BIOLOGY REVIEWER (CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITIES)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Chromosomal Abnormalities
may be due to chromosomal genetic, or environmental factors, or combination of these
chromosomes may fail to separate properly during cell division
Karyotype
individuals complete set of chromosome
Aneuploidy
addition or loss of one or more chromosomes
Trisomy (2N+1), Monosomy (2N-1)
Polyploidy
addition of chromosome sets
Triploidy (3N), Tetraploidy (4N)
Aneuploidy
Disjunction
Nondisjunction
Changes in chromosomes structure
Disjunction
normal separation of chromosomes in Meiosis I or sister chromatids in Meiosis II
Nondisjunction
chromosomes don’t separate properly during meiosis
problems with meiotic spindle cause errors in daughter cells
zygote has wrong chromosome number
Changes in chromosomes structure
Deletion
Duplication
Inversion
Translocation
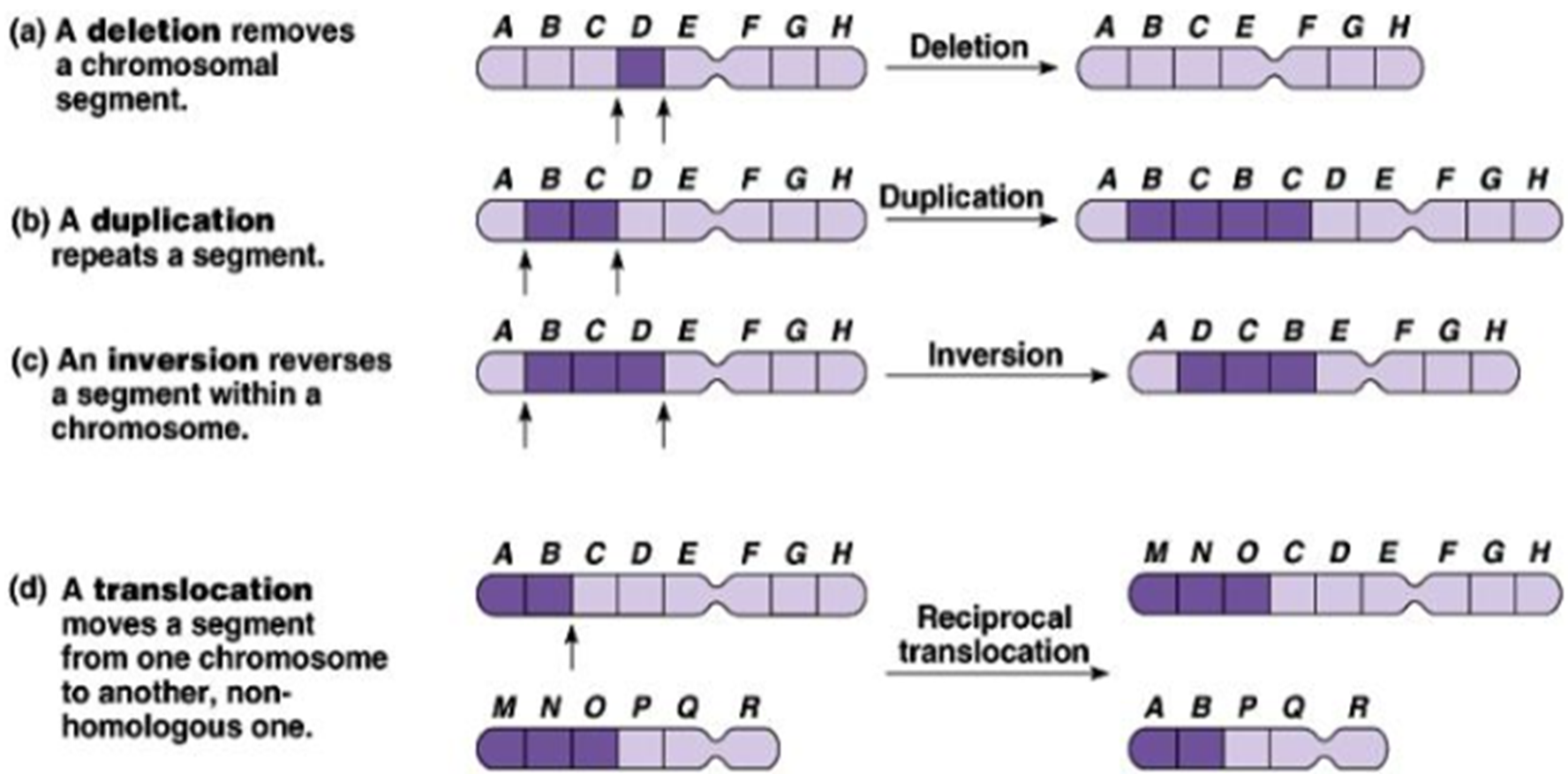
Deletion
removes a chromosomal segment
Duplication
repeats a segment
Inversion
reverses a segment within a chromosome
Translocation
moves a segment from one chromosome to another, non-homologous one.
