Chapters 7, 8, 9, 10 Marketing 200 / Simpson College / MG CLASS
1/303
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
304 Terms
What does ROI stand for?
Return on Investment
What does P&G stand for?
Proctor & Gamble
What does SKU stand for?
Stock Keeping Unit
What does TQM stand for?
Total Quality Management
What does ISO 9000 set rules on?
Quality Management and Requirements
What does ISO 14000 set rules on?
Environmental Management
What does ISO stand for?
International Standard of Organization
What does DMAIC stand for?
Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control
What does PLC stand for?
Product Life Cycle
What does UPC stand for?
Universal Product Code
Information on Aaron Keller: Capsule/Patagonia.
Capsule is a consultant agency that gives advice. When coming to Patagonia who focuses on sustainability, they did a complete package redesign.
What happen with Fiat and the 500s?
They come to the US and thought people would just buy them because their foreign like pasta or gelato.
Steps in Managing Products
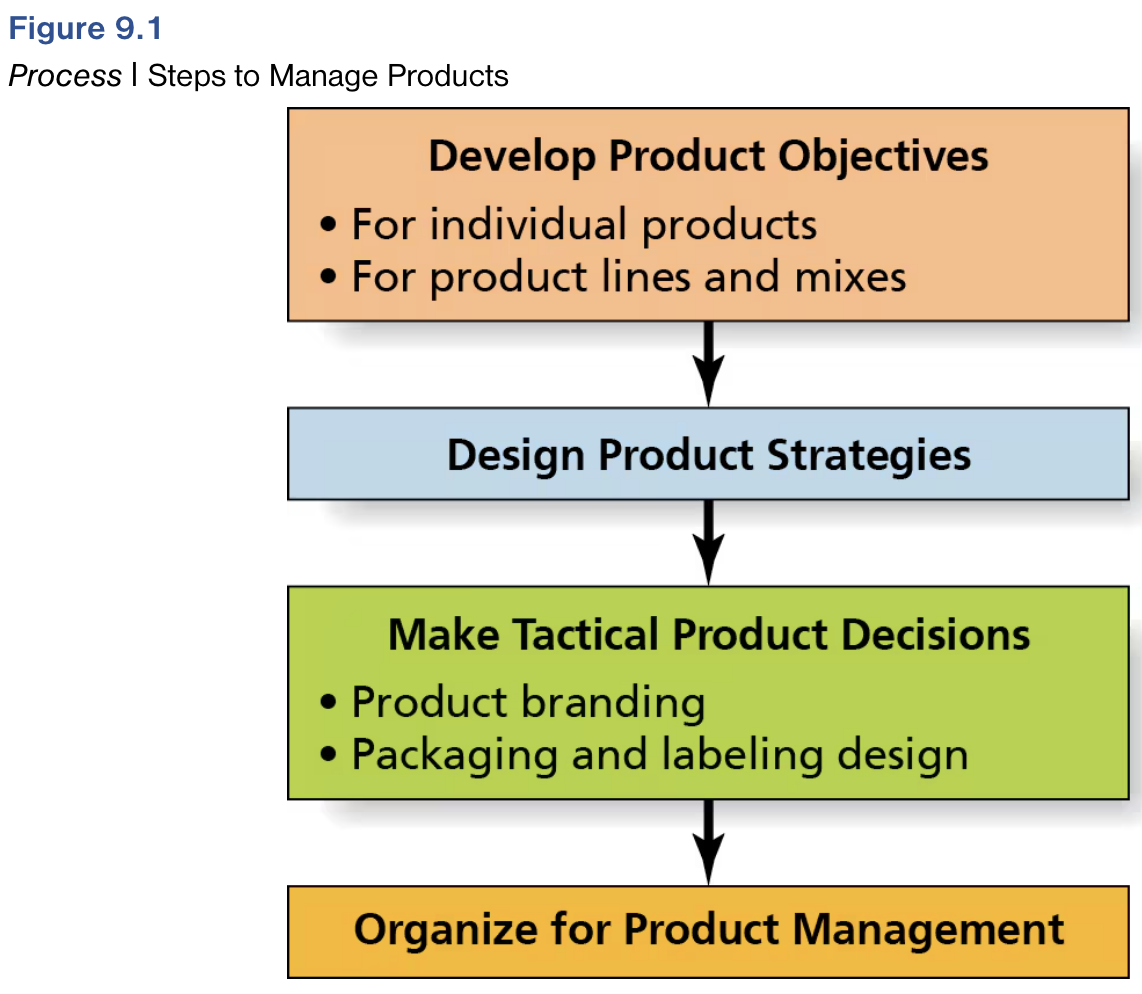
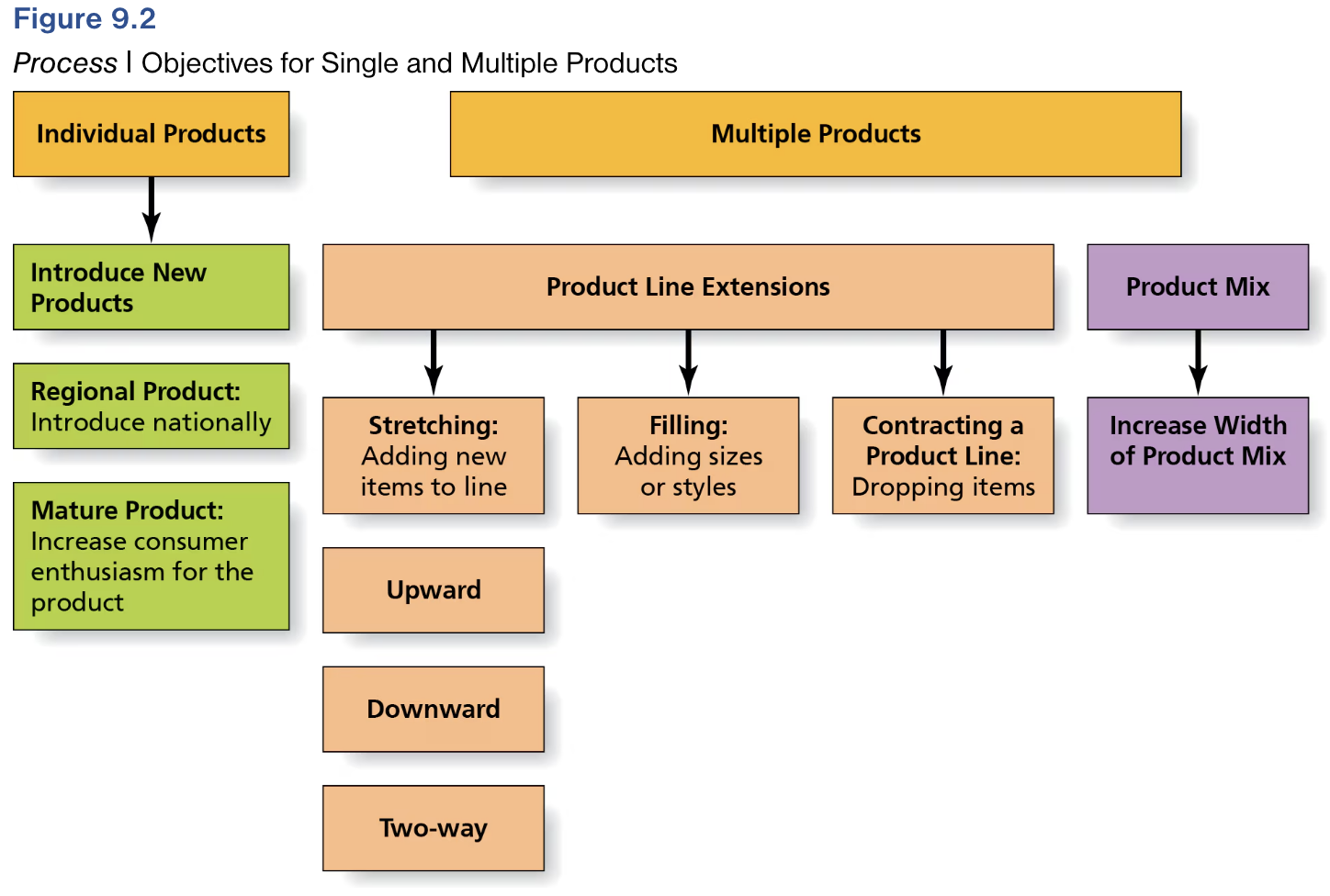
