DNA, Genes, Chromosomes, and Genetic Expression
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, genetic material in cells.
Nucleotide
Building block of DNA; contains sugar, base, phosphate.
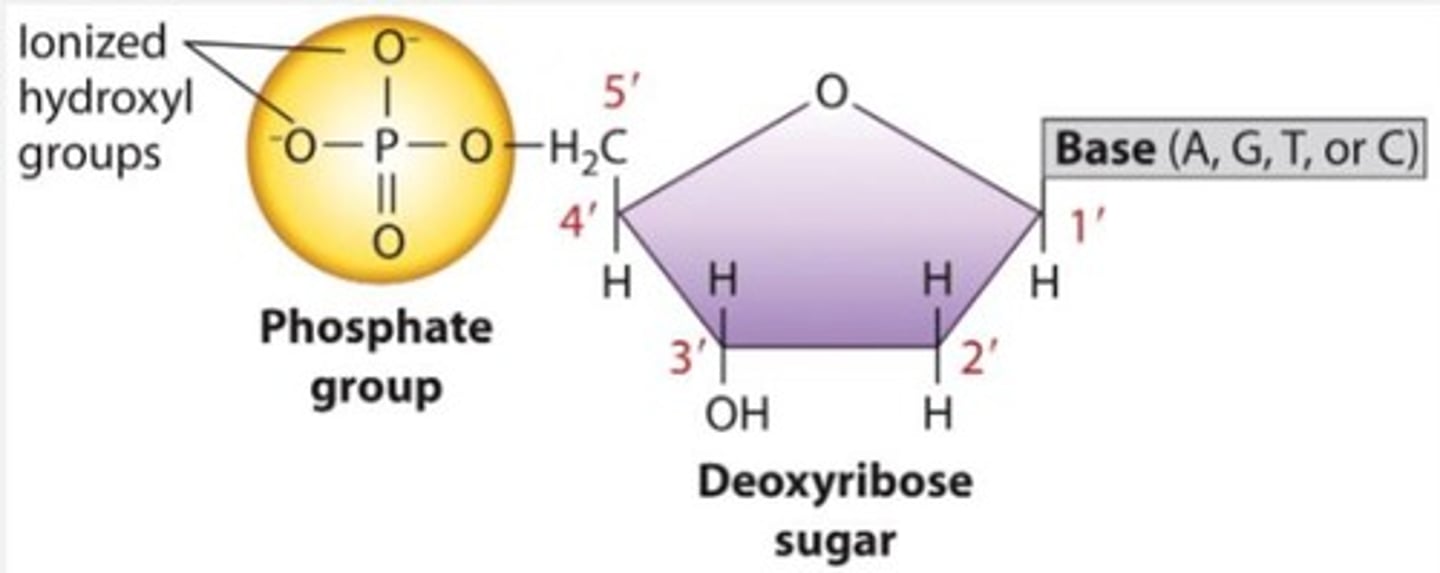
Nitrogenous Bases
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine in DNA.
Purines
Double-ringed nitrogenous bases: Adenine and Guanine.
Pyrimidines
Single-ringed nitrogenous bases: Thymine and Cytosine.
Nucleoside
Sugar and nitrogenous base without phosphate.
Phosphodiester Bond
Bond linking nucleotides in DNA strand.
5' End
Free phosphate group at the beginning of DNA.
3' End
Free hydroxyl group at the end of DNA.
Antiparallel Strands
Two DNA strands run in opposite directions.
Double Helix
Twisted ladder structure of DNA.
Hydrogen Bonds
Hold complementary base pairs together in DNA.
A-T Pairing
Adenine pairs with Thymine via two hydrogen bonds.
G-C Pairing
Guanine pairs with Cytosine via three hydrogen bonds.
Griffith's Experiment
Showed DNA as the central molecule of life.
Avery-Macleod-McCarty Experiment
Identified DNA as the genetic material.
