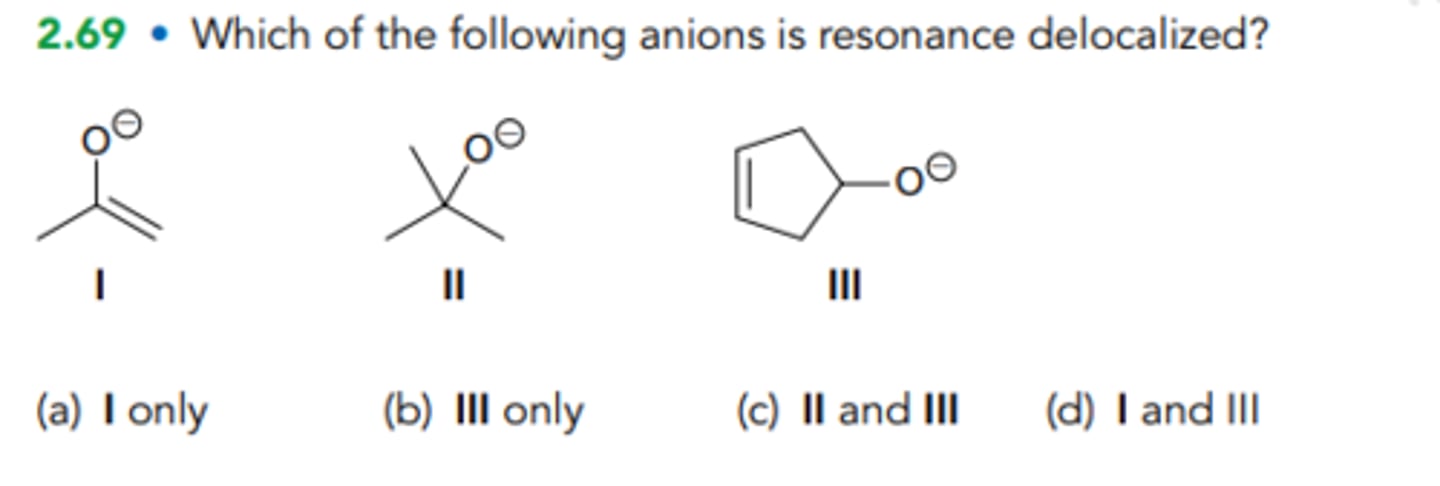
A
The following cation has a total of how many resonance structures?
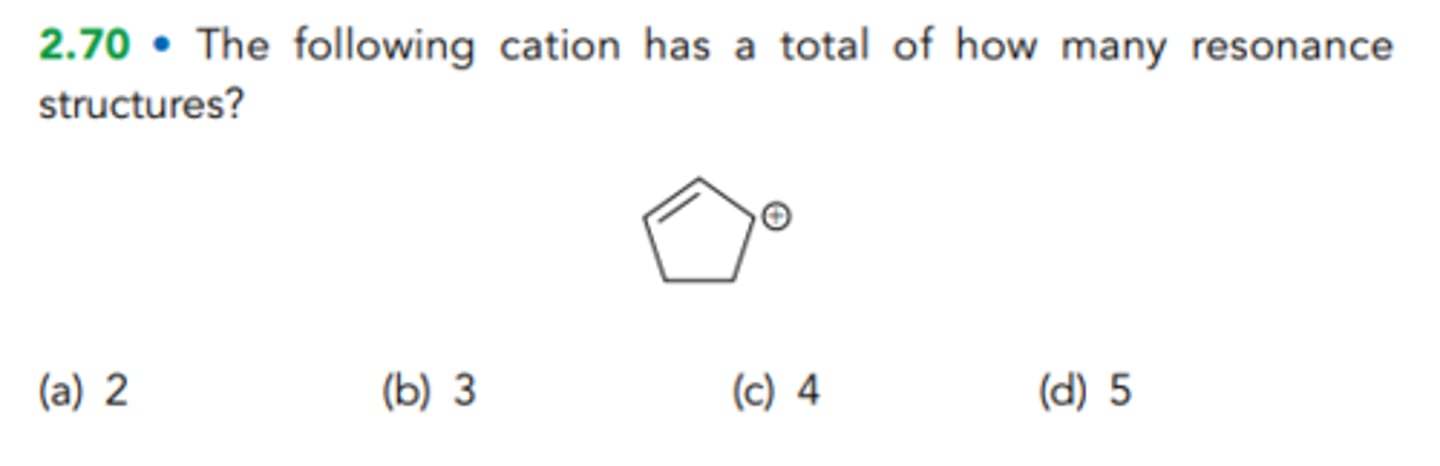
D
Which of the following best represents the resonance hybrid of the given anion?
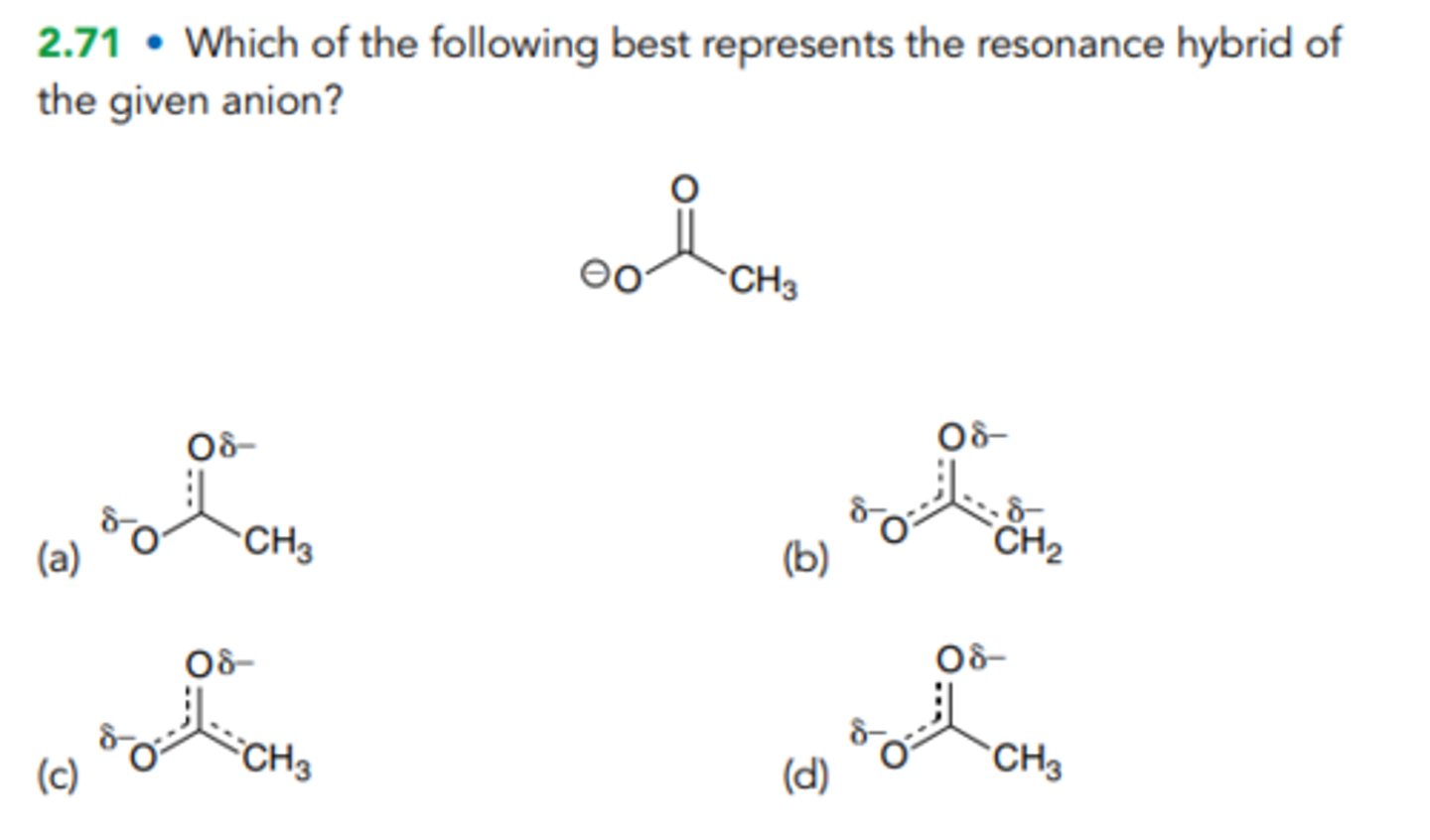
B
Which of the following does NOT represent a pair of resonance structures?
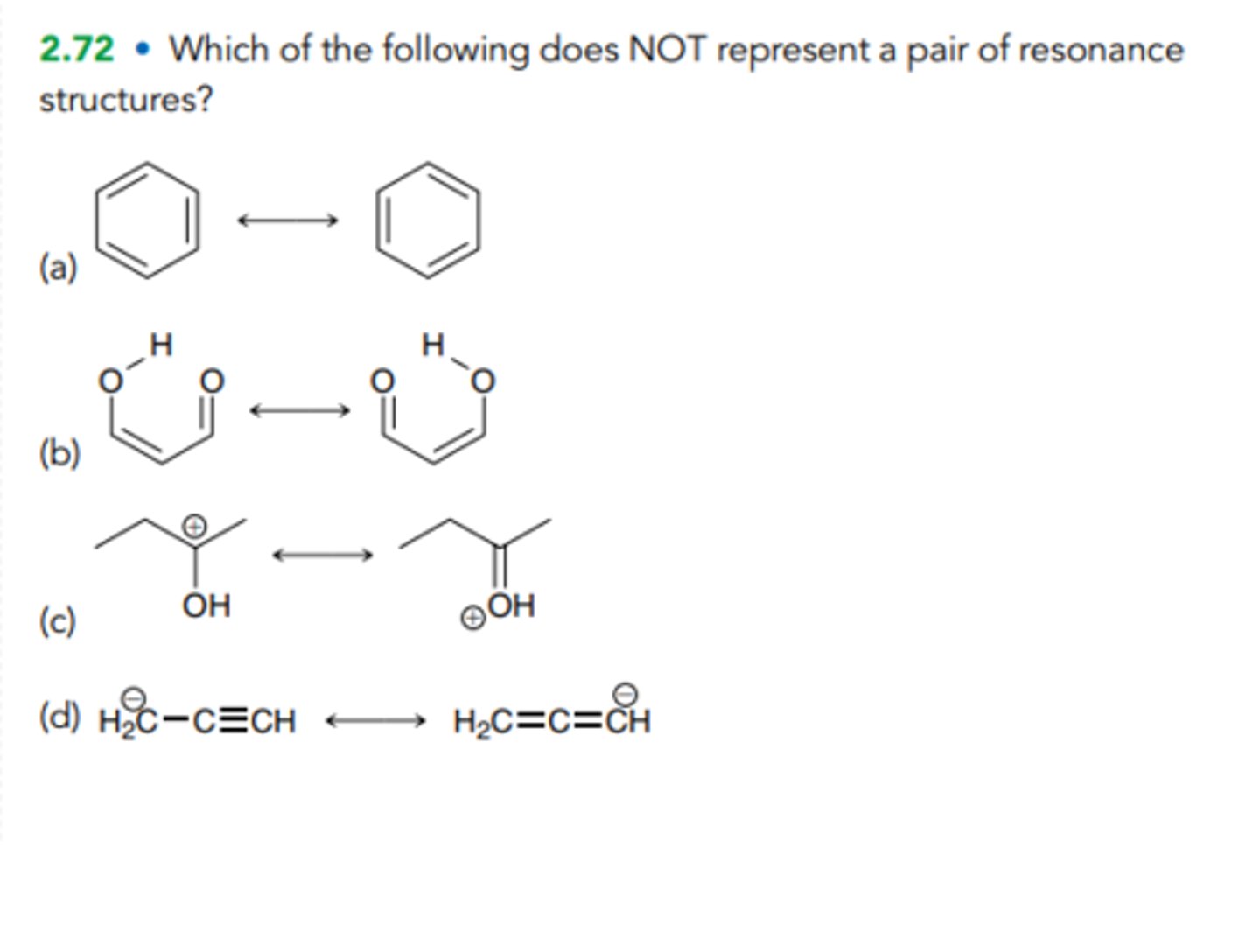
C
What is the strongest base that is present after methyl magnesium bromide (CH3MgBr) is treated with water?
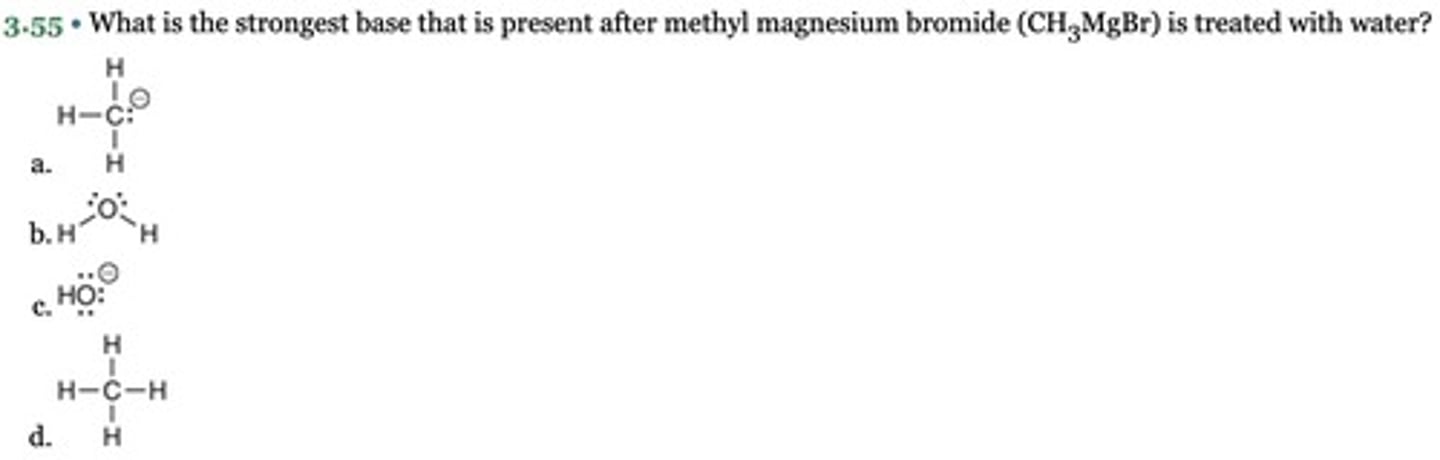
The right side
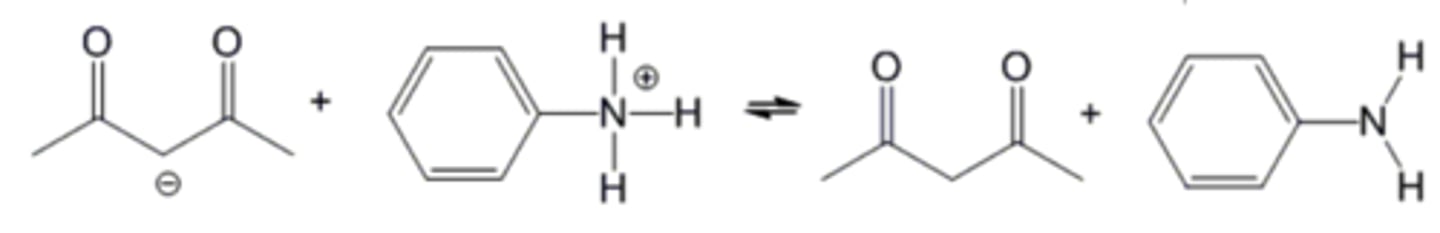
Which side of the following equilibrium is favored?
The right side.
The left side.
Depends on temperature.
Cannot determine without more information.
C
All of the following are more acidic than water (H2O) EXCEPT:
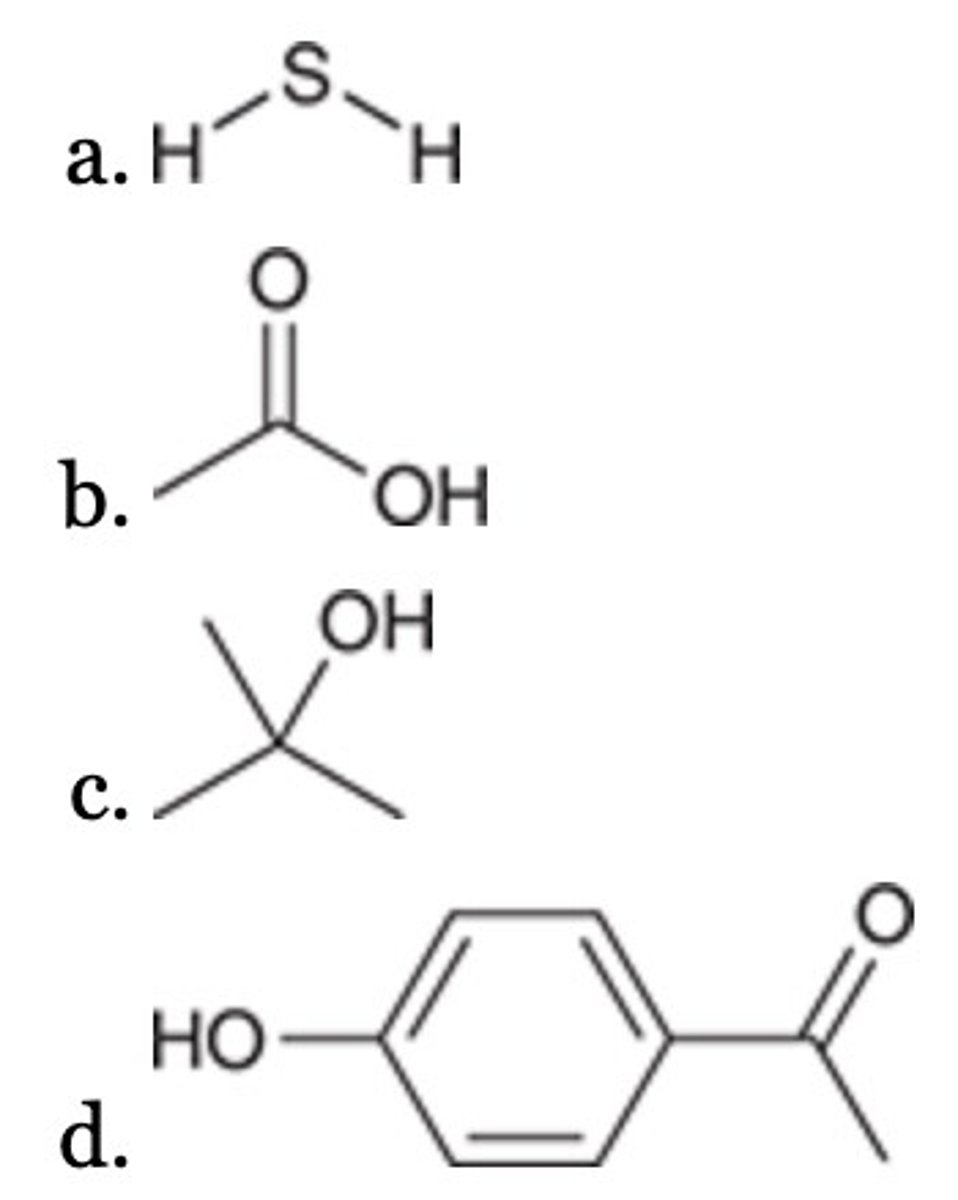
D
All of the following are Lewis bases EXCEPT:
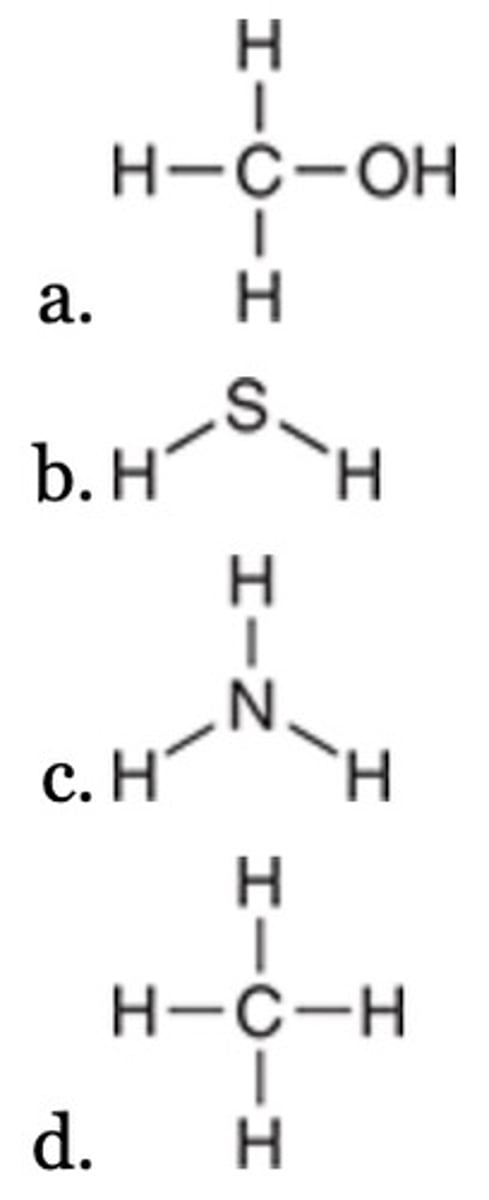
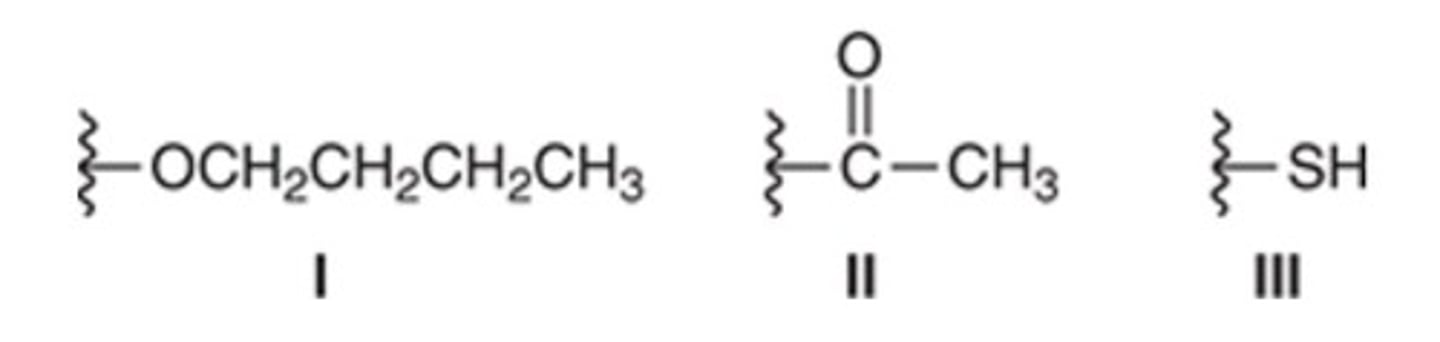
II < III < I
Arrange the following compounds in order of increasing acidity, from the weakest acid to the strongest acid.
II < I < III
II < III < I
I < III < II
III < II < I
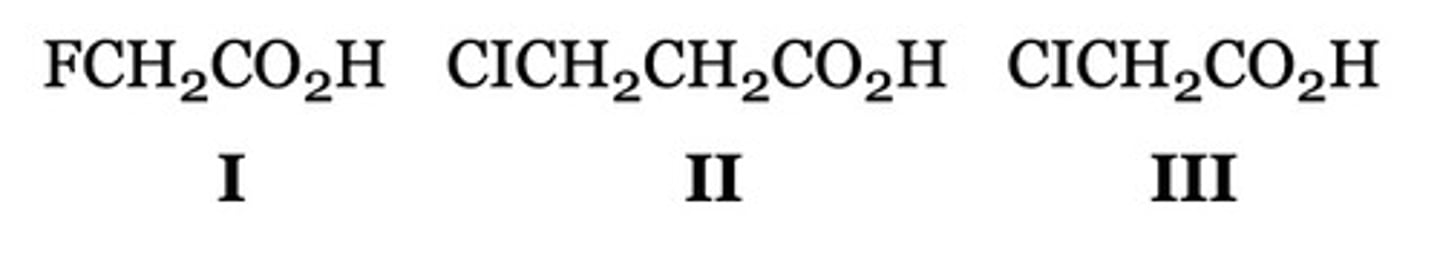
HBr is the stronger acid because Br is larger than Cl.
Which is the stronger acid, HCl or HBr? Explain briefly.
HCl is the stronger acid because Cl is more electronegative than Br.
HCl is the stronger acid because Cl is smaller than Br.
HBr is the stronger acid because Br is less electronegative than Cl.
HBr is the stronger acid because Br is larger than Cl.
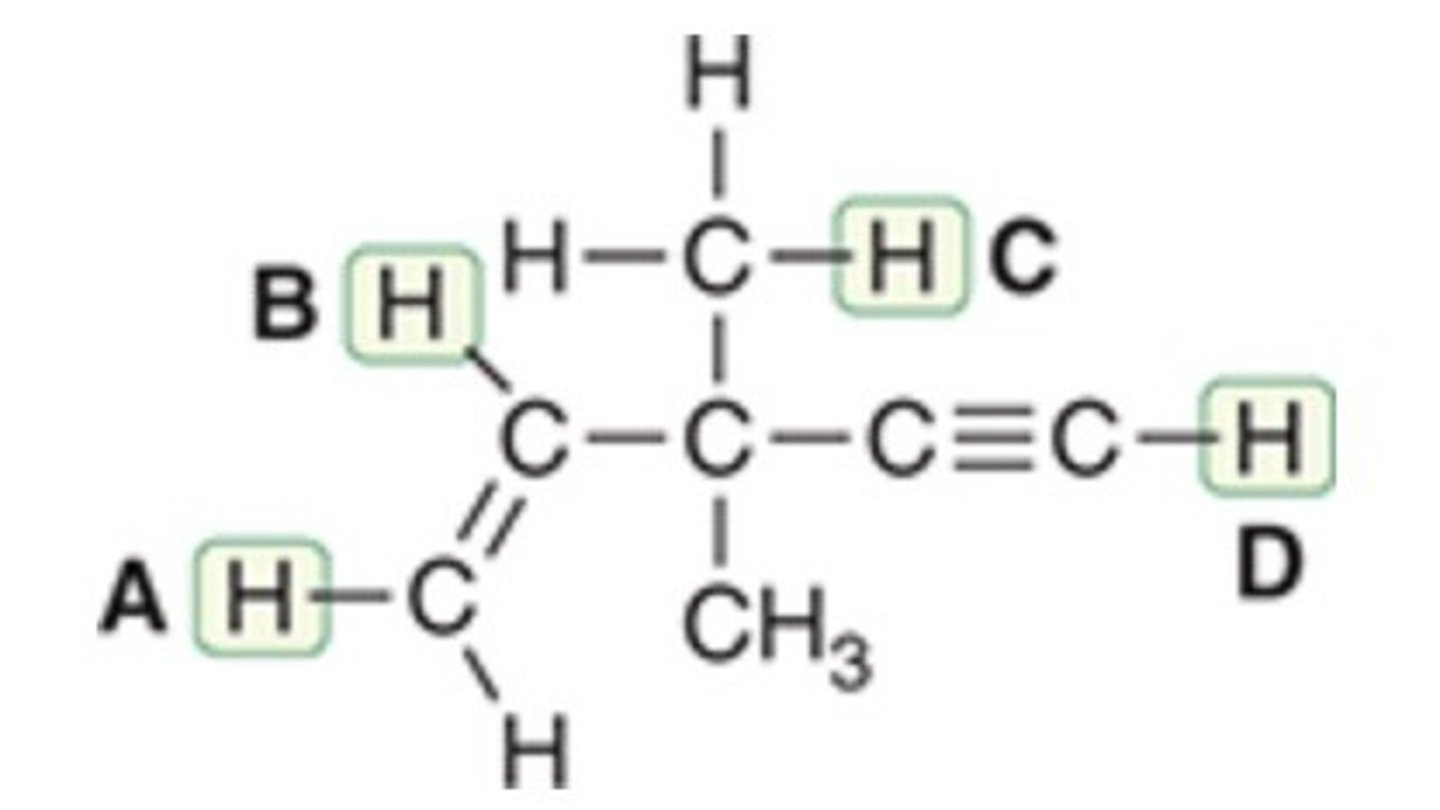
Proton D
Which of the indicated protons in the given compound is the most acidic?
