(CIE A2 Biology) Natural selection basics (based on SaveMyExams revision notes)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Natural Selection
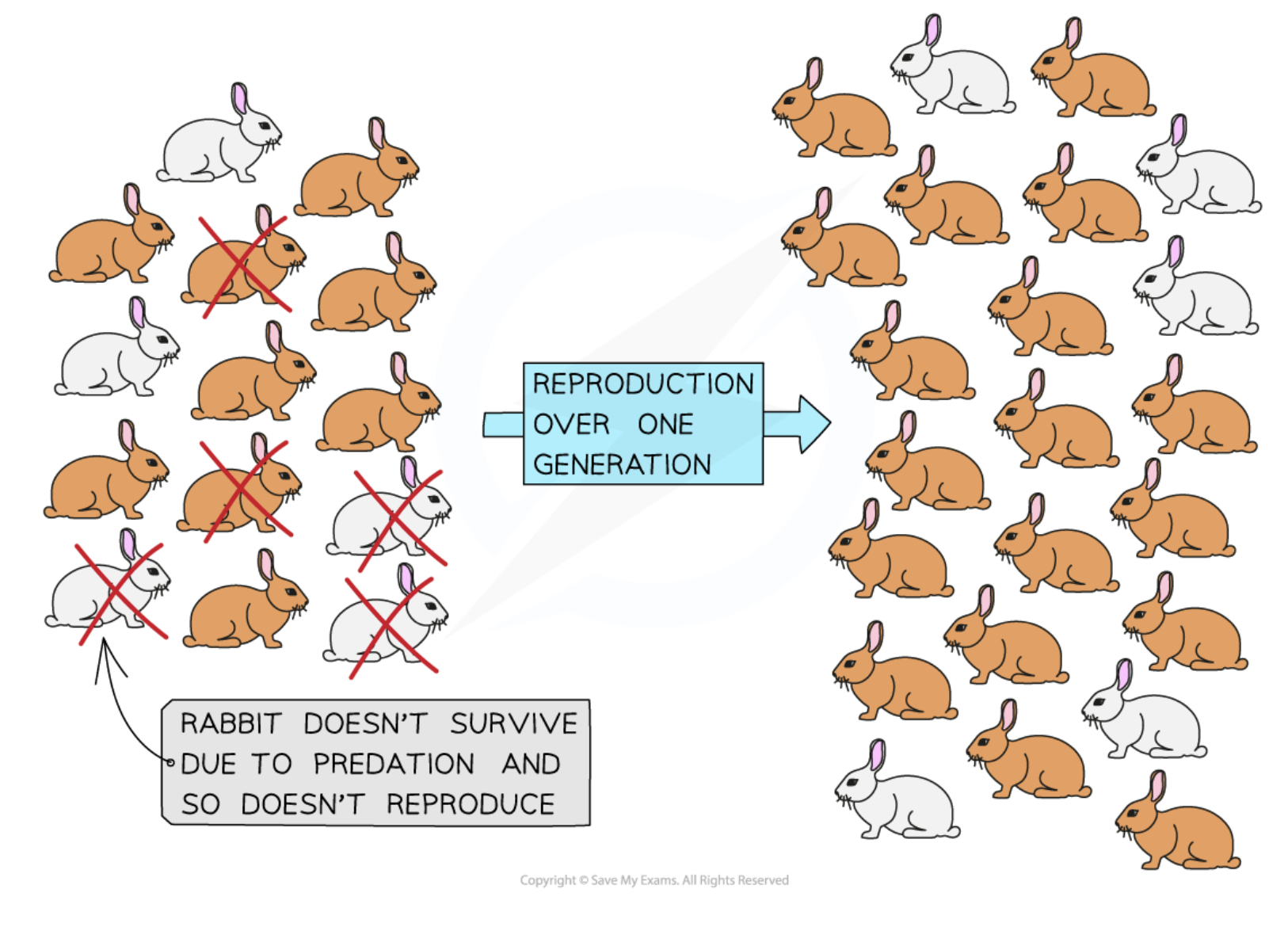
The process by which individuals with advantageous phenotypes are more likely to survive and reproduce, increasing the frequency of those traits in a population.
