12-13 Bioenergetics, Metabolism and, ATP
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What is the primary concept of energy flow in biological systems?
Energy flow is often represented as a food chain, involving producers and consumers, herbivores and carnivores.
What defines equilibrium in a biological context?
Equilibrium is a state of 'no change' where everything remains the same over time.
Why isn't the universe in a state of equilibrium?
The universe isn't in equilibrium due to changes driven by free energy and the second law of thermodynamics.
What does diffusion illustrate in terms of change?
Diffusion shows that the direction of change is governed by probability, leading to a more random distribution of molecules.
What do the laws of thermodynamics describe?
The laws of thermodynamics describe energy changes and the direction of those changes in all systems.
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
The first law states that total energy remains constant.
What is the second law of thermodynamics?
The second law states that for any change, the distribution of energy becomes more random, leading to increased entropy.
How is Gibbs Free Energy (G) significant in biology?
Gibbs Free Energy is used to predict whether a change, such as a chemical reaction, is possible.
What does ΔG represent?
ΔG represents the change in Gibbs Free Energy, indicating whether a process is spontaneous or not.
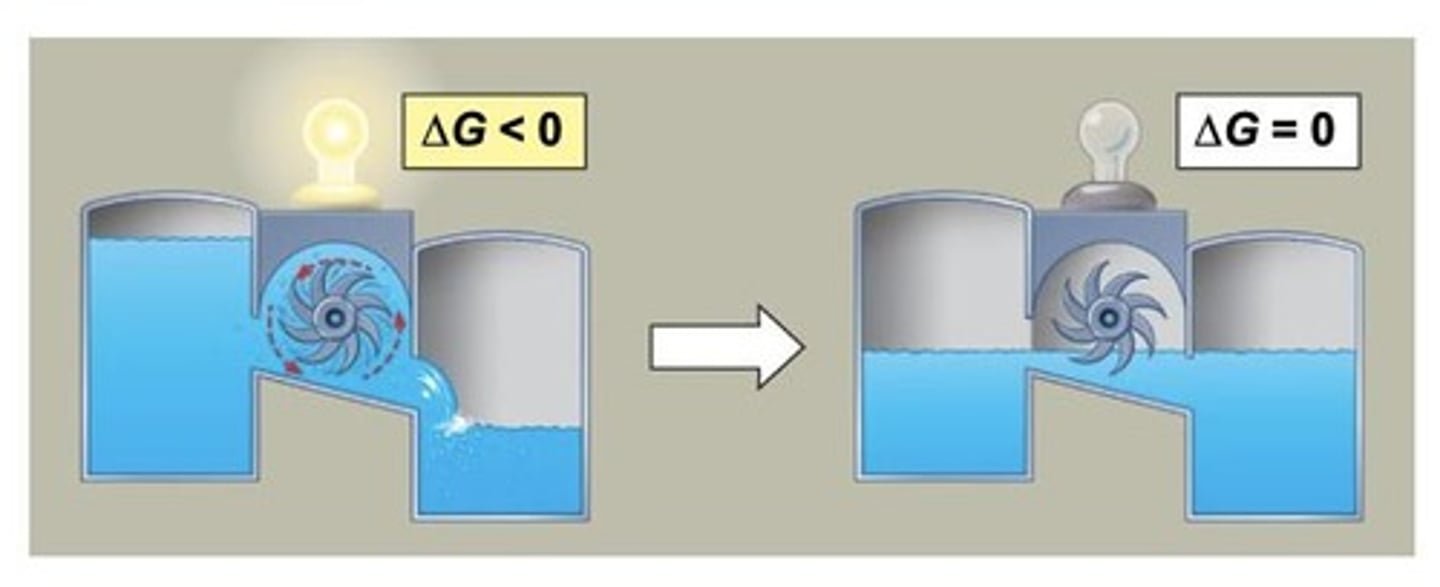
What is the condition for spontaneous change according to the second law?
For spontaneous change, ΔG must be less than zero (ΔG < 0).
What happens at equilibrium in terms of free energy?
At equilibrium, ΔG equals zero (ΔG = 0), meaning no work can be done.
