Oncology 1 Section 3 Exam
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
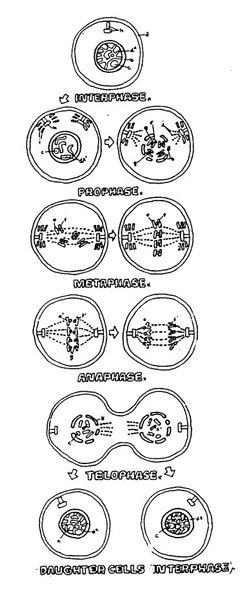
phases of mitosis
interphase - DNA replicates, cell prepares for division
prophase - centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell and ch romatin granules organize into chromatids
metaphase - chromatin granules align and attach to centrosomes
anaphase - chromosomes formed
telophase - division of the cytoplasm, two new nuclear membranes appear to enclose each new set of chromosomes
first step in healing process
inflammation
cardinal signs of inflammation (first person)
tumor - swelling
dolar/dolor - pain
calor - heat
rubor - redness
functio laeso/laesa - loss of function
first described by Celsus/Celsius
pus
result of the death of millions of leukocytes
embolus
circulating blood clot that has become detached or particle
types of anoxia
stagnant anoxia - due to ischemia
anoxic anoxia - insufficient pulmonary oxygenation
anemic anoxia - reduced hemoglobin
histotoxic anoxia - inability of cells to utilize oxygen effectively
round cells
characteristically found in chronic inflammation
“constant warriors”
monocytes
macrophages
lymphocytes
plasma cells
common tumor markers
carcinogenic embryonic antigen (CEA)
most commonly used
normal range: 0-3.0
non-specific
recurrent colorectal disease
breast, lung, ovarian, and pancreatic cancer
may be elevated in patients who smoke or have malignant liver disease
prostate specific antigen (PSA)
normal range: 1-4
helpful but not diagnostic (DRE)
alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)
monitor some liver and some testicular cancers
beta human chorionic Gonadotropin (b-HCG)