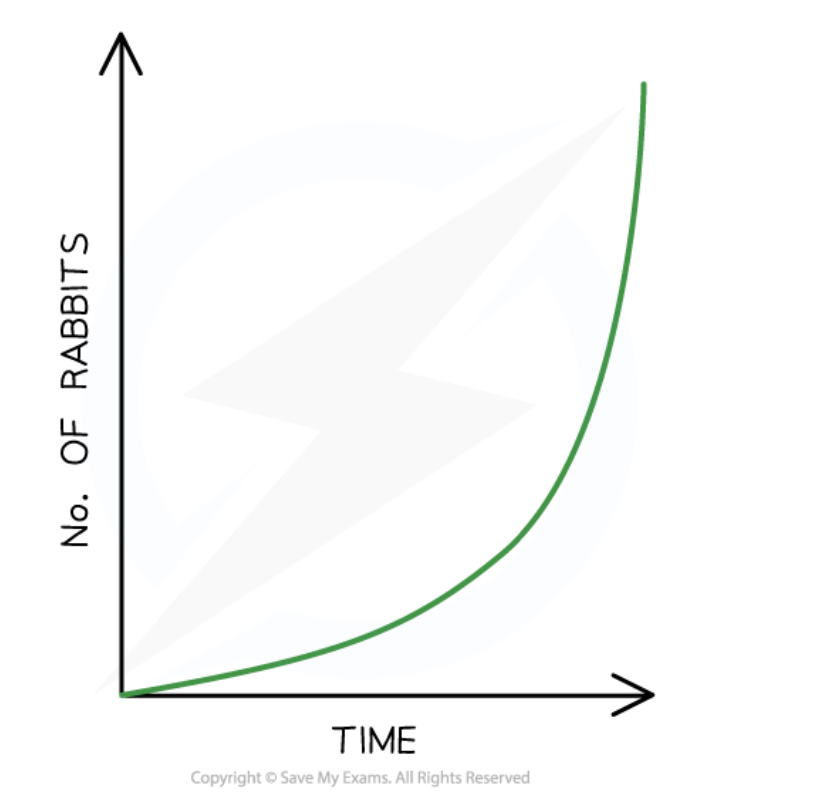
Exponential Growth
A type of population growth where every individual reproduces and all offspring survive, leading to a rapid increase in population size.
Biotic Factors
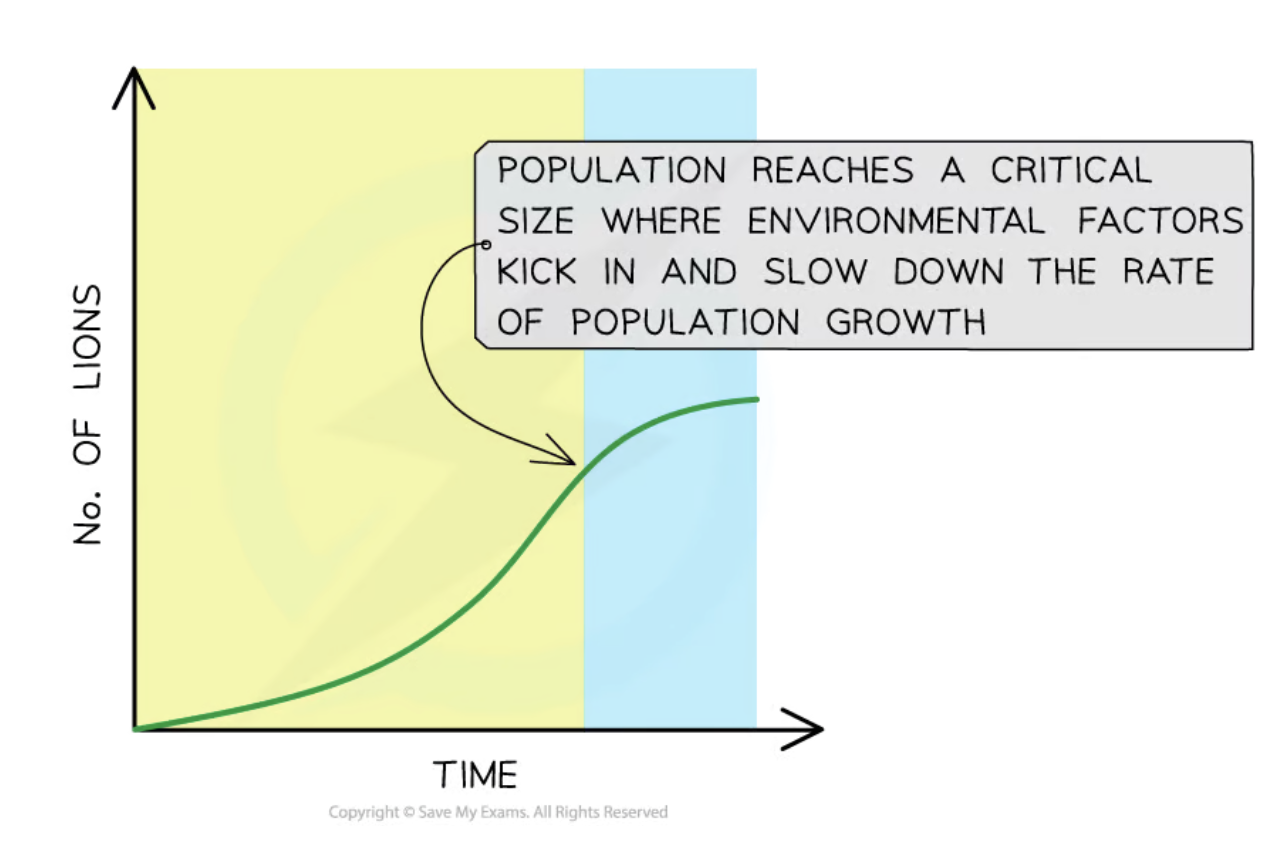