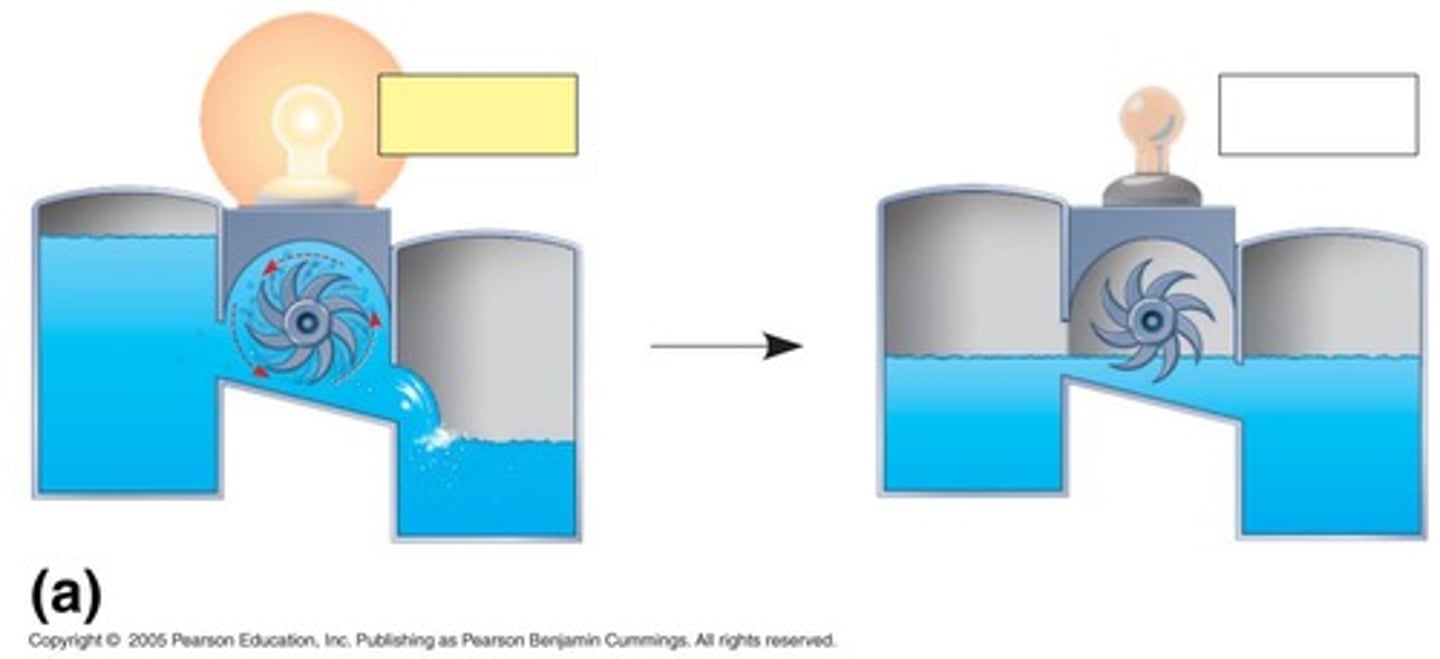
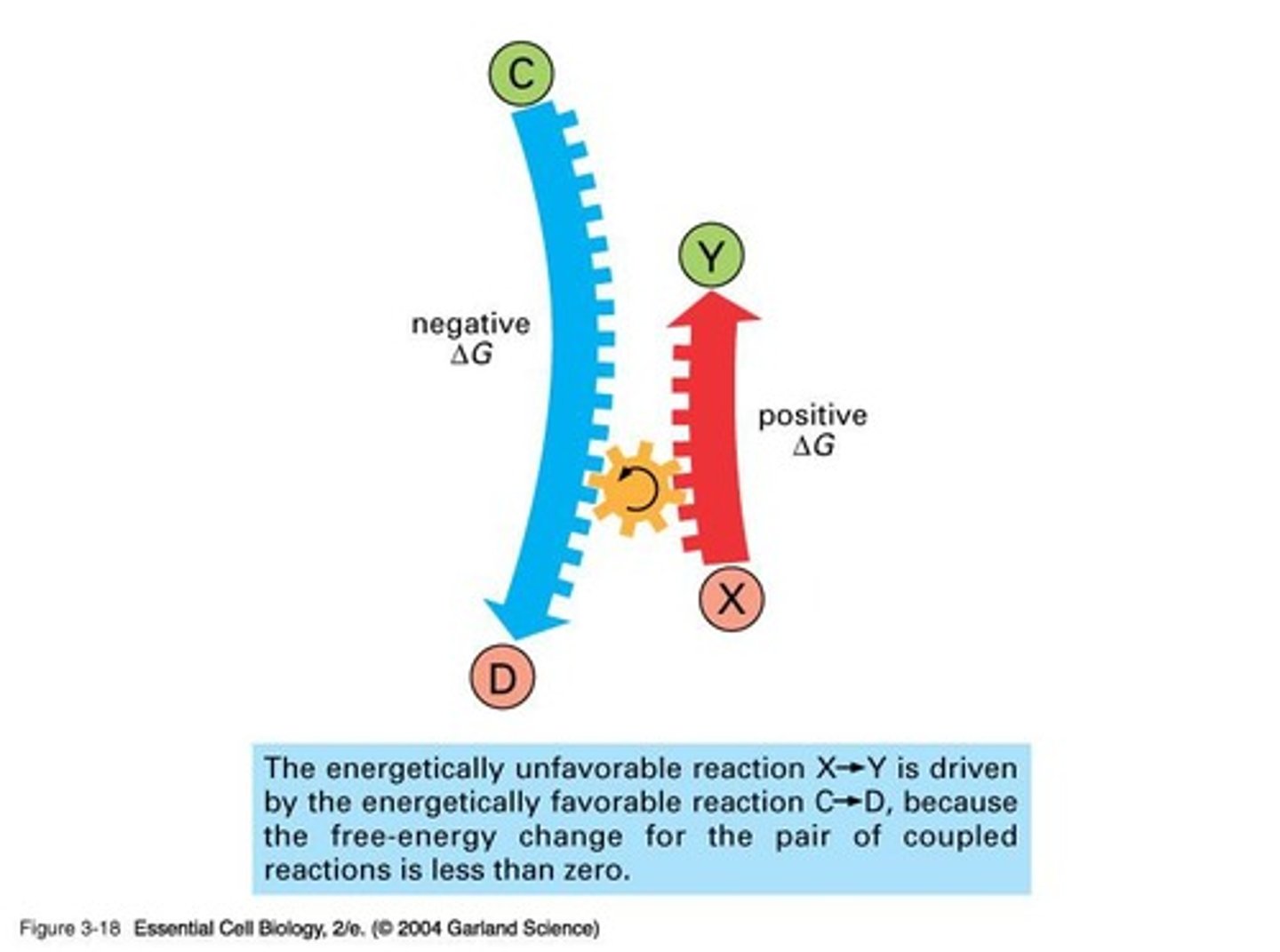
How can energy be coupled to perform work?
Energy can be coupled by linking a spontaneous process with a non-spontaneous process to maintain a negative ΔG overall.
What is an example of coupling in energy transformation?
Using the flow of water to drive a turbine that lights a bulb is an example of coupling energy transformations.
What is the pessimistic view of the second law of thermodynamics?
The pessimistic view suggests that the second law leads to the 'heat death' of the universe.
What is the optimistic view of the second law of thermodynamics?
The optimistic view sees the second law as a creative force leading to the development of complex systems like life.
How does life relate to energy transformation?