Human Chromosome Disorders
High frequency in humans
Certain conditions are tolerated
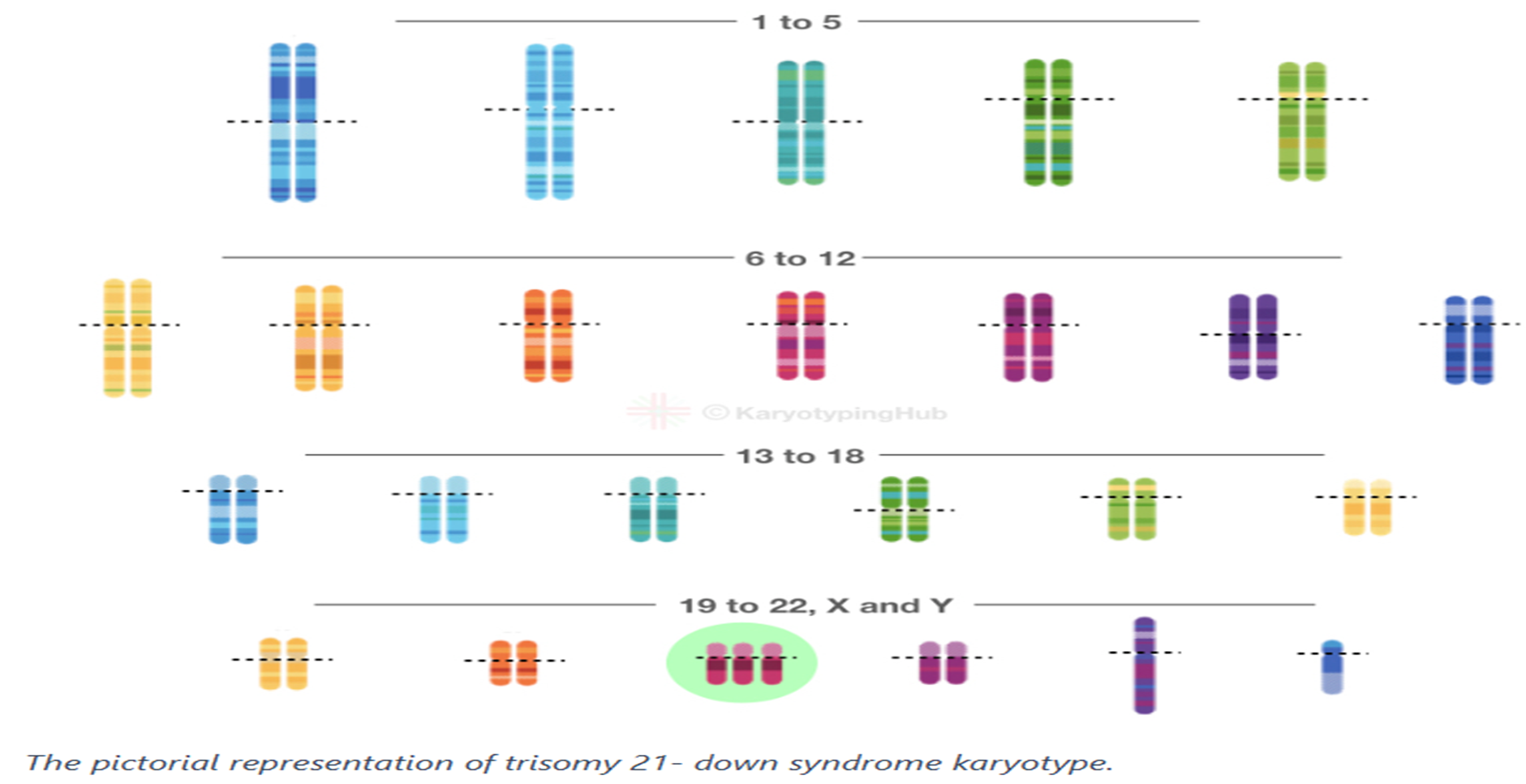
Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome)
decreased muscle tone at birth
excess skin at the nape of the neck
flattened nose
upward slanting eyes
small ears and mouth
wide, short hands with short fingers