Living components of an environment, such as predation, competition, and disease, that affect population sizes.
Abiotic Factors
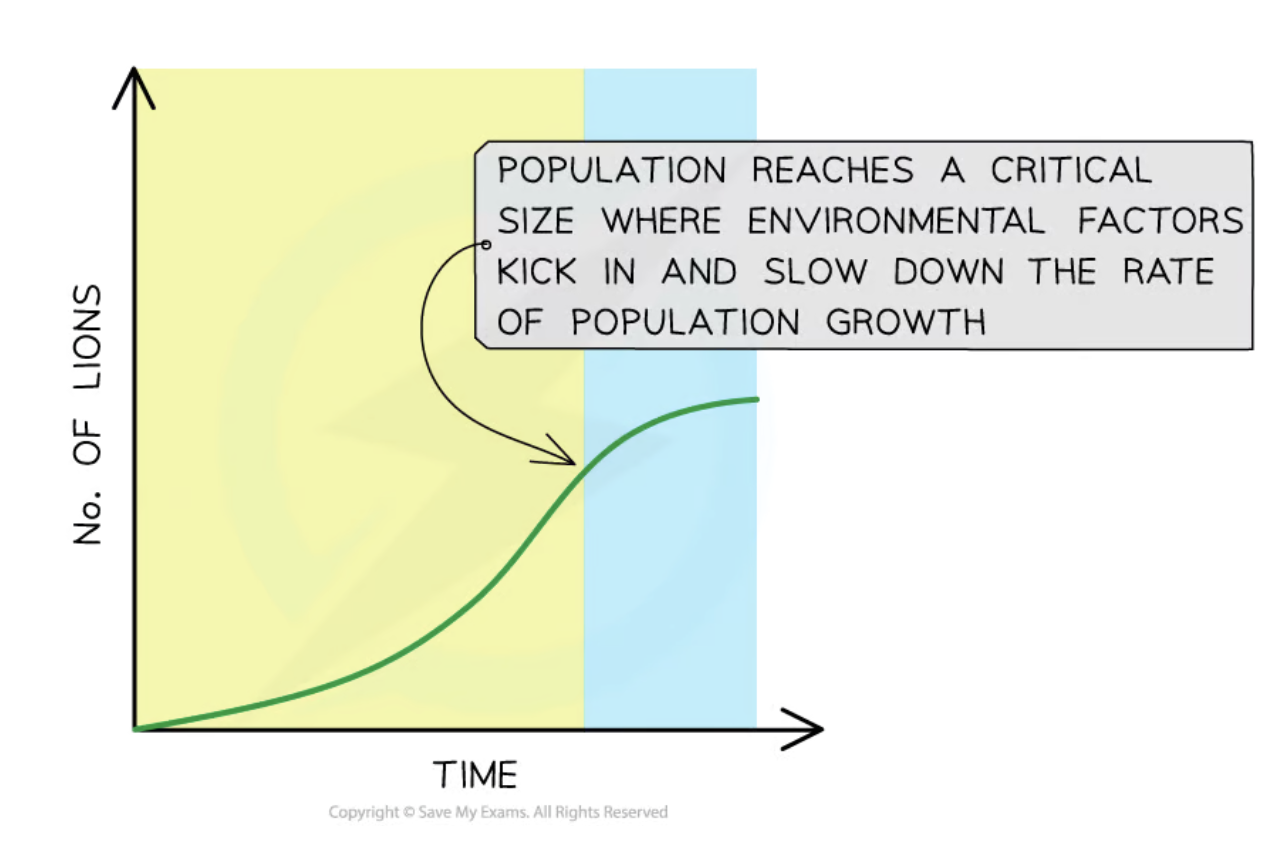
Non-living components of an environment, such as light availability, water supply, and soil pH, that influence survival and reproduction.