Learn the Objectives for Single and Multiple Products
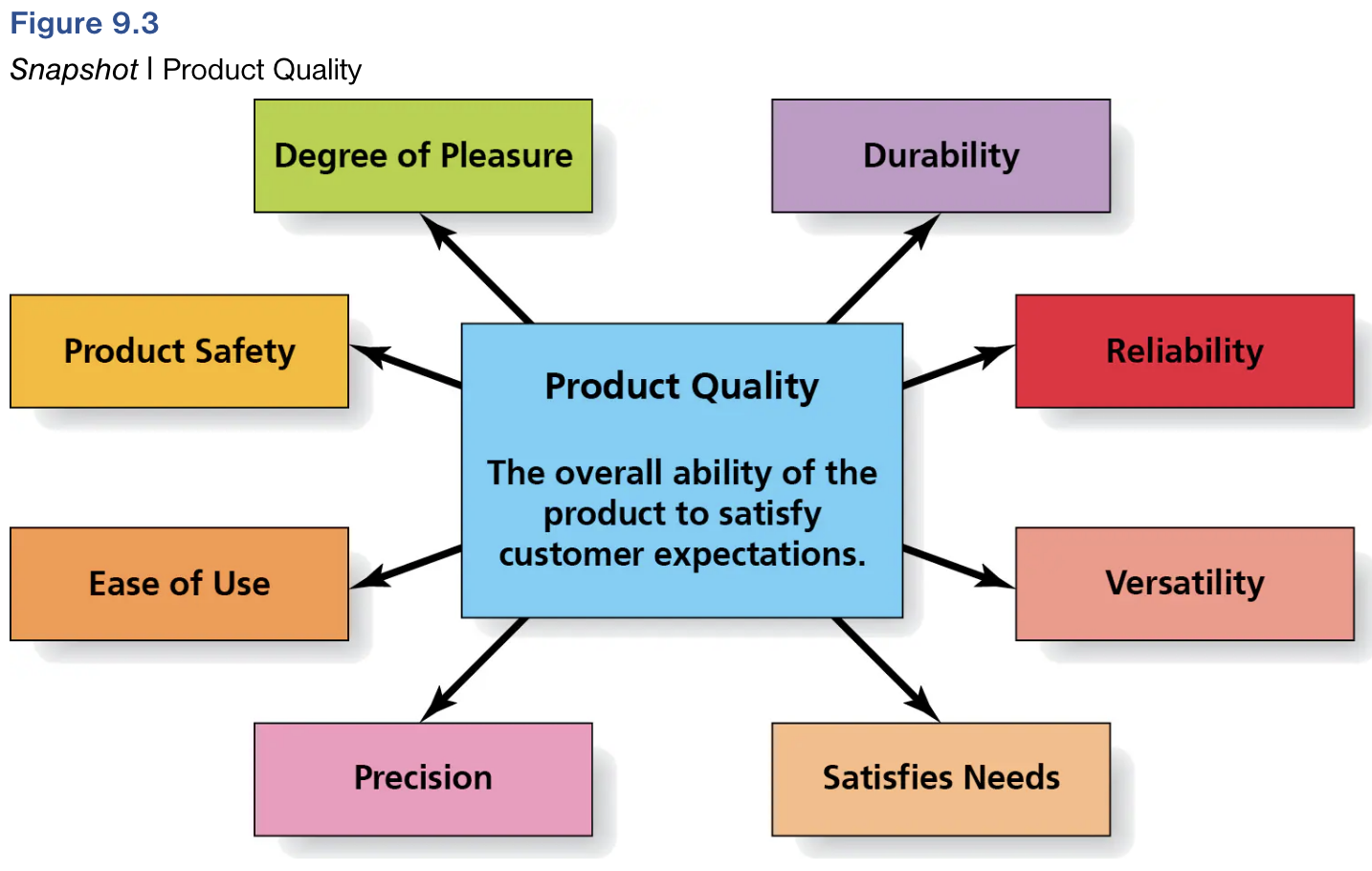
Different aspects of Product Quality
Test Question! Lay Potato Chips are in what stage of PLC and their new flavors represent what kind of Innovation?
Mature stage, Continuous Innovation
Example of Portfolio at work.
P&G bought a consumer health product company, expanding portfolio, and line extension branching out what they offer.
Define Product Line Extension.
Strategy to expand an existing product line by adding more brands or models.
Define Cannibalization.