very specific and very sensitive for choriocarcinoma (aggressive form of testicular cancer)
Ca 15-3
breast cancer antigen test
relatively new for monitoring breast cancer
Ca 19-9
primarily used for colorectal cancer
also can be used for pancreatic and stomach cancer
Ca 125
helpful for monitoring ovarian cancer
alkaline phosphatase/acid phosphatase
indicative of bone metastases
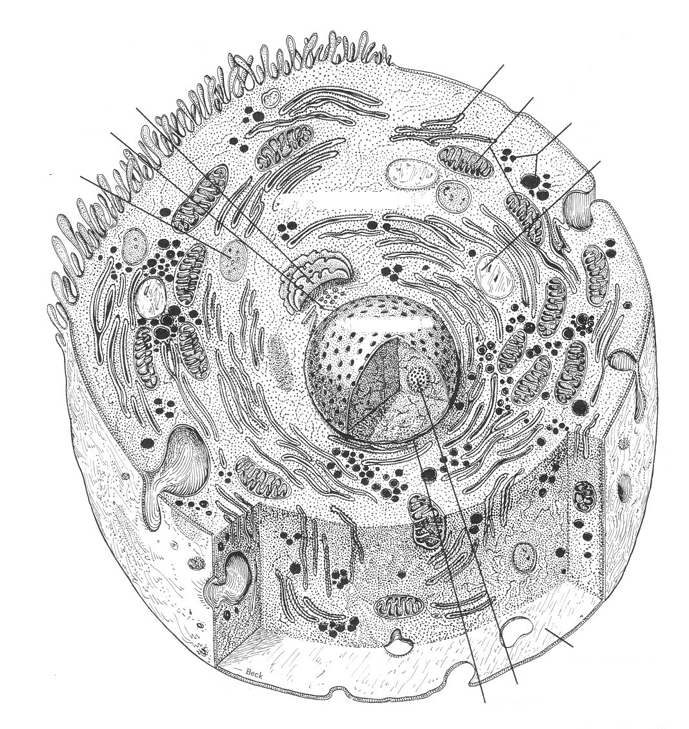
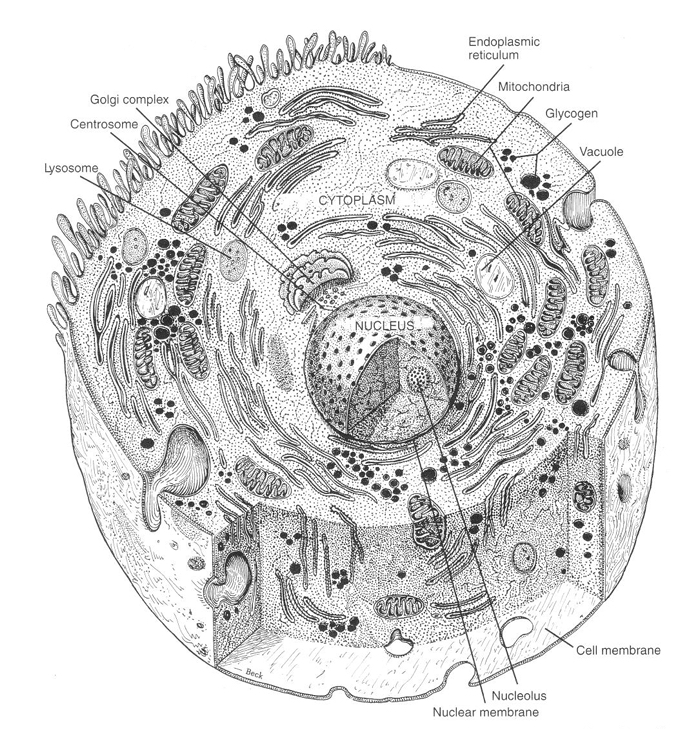
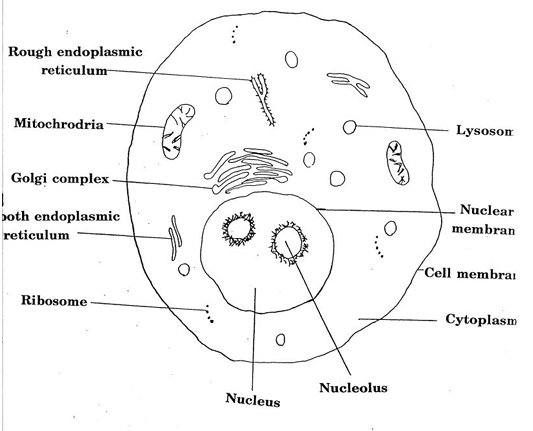
lysosomes
digestive system of the cell
nitrogenous bases of DNA
Adenine attached to Thymine
Cytosine attached to Guanine
types of muscle cells
smooth - one oval nucleus
skeletal - multi-nucleated and contain a large number of mitochondria which supply energy for contraction
cardiac
chemotaxis
direct migration of inflammatory cells toward an inured area
leukocytosis
increase in the number of circulating leukocytes (white blood cells) associated with the inflammatory reaction
anergy
a condition in which a proper inflammatory response does not or cannot occur
necrosis
irreversible change resulting in local death of the cell
histotoxic anoxia
anoxia caused by an inability of the cells to utilize oxygen
B-cell vs T-cell lymphocytes
B-cells
responsible for the humoral response
derived from the bone marrow
protect against bacteria
T-cell
responsible for the cellular mediated response
derived from thymus
protect against tumors, bacteria, viruses, and transplant rejection
antigen
any substance that is capable of triggering an immune response
ribosomes
synthesize proteins
infarct
complete blockage of blood to an area
hematoma