Proton A
Proton B
Proton C
Proton D
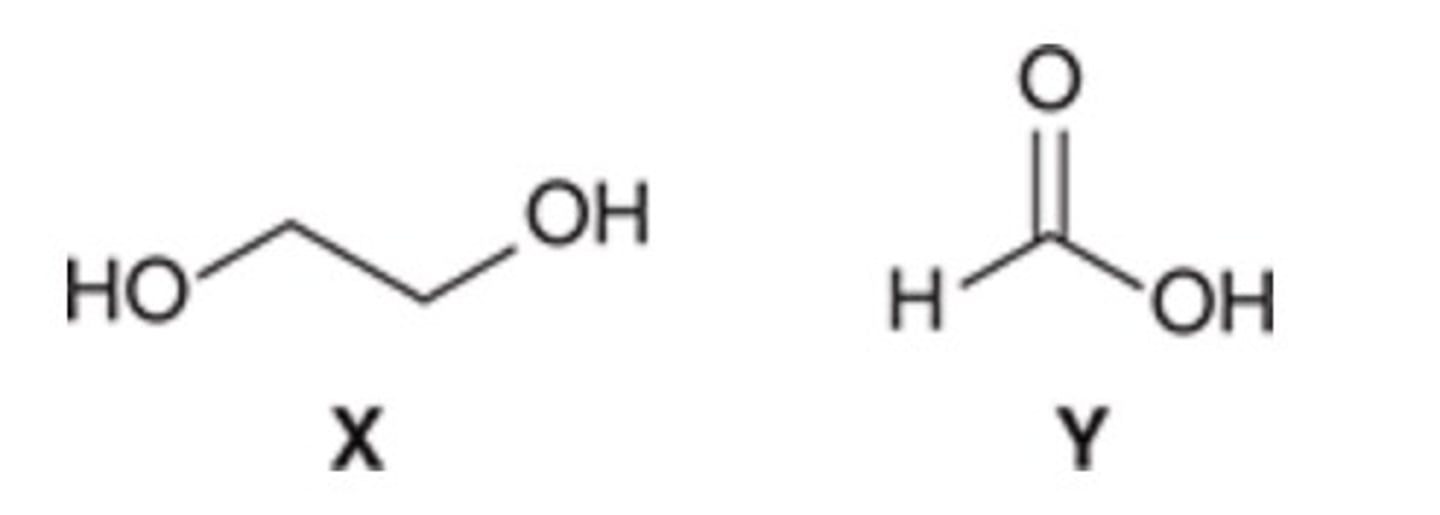
Y is the stronger acid because its conjugate base is stabilized by resonance.
Which of the given compounds is more acidic? Briefly explain.
X is the stronger acid because the acidic proton is on a more electronegative atom.
X is the stronger acid because its conjugate base is stabilized by inductive effects.
Y is the stronger acid because its conjugate base is stabilized by resonance.
Y is the stronger acid because the acidic proton is stabilized by inductive effects.
A
Of the following, which is the strongest base?
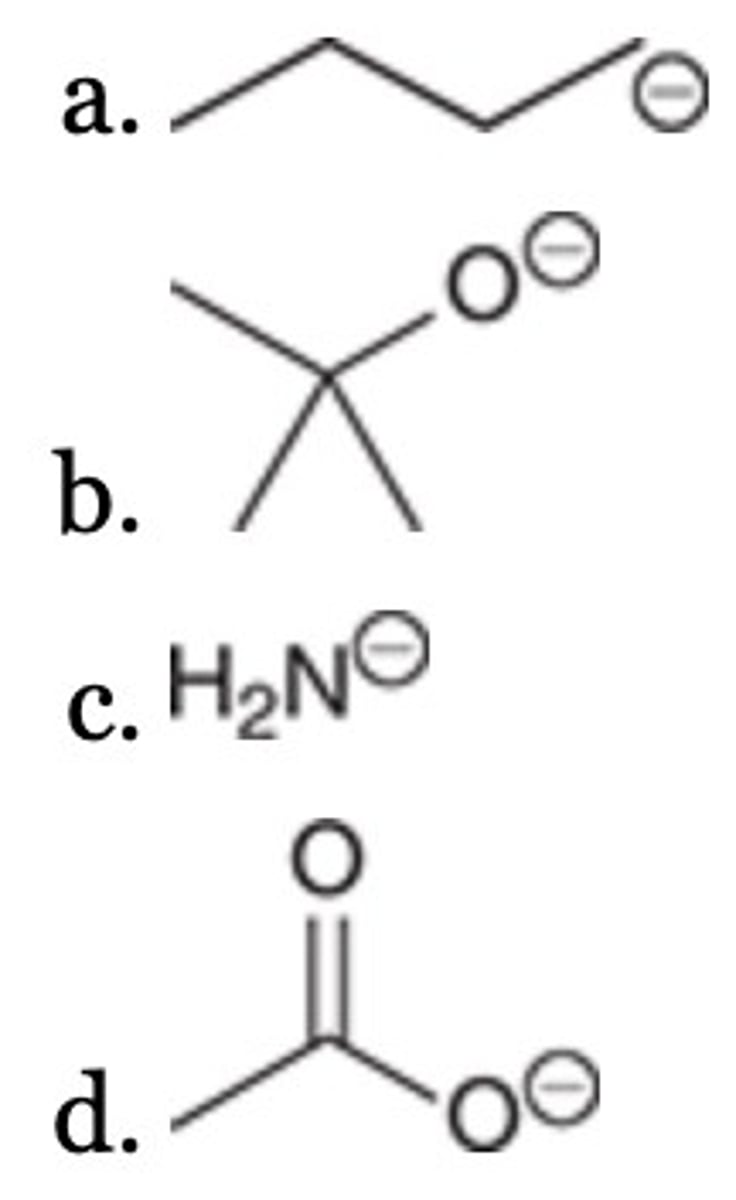
D
All of the following are representations of cis-1,2-dimethylcyclohexane, EXCEPT:
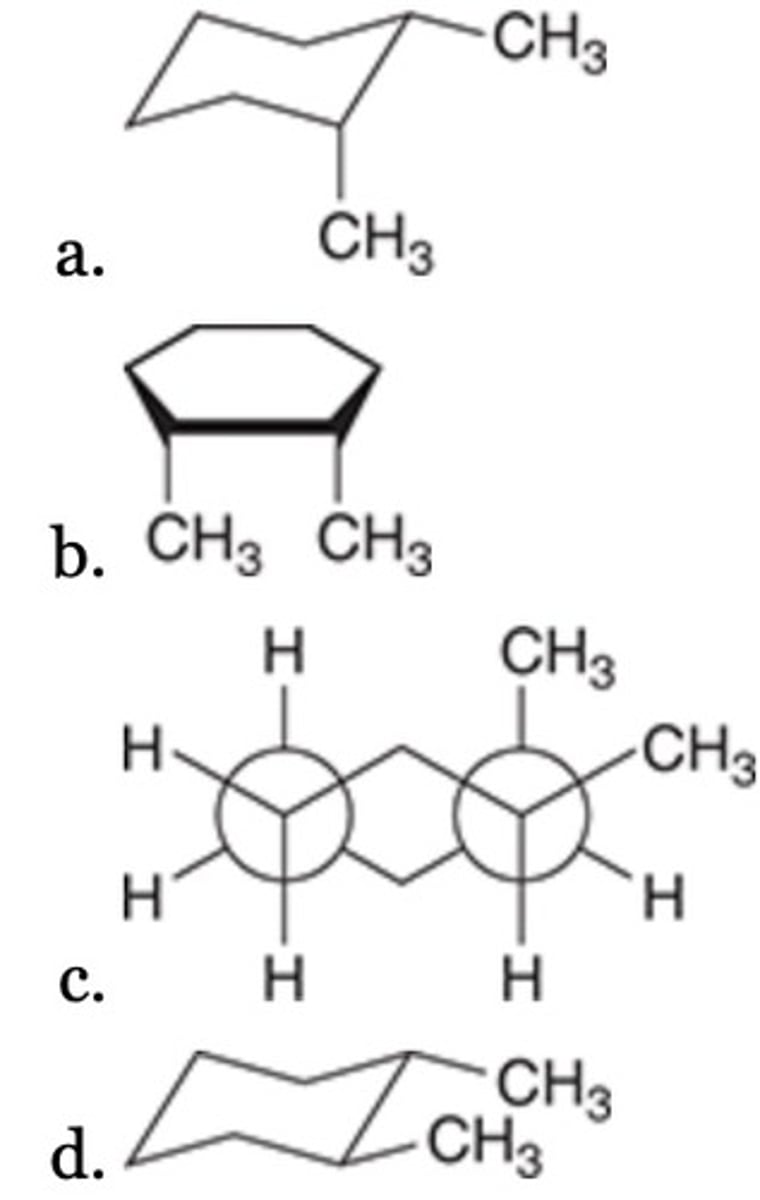
B
All of the following are representations of 2-methylpentane, EXCEPT:
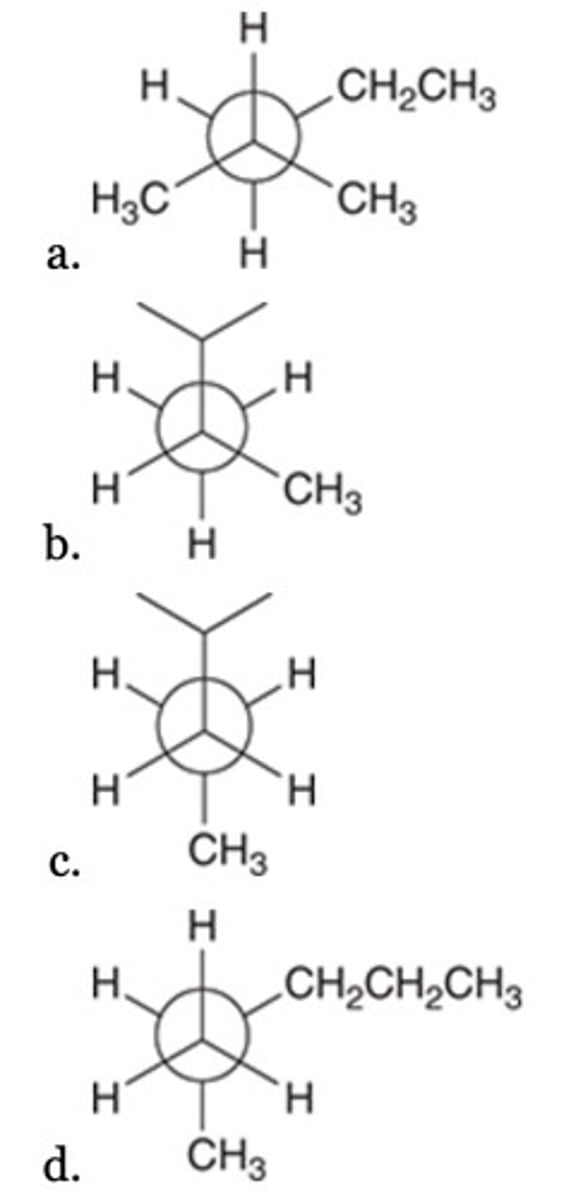
C
Which of the following is expected to have the largest heat of combustion?
D
Which of the following is a constitutional isomer of heptane?
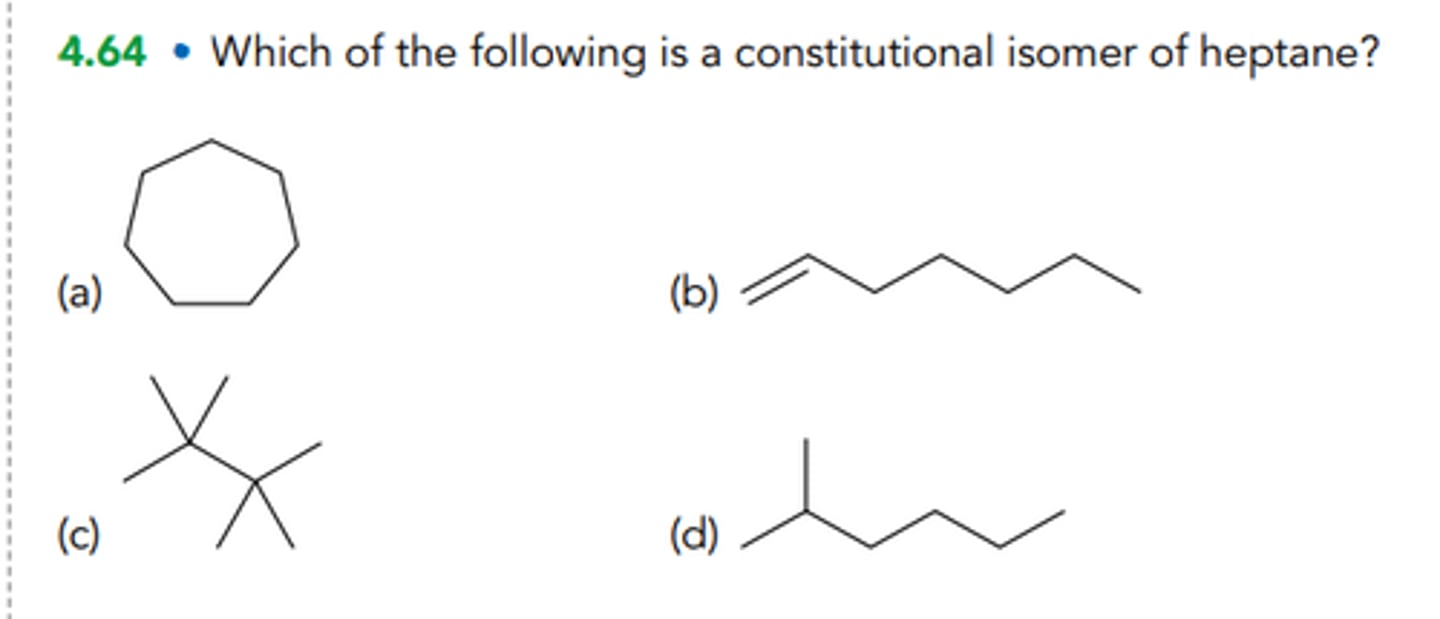
2,3-dimethylhexane
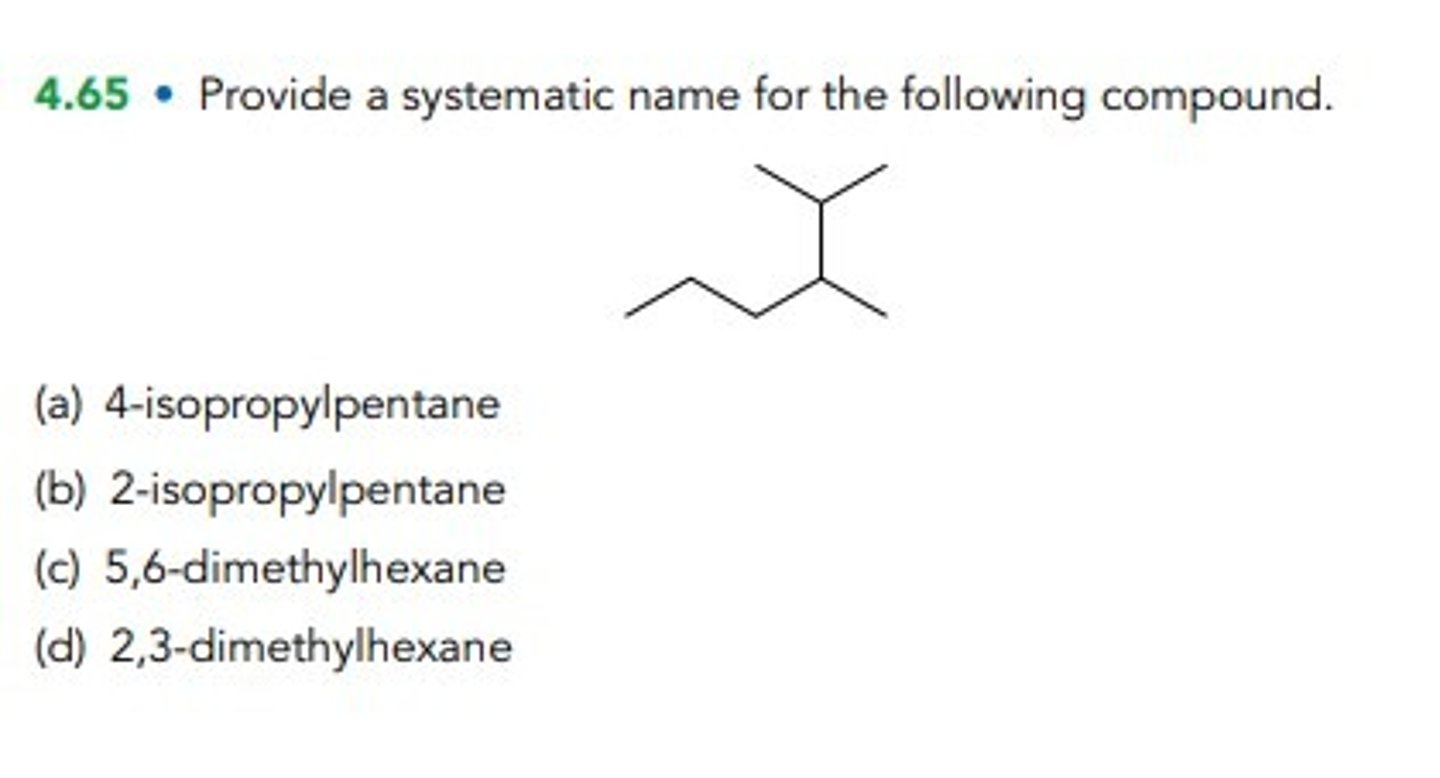
Provide a systematic name for the following compound.
4-isopropylpentane
2-isopropylpentane
5,6-dimethylhexane
2,3-dimethylhexane
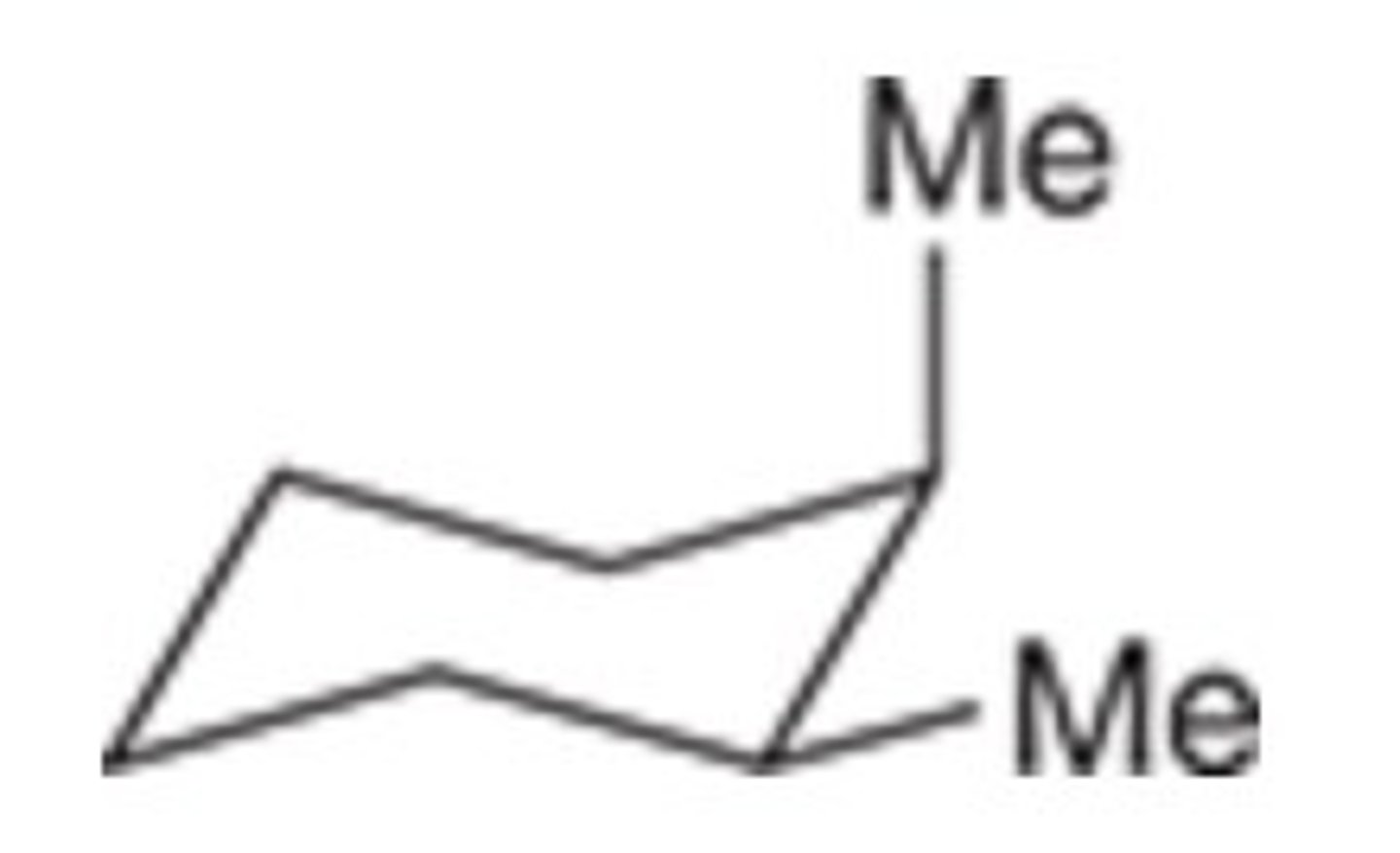
C
Which of the following represents the most stable conformation of cis-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane?
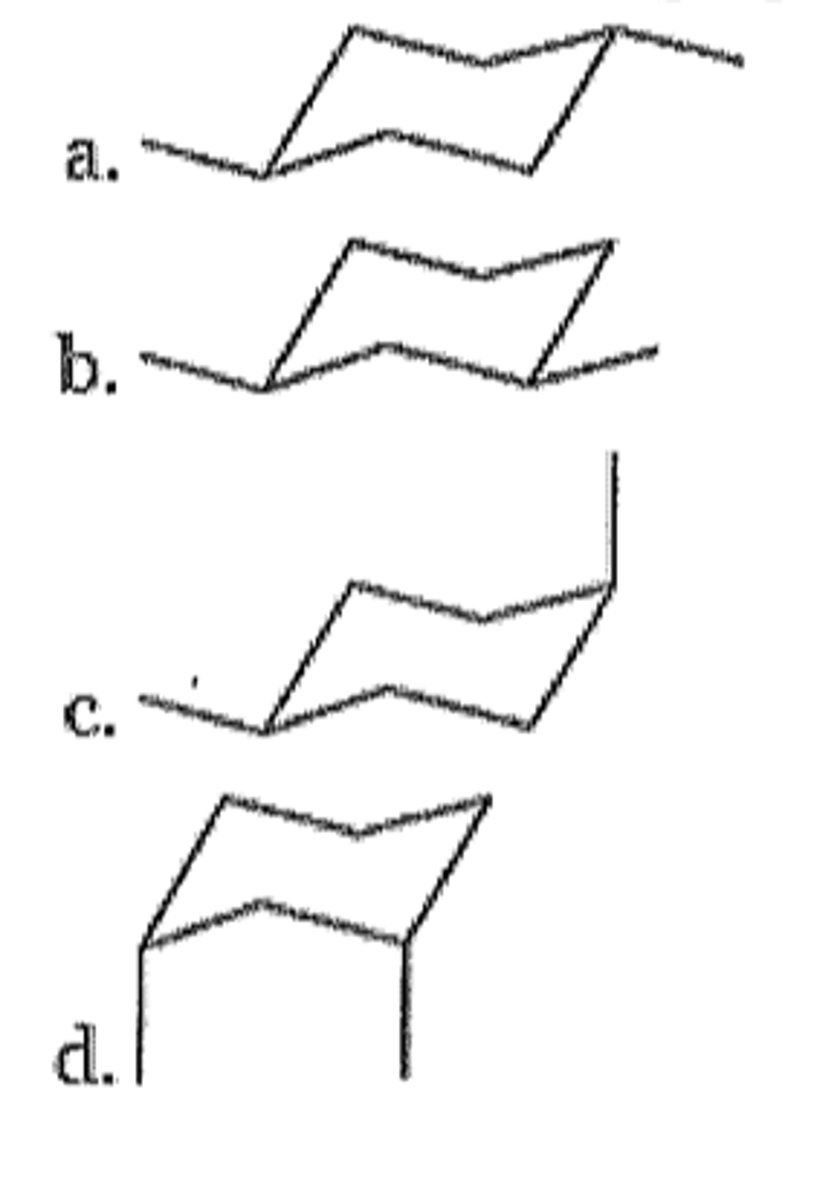
B
Which of the following conformers has one or more gauche interactions?
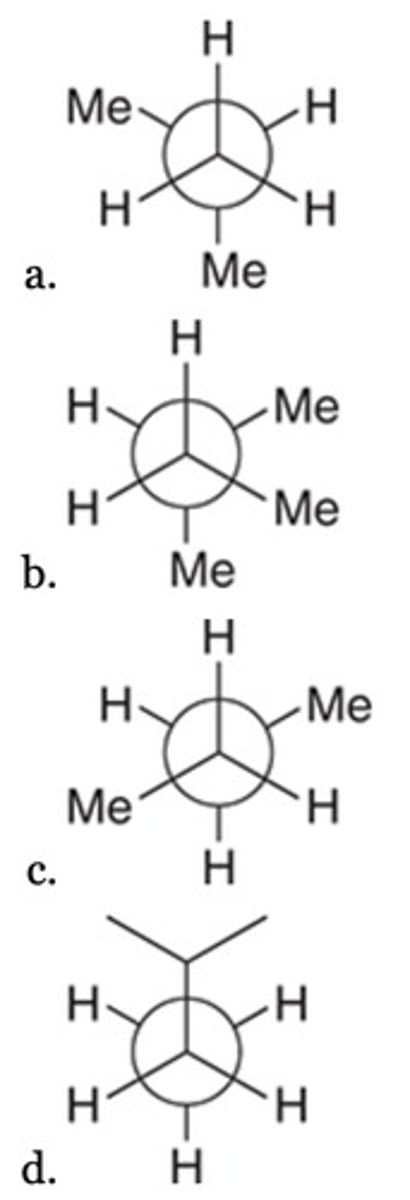
C
Which of the following represents the most stable conformation of the given compound?