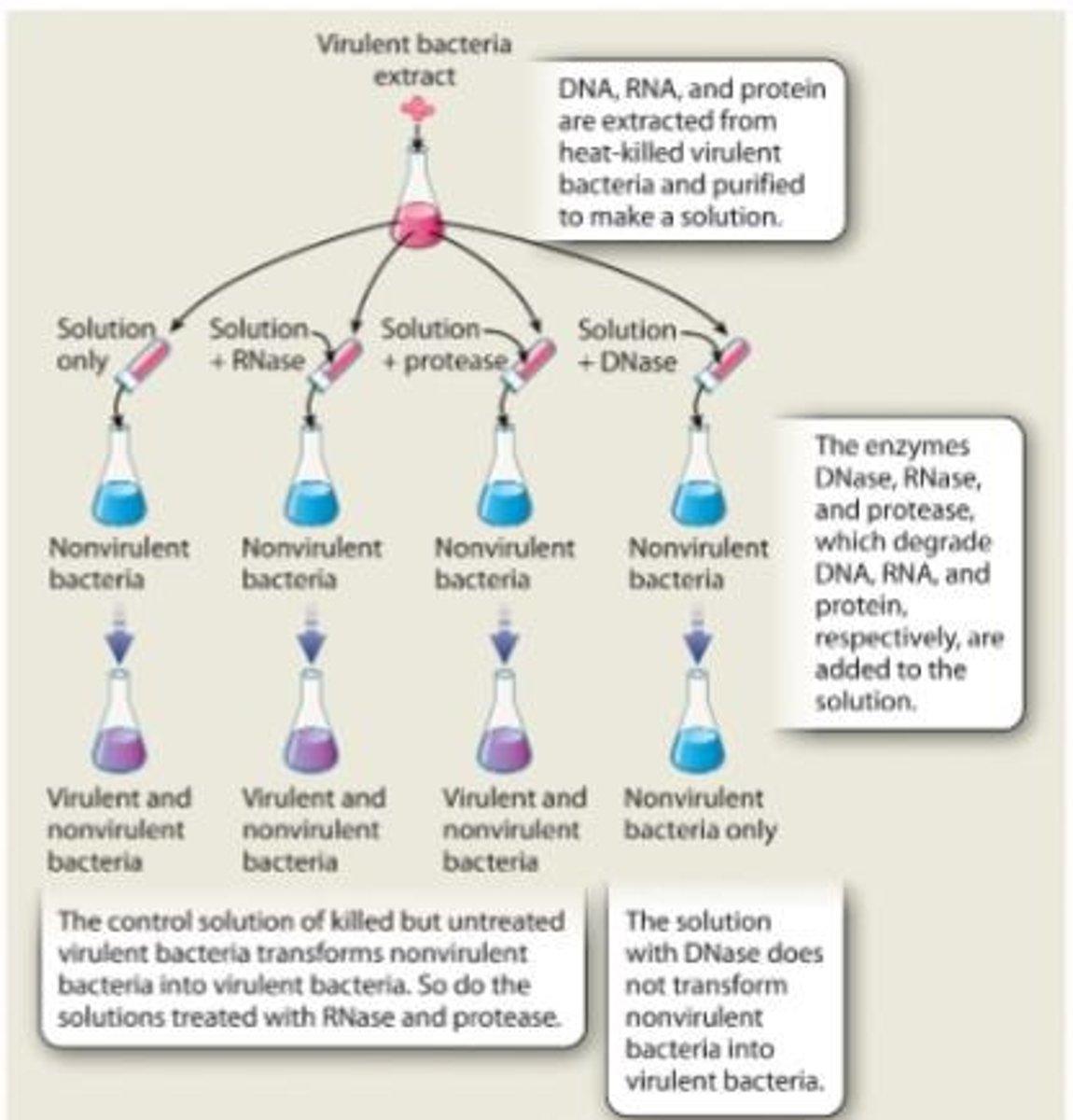
Transformation
Process of nonvirulent bacteria becoming virulent.
Gene Propagation
Transmission of genetic information across generations.
Base Pairing Rules
A=T and G=C in DNA structure.