hemorrhage involving an accumulated swelling of blood such as a blood blister
acquisition of immunity
active natural - acquired when body is exposed to a pathogen/antigen like a virus or bacteria and immune system creates antibodies
active artificial - e.g., inoculation or vaccinations, on every subsequent occasion that a person is exposed to the disease, immunologic memory mobilizes a response so fast that the toxin is neutralized before it produces the disease (amnestic response) which generally diminishes as times goes by but boosters can re-awaken the waning immunity
passive natural - transfer of antibodies from mother to fetus or infant through the placenta or breast milk
passive artificial - transfer of antibodies from a previously immune person, e.g., bone marrow transplant
macrophage
cell type responsible for recognizing, phatocytosing, and transporting antigenic material to the lymph nodes
antigens
substance that, when introduced into the body, initiates an immune response
usually foreign to the host
infectious agents
foreign proteins
tissue grafts
opportunistic infections
infections that occur during times of low resistance
causes of inflammation
microbes - most common
hypoxia
ionizing radiation
chemicals
allergic or immune reactions
cancer
endoplasmic reticulum
circulatory system of the cell
principle component of cytoplasm
mitochondria
“power plant” of the cell
produces energy (ATP) for the cell from sugars and other organic fuels
keloid treatment
resections and steroid injections
resection followed by low dose radiation (900-1200 cGy in 3 fractions) if not successful
prognostic factors for breast cancer
S-phase index - number of cells that activiely dividing