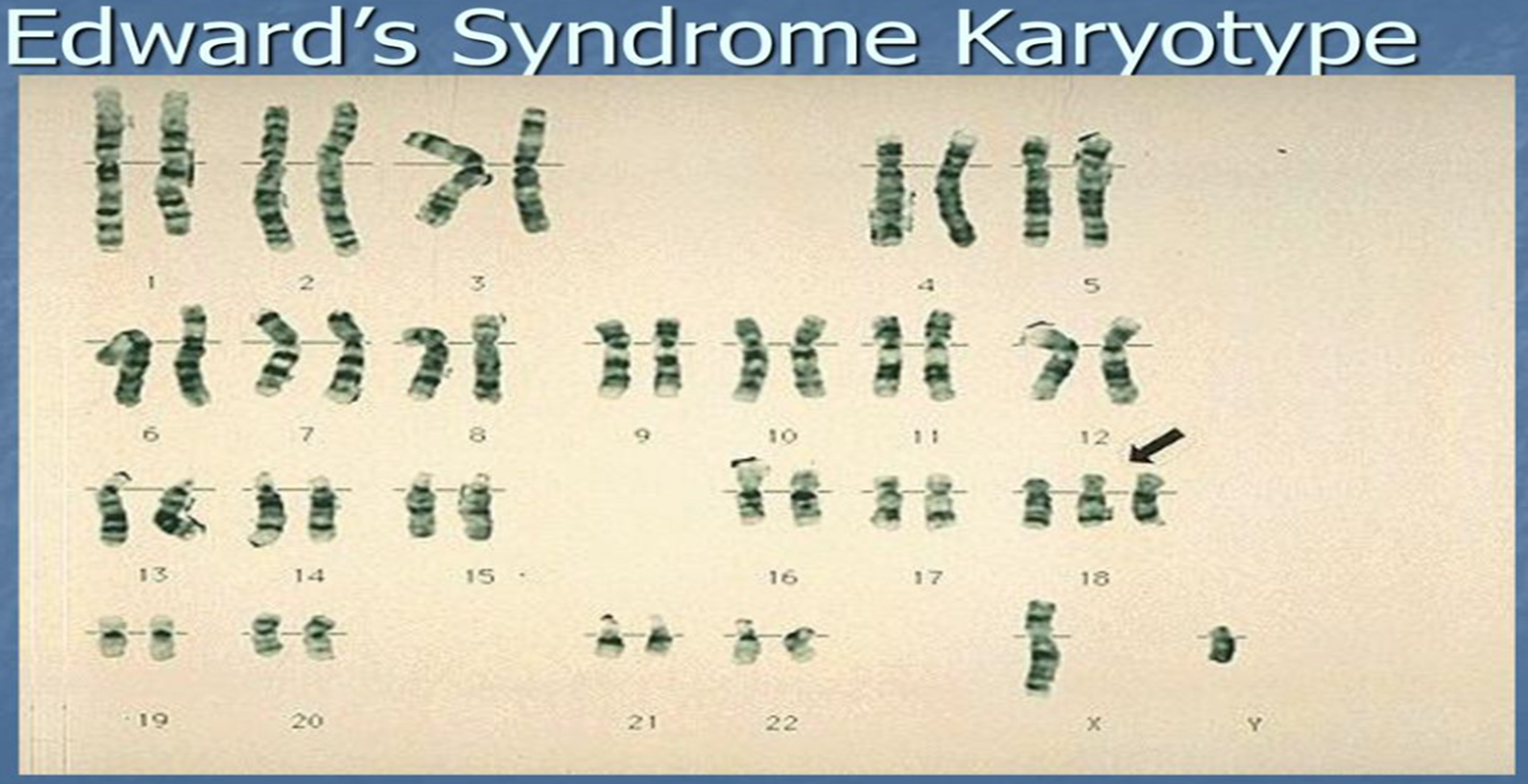
Trisomy 18 (Edward’s Syndrome)
mouth and jaw are small
ears are malformed and lowset
severe psychomotor and growth retardation are invariably present for those who survive beyond infancy
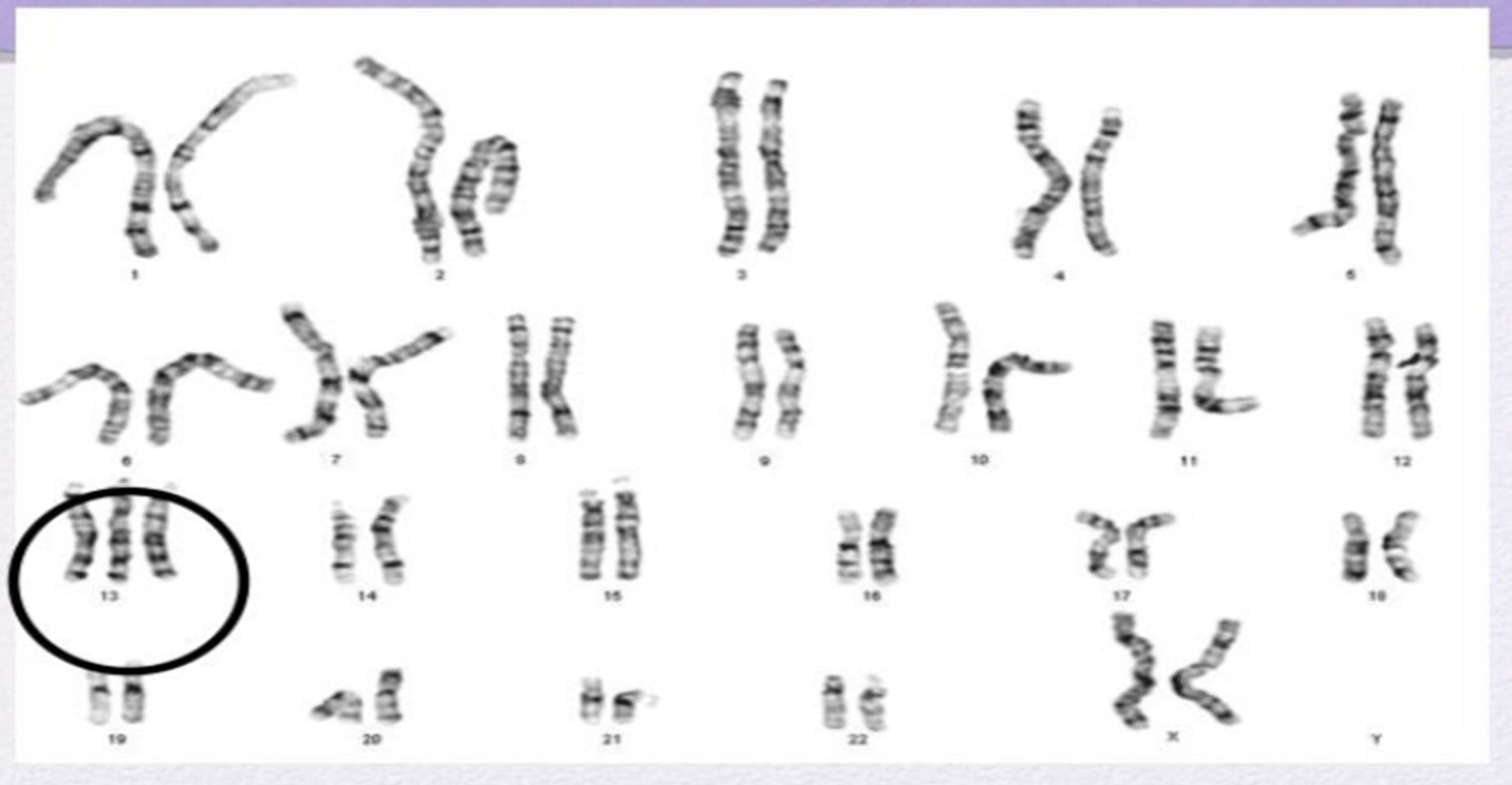
Trisomy 13 (Patau Syndrome)
More than half of the children with this syndrome don’t survive past the first month if birth.