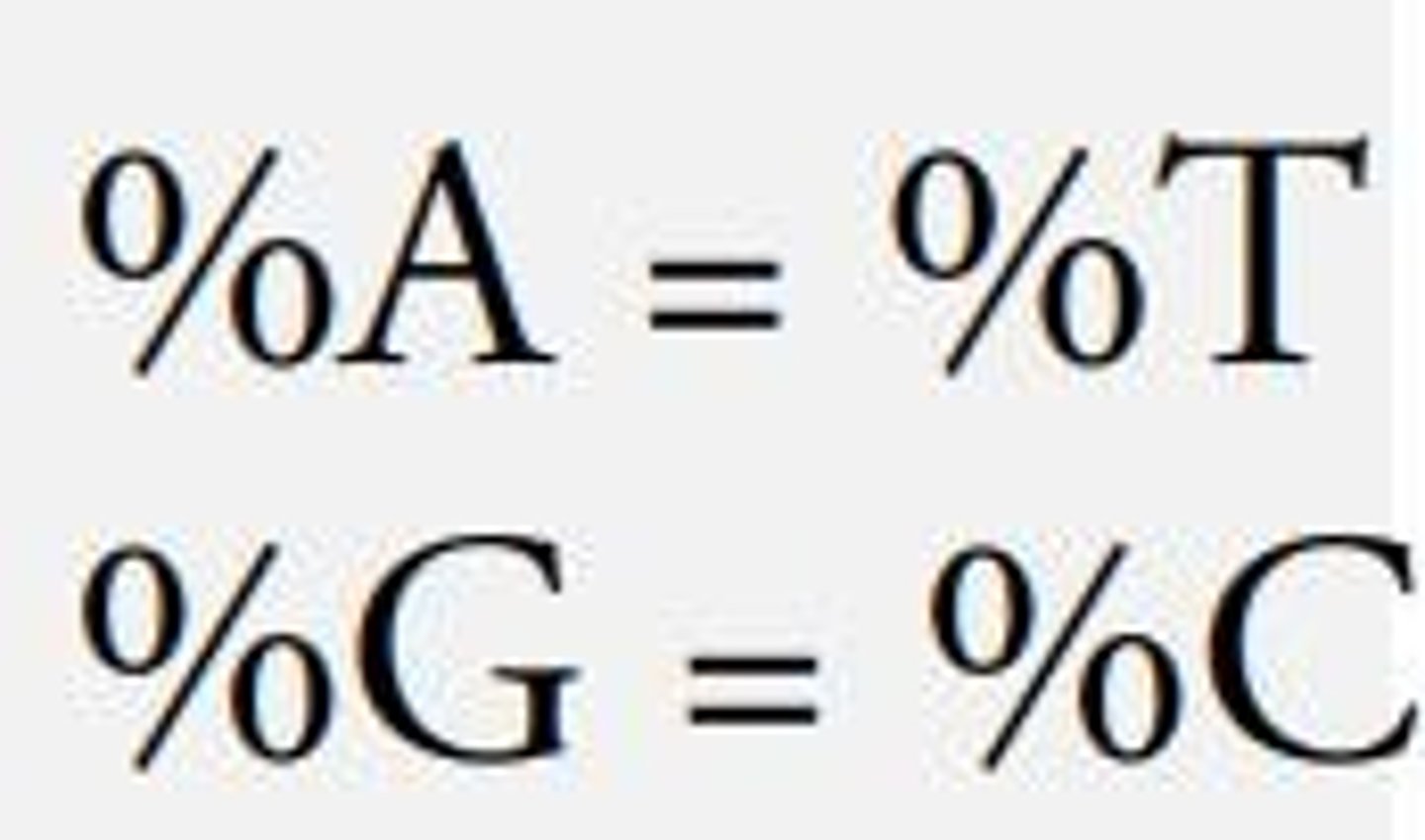
DNA Stability
Maintained by hydrogen bonding and base stacking.
DNA Compaction
Necessary for fitting DNA within cellular dimensions.
Free 5' Phosphate
Unattached phosphate group at the 5' end.
Free 3' Hydroxyl
Unattached hydroxyl group at the 3' end.
Direction of Synthesis
DNA is synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction.
Chromosome
Linear DNA molecule packaged with proteins.
Histones
Proteins that interact with DNA to form chromatin.
Chromatin
Histone-DNA complexes that compact DNA.
Karyotype
Visual representation of an organism's chromosomes.
DNA Replication
Process of copying DNA to create daughter strands.