ploidy - amount of DNA that each cell contains
estrogen receptor
progesterone receptor
Cathepsin D - relatively new prognostic marker that measures an enzyme present in cells which is directly related to aggressiveness of tumor
cancers associated with Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)
Hodgkin’s disease
Nasopharyngeal cancer
Burkitt’s lymphoma
immunoblastic lymphoma
petechiae
very small “pin point” hemorrhage
composition of “ingredients” in cells
80% water
15% protein
3% lipids
1$ carbohydrates
1% nucleic acid
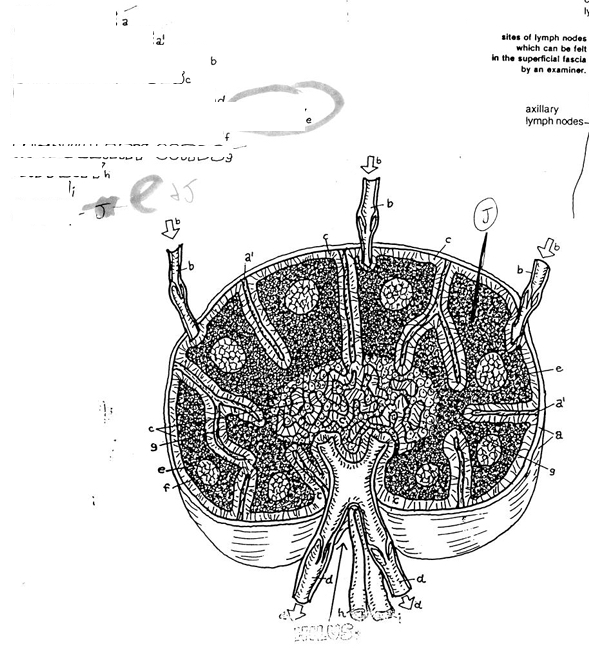
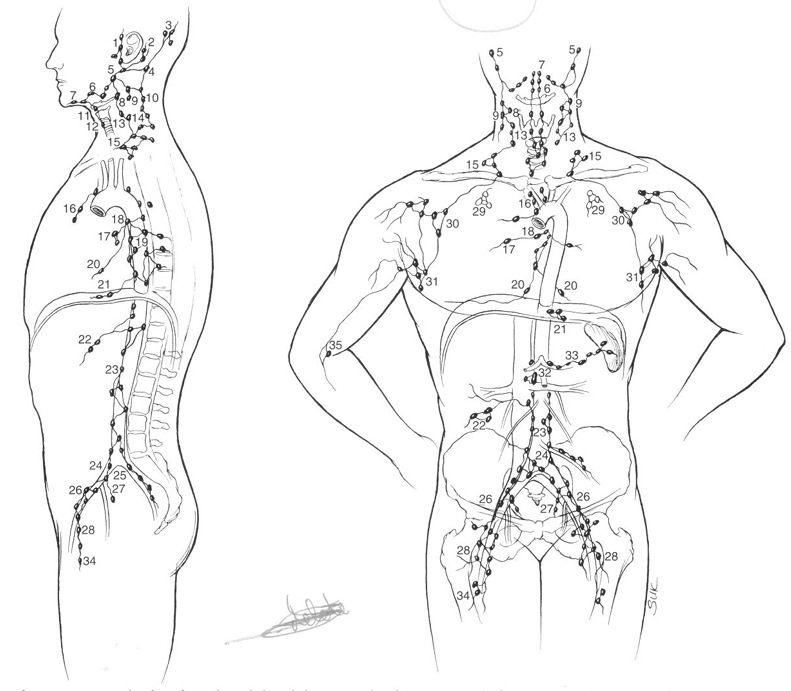
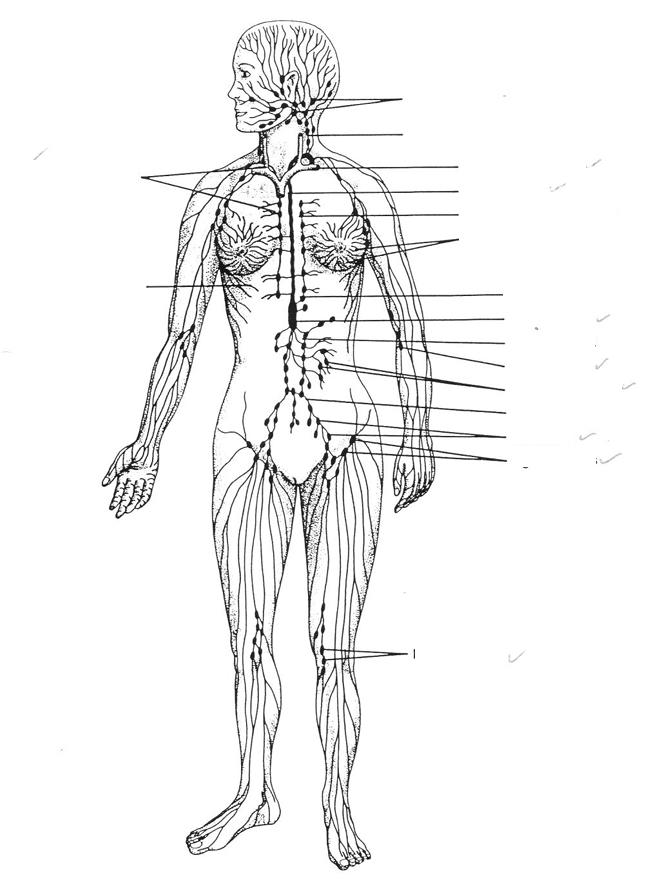
superficial lymph node groups
cervical
axillary
inguinal
collateral circulation
developing new pathways to lymph vessells
methods by which lymph is circulated through the body
skeletal muscle contractions
respiratory movements
organ that assumes the function of the spleen if removed
liver
size of a typical normal lymph node
1-25 mm in length (kidney bean)
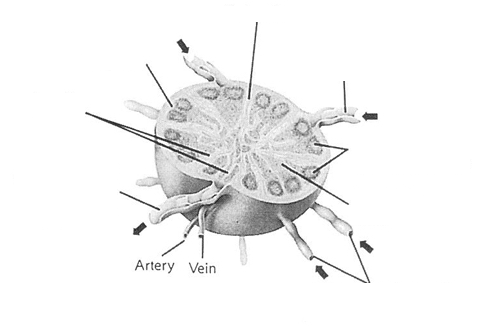
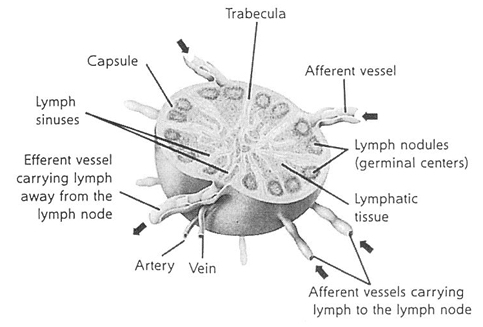
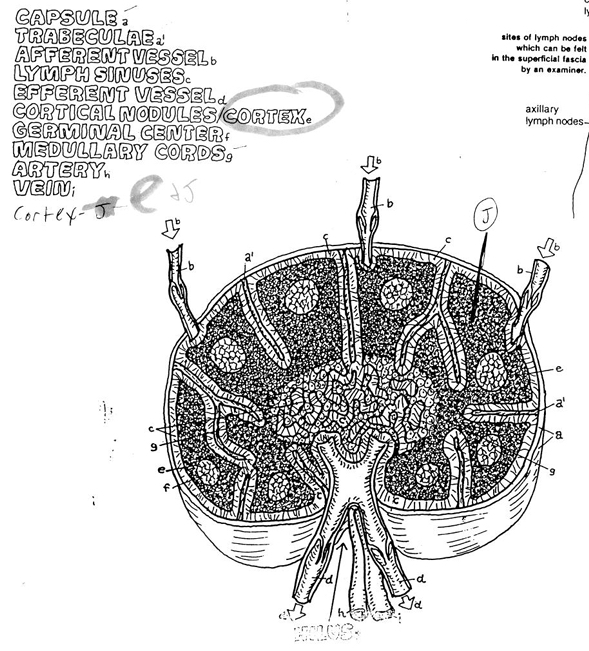
afferent vessels vs efferent vessels vs lymph sinuses
afferent vessels - lead into node
efferent vessels - lead away from the node
lymph sinuses - maze inside node
first part of maze in lymph sinuses
corridor
spinal cord compression (treatment, symptoms, diagnosis)
treatment
surgery = laminectomy + placement of stabilizing rods
RTT - higher doses for first few days than normal 300 cGy/day for 10 days
PA single 6cm wide field only
steroids - relieve pain and improve symptoms
analgesics/narcotics - control pain