Life represents an 'island of increasing order' in a universe that is becoming increasingly disordered.
What distinguishes living systems from isolated systems?
Living systems are open systems that exchange energy with their environment and cannot reach equilibrium.
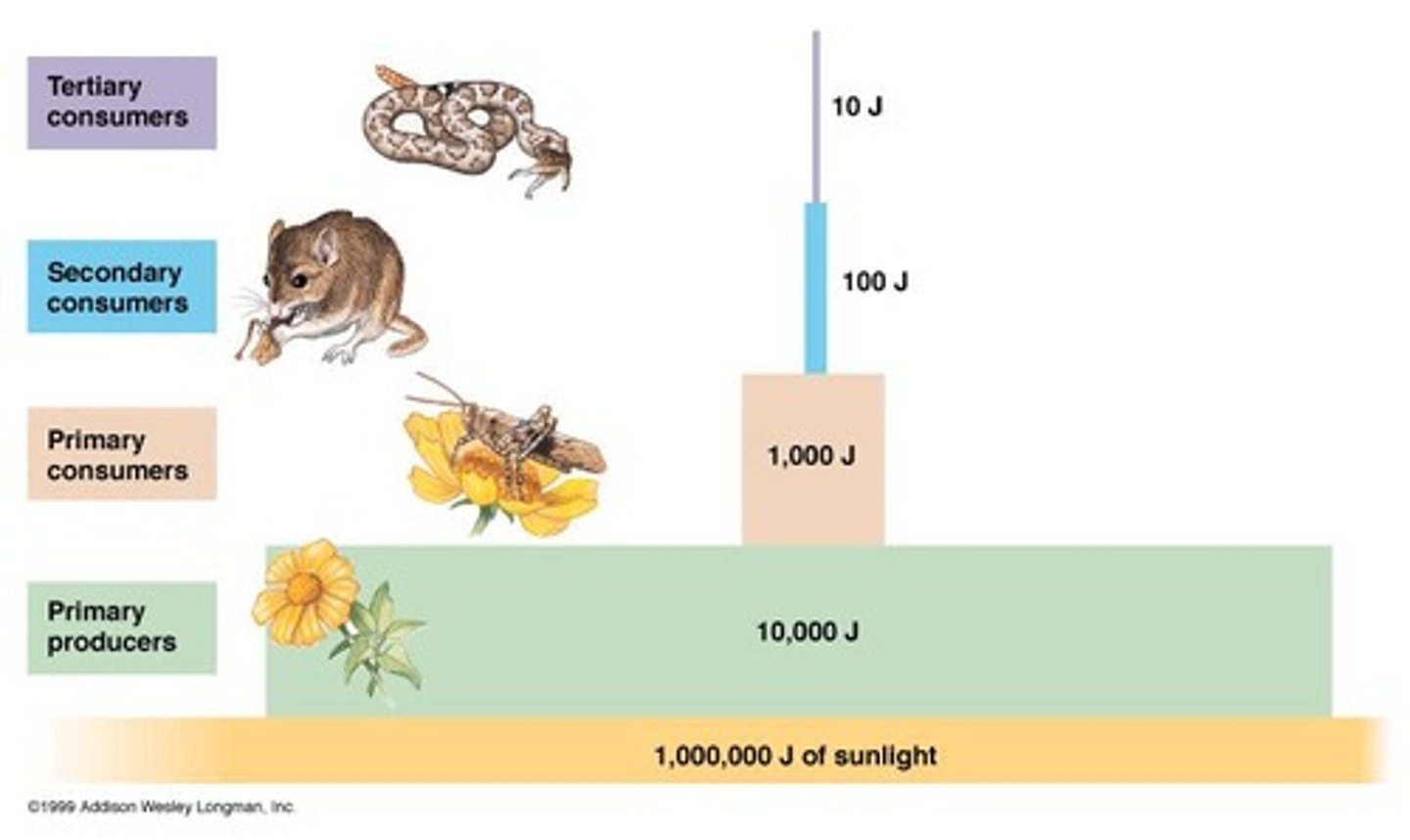
What is the role of ecosystems in energy flow?
Ecosystems are emergent properties of energy flow and nutrient cycling, where energy enters as sunlight and exits as heat.
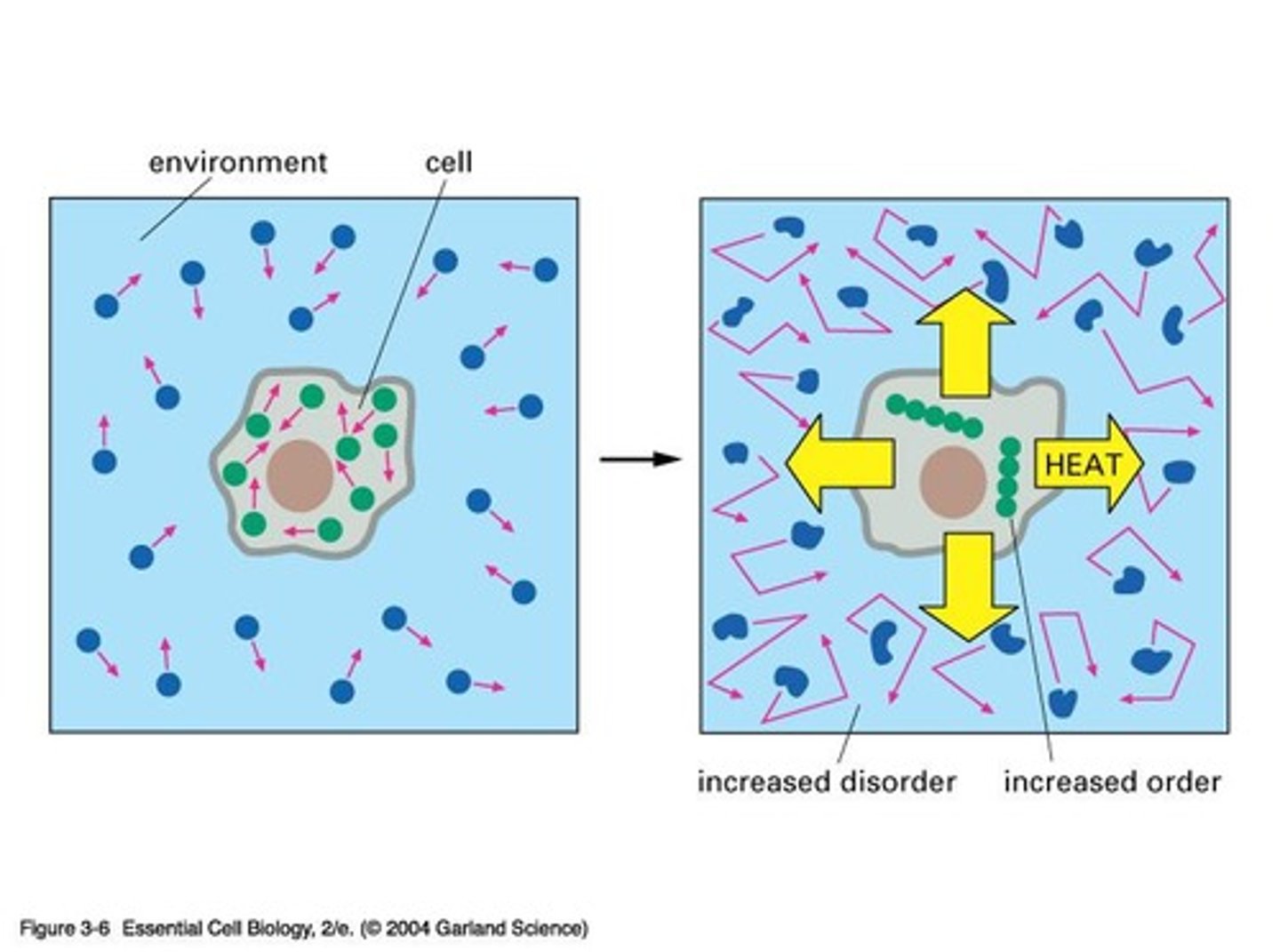
What is entropy in the context of thermodynamics?
Entropy refers to the measure of disorder in a system, which tends to increase over time.
What is the relationship between free energy and work?
Free energy is the 'useful' energy available for doing work; as it decreases, work can no longer be performed.