Loss of sales of existing brand when a new item is a product line or product family is introduced.
-Ex. different colors of ketchup, Coors water
Full-line vs Limited-line strategy.
Full-Line target many customer segments for boosted sale potential, Limited-line do fewer product variations to be exclusive to one thing and specialize in a certain market.
-Limited Line example: Rolls Royce
What can we learn about Stretching from Kia
They tried to make a more expensive car in an upward stretch and failed.
What aspect of product quality is McDonalds?
Reliable
What aspect of product quality is the Bronco Goat Mode?
Versatility
Which aspect of product quality was the issue with Mattel’s lead paint crisis with toy recalls?
Product Safety
Trust is one facet of Quality. True or False.
True
How the 10 most-trusted brands do it:
Get personal: Amazon
Sell happiness: Coca-Cola
Live up to your promise: FedEx
Keep it cool: Apple
Design and experience: Target
Stay consistent: Ford
Can-do attitude: Nike
Forge connections: Starbucks
Serve up the quirky: Southwest Airlines
Focus on the customer: Nordstrom
How is a machine tested?
Based on the satisfaction it gives you.
Absence of Quality is the essence of squareness. T or F.
True
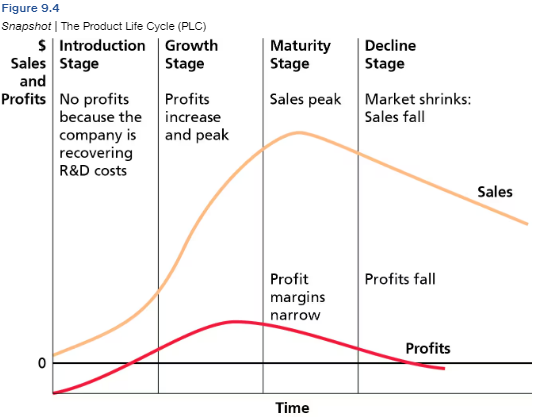
Learn this information of PLC
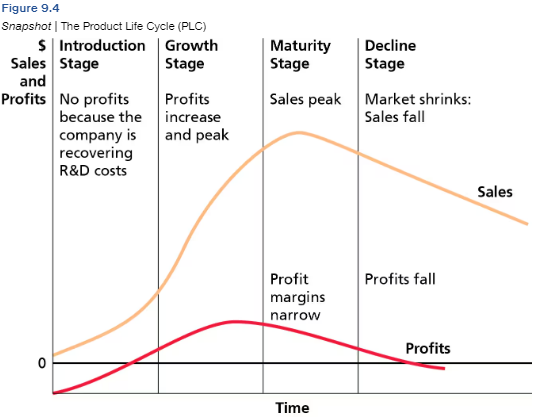
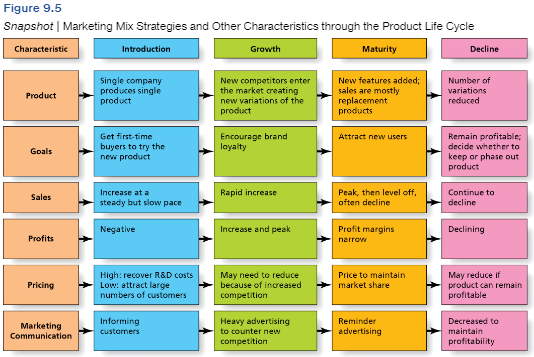
Learn this
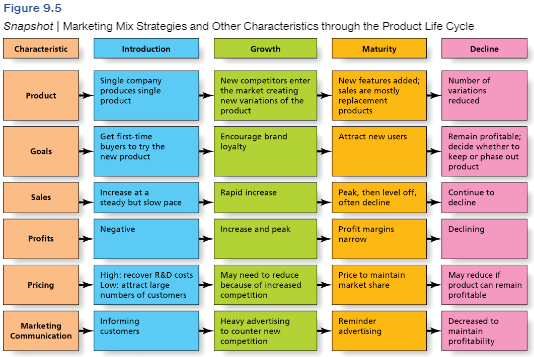
What is the goal of PLC: Introduction
Inform customers, induce trial, get first time buyers to try the product.
95% of new products fail
H-P Touchpad
Flip camcorder
Dodge Dart
What is the goal of PLC: Goal
Encourage brand loyalty by investing in advertising.