chemotherapy - may help if primary is chemosensitive
symptoms
back pain
paresthesia
coldness, especially in extremities
incontinence (urgency)
diagnosis
MRI is best practical since patient would have to lie for long periods
myelogram
trabeculae
supporting structure or “skeleton” of a node
common presentation for SVC
upper thoracic and/or facial swelling (upper edema)
cancer patients that have some sort of pericardial involvement
20%
thymus gland
somewhat obscure function but has some role in immunity
can secrete hormones that regulate growth and development in small amounts
considered an endocrine gland by some
larger in children thatn in adults
located in upper thoracic cavity
chyle
lymph from digestive tract that is milky in appearance due to presence of fats
thoracic (left) lymphatic duct
begins at the cisterna chyli and empties into left subclavian vein
drains all lymph from every part of the body except the upper right quadrant
largest mass of lymphatic tissue in the body
spleen
primary functions of spleen
to phagocyte bacteria and worn out blood elements
produce lymphocytes
store and release blood
effusion
escape of fluid into a part
tamponade
excess fluid in the pericardium
standard dose/fractionation for treating SVC
400 cGy/day for 3 days, then resume normal 180 cGy/day
paresthesia
numbness or tingling in extremities
cisterna chyli
dilated sac that serves as a reservoir for lymph from the intestines (chyle)
traditional RTT oncologic emergencies
superior vena cava syndrome (SVC)
spinal cord compression
hemorrhages (usually from gynecological cancers)
spinal level of cisterna chyli
second lumbar vertebra (L2)
The microscope was introduced in the early part of what century?