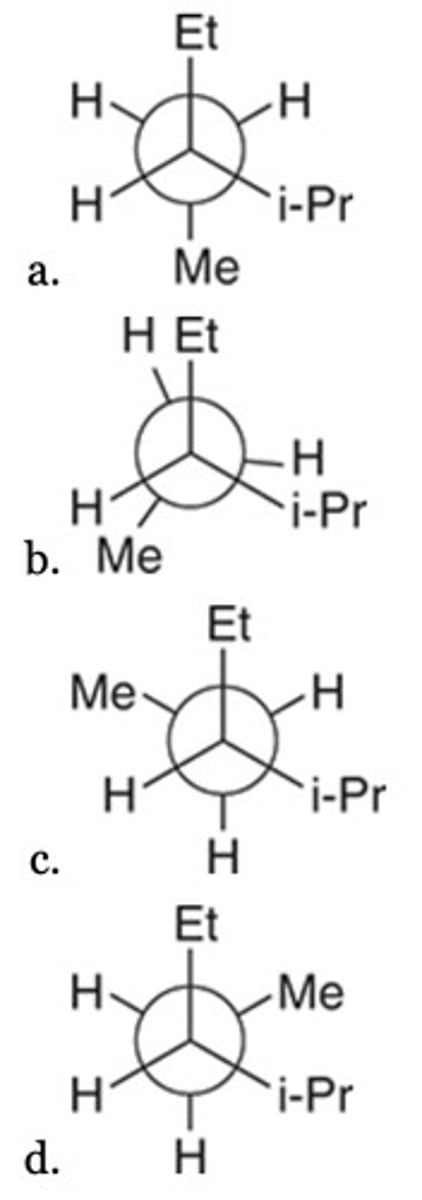
(1,1-dimethylethyl)
Which of the following is the correct IUPAC name for the tertbutyl substituent?
(1,1-dimethylethyl)
(1,1,1-trimethyl)
(1-methyl-2-propyl)
2-methyl-2-propyl)
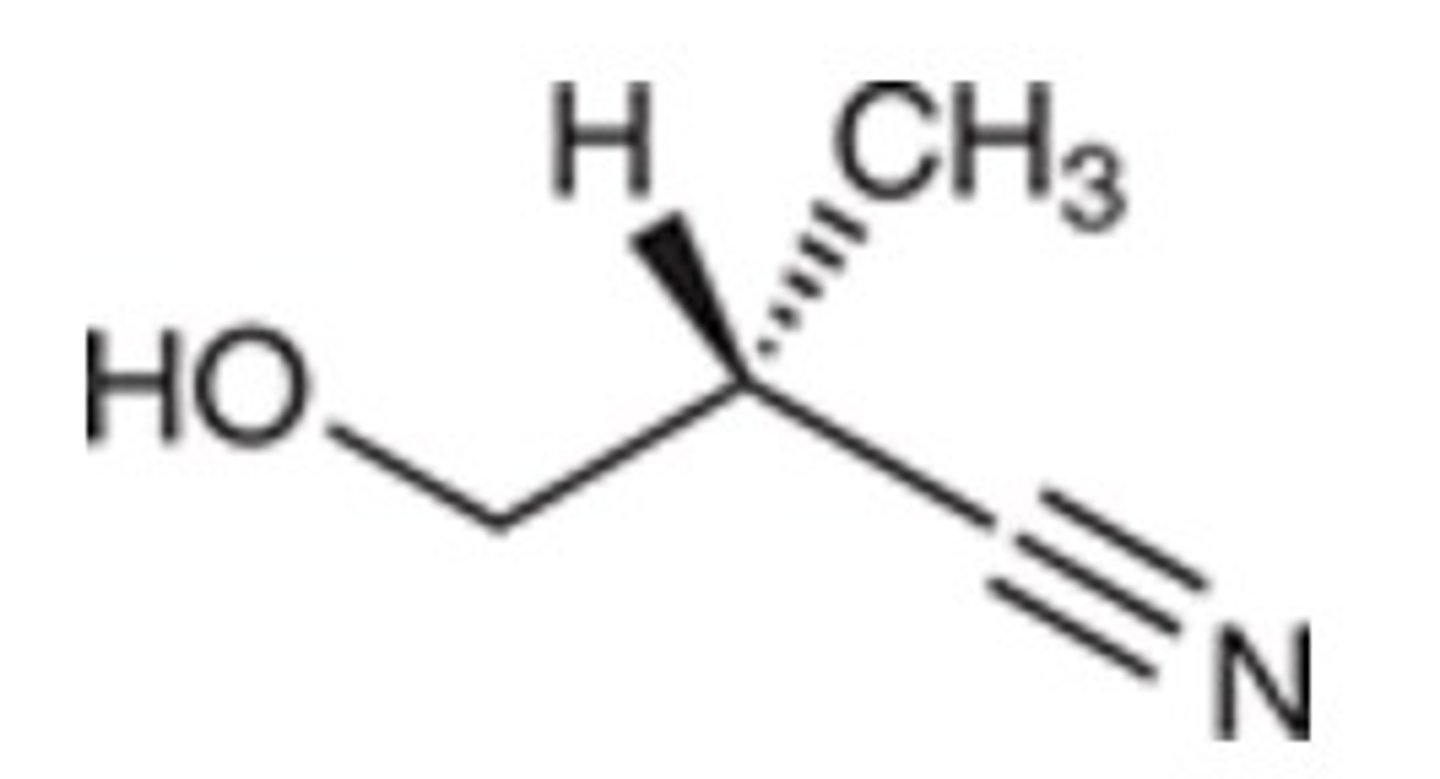
R
What is the configuration of the chiral center in the following compound?
R
S
Z
Depends on T
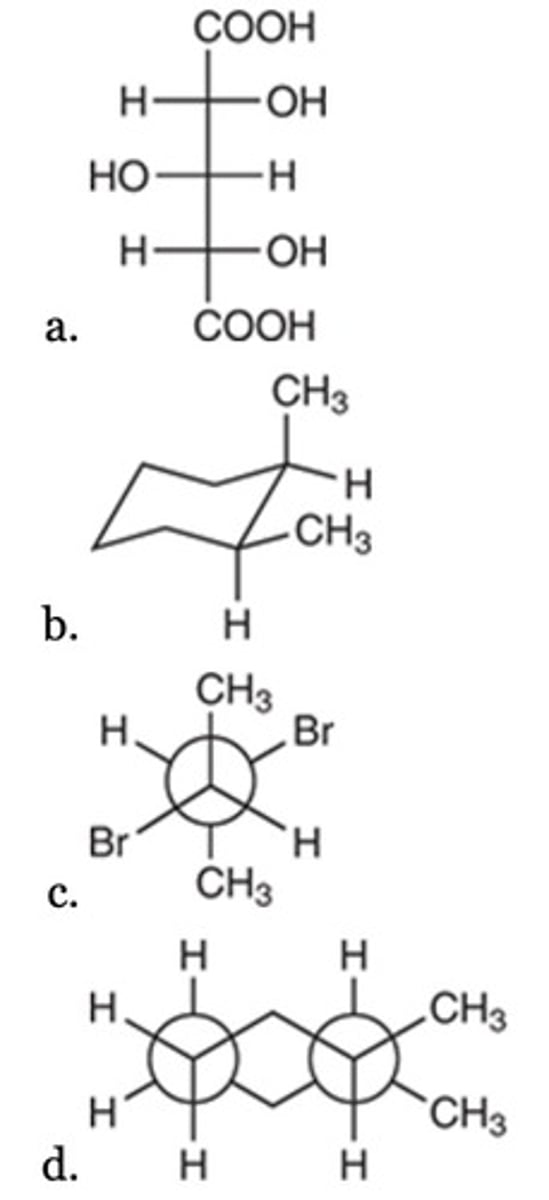
Diastereomers
What is the relationship between the following two compounds?
Enantiomers
Diastereomers
Constitutional isomers
Resonance forms
D
Which of these compounds is expected to be optically active at room temperature?
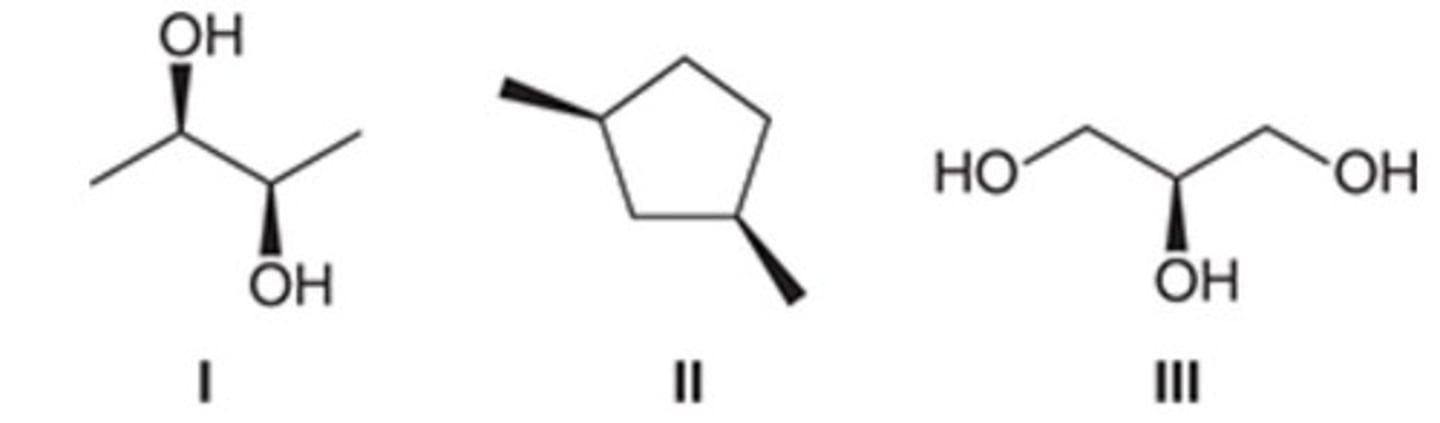
II only
Identify the meso compound(s).
I only
II only
I and III only
I, II, and III
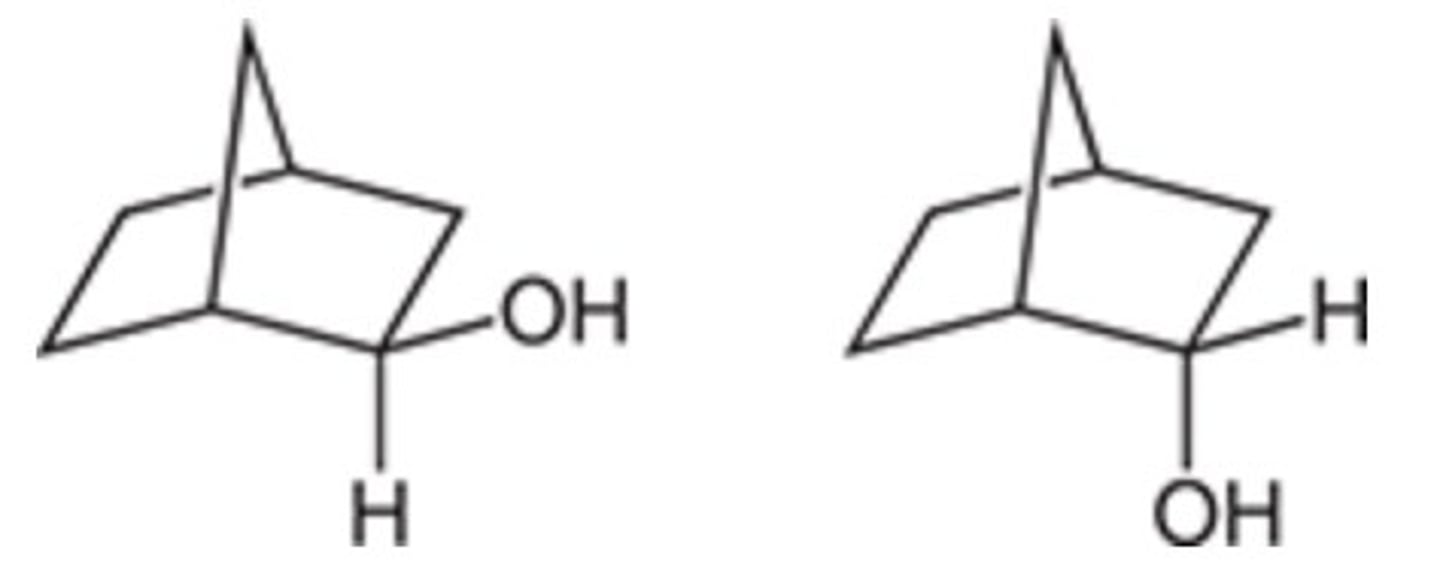
It is not chiral, and it does not have an enantiomer.
Is the following compound chiral, and does it have an enantiomer?
It is not chiral, and it does not have an enantiomer.
It is not chiral, but it does have an enantiomer.
It is chiral, and it has an enantiomer.
It is chiral, but it does not have an enantiomer.
II < I < III
Arrange the given substituents in order of increasing priority (based on Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules), from lowest to highest priority.
III < II < I
III < I < II
II < I < III
I < II < III
Keq > 1
For a reaction with ΔG < 0, which of the following MUST be true?
The reaction must be exothermic
The reaction must be endothermic
Keq > 1
None of the above
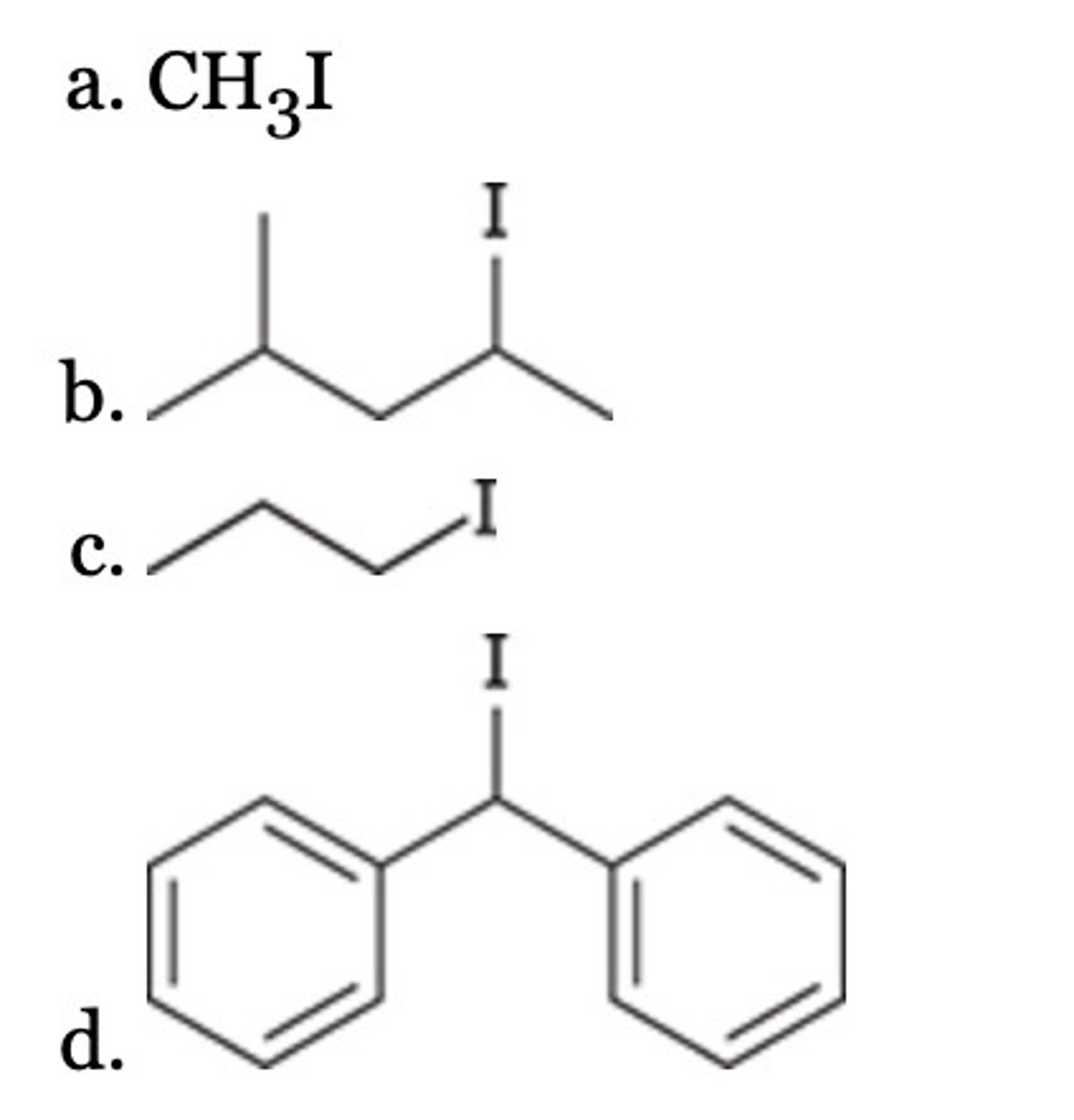
D
Which of the following can serve as a nucleophile?
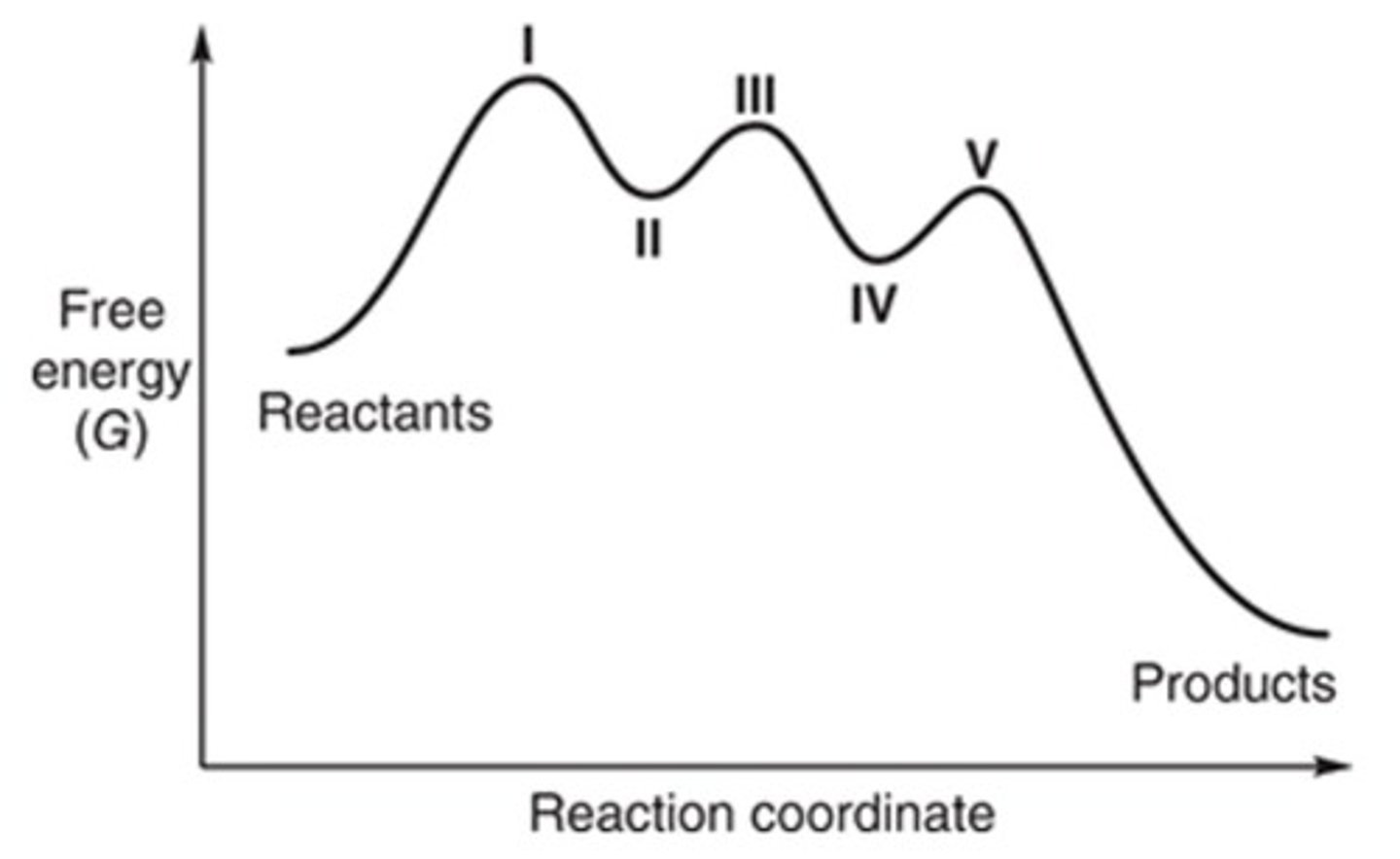
II and IV
In the following energy diagram showing the progress of a reaction, which location(s) represent an intermediate?
I, III, and V
II and IV
Only III
I, II, III, IV, and V
ΔS < 0
Which best describes the change in entropy for the following reaction?
ΔS > 0
ΔS = 0
ΔS < 0
ΔS = 1

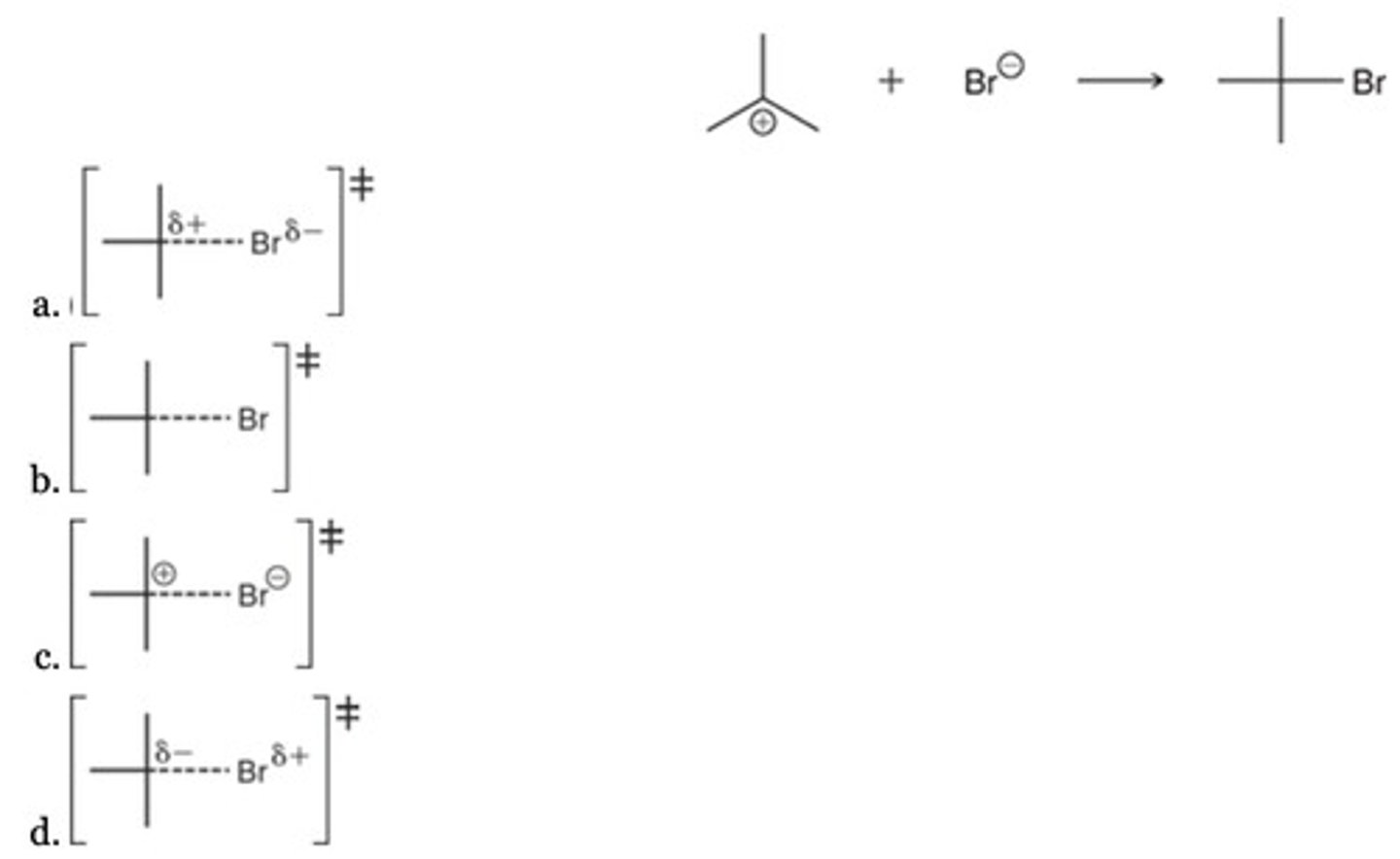
A
Which best represents the transition state of the following reaction?
The bonds broken are weaker than the bonds formed.
For a reaction with ΔH < 0, which of the following must be true?
All bonds are broken homolytically.
All bonds are broken heterolytically.
The bonds broken are stronger than the bonds formed.
The bonds broken are weaker than the bonds formed.
bimolecular
The rate expression for a reaction was found to be:
Rate=k[Et Br][Na Sh]
This reaction is best described as
zero order
bimolecular
unimolecular
rate-determining
proton transfer, followed by loss of a leaving group
What type of reaction steps are represented below?
loss of a leaving group, followed by loss of a leaving group
proton transfer, followed by loss of a leaving group
nucleophilic attack, followed by proton transfer
proton transfer, followed by nucleophilic attack
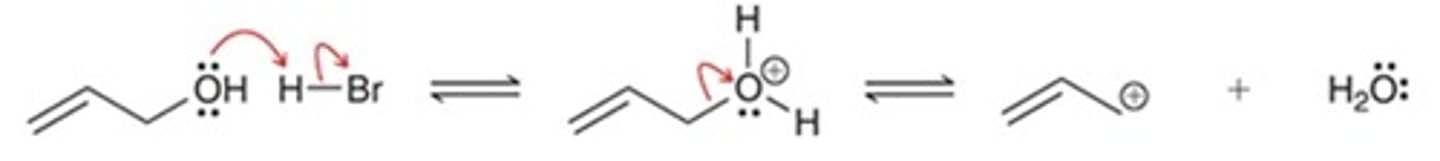
The reaction proceeds via a carbocation intermediate.