Selection Pressure
Environmental factors that affect the survival and reproduction of individuals, leading to changes in allele frequencies within a population.
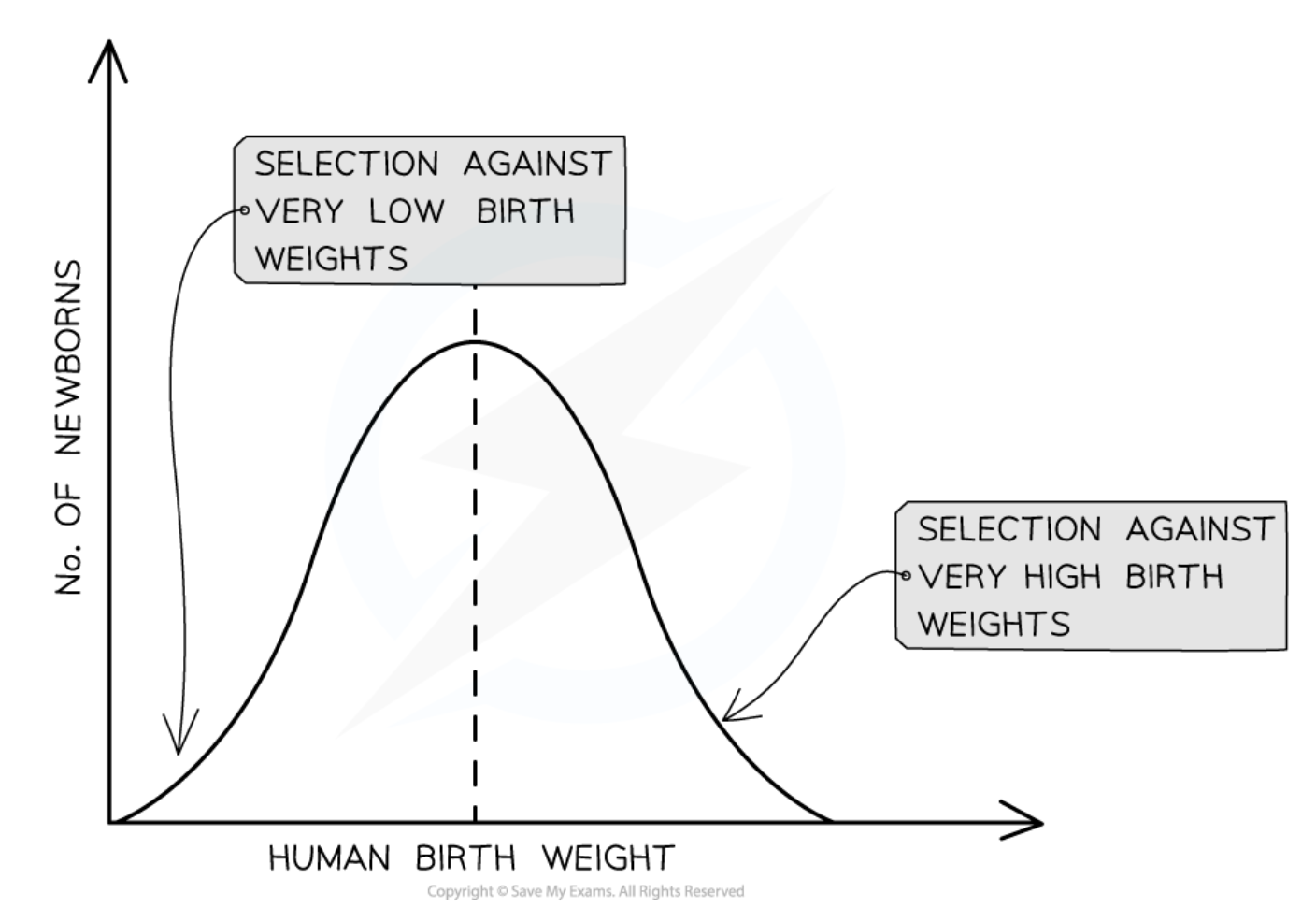
Stabilising Selection
Natural selection that preserves intermediate phenotypes and maintains allele frequencies in a population.