Segmentation and positioning
What is the goal of PLC: Maturity
Attract new users by emphasizing distribution.
Longest stage
Ex. Lays
What is the goal of PLC: Decline
Maintain profitability; determine is termination is needed
Define Brand
Name, Term, Symbol, or element of a product that identifies a firm
A brand name should be easy to say, spell, read and remember. True or False.
True
A brand is a promise to what?
A brand is a promise to deliver a set of benefits or satisfactions
Mercedes stands for delivering a quality promises no matter where its produced
What aspects does a good brand name fit according to Rene Magritte?
The target market
The Product benefits
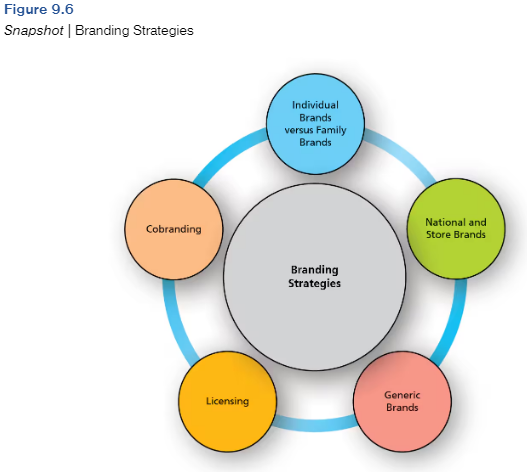
Learn these branding strategies.
The three types of product management.
Brand managers
P&G
Category managers
Market managers
Define Skunk Works.
Small and often isolated department or facility that functions with minimal supervisions.
Notes on Mini Cooper.
Didn’t have a big advertising budget
Print, billboards, and online ads, NO tv ads
Parent company is BMW
Notes on Oreo.
A mature product
Focusing new varieties
limited edition flavors
Ran a contest to guess the Oreo flavor for $50k
Notes on Kia.
Tried to stretch its low-priced items upwards.
Failed
Notes on P&G.
Basically invented the Product Management System
Expanded its line of liquid dish detergents
Gain moved from laundry soap to now also dishwashing liquids
Gain also prioritizes a good smell
P&Gs Charming toliet paper made SitOrSquat to help find nearest bathroom.
Notes on Tesla.
Tesla 3 usurped everything at the top of the introduction quadrant
Demand was crazy
Production was slowing with the rate of orders; this could have caused failure to the growth stage.
Notes on Airbnb.
Used brand storytelling to connect with consumers
Underwent a rebrand to “Belo” to create a story and have more meaning.
Notes on Coca-Cola.
Announced a “One Brand” global strategy to address complexity among sub-brands
Unclear if it worked
Now follows “Coke’s Way Forward”
evolving its business strategy to be a total beverage company by providing more drinks people want, including low and no sugar.
Notes on Aldi.
90% of its products under private label brands
Focuses on highest quality products at a cheap price.
Healthy food like free of synthetic colors, trans fats, and MSG
Why brands matter.
Brand Equity
Brand Meaning (Meaning Management)
Brand Storytelling (The goal is engagement)
Brand extensions (Attatching brand to new product category)
Sub-Branding
Define Brand Equity.
Brands value over and above the value of generic version of the product. (Value of brand to an organization)
Define Brand Meaning.
The beliefs and associations that a consumer has about the brand.
Define Brand Storytelling
Compelling stories told by markets about a brand to engage consumers.
Brand Extensions.
New products it sells with the same brand name
Brand Extension brings the risk of what?
Brand Dilution: The contrast between the brand extension’s less positive characteristics and the more positive characteristics of the brand can lead to a shift in how consumers perceive the brand.
Define sub-branding.
Creating a secondary brand within a main brand that can help differentiate a product line to a desired target group.
What company follows Family Branding/Umbrell Brand Strategy?
Campbell puts their name on all different types of soup. “Cambells chick with Rice or Campbells Chick Noodle”
On the opposite there is P&G with individual branding, Its not “P&G Gain” its just Gain
Info on Helen of Troy (Hydro Flask)
First for county fair and farmers markets to hikers and campers
Focused on aesthetic with its cooling
Variety of colors
People love the company and the brand not just the bottle
VSCO Girls take to the hydro flasks
Not just for teens, millennials are owning them also
“Just one more” Market strategy
What does ISO 22000 work towards?