For the following substitution reaction, which statement is FALSE?
The process is bimolecular.
Increasing the concentration of hydroxide will cause an increase in the rate of reaction.
The use of a polar aprotic solvent will enhance the rate.
The reaction proceeds via a carbocation intermediate.
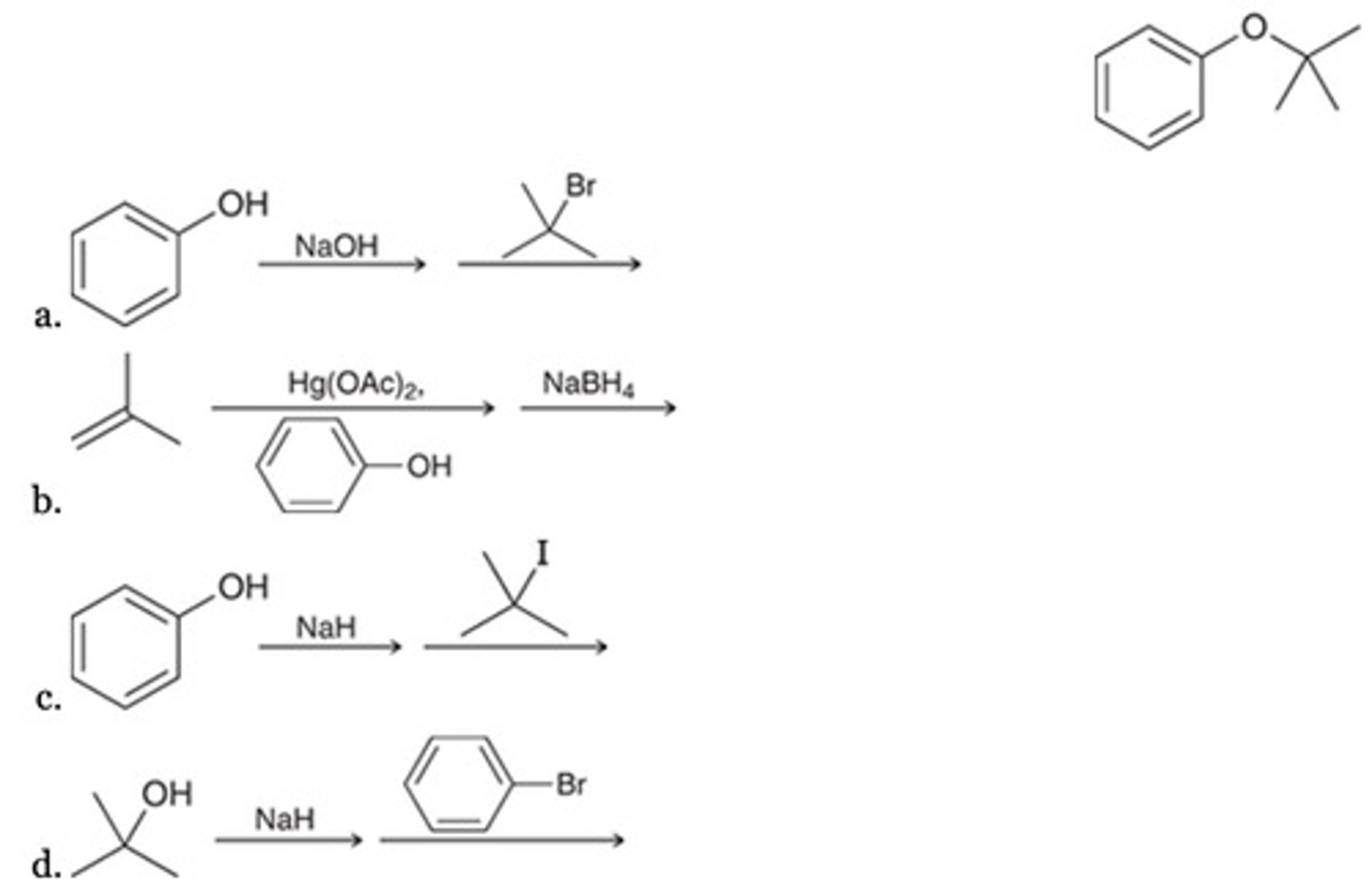
D
Which is the major product of this reaction?
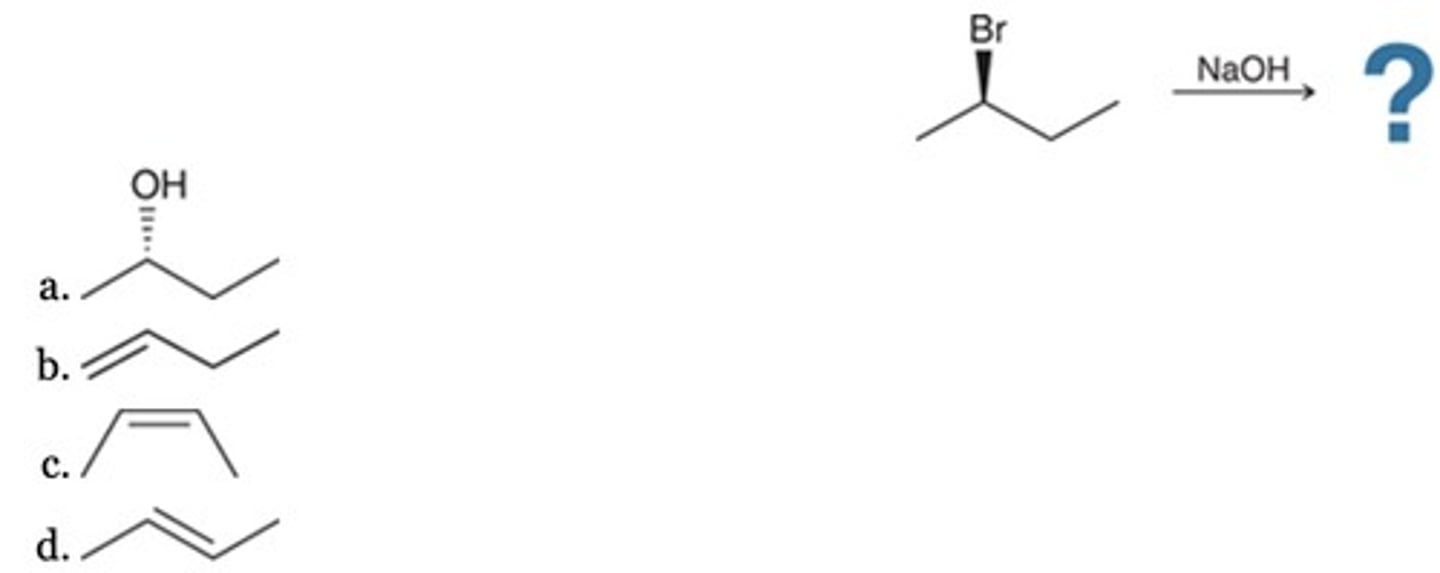
C
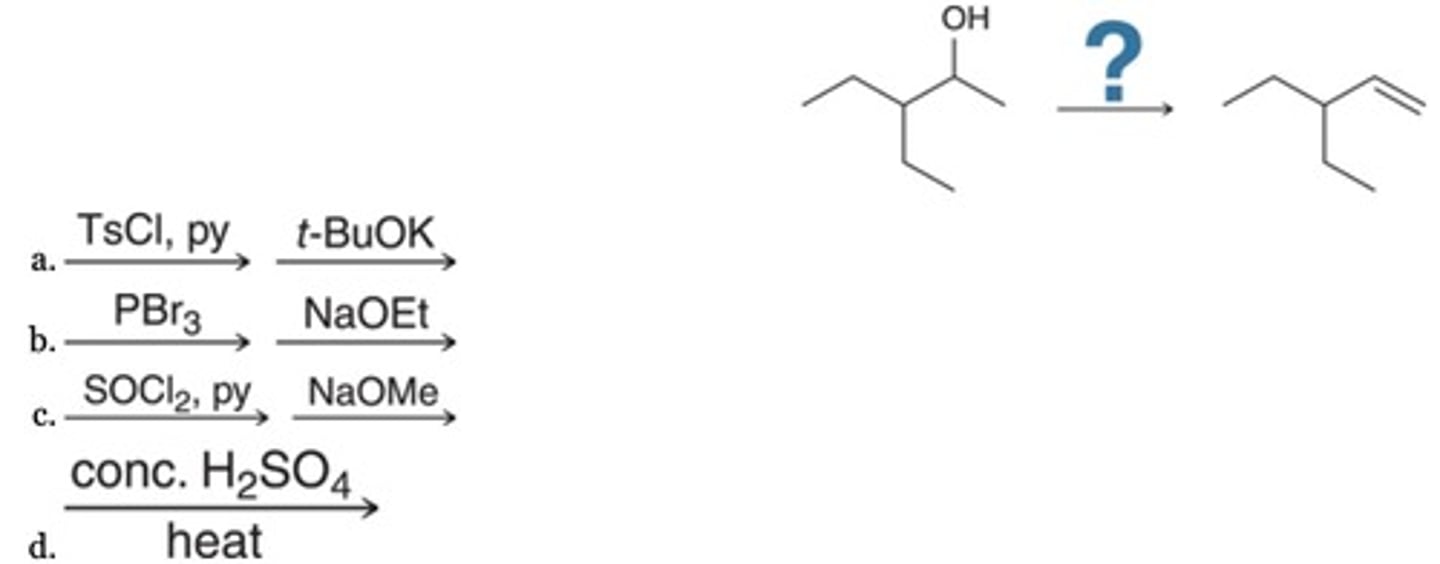
Of the following, which is the most efficient synthesis of 1-butene (CH3CH2CH═CH2)?
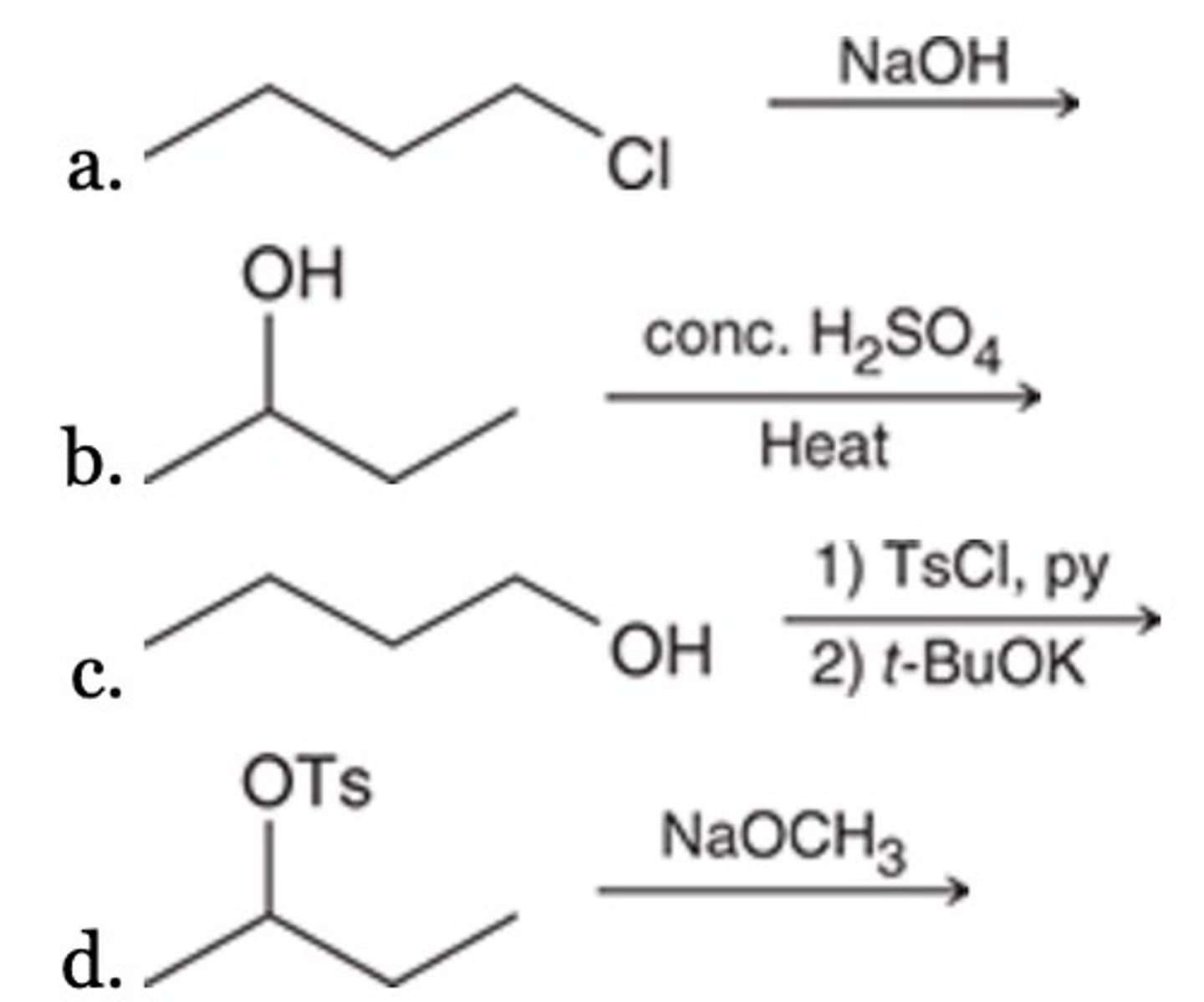
Increased steric hindrance
Which of the following is NOT favorable for an SN2 reaction?
A leaving group on a primary carbon atom
A polar aprotic solvent
A strong nucleophile
Increased steric hindrance
SN1
Which mechanism involves a carbocation electrophile reacting with a weak nucleophile?
SN1
SN2
E1
E2
B
Which of the following best represents the transition state of the rate-determining step for the given reaction?
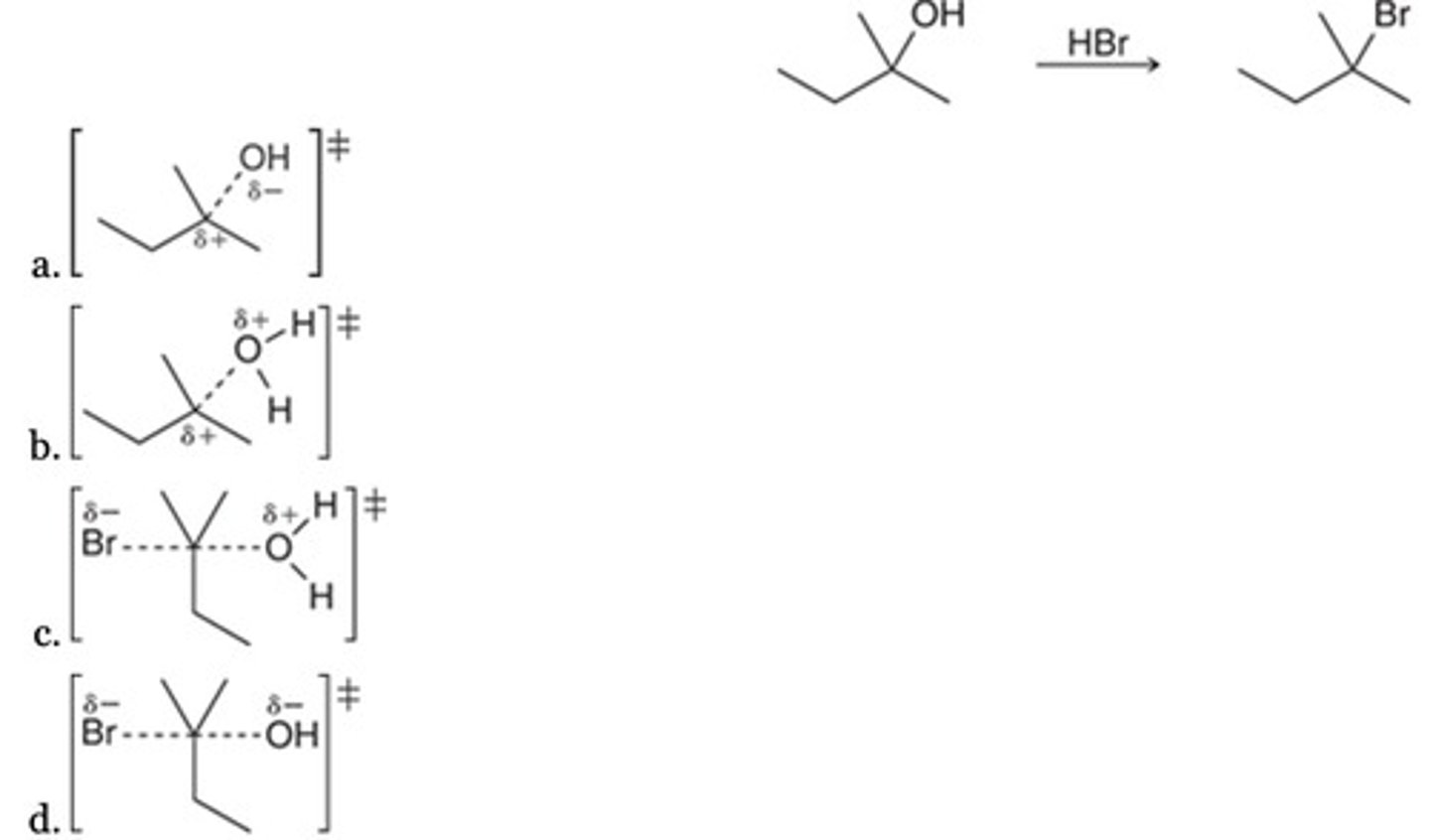
c. II and IV
Sodium ethoxide (NaOEt) is a suitable reagent to promote which mechanism(s)?
SN1
SN2
E1
E2
a.I and II
b.I and III
c. II and IV
d. III and IV
t-BuOK
Which is the best reagent to achieve the following transformation?
t-BuOK
NaOH
CH3OH
Conc. H2SO4
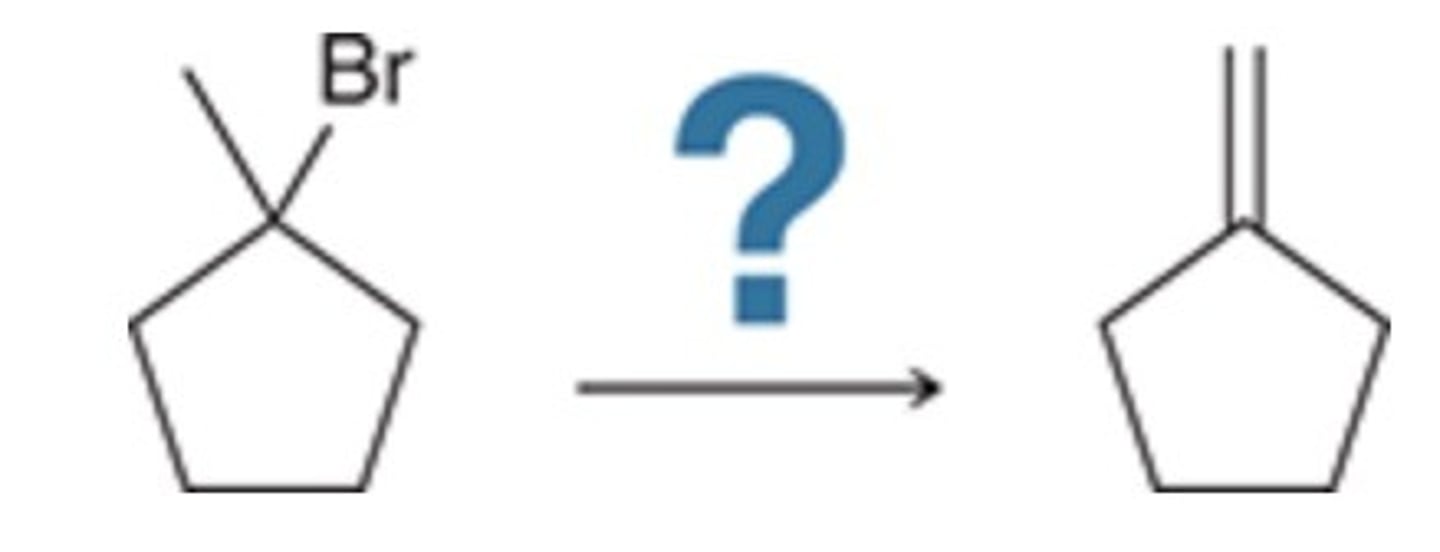
D
Which substrate undergoes the fastest solvolysis reaction with methanol (CH3OH)?
I is faster because it has less steric hindrance.
Which is the faster reaction and why?
I is faster because it has a better nucleophile.
I is faster because it has less steric hindrance.
II is faster because it has the better leaving group.
II is faster because it has the more stable carbocation.
C
Which disconnection leads to the most reasonable retrosynthesis of the given target molecule?
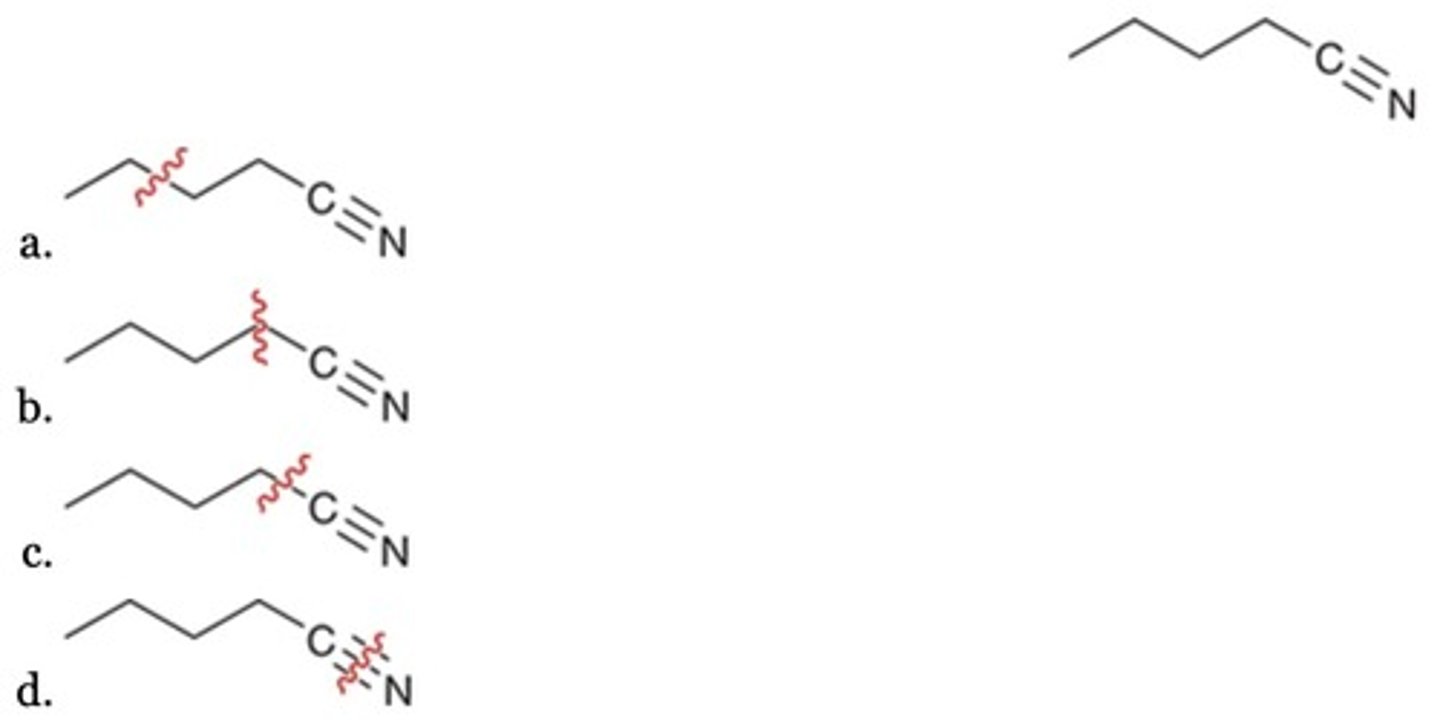
A
Which of the following is not a reasonable retrosynthesis?