What is a coupling mechanism in biological systems?
A coupling mechanism links spontaneous and non-spontaneous processes to facilitate energy transformations without violating thermodynamic laws.
What happens to free energy as a system approaches equilibrium?
As a system approaches equilibrium, free energy continuously decreases until it reaches zero.
What is the significance of the phrase 'life as an exotic coupling mechanism'?
It highlights how complex biological systems utilize energy transformations to maintain order and perform work.
What is a chemical reaction?
A rearrangement of atoms where chemical bonds get broken and new ones are formed.
What is the difference between reactants and products in a chemical reaction?
Reactants are the starting substances, while products are the substances formed as a result of the reaction.
How do you balance a chemical equation?
By ensuring that the number of atoms for each element is equal on both sides of the equation.
What is an exergonic reaction?
A reaction that releases free energy and can occur spontaneously (ΔG < 0).
What is an endergonic reaction?
A reaction that requires free energy and does not normally occur (ΔG > 0).
How is metabolism defined?
The totality of an organism's chemical reactions, organized into metabolic pathways.
What are metabolic pathways?
Series of chemical reactions that begin with a specific molecule and end with a product, each step catalyzed by a specific enzyme.
What are the two main types of metabolic pathways?
Anabolic pathways (build complex molecules) and catabolic pathways (break down complex molecules).