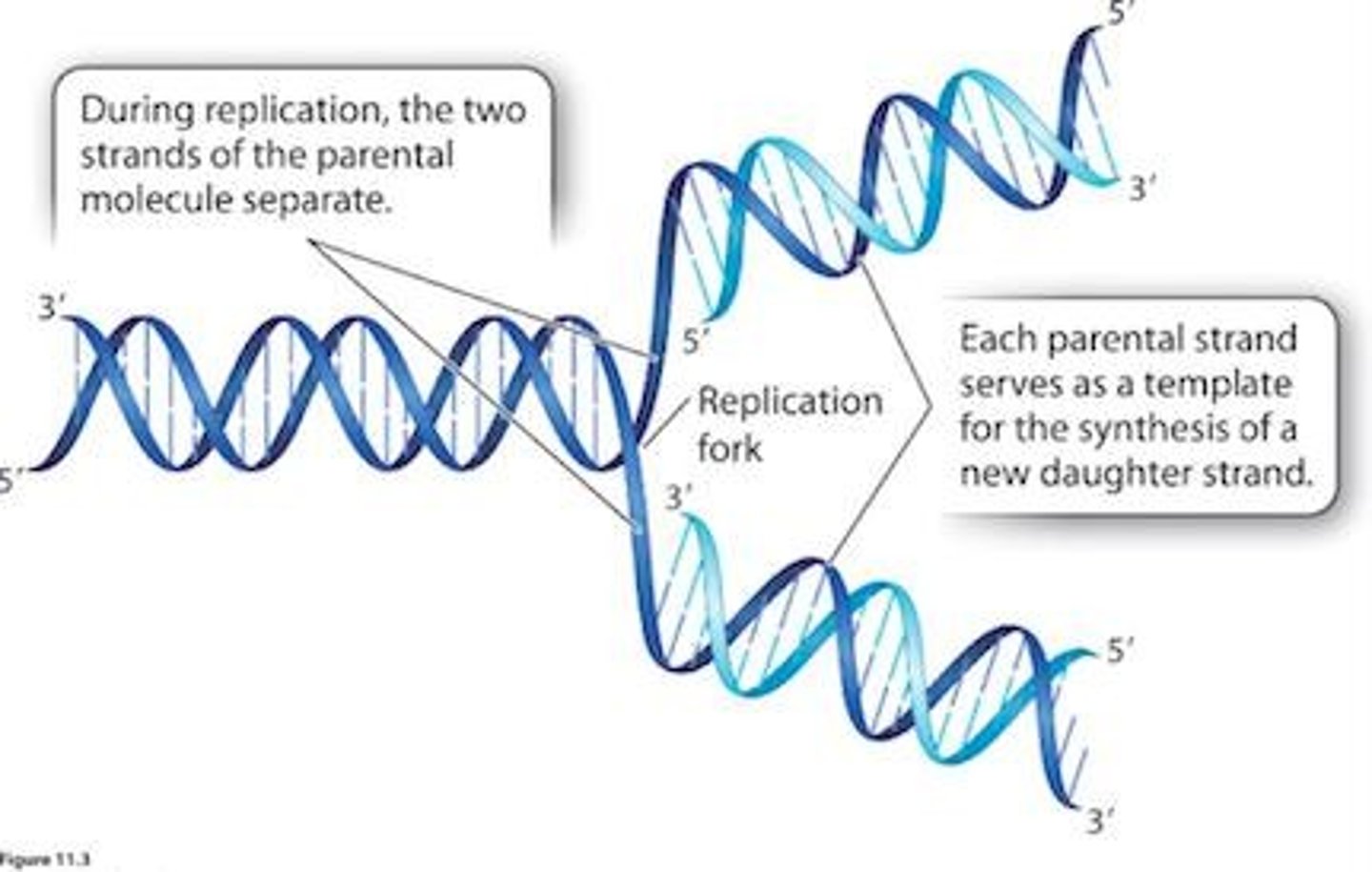
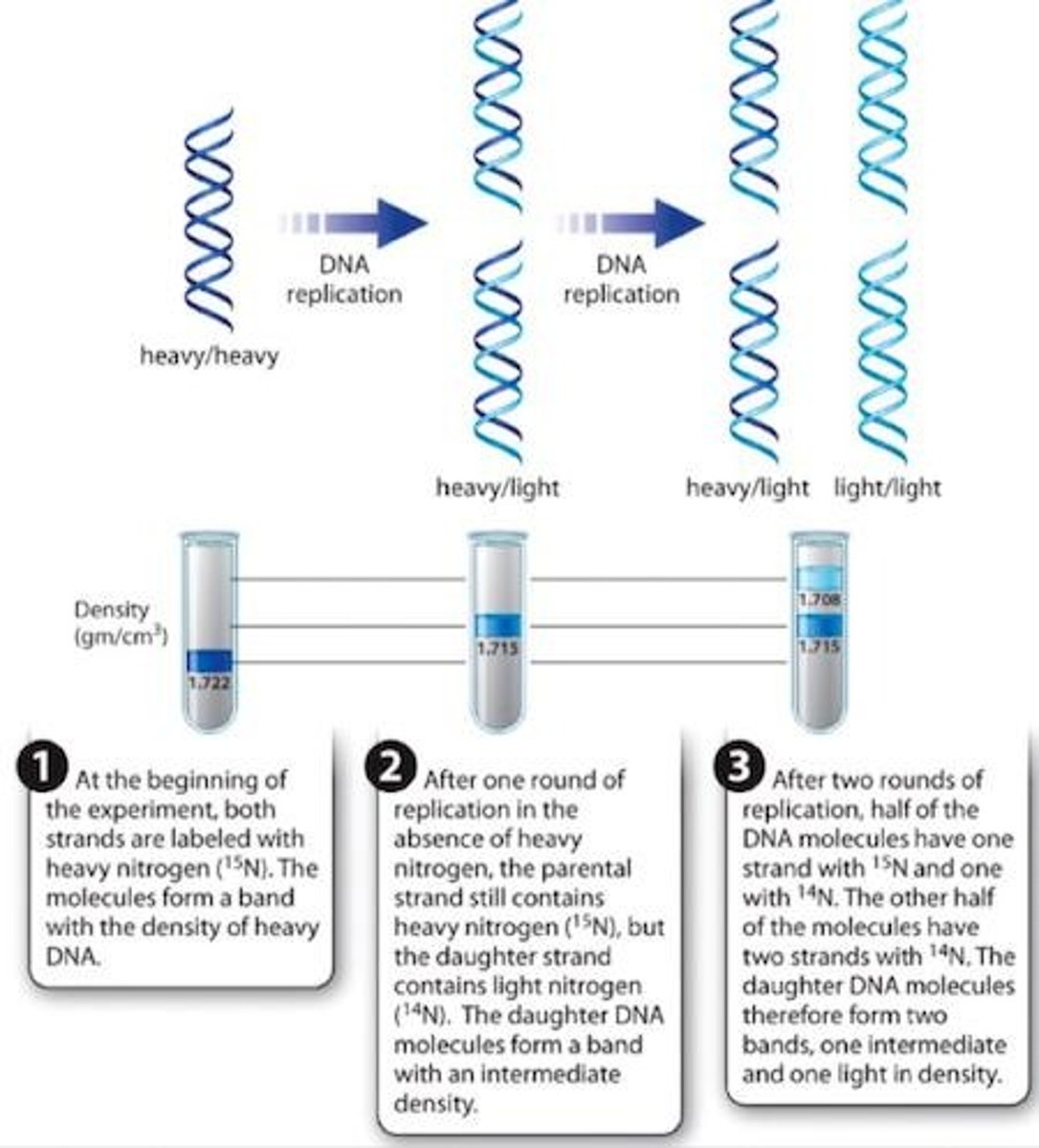
Semiconservative Replication
One parental strand and one new strand produced.
Conservative Replication
Both strands are newly synthesized, leaving parental strands.
Meselson & Stahl Experiment
Confirmed semiconservative nature of DNA replication.
Eukaryotic DNA Replication
Follows semiconservative principles in eukaryotic cells.
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme that adds nucleotides to growing DNA strands.
RNA Primer
Short RNA sequence necessary for DNA synthesis initiation.
Continuous Replication
Smooth replication on leading strand, same direction as fork.
Discontinuous Replication
Fragmented replication on lagging strand, opposite direction of fork.
Okazaki Fragments
Short DNA segments formed during lagging strand replication.
DNA Ligase
Enzyme that joins Okazaki fragments into continuous DNA.
3'-OH Group
Free hydroxyl group needed for DNA polymerase action.
Helicase
Enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix.