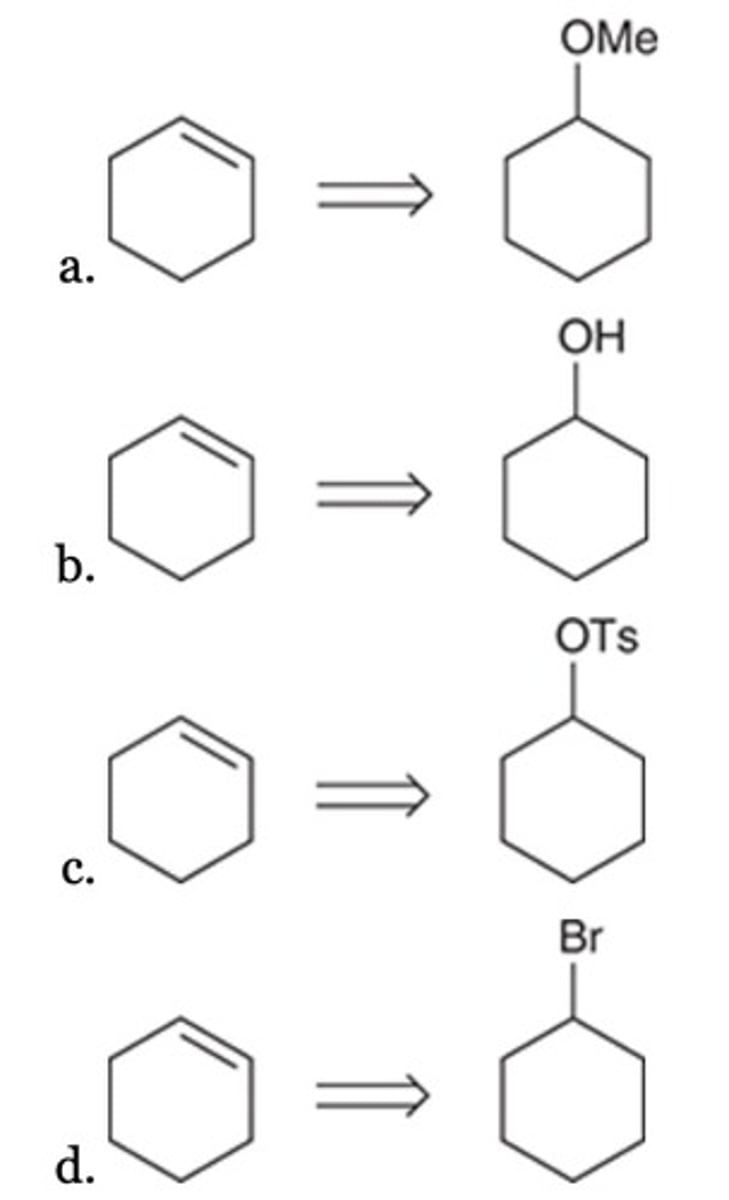
C
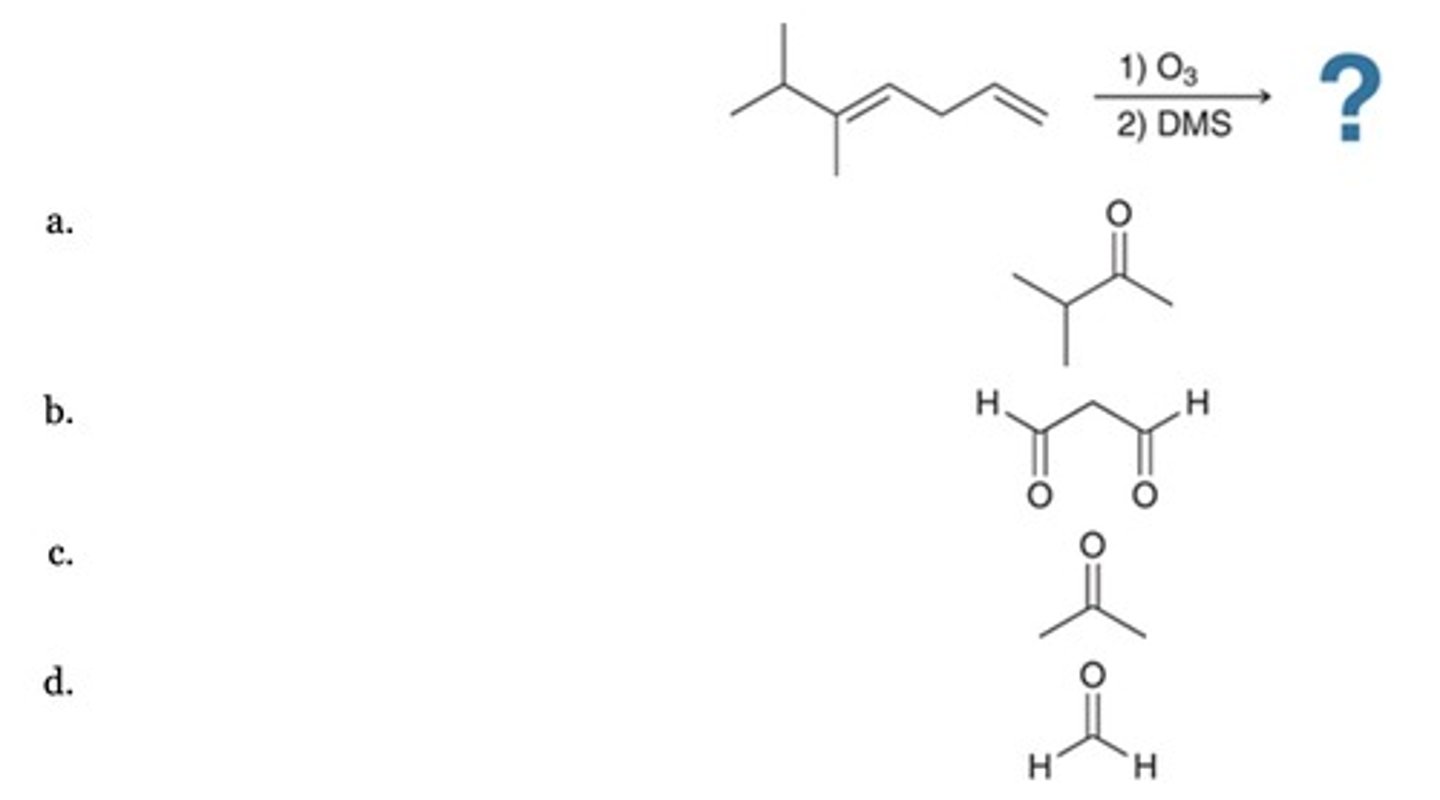
Which of the following compounds is NOT a product of this ozonolysis reaction?
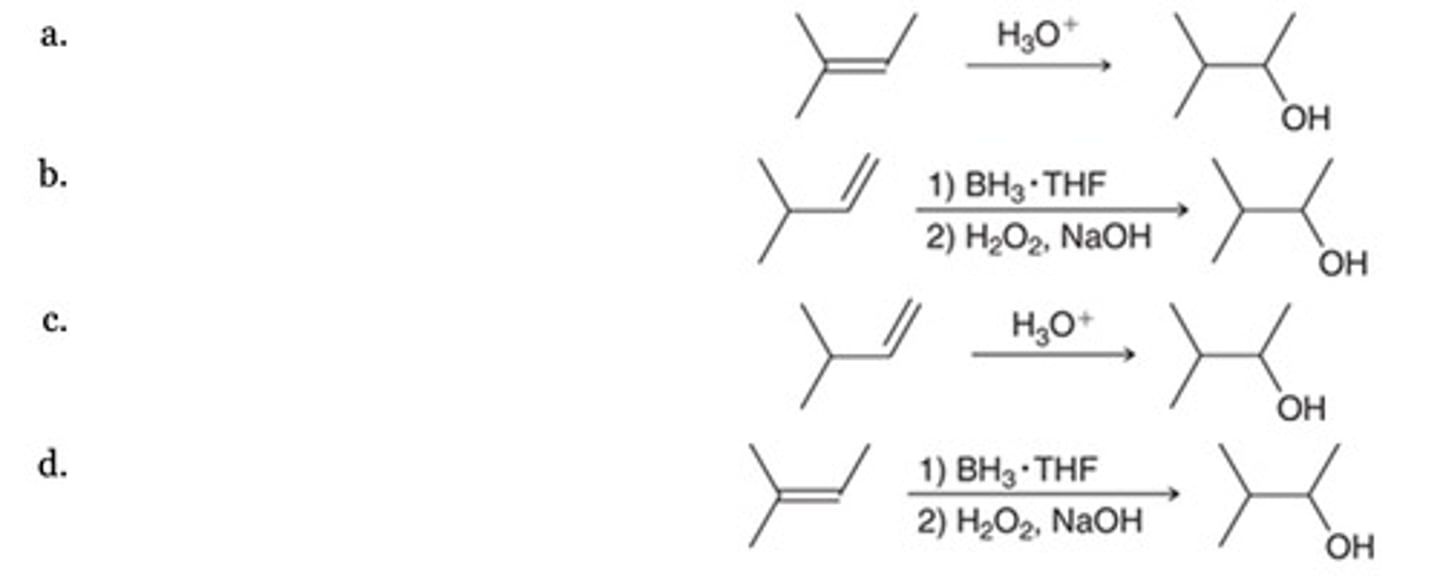
D
Which of the following represents an efficient method for preparing the alcohol shown?
I and II
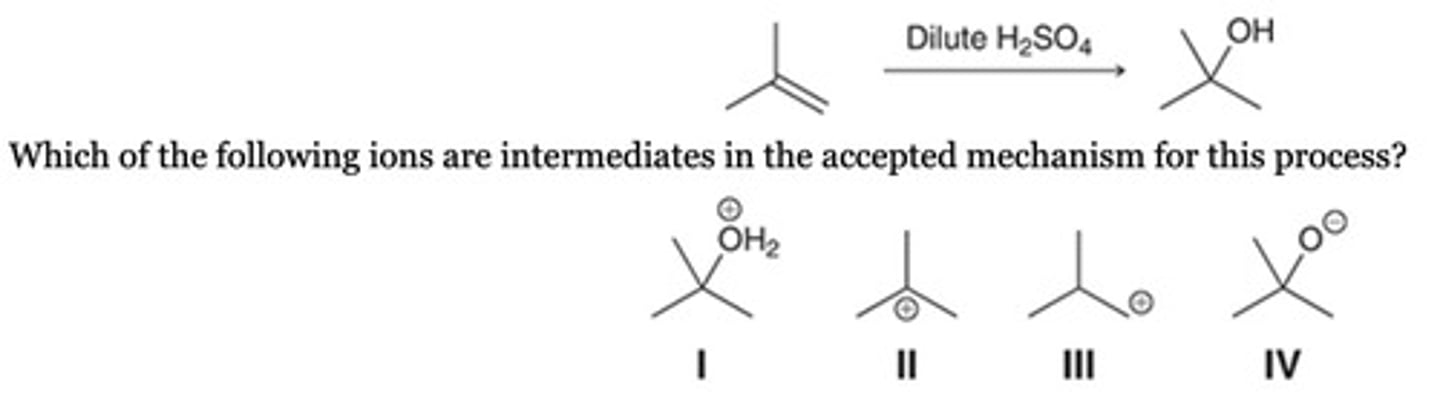
Consider the following acid-catalyzed hydration reaction:
Which of the following ions are intermediates in the accepted mechanism for this process?
I, II, and III
I and II
None of the above. The process is concerted.
Only IV
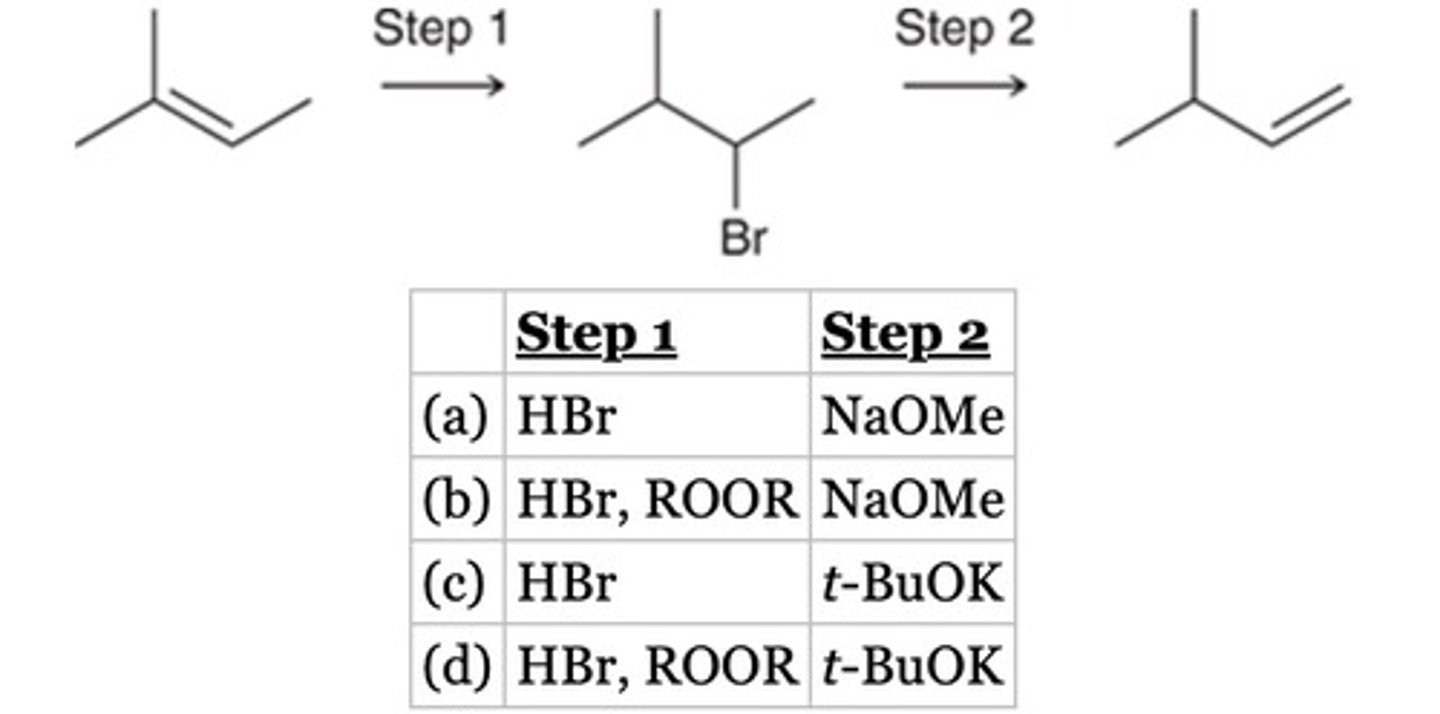
D
Provide suitable reagents for the following transformation.
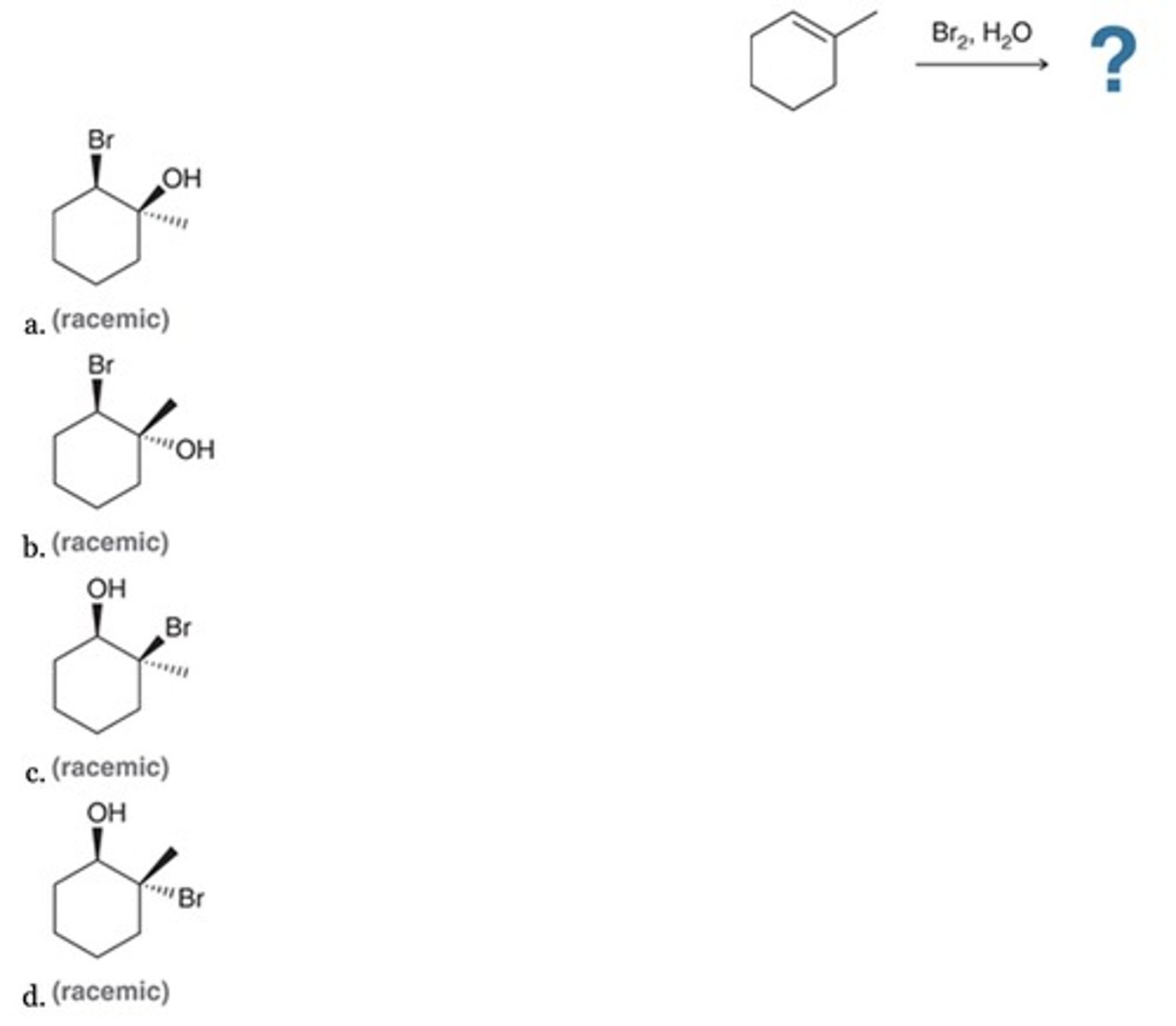
B
Predict the major product of the following reaction.
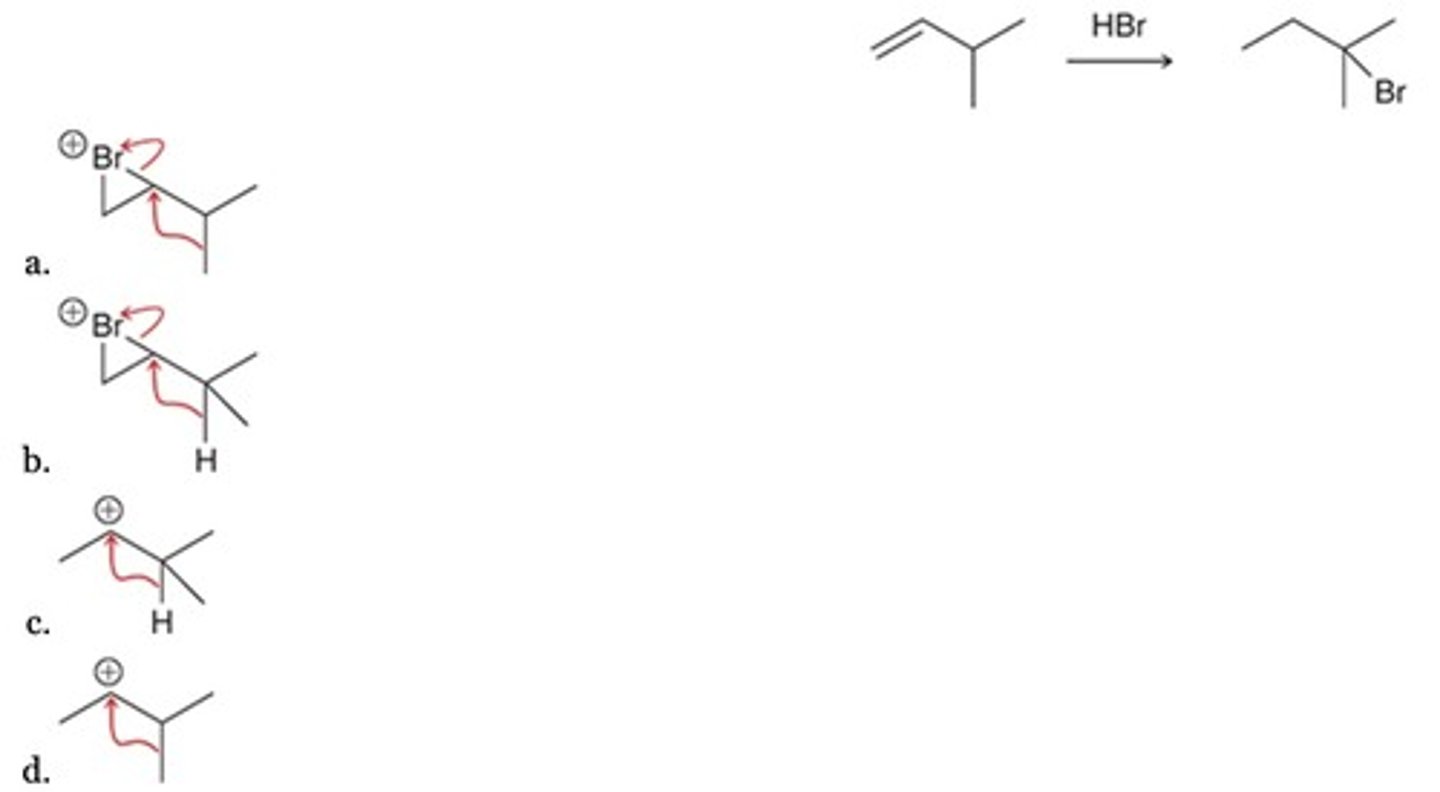
C
Which of the following represents a likely step in the mechanism of the given reaction?
D
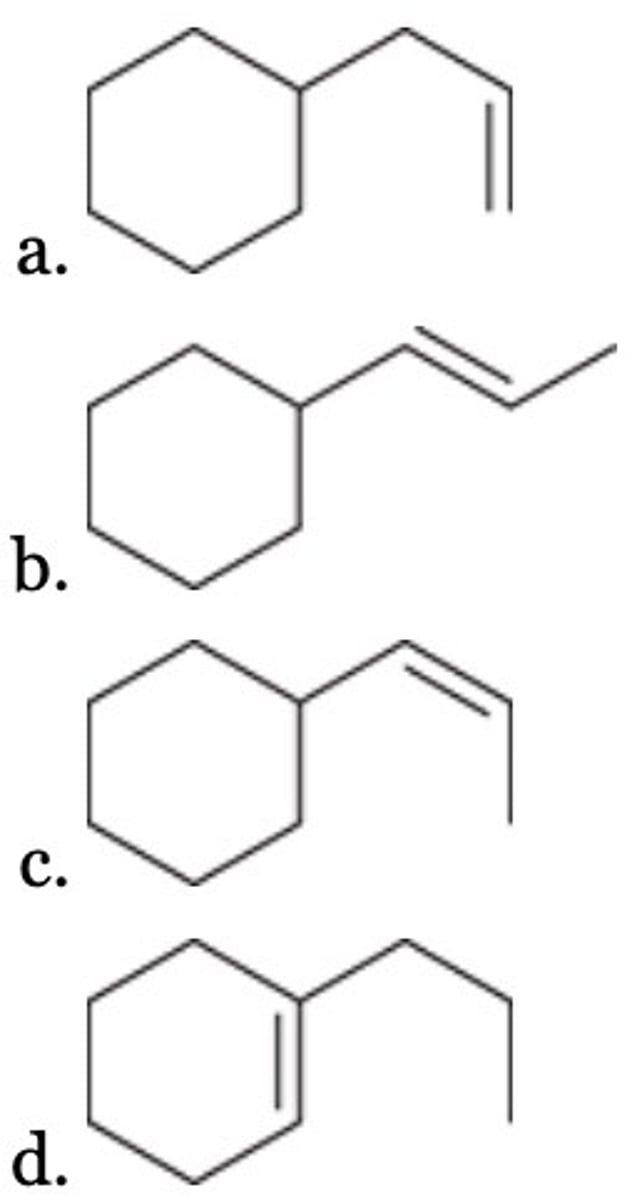
Of the following, which is the most stable alkene?
(E)-3-(1-methylethyl)-2-heptene
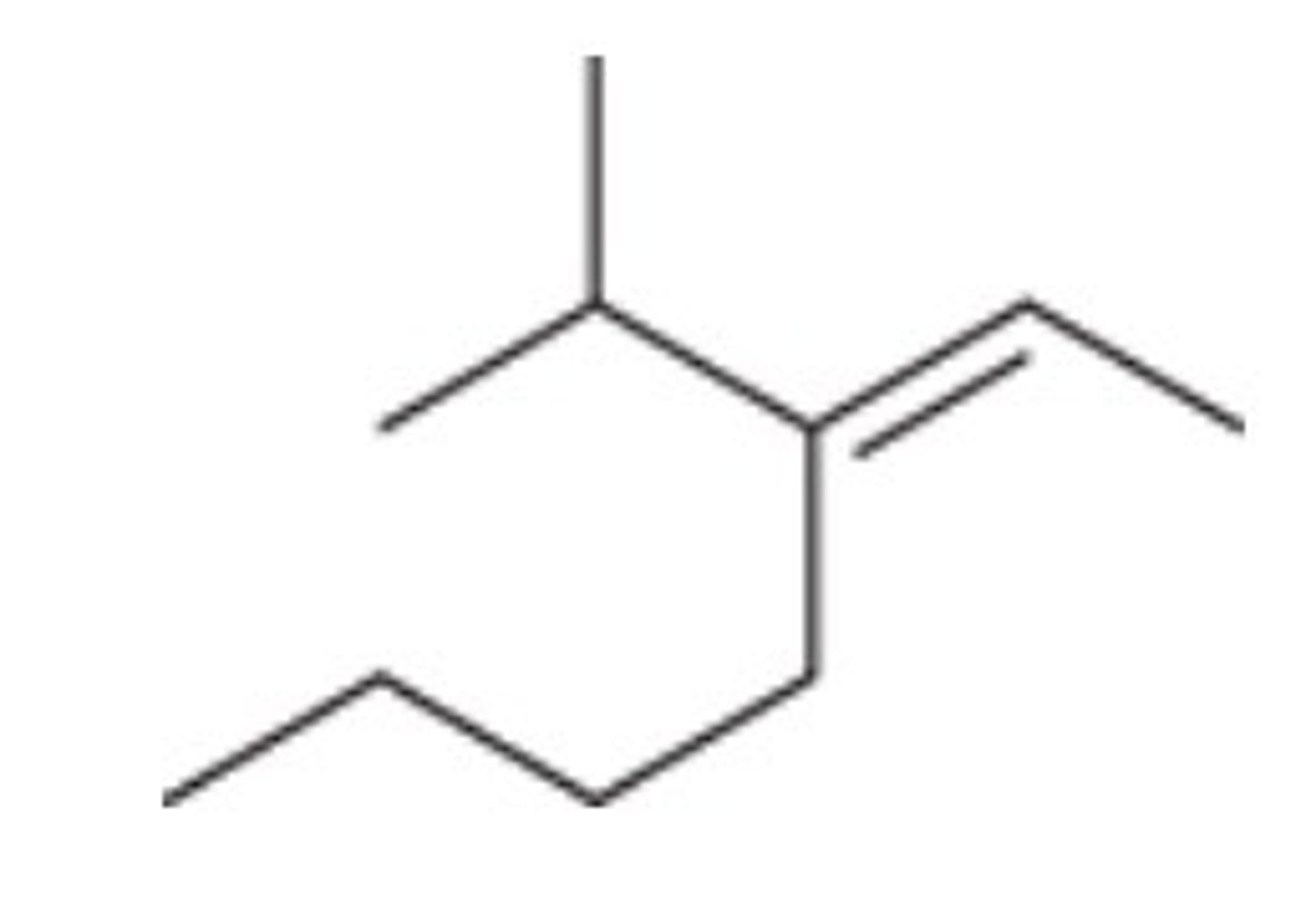
What is the IUPAC name of the given compound?