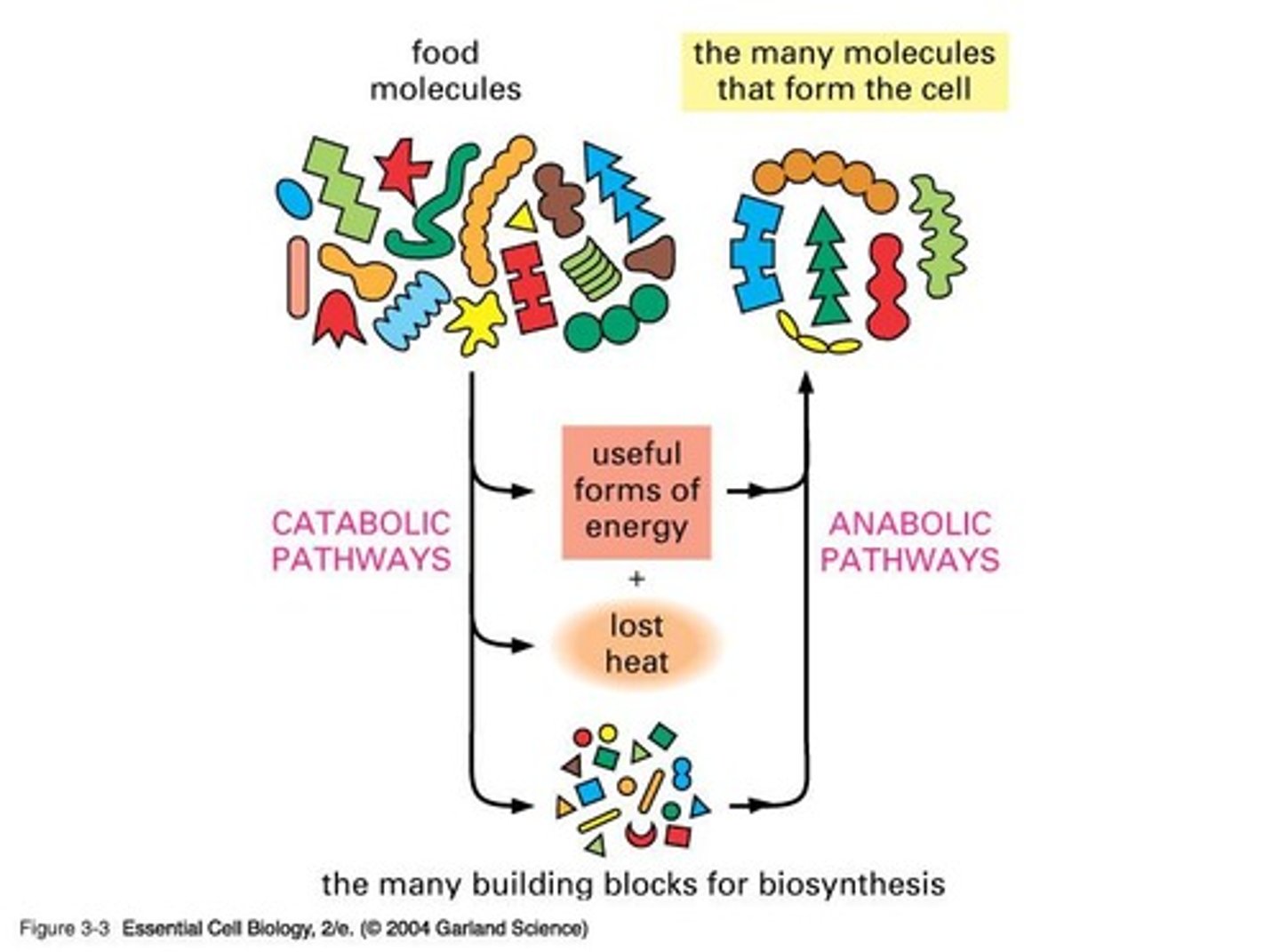
What characterizes anabolic pathways?
They build complex molecules from simple ones and are generally endergonic (ΔG > 0).
What characterizes catabolic pathways?
They break down complex molecules into simple ones and are generally exergonic (ΔG < 0).
How do anabolic reactions become possible?
By coupling them to catabolic reactions, resulting in an overall negative ΔG.
What is ATP and why is it important?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the most important energy carrier in cells, acting as a 'common energy currency.'
What is the structure of ATP?
ATP is a nucleotide consisting of adenine, ribose, and three phosphate groups.
What happens during the hydrolysis of ATP?
Energy is released when the terminal phosphate group is broken off, resulting in ADP and inorganic phosphate.
What is phosphorylation?
The transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to another molecule, often activating it.
What is the ATP cycle?
The process by which ATP is generated by exergonic reactions and used to drive endergonic reactions.
What cellular activities release energy?
Exergonic reactions, catabolic reactions, and the breakdown of ATP.
What cellular activities require energy?
Endergonic reactions, anabolic reactions, and the formation of ATP.
What is the relationship between exergonic and endergonic reactions?
An endergonic reaction can occur only if it is coupled to an exergonic reaction that releases energy.
What does the second law of thermodynamics state in relation to cells?
Cells do not violate the second law because there is a net increase in disorder (entropy) overall.