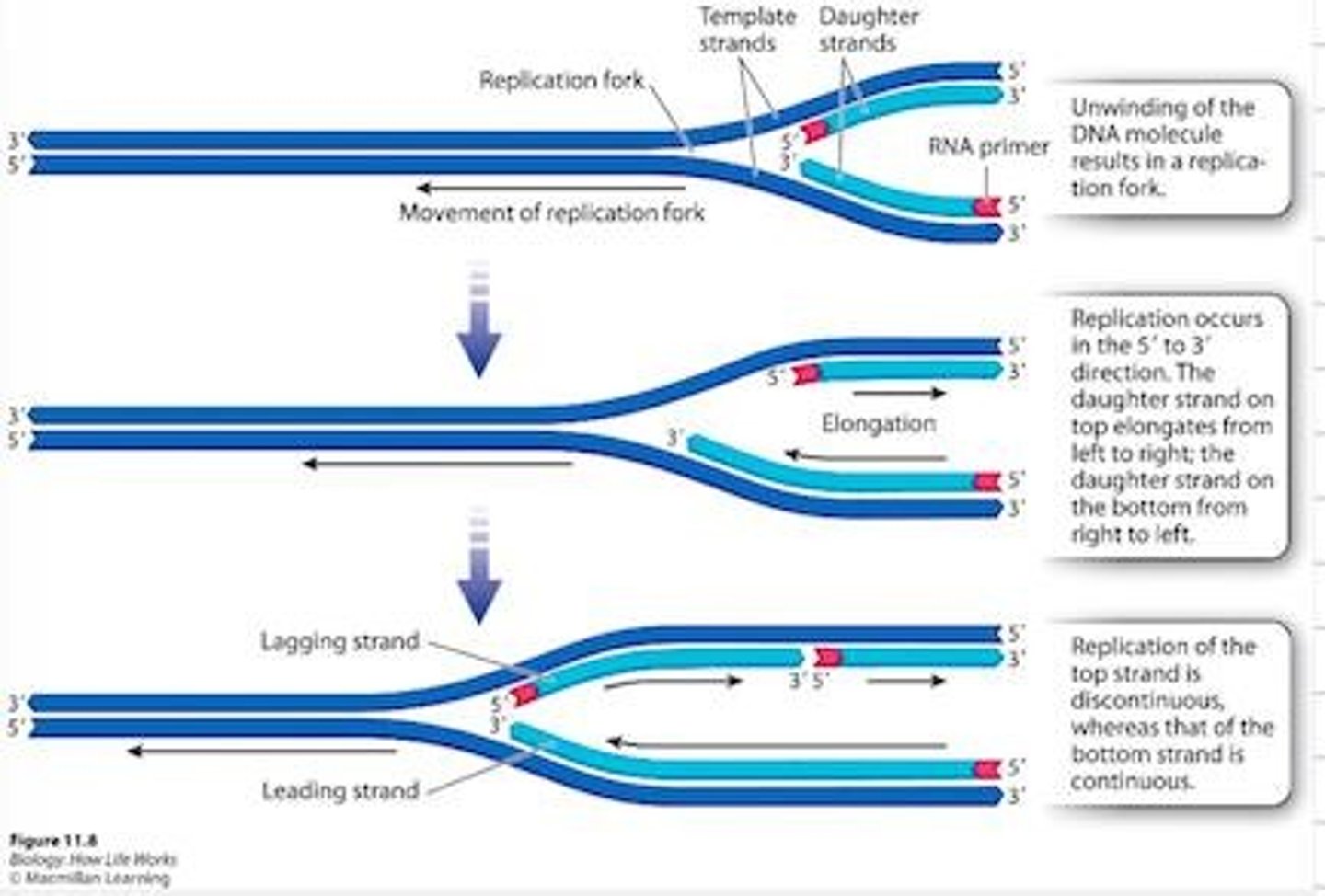
Topoisomerase II
Relieves tension during DNA unwinding.
Single Stranded Binding Proteins (SSBP)
Stabilize single DNA strands during replication.
Trombone Model
Simultaneous synthesis of both DNA strands.
Proofreading
Error-checking process after nucleotide addition.
Mutations
Errors in DNA sequence during replication.
S-phase
Cell cycle phase where DNA replication occurs.
DNA polymerase
Enzyme that synthesizes DNA strands during replication.
Proofreading
Error-checking mechanism of DNA polymerase.