(E)-3-butyl-4-methyl-2-pentene
(Z)-3-butyl-4-methyl-2-pentene
(E)-3-(1-methylethyl)-2-heptene
(Z)-3-(2-propyl)-2-heptene
A
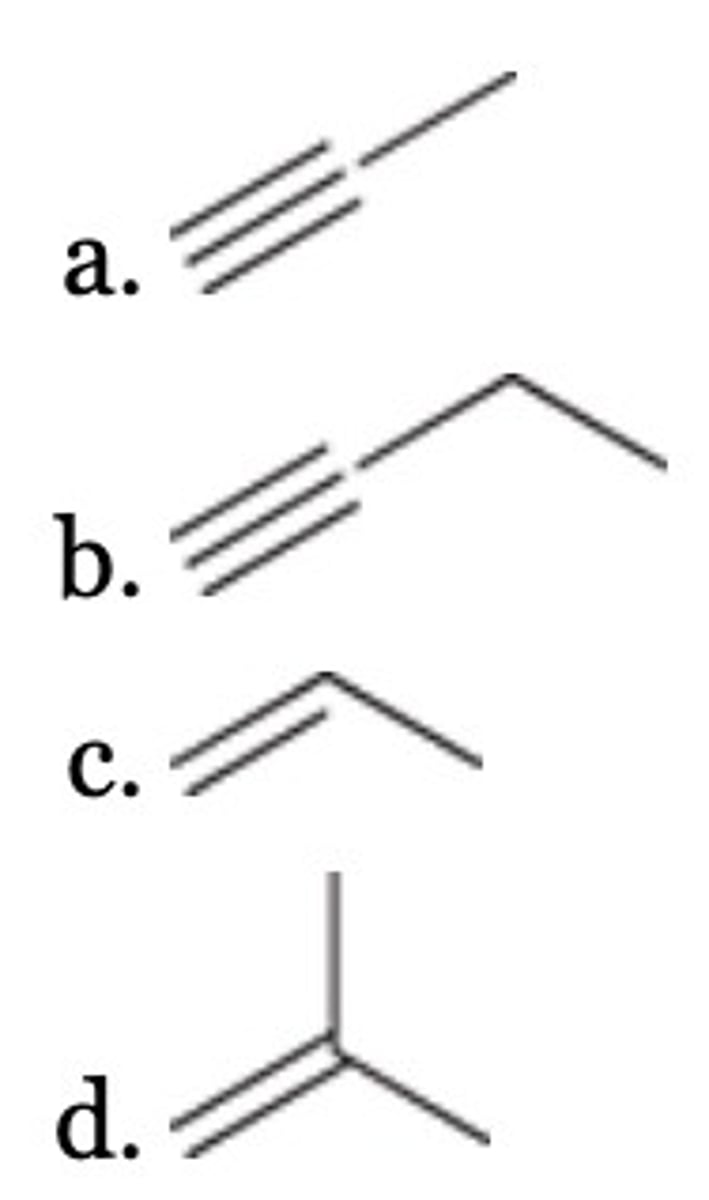
Which of the following compounds is converted into carbon dioxide and acetic acid (CH3CO2H) upon ozonolysis?
C
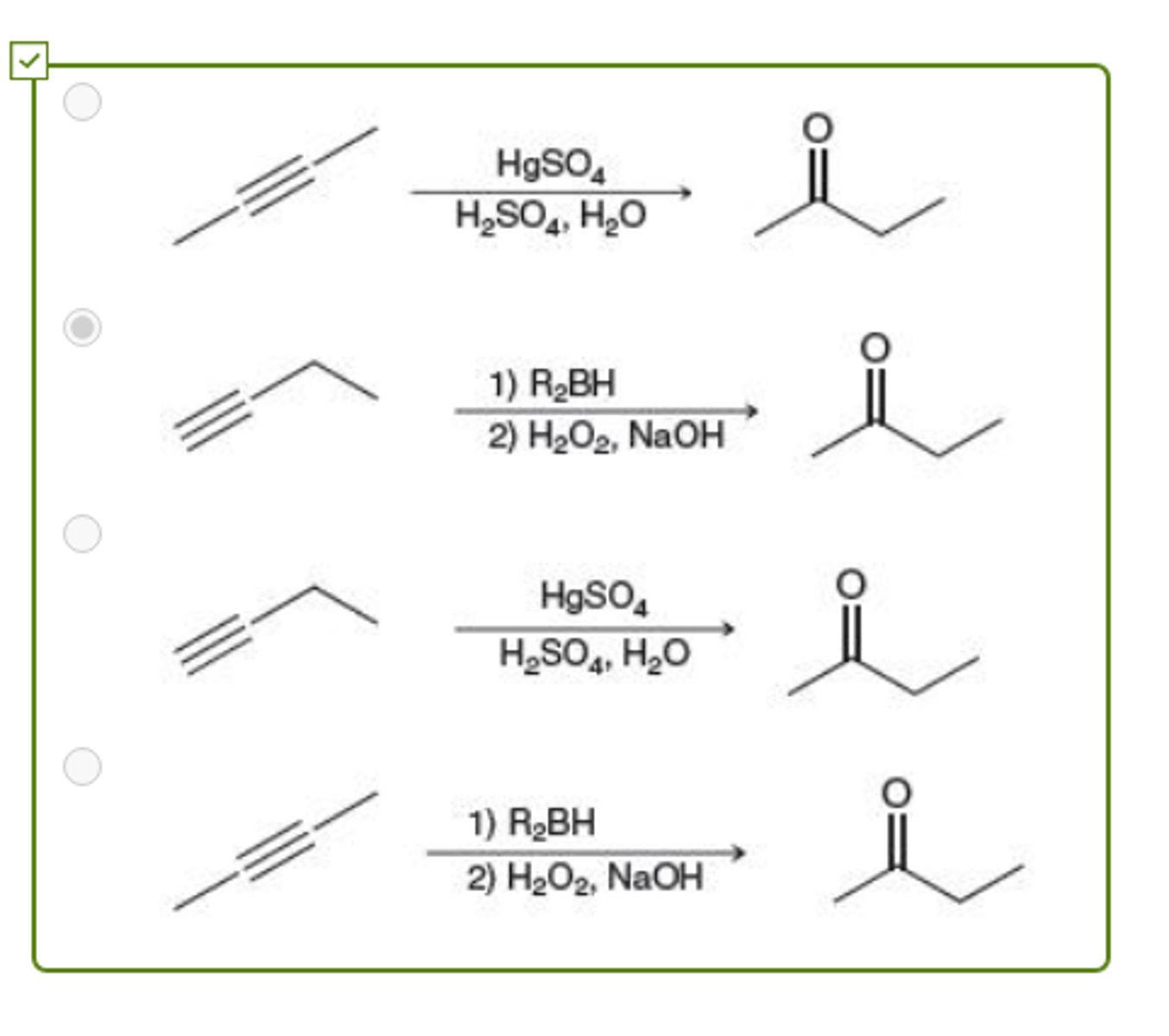
All of the following methods can be used to prepare 2-butanone (CH3COCH2CH3) EXCEPT:
Na, NH3
Which reagents will achieve the following transformation?
H2, Pt
NaNH2/NH3
Na, NH3
H2, Lindlar's catalyst
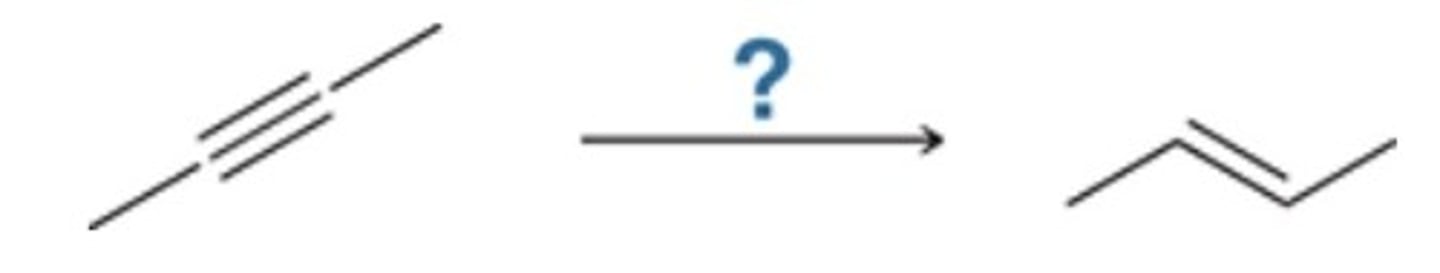
xs HBr
Which reagent (or reagents) will achieve the following transformation?
Br2
Br2, H2O
xs HBr, ROOR
xs HBr
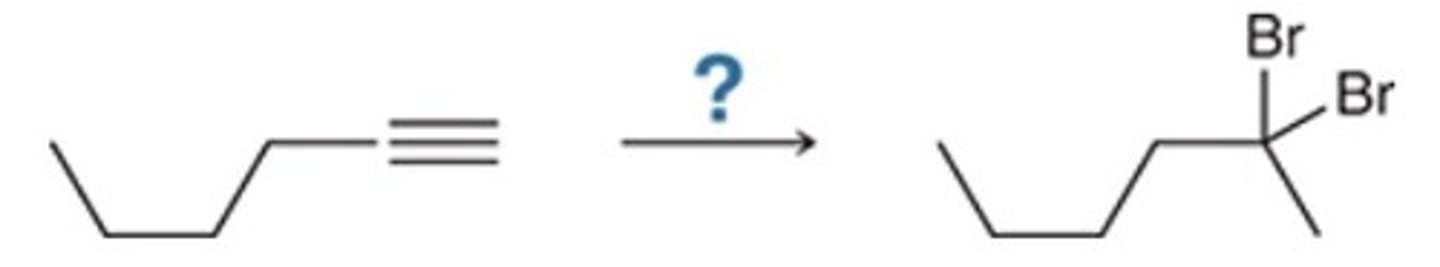
B
Which reagents will achieve the following transformation?
A. 1) H2, Lindlar's cat.; 2) RCO3H; 3) H3O+
B. 1) H2, Lindlar's cat.; 2) KMnO4
C. 1) Na, NH3; 2) KMnO4
D. 1) KMnO4; 2) H2, Pd
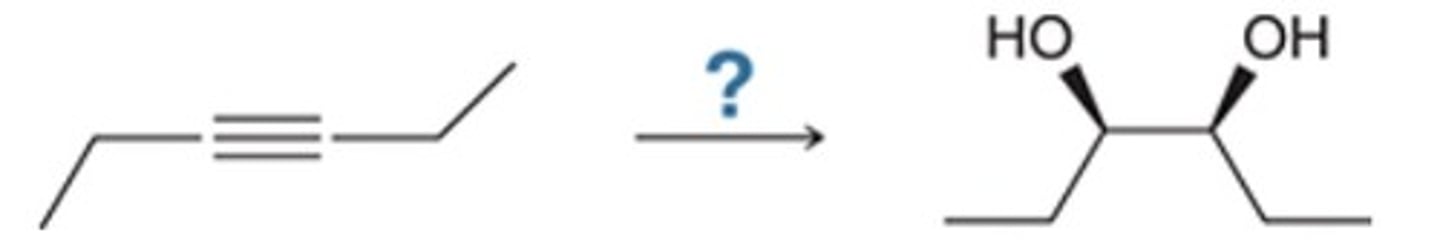
B
Which is the best retrosynthesis of the given target molecule?
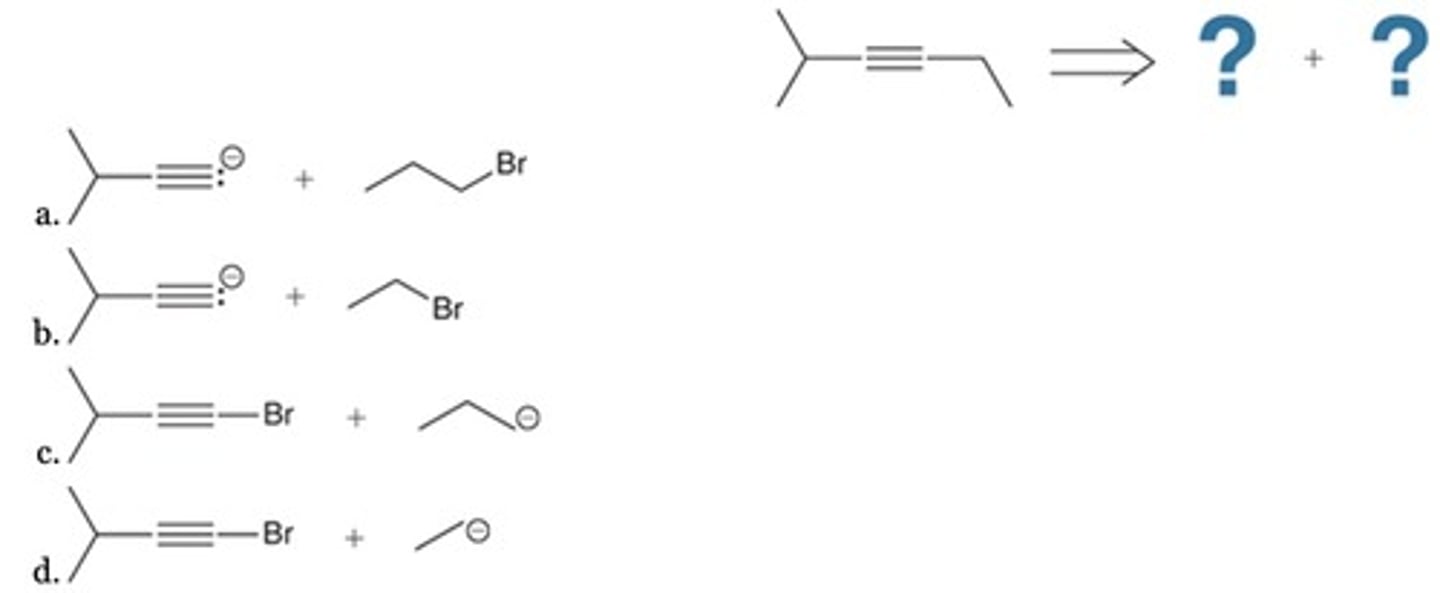
C
Which disconnection leads to the most reasonable retro-synthesis of the given target molecule?

D
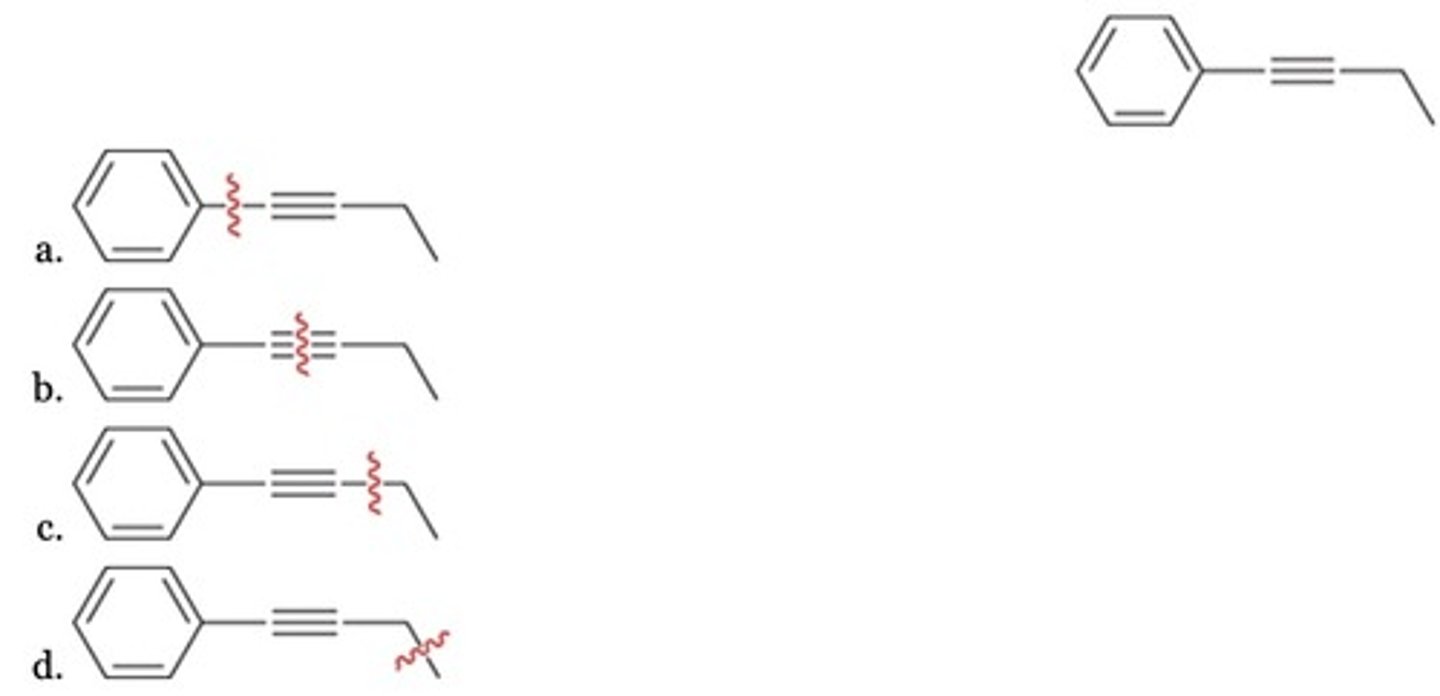
Predict the major product of the following reaction sequence:
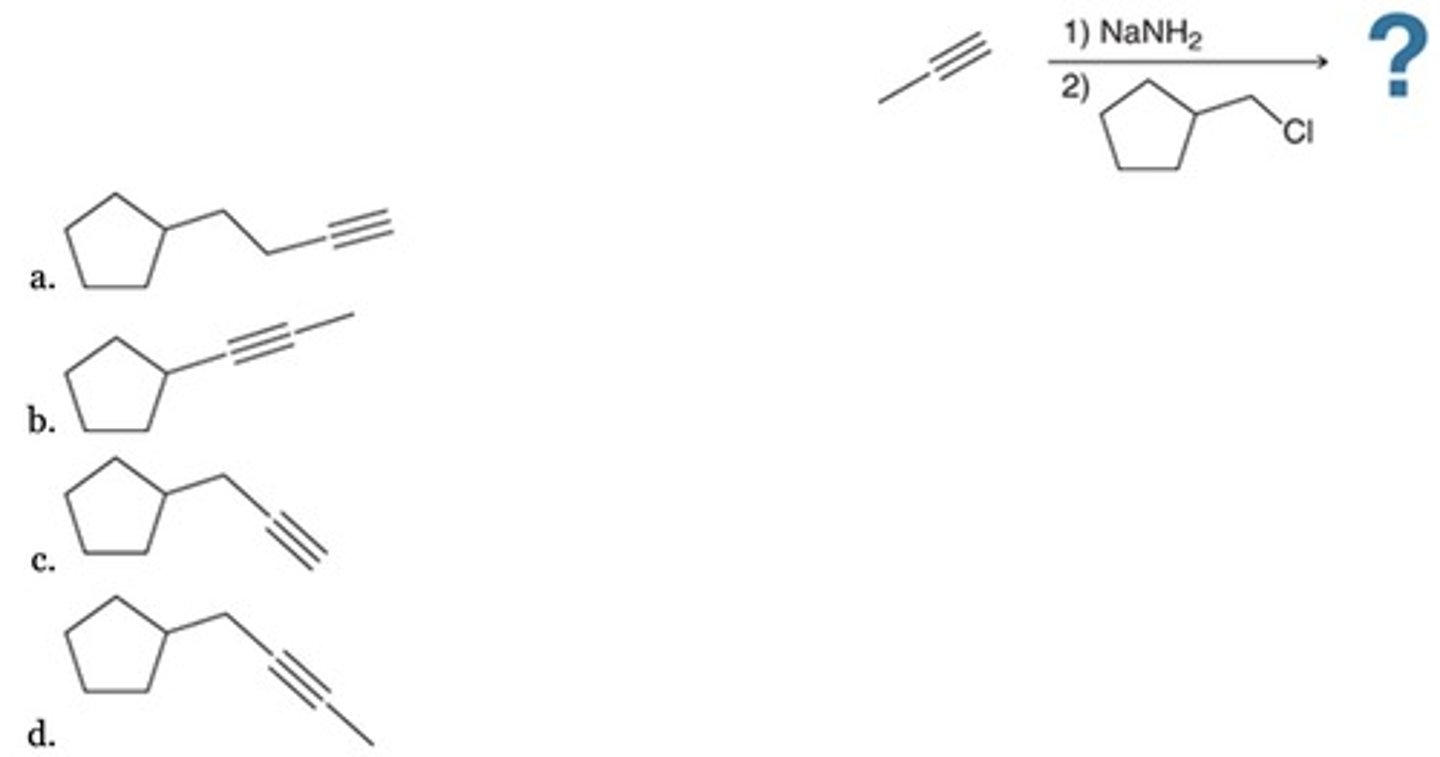
C
What is the major product of the following reaction?
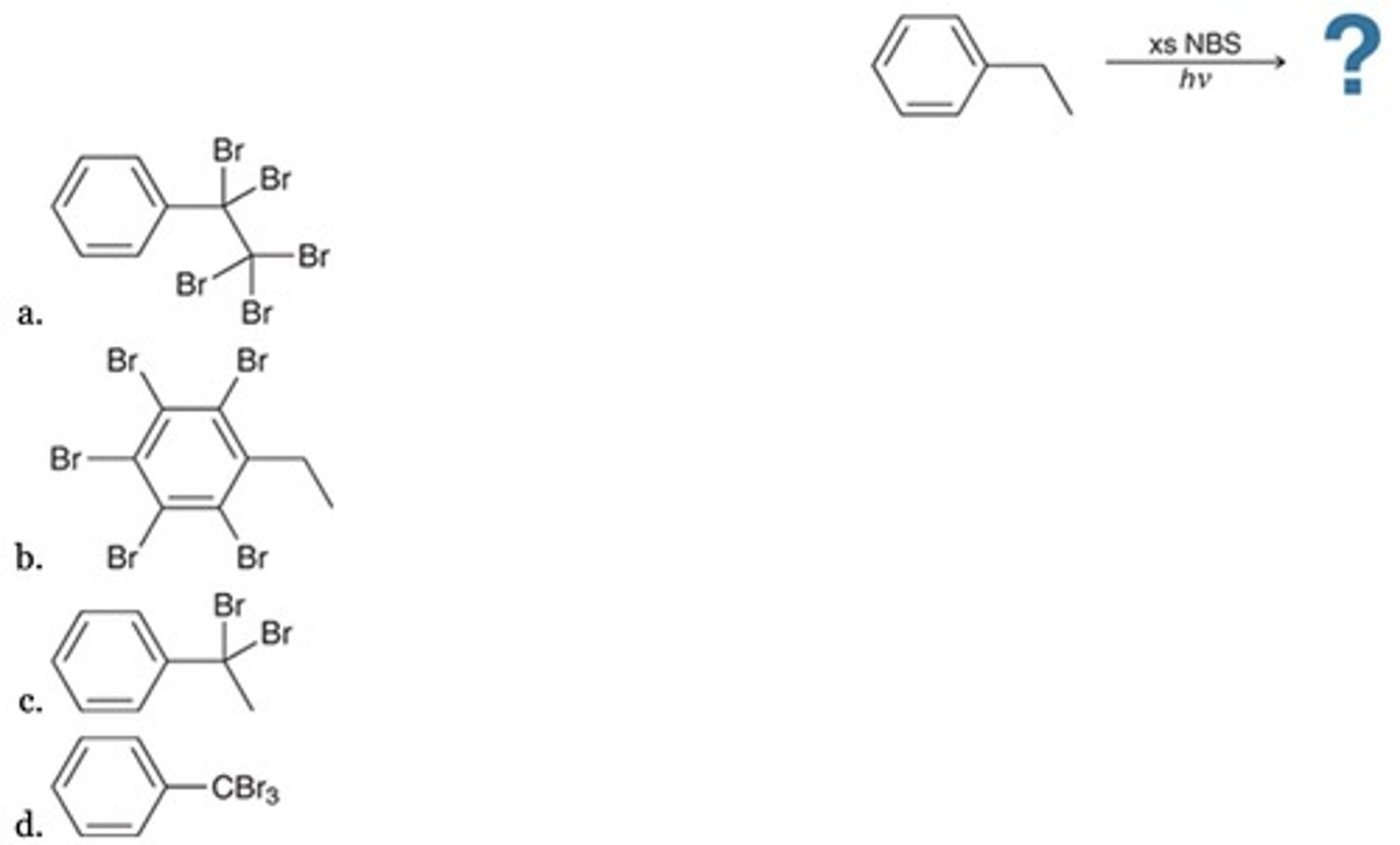
Only I, II, and III
Determine which of the following reactions is expected to be thermodynamically favorable:
I, II, III, and IV
Only I, II, and III
Only III
Only II and III
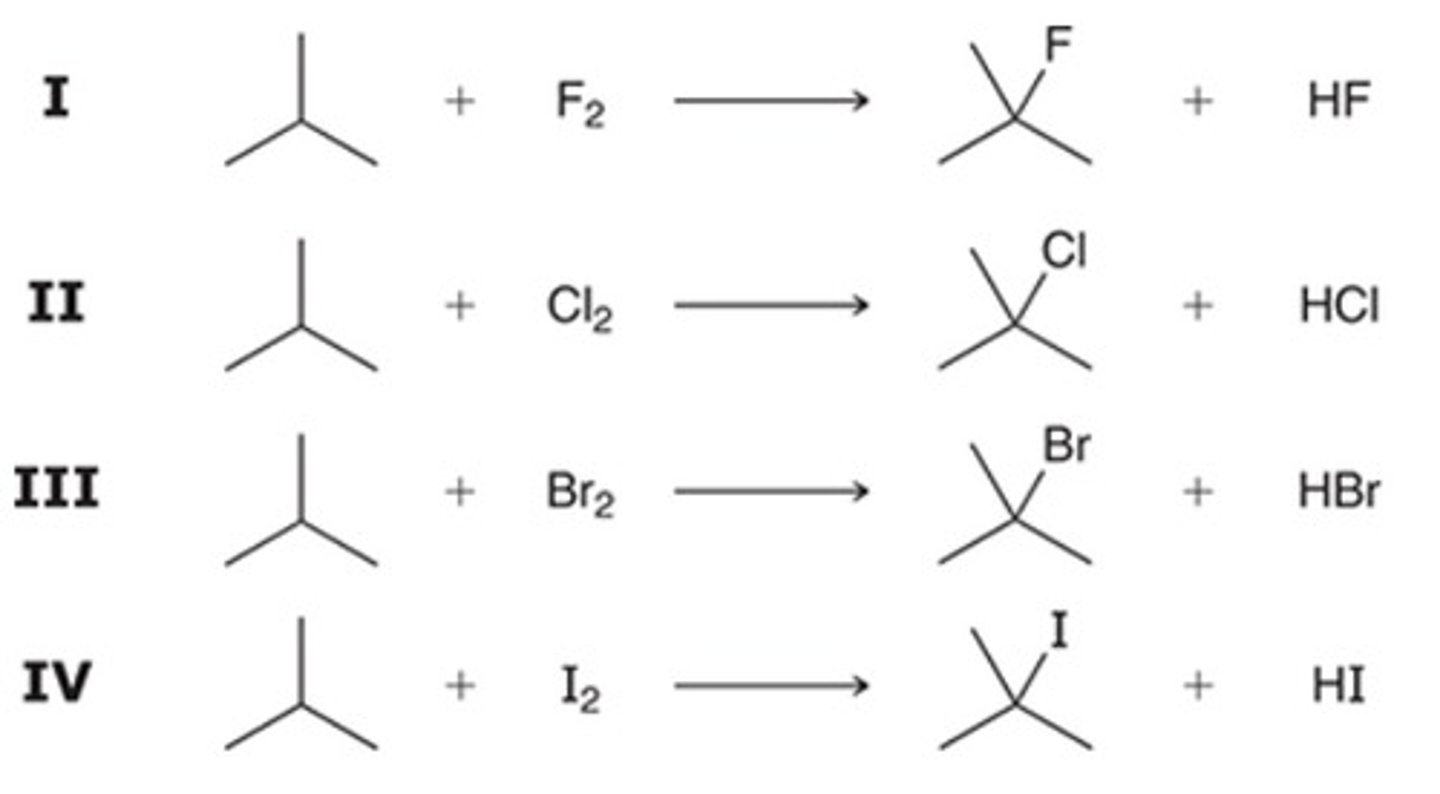
C
Which of the following is an intermediate when 1-butene undergoes radical bromination?