Food Safety Management
What does ISO 27001 work towards?
Information Security
Define Product Relaunch.
Repositioning an existing product for reintroduction into PLC.
What 4 things should brands pass.
Easy to Say, Spell. Read, Remember
What is the Fit Test?
A brand should
Fit the target market
Fir the Products benefits
Fir the customers cultures
Fit the legal requirements
Define Trademark.
Legal term for a brand name.
What are the 4 relationships a person may have with a product.
Self-concept attachment
Nostalgic attachment
Interdependence
Love
Define the relationship: Self-concept attachment.
Product helps to establish a user’s identity
Ex. Clothing brands.
Define the relationship: Nostalgic Attachment
Product serves as link to past self.
Define the relationship: Interdependence.
Product is a part of user’s daily routine.
Ex. Starbucks
Define the relationship: Love
Product elicits emotion bonds of warmth, passion, or other strong emotions
Ex. Hersheys Kiss
Define Product Line.
The Firms total product offering designed to satisfy a single need or desire of target customers
Ex. Campbells soup
Define Product Line Length.
Determined by the number of Stock Keeping Units.
P&Gs line of laundry detergent; Tide, Era, Gain
What does a SKU(Stock Keeping Unit) mean?
Unique identifier for each distinctive product.
Define Upward Product Line Stretch.
Add new items for higher price.
Ex. Kia (Failed)
Define Downward Line Stretch.
Higher price companies adding items for a lower price.
Ex. New Teslas
Define Two-Way Product Line Stretch.
Adds products in a lower and higher price markets.
Difficult to execute
Define Filling Out Product Strategy.
Adding sizes or styles not previously available.
Ex. Reese’s → Reese’s minis
Define Product Mix.
Total set of products a firm offers for sale
Product Mix Width: Number of different product lines the firm produces
Define Product Quality.
Overall ability of the product to satisfy customer expectations.
Define Internal Customers.
Co-Workers who believe everything they do affect outside customers.
Internal Customer Mindset.
An organization culture where all organization members treat each other as valued customers.
Employees who receive my work are customers
Meeting the needs of employees who receive my work is critical to doing a good job
It is important to receive feedback from employees who receive my work
Also focus on requirement of the person who receives my work
The Bottom Line of TQM involves all employees (stockholders, consumers, employees, etc.) to improve quality. T or F
True
Marketing Planning is a major portion of the process and involved: ?
The process of analyzing the market environment
The process of developing the marketing plan
The process of deciding on a market segment
The process of choosing the marketing mix - Product, Price, Promotion, Place
Cleary stated product objectives provide focus and direction. True or False.
True
Quality Movement is strongly associated with Japan. T or F
True
Who is the Father of Scientific Management?
Fred Taylor
Who is the Father of Modern Management?
Peter Drucker
Who is the Father of the Quality Movement?
Edwards Deming
Define the Six Sigma Methodology.
Process allows no more than 3.4 defect per million unites.
Quality management at Motorola
The PLC is a useful way to explain how market response and marketing activities change over the life of a product. T or F
True
What stage of PLC are Tablets and Smartphones in?
Growth, although growth in smartphones has slowed
Sometimes it is hard to know when a product passes from one stage to the next in PLC. T or F
True
Two things that Brand Equity Provides.
Provides competitive advantage
Results in brand loyal consumers and attachment
Individual vs Family Brands.
Family brands share a common brand name, like Campbells chick noodle, while Gain is not called P&G Gain.
National brands are those produced and marketed by a manufacturer. T or F
True
Store (Or private labels) brands are those which are offered by a retail store or chain under an excluesive trade name. T or F.
True
Ex. Costco: Kirkland, Wal-Mart: Sam’s Choice
Define Licensing.
When one firm sells another firm the right to use a brand name for a specific purpose for a specific period of time.
Define Cobranding.
Two brands agree to work together to market a new product
Define ingredient branding.
Branding materials become “component parts” of other branded products
What things do effective packaging consider?
Choice of material and image it projects
Environmental impact of packaging
Shape and color influence on image
Graphic information to be portrayed.
labeling regulations.
Fair Packaging and Lebeling Act (1966)
Make label helpful to consumers by providing useful information
Nutritional Labeling and Education Act (1990)
Law requires food labels to state how much fat, saturated fat, cholesterol, calories, Etc.