Small head size
Either small or no eyes
60% have cleft palate
Extra toes or fingers
80% have heart disease
Trisomy 16 (Mosaic T16)
The most common chromosomal cause of miscarriage.
Most patients will die within the first year of life.
Characteristics of Mosaic T16:
Heart defects and other vascular issues
Delayed growth
Delayed speech and physical development
Reproductive disorders
Kidney problems
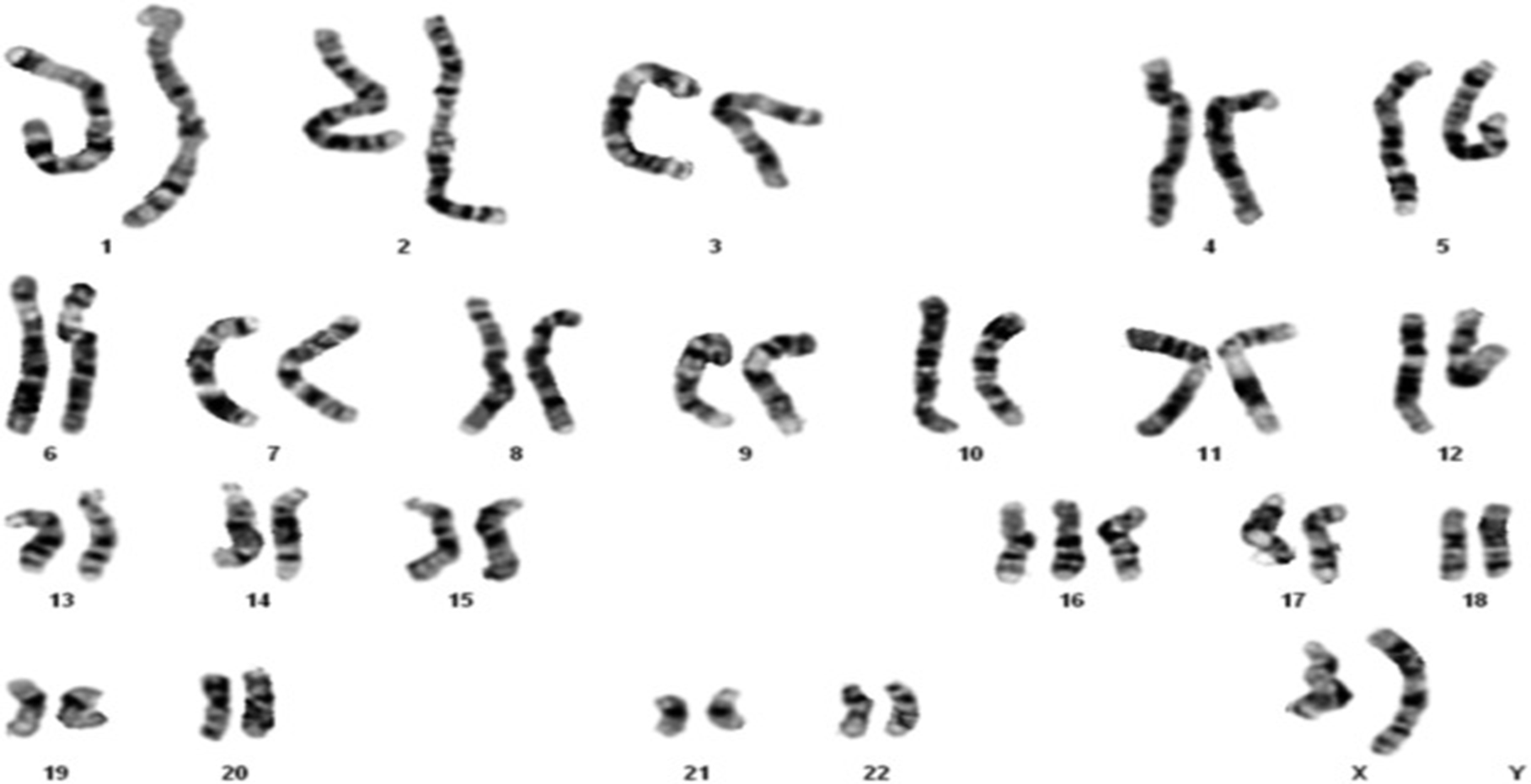
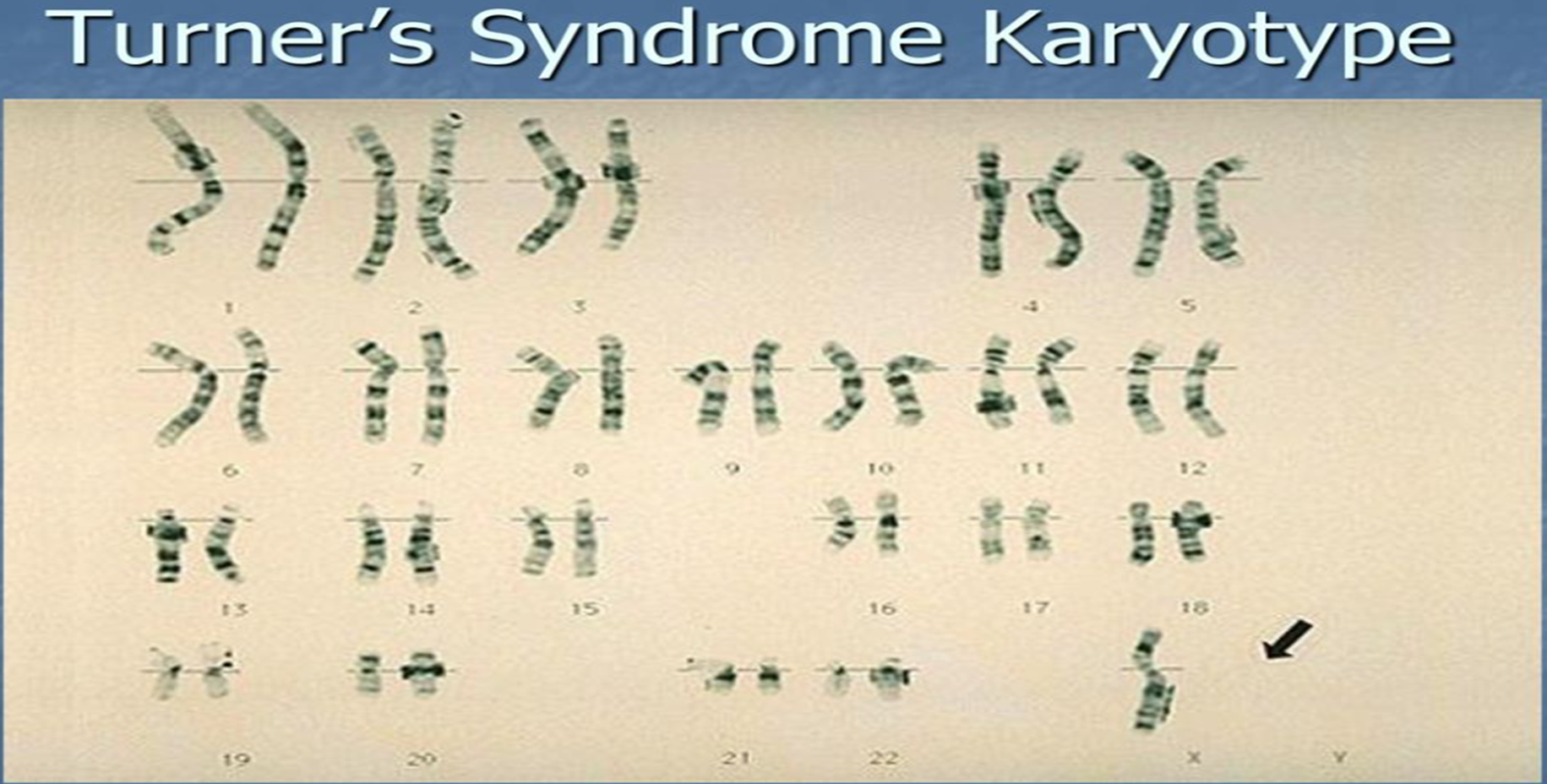
MONOSOMY X (45, XO): Turner Syndrome
Also known as “Gonadal dysgenesis”, it is a female chromosomal abnormality in which all or part of one of the sex chromosomes is absent (missing the Barr body, mostly 45X karyotype).