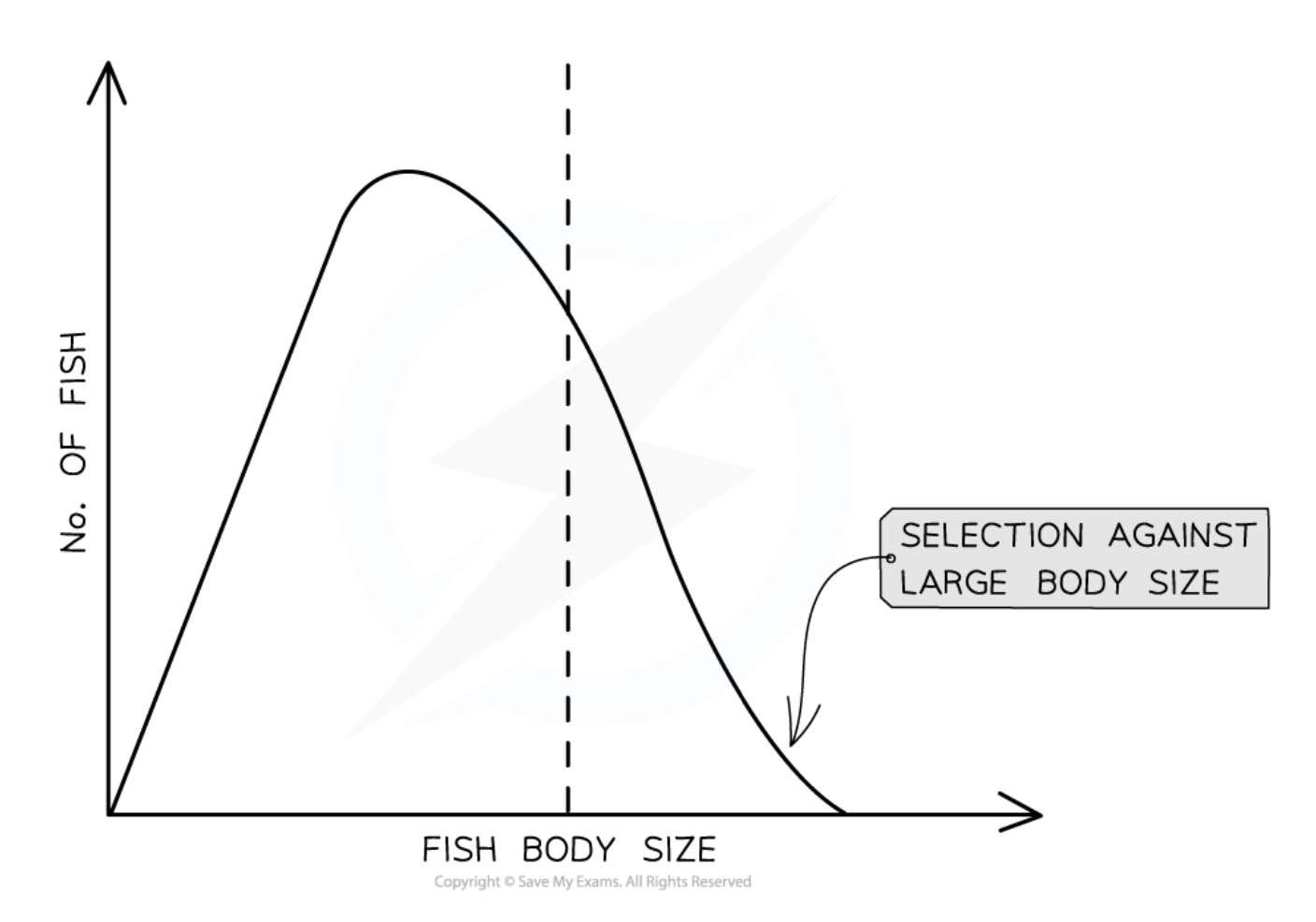
Directional Selection
Natural selection that favors one extreme phenotype, leading to a gradual change in allele frequencies over generations.