Okazaki fragments
Short DNA segments on the lagging strand.
Mutations
Permanent changes in DNA sequence.
Replication origins
Sites where DNA replication begins.
Telomeres
Repeating sequences at chromosome ends.
Telomere repeats
1500-3000 nucleotide sequences at telomeres.
Telomerase
Enzyme that extends telomeres in cells.
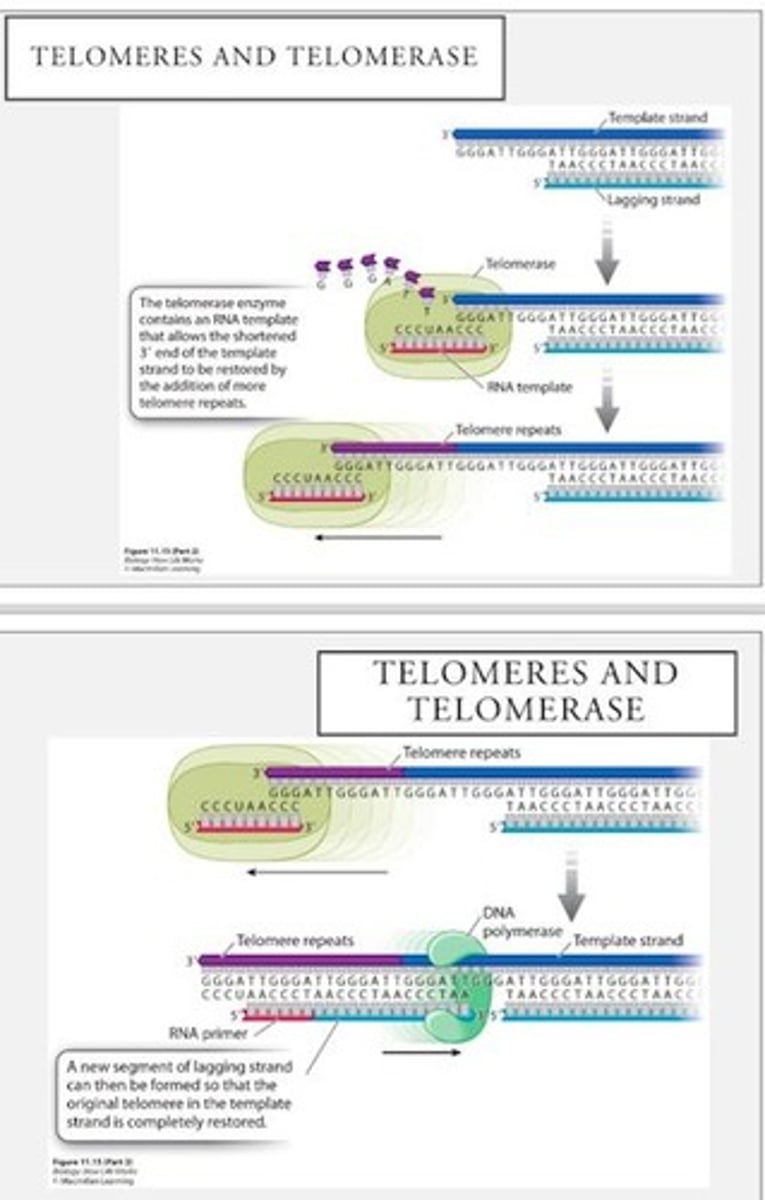
Cell division cessation
Occurs when telomeres shorten to 100 repeats.
Aging indicators
Telomere length correlates with biological age.
PCR
Technique to amplify specific DNA sequences.