Characteristics abnormalities include:
- Gonadal dysfunction(sterility)
- Short stature
- Webbed neck
- Immature sex organs
- “Shield”- type chest (Broad and flat)
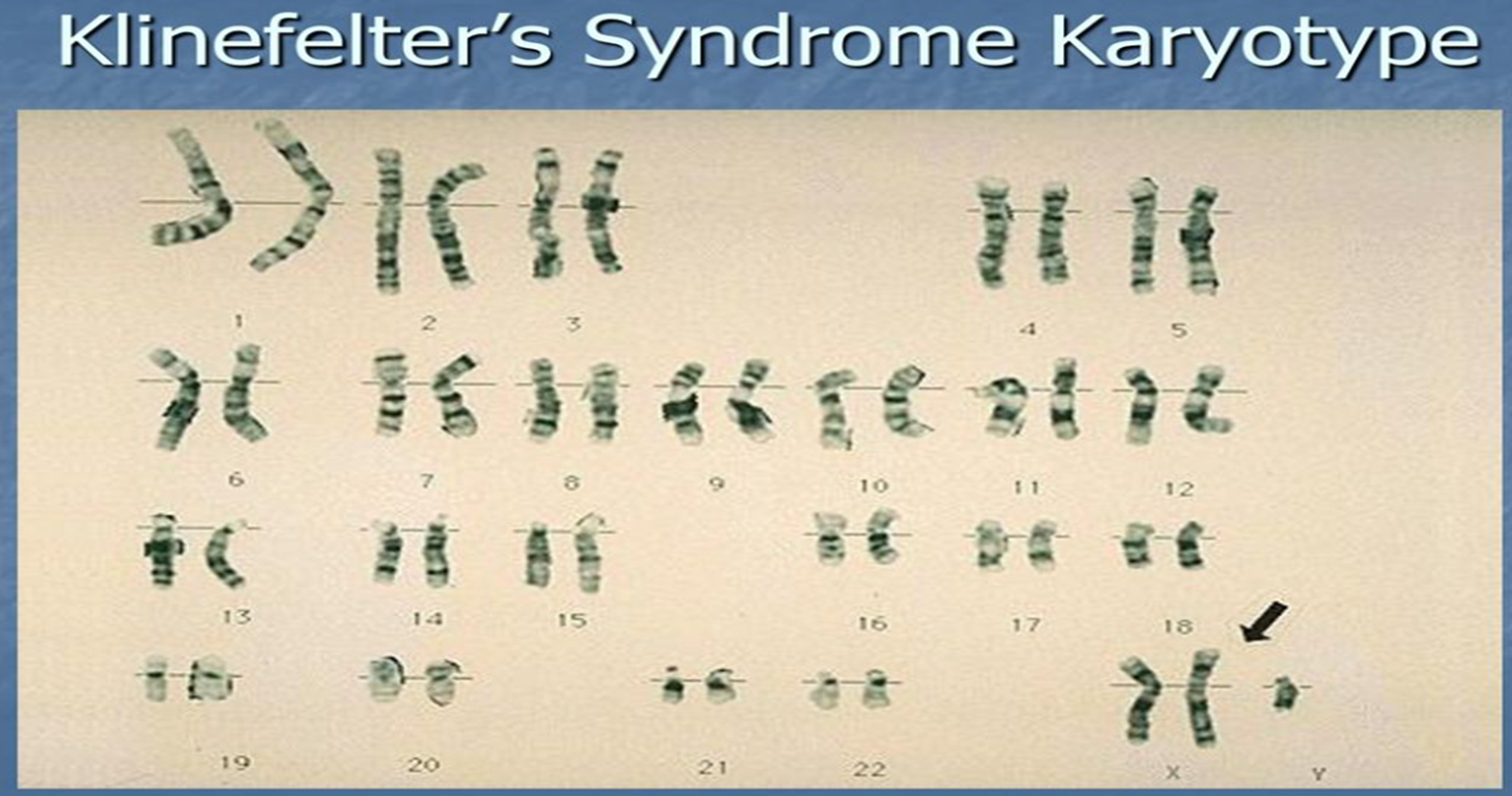
Klinefelter Syndrome: 47,XXY
XXY male
One in every 2000 live births
Have male sex organs, but are sterile
Feminine characteristics (enlarged breast, minimal facial and body hair)
Tall
Normal intelligence
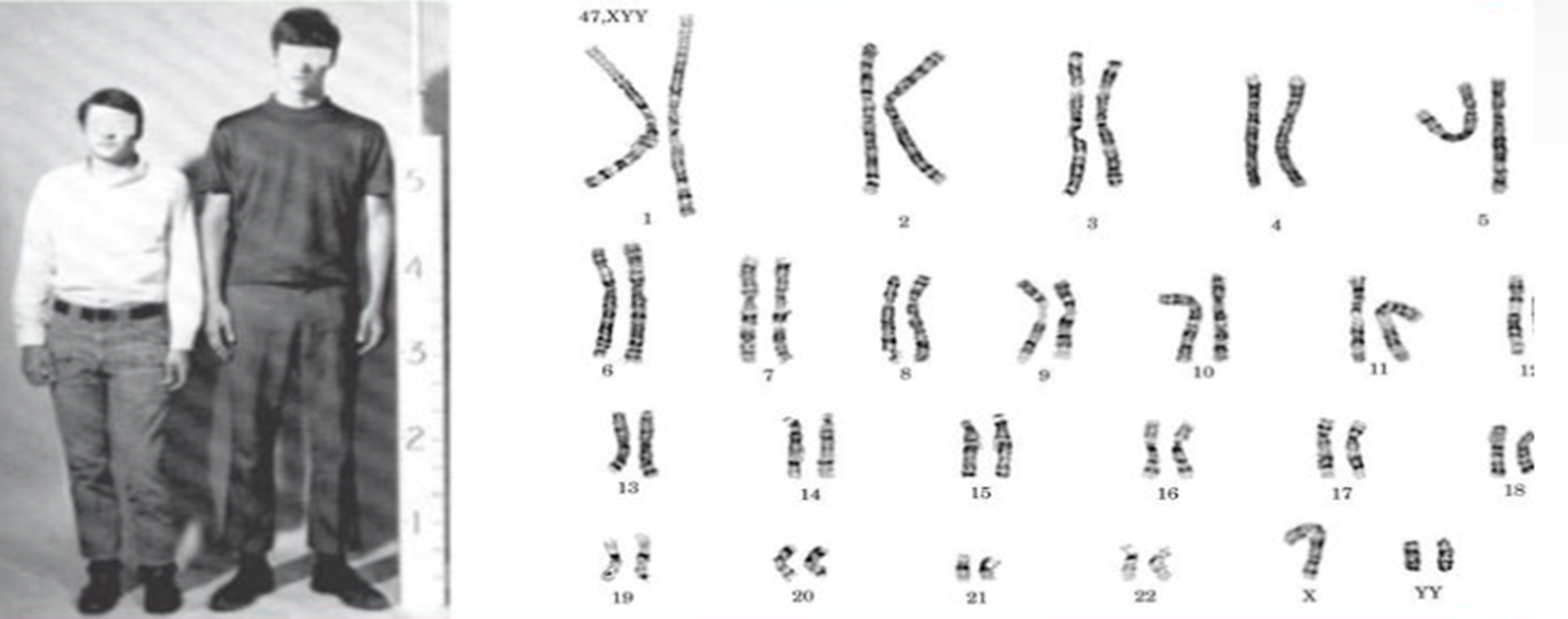