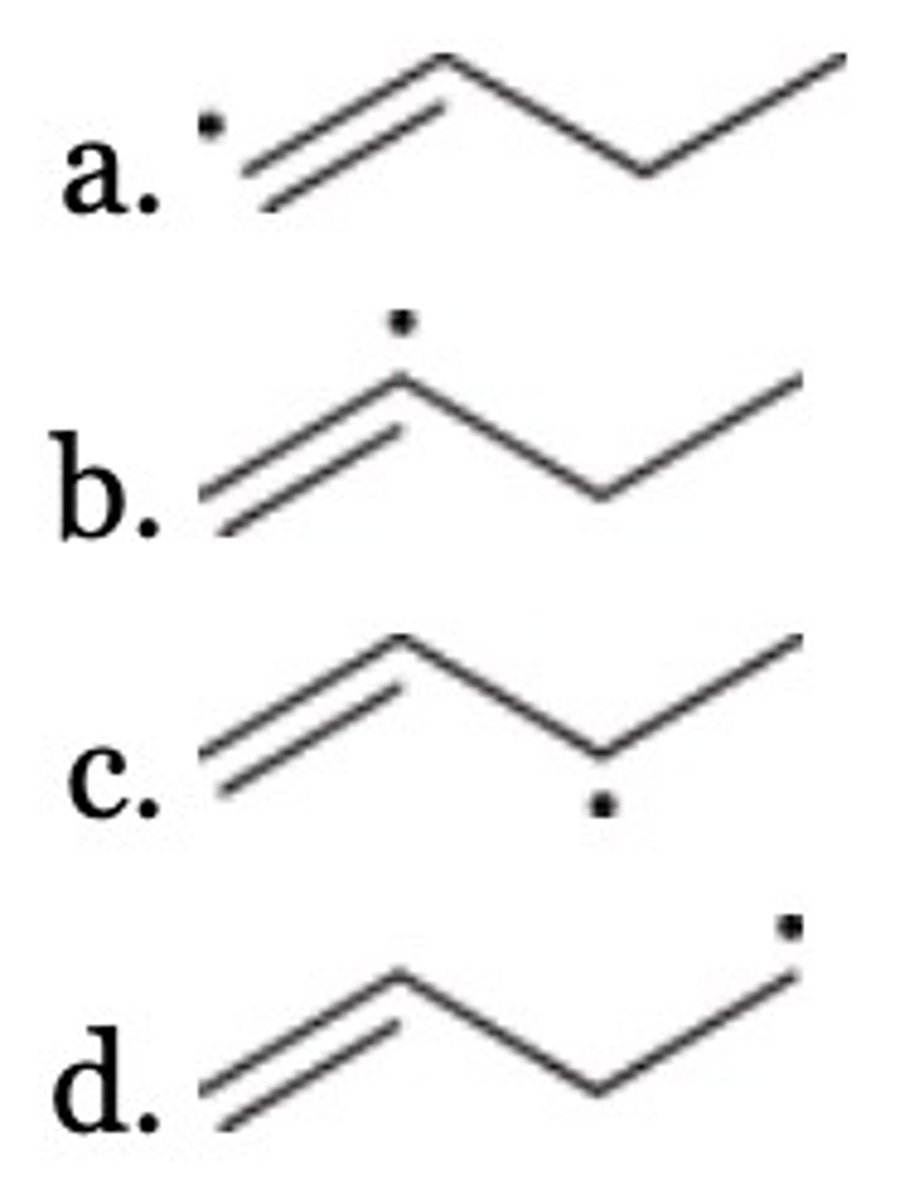
D
Of the following, which is the most stable radical?
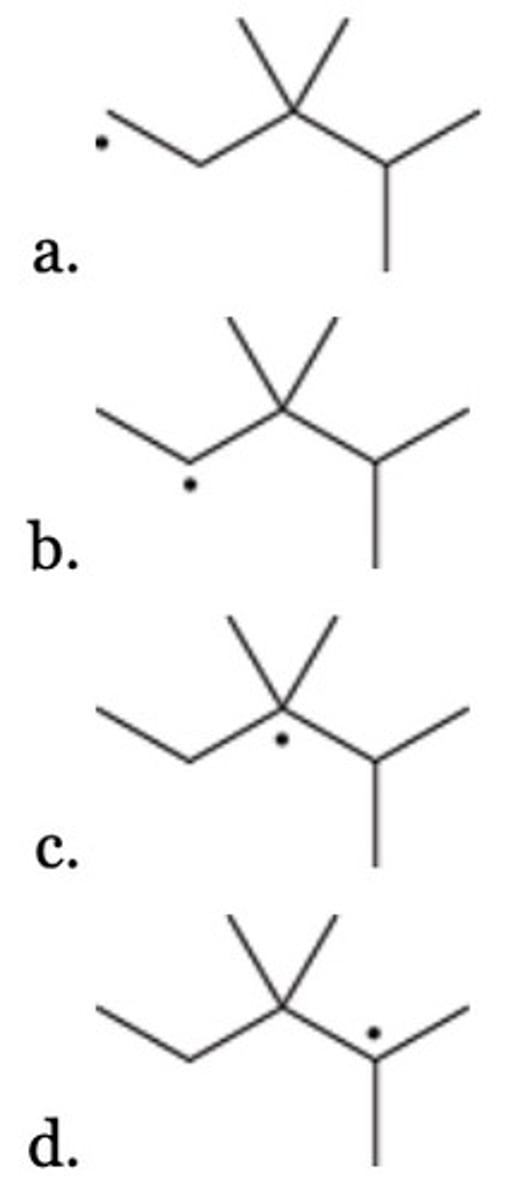
B
Which of the following cycloalkanes gives a total of four monochlorination products (disregarding stereoisomers)?
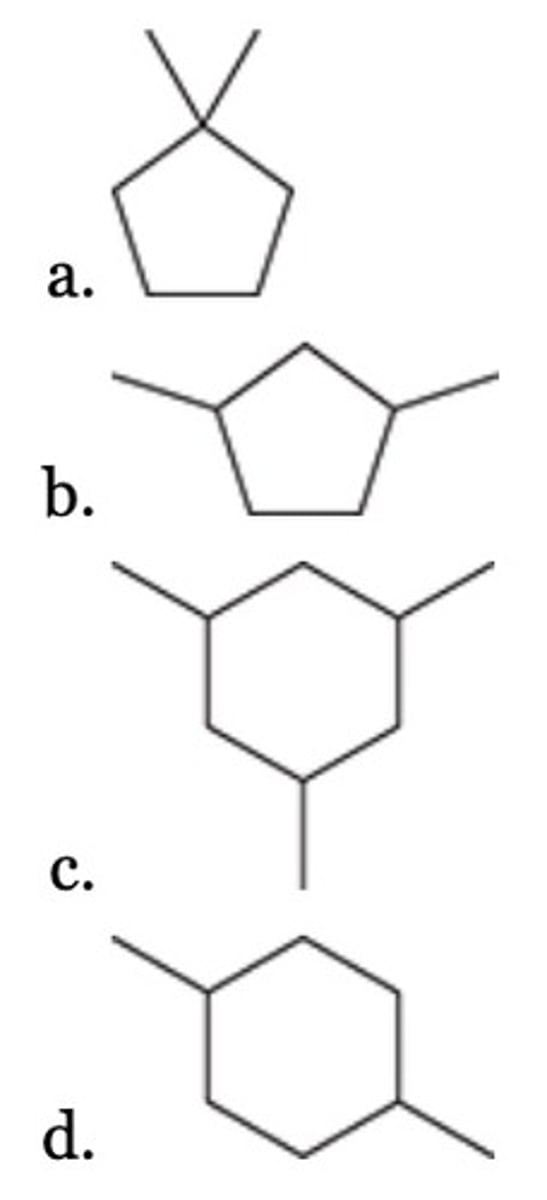
A
Which of the following is a likely intermediate when 1-pentene undergoes addition of HBr, in the presence of peroxides?
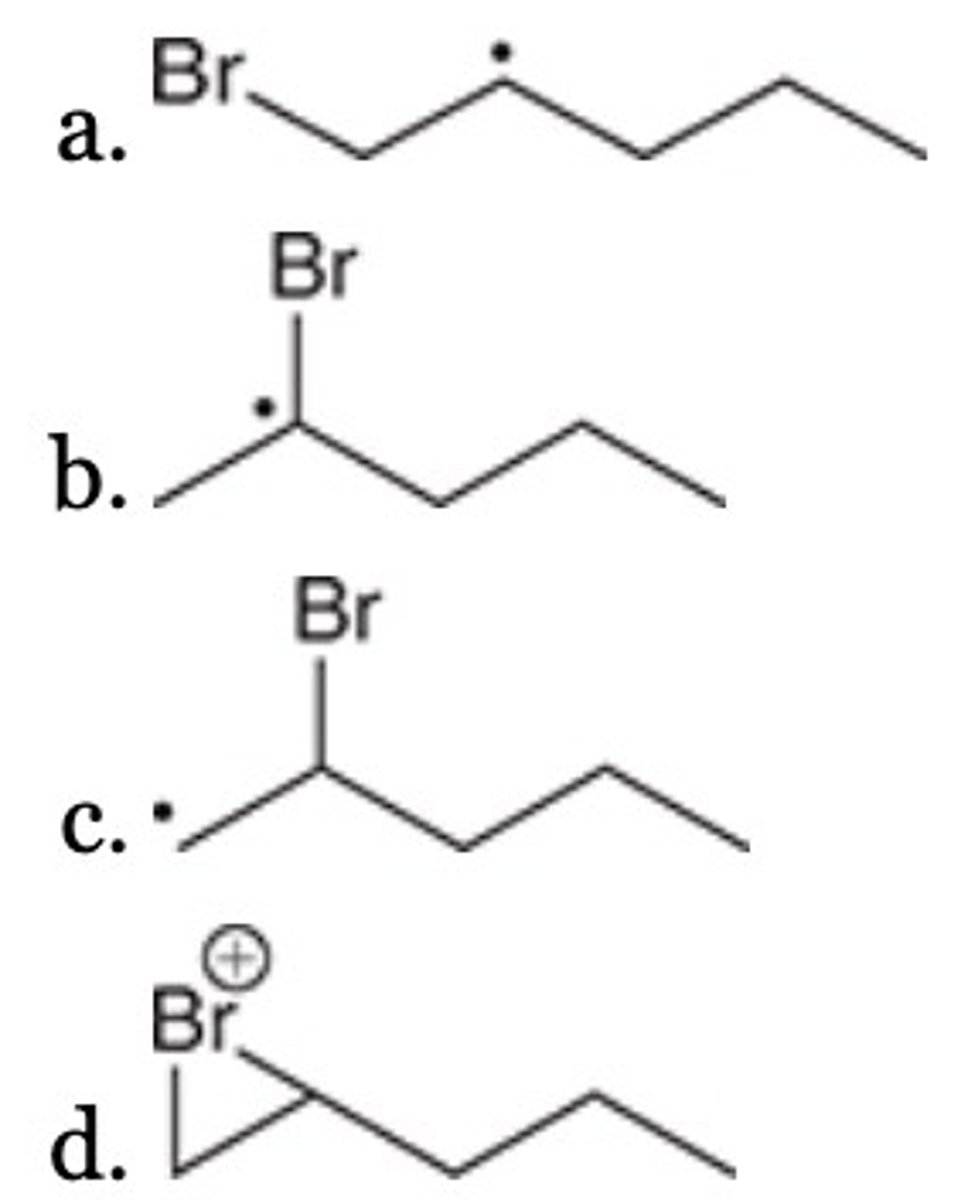
D
Identify the most likely initiation step in the bromination of 2-methylpropane.
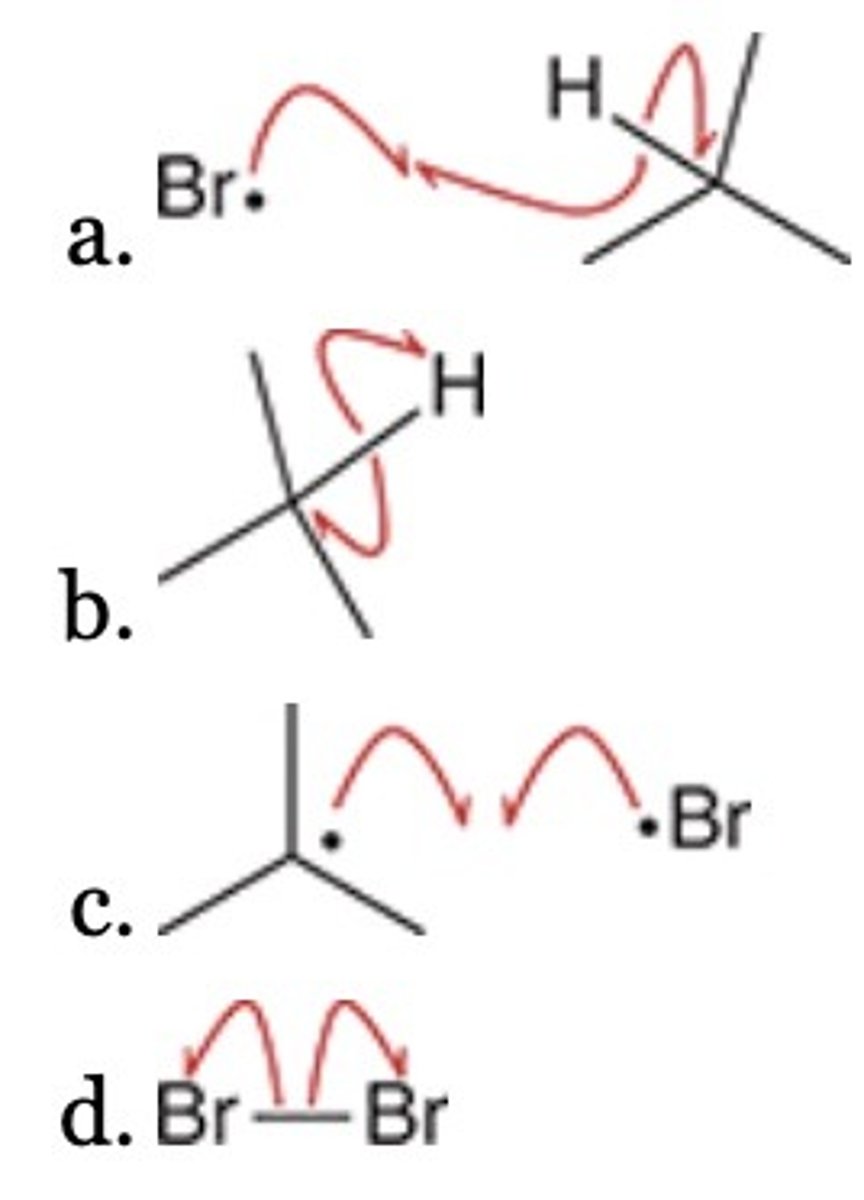
NaC≡CH, followed by H2 and Lindlar's catalyst
What are the best reagents to accomplish this transformation?
t-BuOK
NaC≡CH, followed by H2 and Pt
NaC≡CH, followed by H2 and Lindlar's catalyst
NaOH, followed by t-BuOK
C
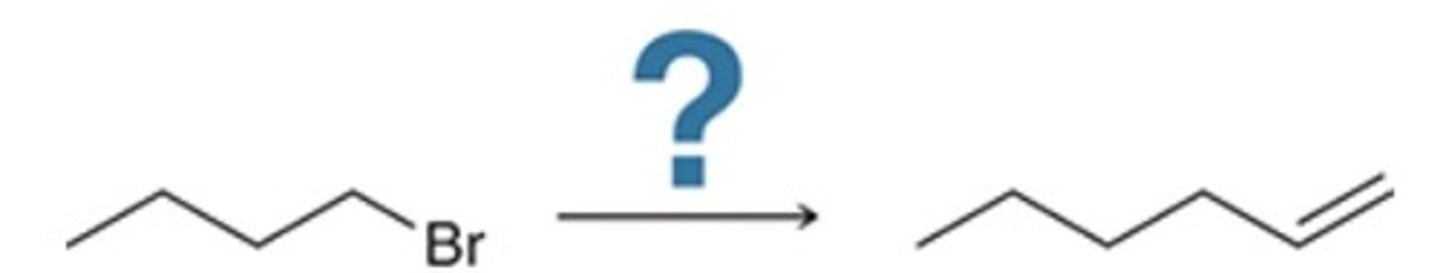
Which of the following represents an efficient synthesis of 1-methylcyclohexene?
D
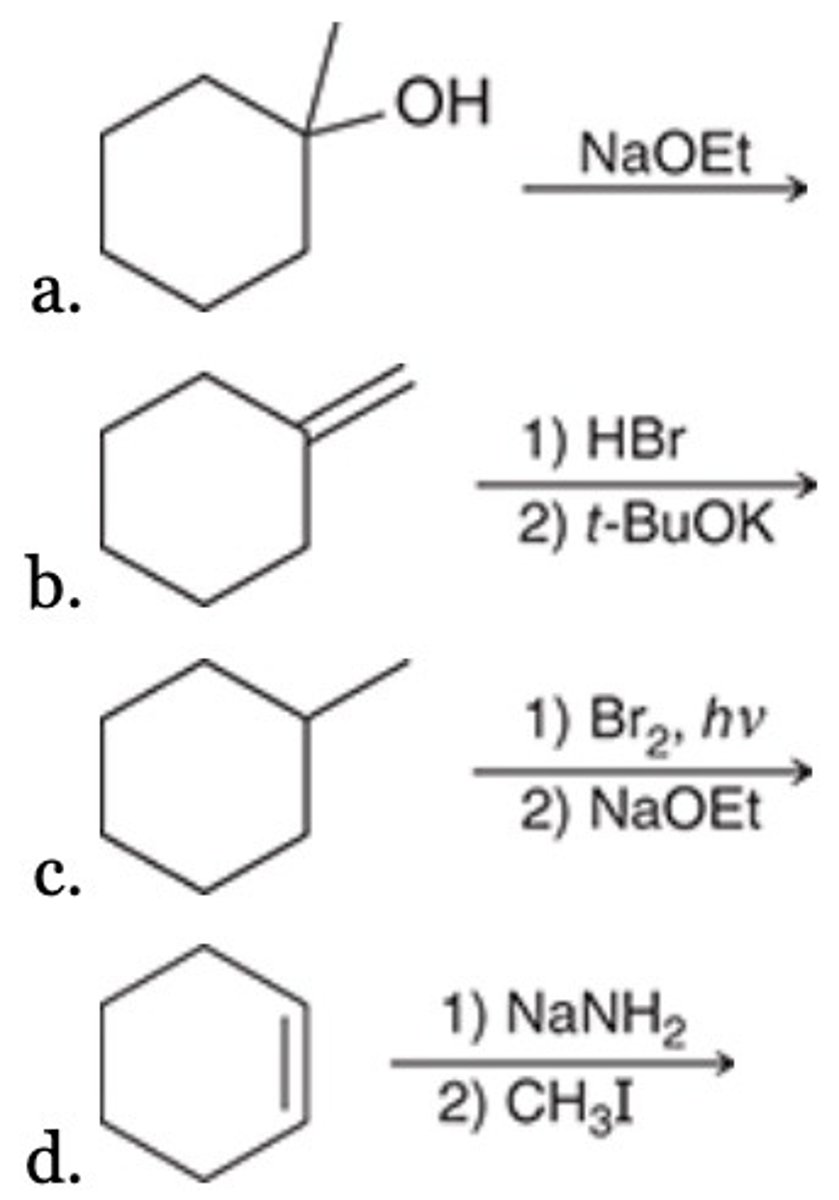
Which reaction sequence best accomplishes this transformation?
Addition, followed by elimination
Which of the following describes an efficient strategy for moving the location of a π bond?
Substitution, followed by addition
Addition, followed by substitution
Elimination, followed by addition
Addition, followed by elimination
Ozonolysis
Which of the following reactions can be utilized to shorten the length of a carbon chain?
Reduction
Elimination
Ozonolysis
Epoxidation
B
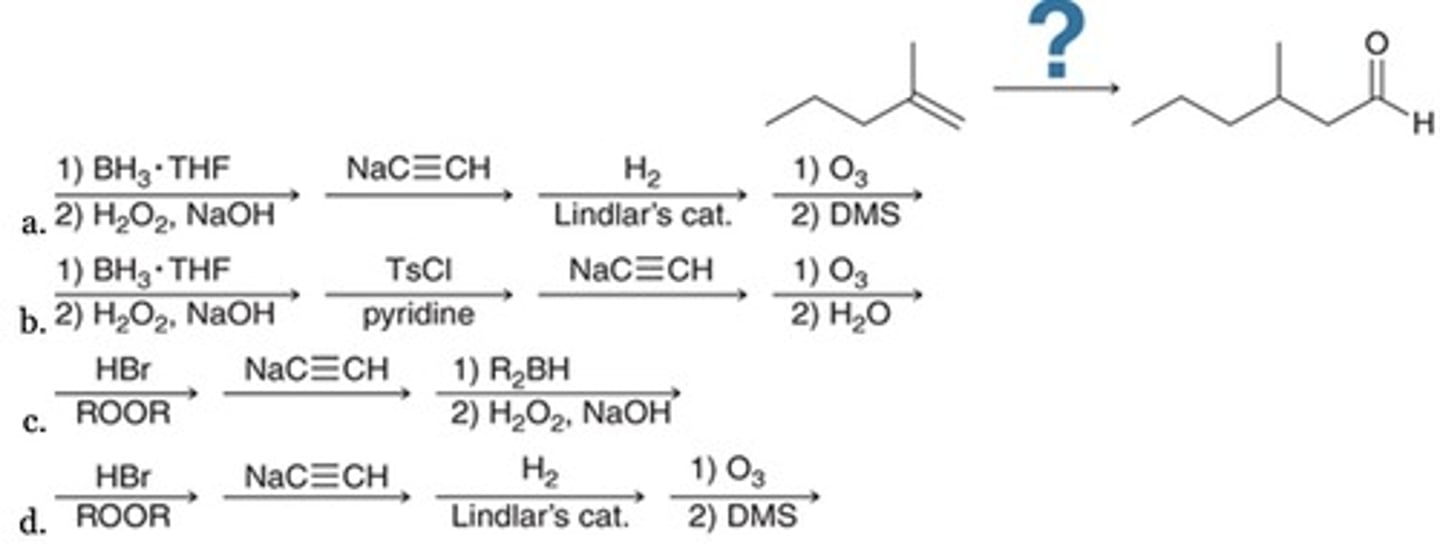
Which reaction sequence best accomplishes the given transformation?
A
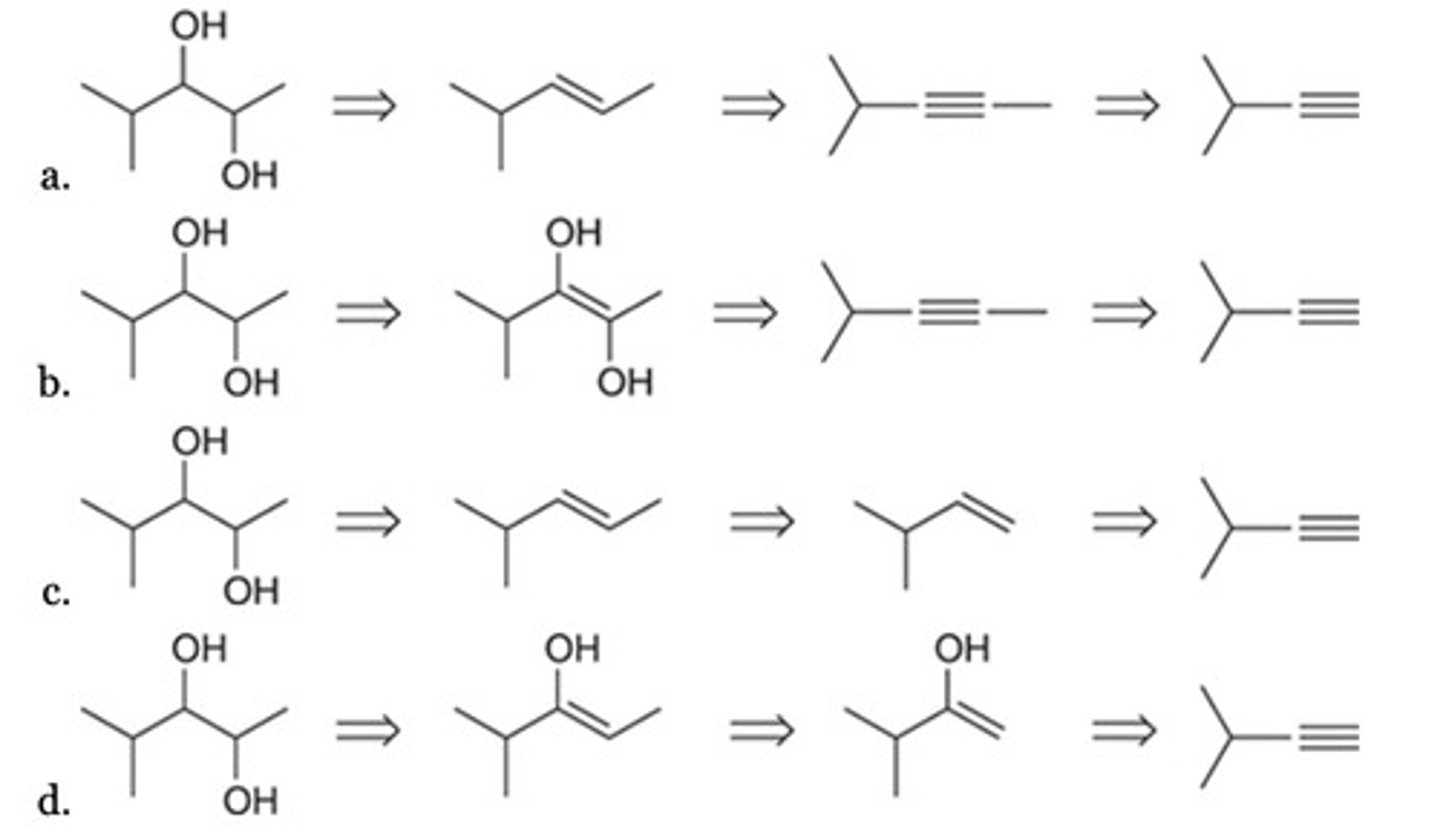
Which of the following represents a logical retrosynthesis of the given diol target molecule?