17th century
clinical disease has its inception with some kind of cellular injury or malfunction that is ultimately expressed at what level of function
molecular/cellular
homeostatic state
a set of circumstances in which cellular processes associated with life proceed normally and in accordance with the function genetically assigned to that cell
hallmark of reversible damage
cellular swelling
most common cause of tissue damage
hypoxia
6 important causes of cell damage and common pathway
radiation
hypoxia
chemicals
microorganisms
immunologic reactions
neoplasms
common pathway to causing damage - free radicals
chromosomes
specific positions (or loci) on protein structures that genes are assigned to
cytosol
semi-liquid material that make up cytoplasm
golgi apparatus
important in the storage and management of intracellular chemical substances
synthesizes carbohydrates
storehouse of the cell
ATP
adenosine triphosphate
phase of the cell cycle in which living cells are fully functional but not programmed for mitosis and will not divide
G0 or G1
shortest phase of the cell cycle
M or mitosis phase
phase of the cell cycle where in nuclear DNA is synthesized
S or synthesis phase
chemical components of nucleotides
phosphate
sugar (S. carbon)
nitrogenous bases
nitrogenous base that substitutes for thymine in RNA
uracil
“building blocks of life”
proteins
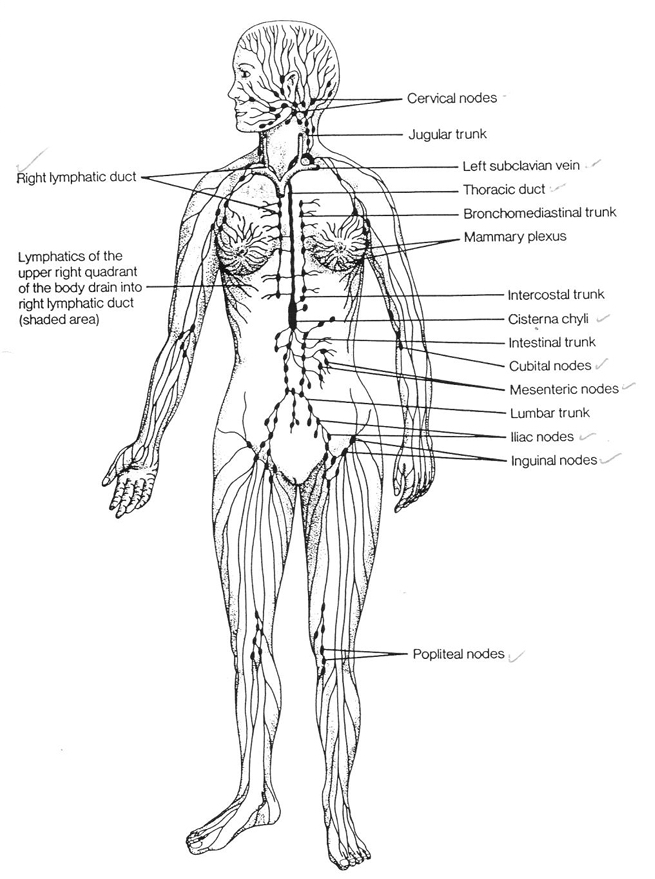
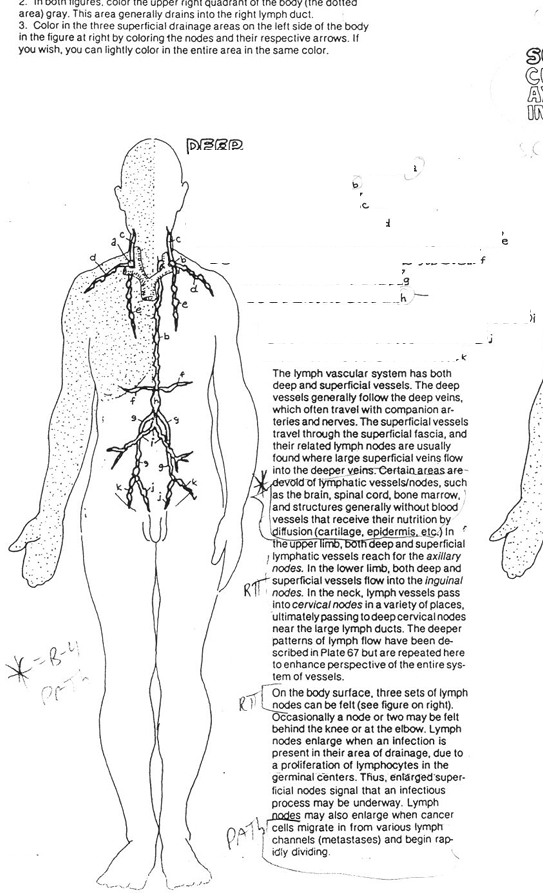
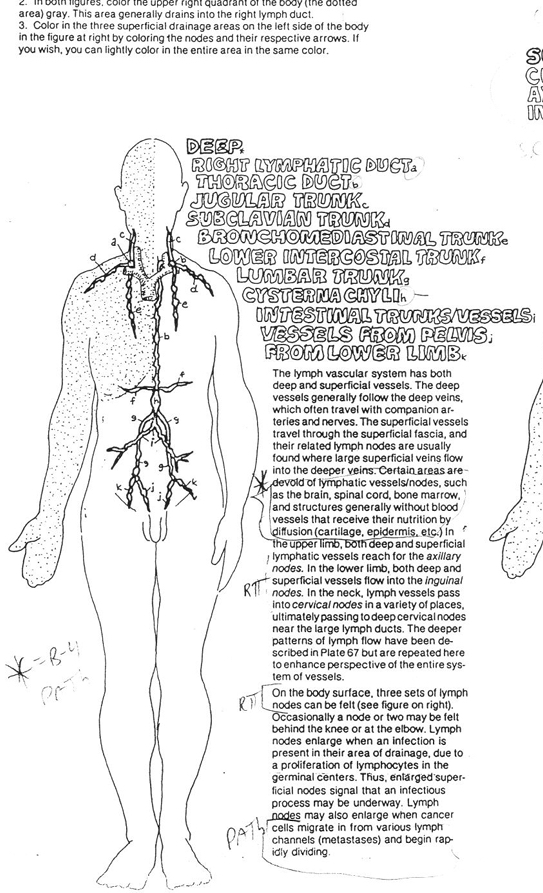
body areas that do not typically have any access to lymph
brain (due to CSF)
spinal cord
cornea
epidermis (skin, hair, nails)
very little in skeletal muscles