Jacob/ XYY Syndrome (47, XYY)
1/1000 births
Affected individuals are usually very tall and thin
Many experience severe acne during adolescence
Additional symptoms may include antisocial or behavioral problems and learning disabilities.
Intelligence is usually normal, although IQ, on average , is 10 to 15 points lower than siblings
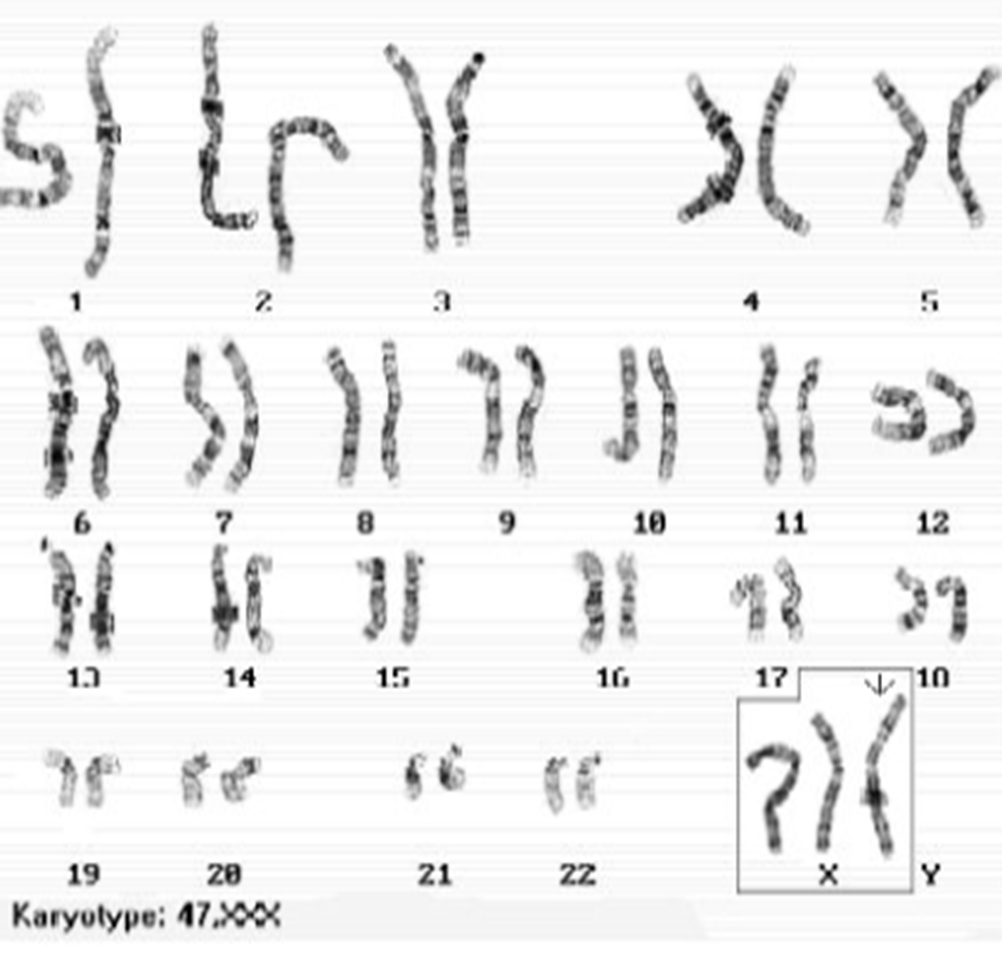
Metafemale/ XXX Syndrome
A metafemale is a woman who has an extra X chromosome.