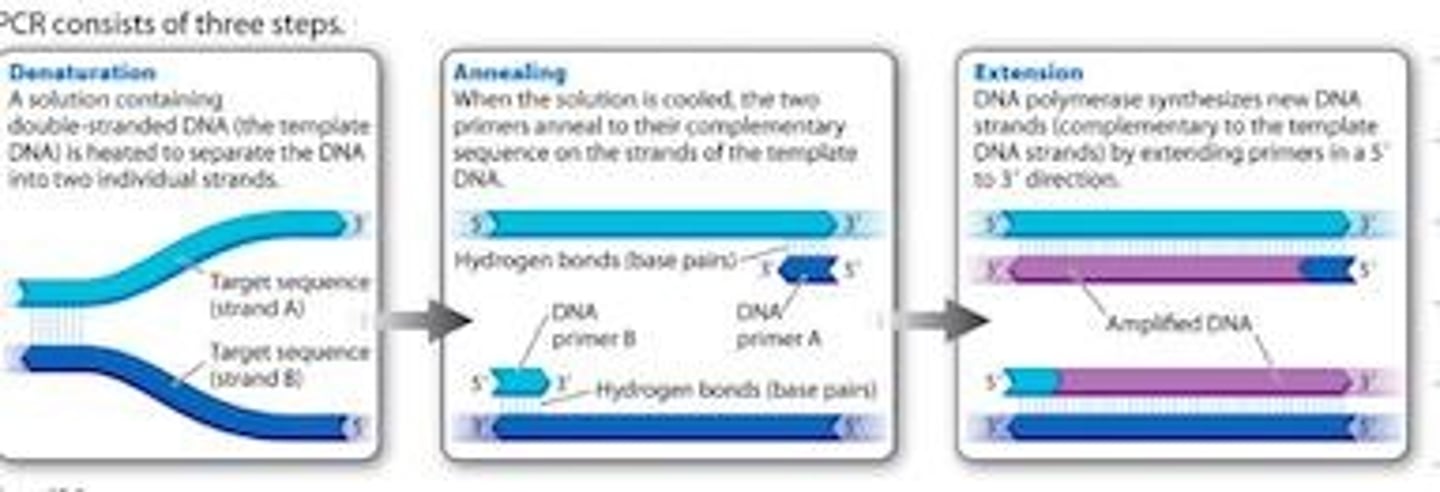
Template DNA
Original DNA strand used in PCR.
Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates
Building blocks for DNA synthesis in PCR.
Primers
Short DNA sequences that initiate PCR amplification.
Amplification cycle
Each PCR cycle doubles the DNA amount.
Gel electrophoresis
Technique to separate DNA by size and charge.
DNA editing
Techniques to modify DNA sequences.
CRISPR/Cas
Tool for precise DNA editing.
CFTR gene
Gene coding for chloride ion channel.
Cystic fibrosis
Disease caused by CFTR gene mutations.
Hydration of airways
Prevents mucus buildup in cystic fibrosis.
Organoid
Cell assembly mimicking an organ for research.
CFTR
Chloride channel activated by forskolin.
F508Del
Mutation causing cystic fibrosis in CFTR.
Deletion
Genetic mutation removing a segment of DNA.
Forskolin
Chemical that activates CFTR channels.
CRISPR
Gene-editing technology correcting genetic mutations.
mRNA
Messenger RNA transcribed from DNA.
Transcription
Process of synthesizing RNA from DNA.
Central Dogma
Framework describing DNA to RNA to protein.
Ribose
Sugar in RNA with hydroxyl (-OH) group.
Deoxyribose
Sugar in DNA lacking hydroxyl (-OH) group.
Uracil
RNA base replacing thymine found in DNA.
Thymine
DNA base with a methyl group.
RNA Polymerase
Enzyme synthesizing RNA from DNA template.
Nucleoside Triphosphate
Building block for RNA synthesis.
RNA Primer
Short RNA segment initiating DNA synthesis.
Nucleotide
Basic building block of nucleic acids.
Amino Acid
Building block of proteins, represented by F.
Nucleoside Monophosphate
Basic building block of DNA formed first.
RNA World Hypothesis
Theory suggesting RNA was first nucleic acid.
Enzymatic Properties of RNA
RNA can catalyze biochemical reactions.
Stability of DNA
DNA is more stable than RNA molecules.
RNA Functions
RNA stores information and has coding sequences.
Central Dogma
Describes flow of genetic information: DNA to RNA.
Transcription
Process where DNA is converted to RNA.
Template Strand
DNA strand used to synthesize RNA transcript.
Nontemplate Strand
Complementary DNA strand not used for transcription.
Promoter Sequences
DNA regions where transcription factors bind to start transcription.
TATA Box
Conserved DNA sequence in eukaryotic promoters.
Transcription Factors
Proteins that bind to DNA to initiate transcription.
RNA Polymerase
Enzyme that synthesizes RNA from DNA template.
Terminator
Sequence where transcription ends.