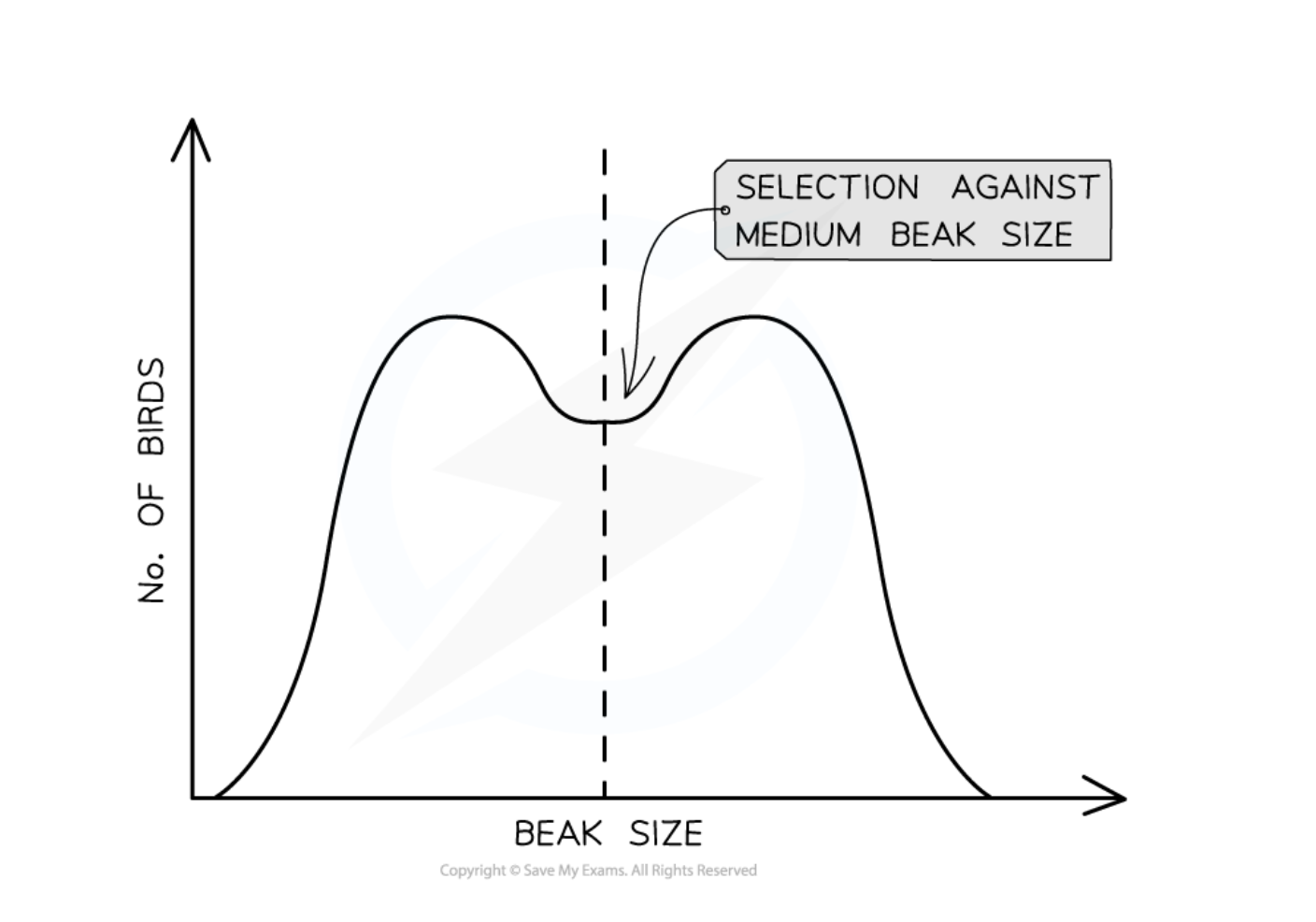
Disruptive Selection
Natural selection that favors extreme phenotypes at both ends of the spectrum while selecting against intermediate phenotypes.
Fitness
The ability of an organism to survive and pass on its alleles to its offspring, which is influenced by its adaptations to the environment.
Genetic Variation
Differences in DNA among individuals within a species, which can lead to different phenotypes and influence natural selection.