In most cases, there will be no unusual physical features or medical problems resulting from Triple X Syndrome.
This is because in all female cells, there is only one active X chromosome at any one time.
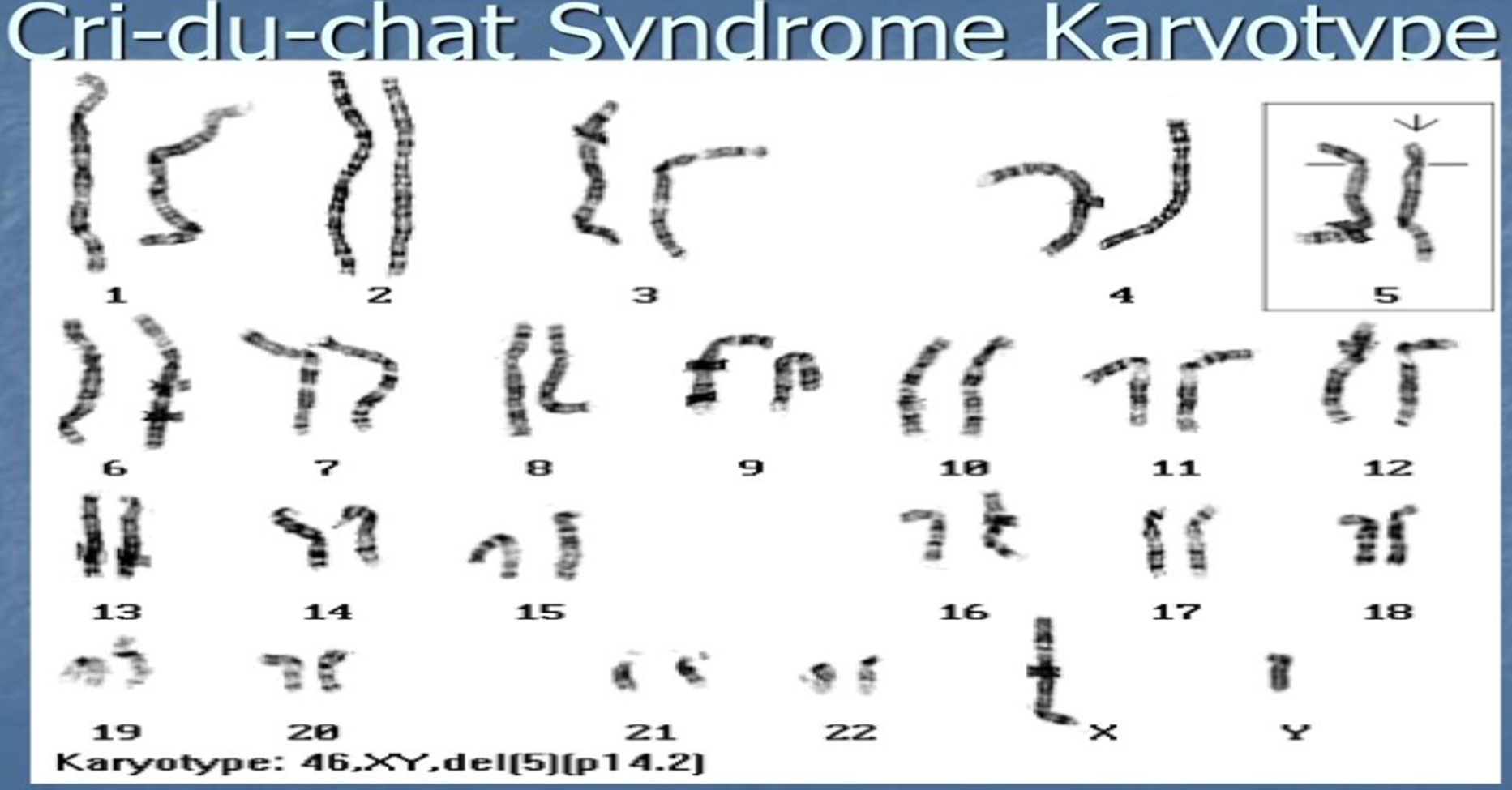
Cri-du-chat Syndrome
Affects on the body:
Physical features and medical problems vary widely from child to child
Monotone, weak, cat-like cry
Small head(microcephally) with a round face
High palate
Small receding chin(micrognathia)
Widely spaced eyes (hypertelorism)
Folds of skin over the upper eyelid (epicanthic folds)
Distinctive palmar creases (creases on the palms of the hands)