PCC, CH2Cl2
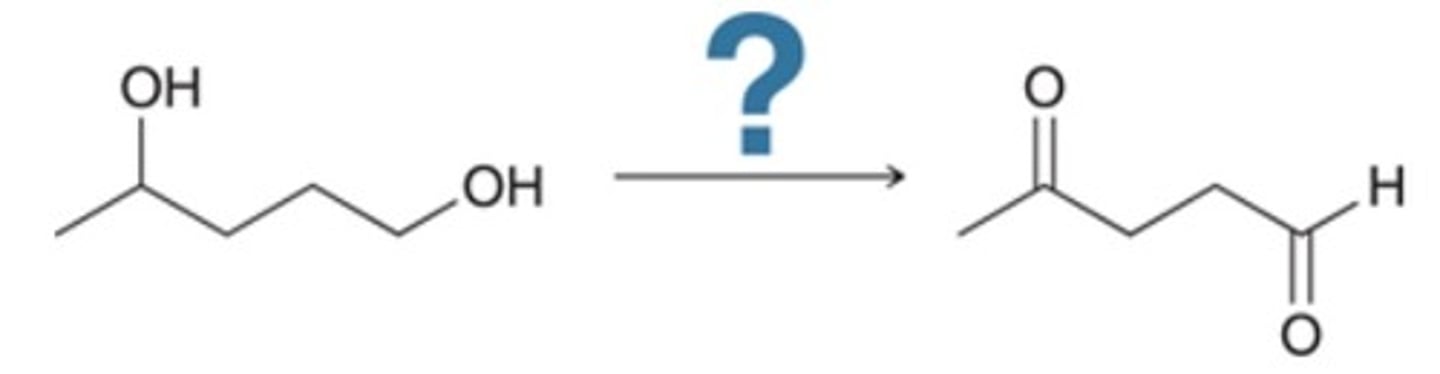
Of the following, which are the best reagents to perform the given transformation?
Na2Cr2O7, H2SO4, H2O
CrO3, H3O+, acetone
PCC, CH2Cl2
KMnO4, NaOH, cold
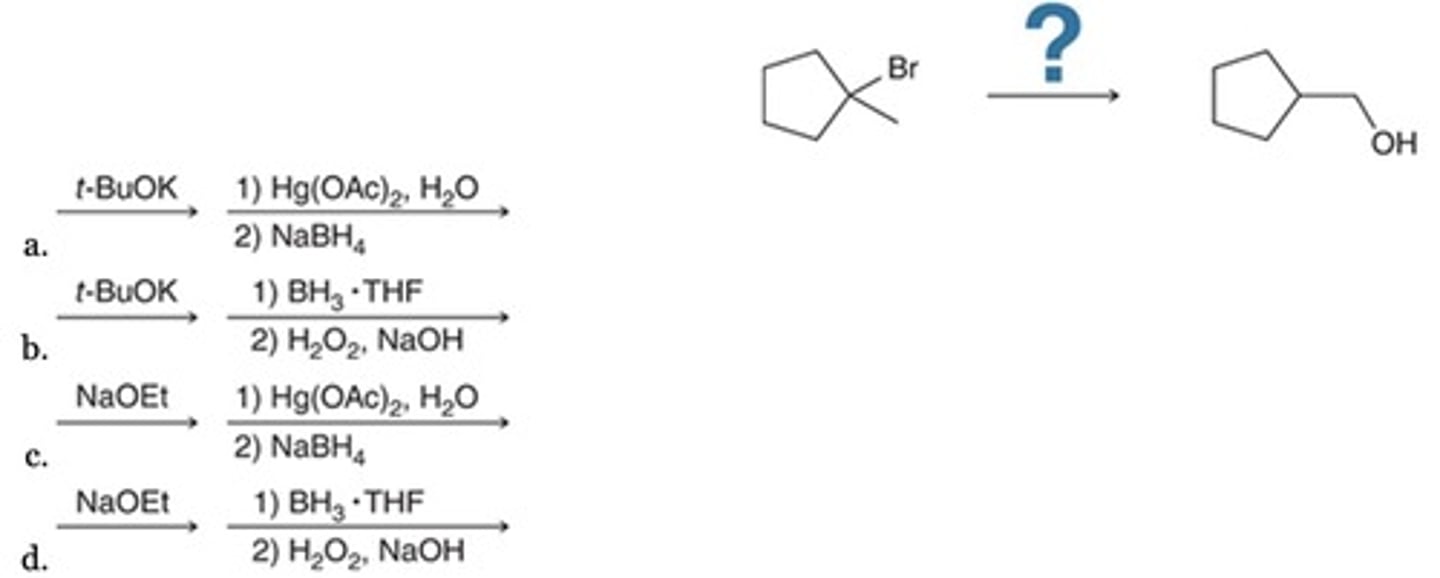
D
Which of the following is NOT an efficient synthesis of 2-methyl-2-pentanol?
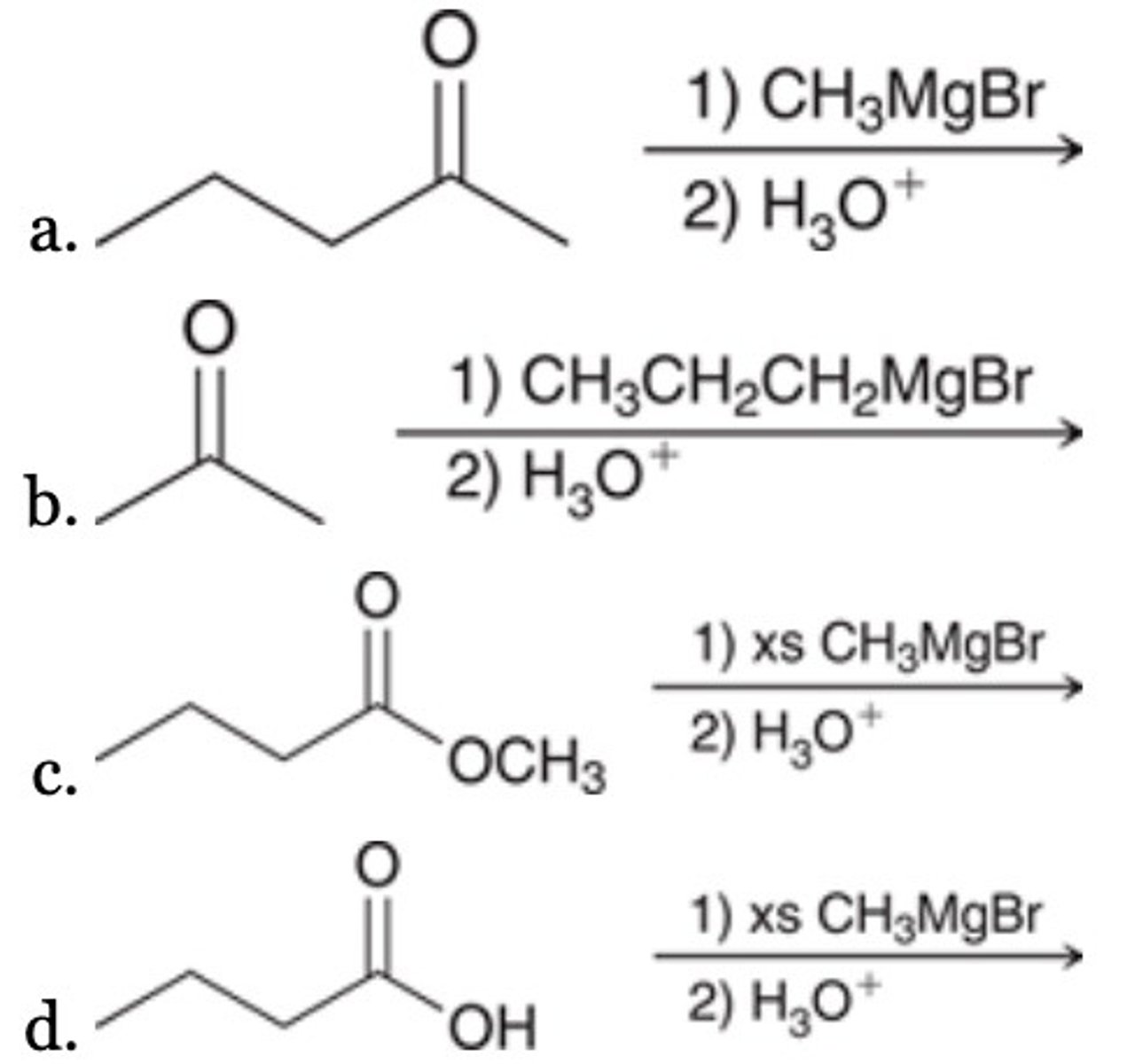
B
What is the major product of the given reaction?
D
A logical retrosynthesis of the given target molecule leads to which Grignard reagent?
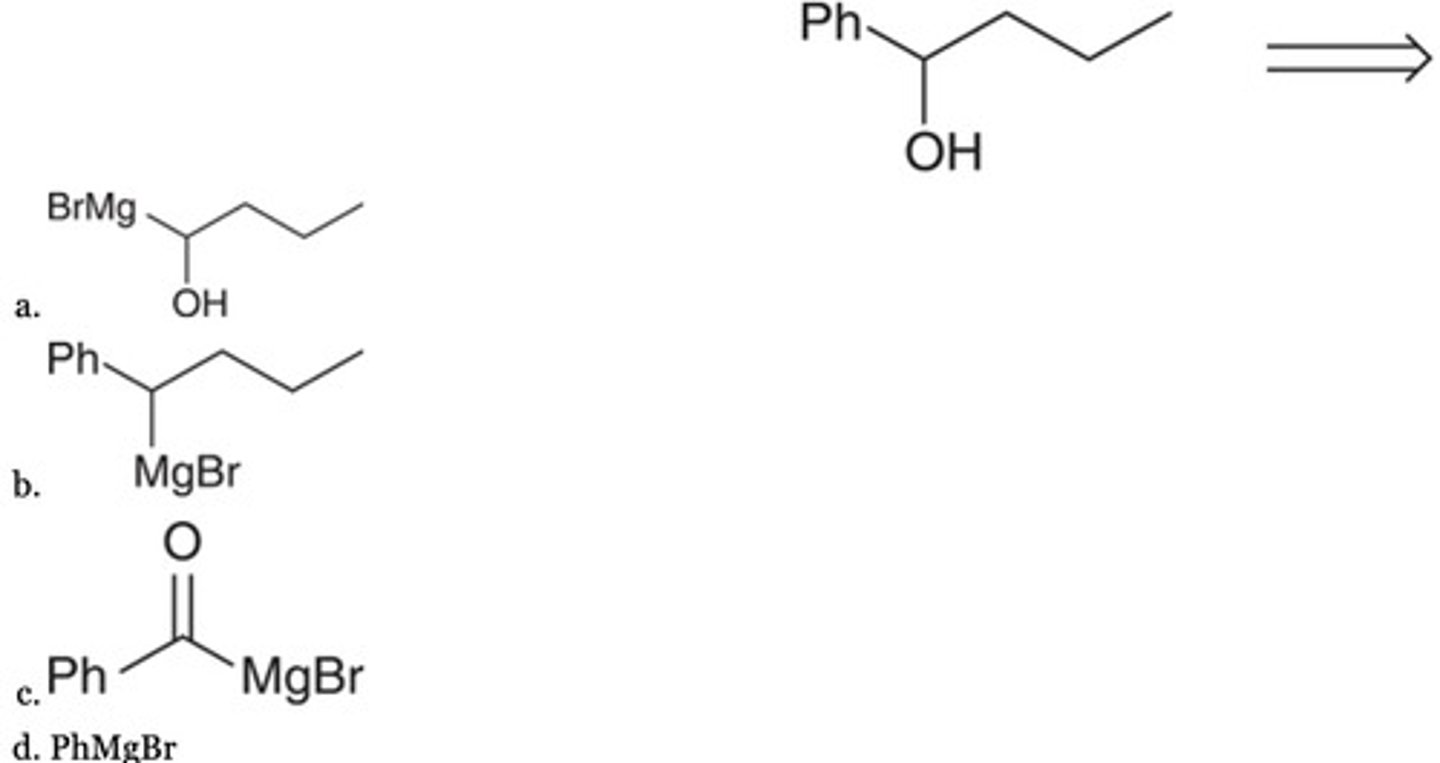
C
Predict the major product of the following sequence of reactions.
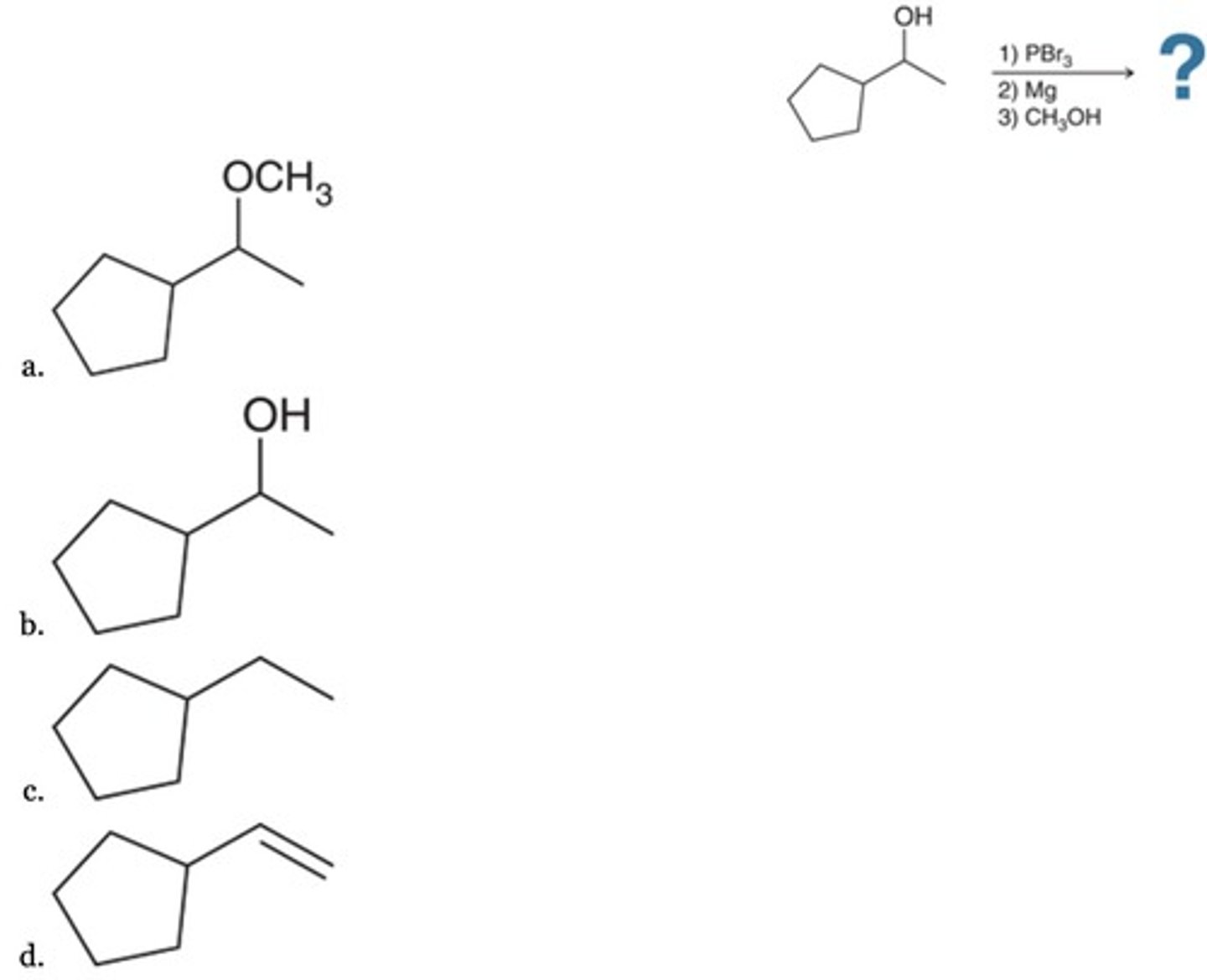
B
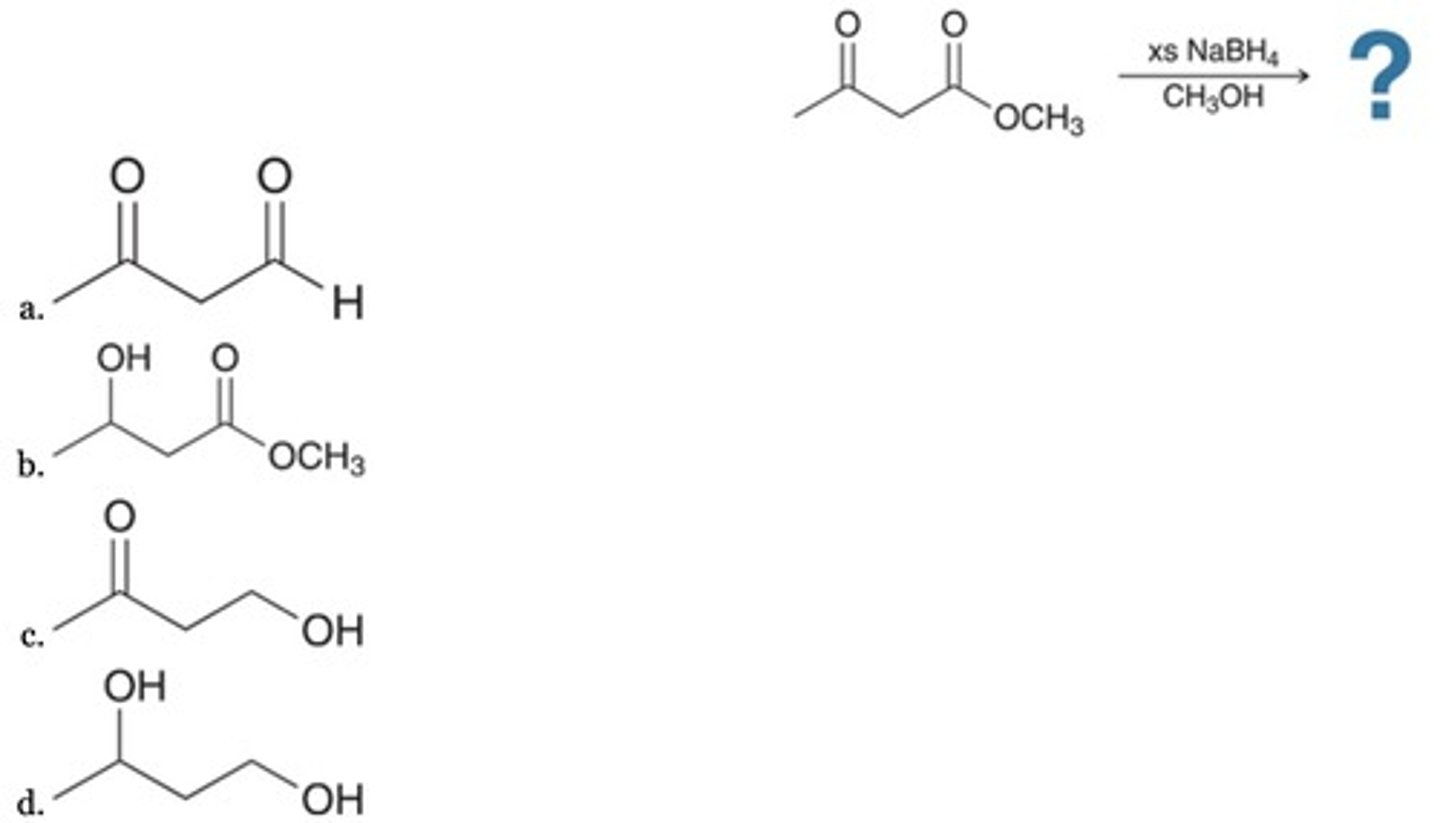
What is the missing reagent in the following synthesis?
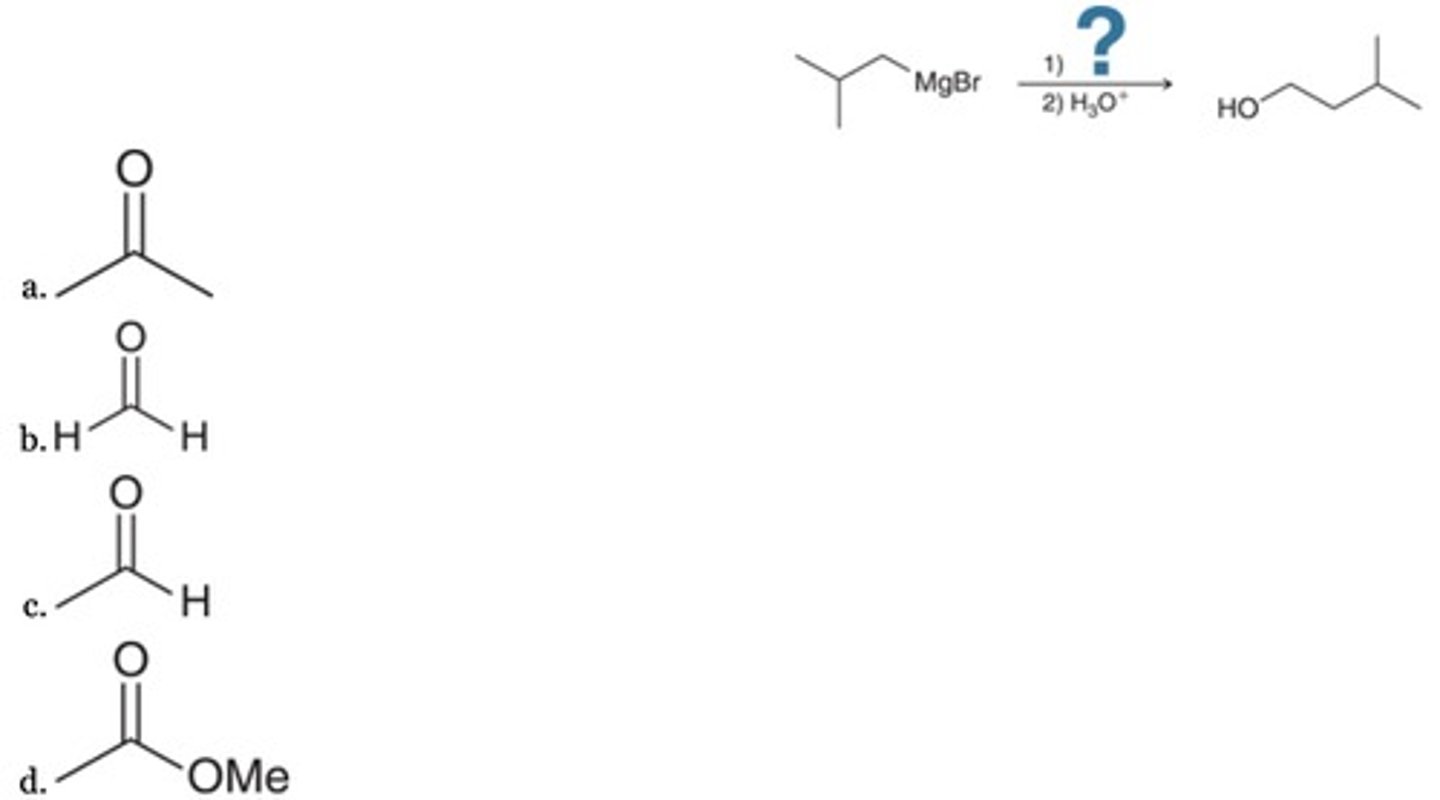
A
Predict the major product of the following sequence of reactions.
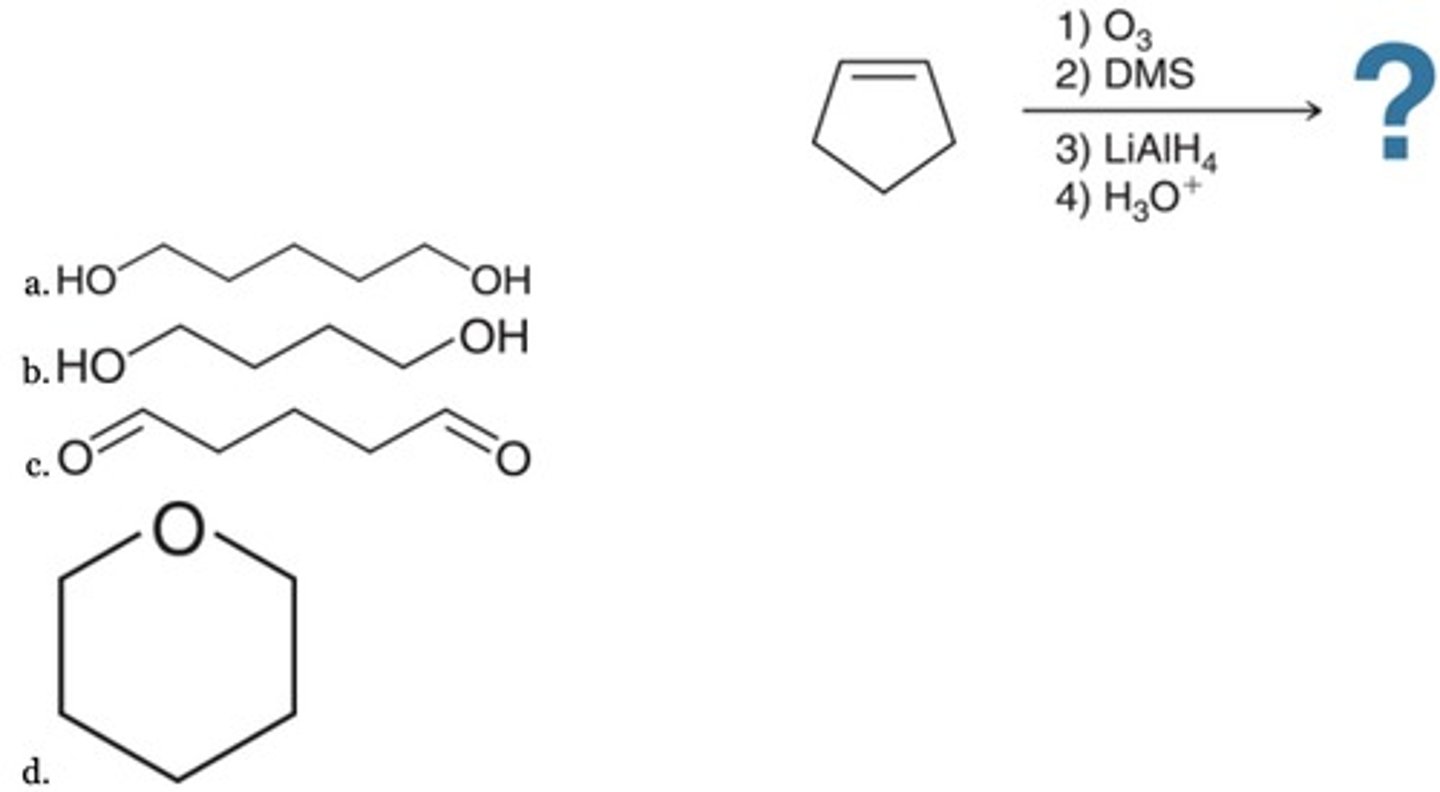
A
Which reagent (or reagents) will efficiently achieve the following transformation?
B
Which of the following methods would successfully prepare the given target molecule?