Skeletal Muscles
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Functions of Skeletal Muscles
force production for locomotion and breathing
force generation for postural support
heat production
considered and endocrine organ and assist in regulating a variety of body systems
Epimysium
plasma membrane that surrounds the entire muscle
Perimysium
Surrounds bundles of muscle fibers
Endomysium
surrounds individual muscle fiber
Sarcolemma
Muscle cell membrane
Breakdown of a Muscle
muscle - the whole structure
fascicle - bundle of muscle fibers
muscle fibers - single muscle cell (myofiber)
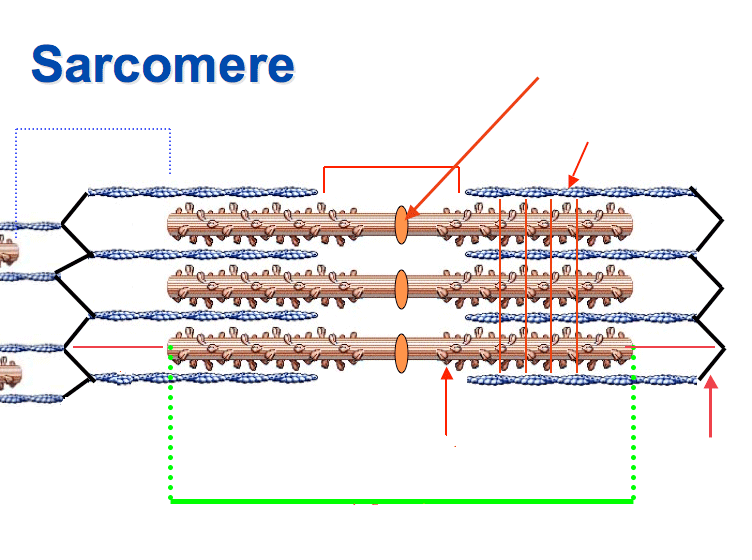
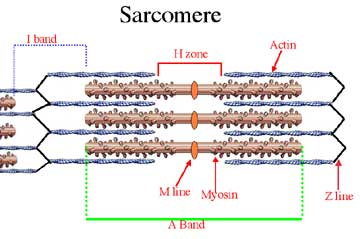
myofibril - long cylindrical structure within the muscle fiber, consisting of repeating units of sarcomeres
sarcomere - smallest functional unit of a muscle fiber
Neuromuscular Junction (NMJ)
junction between motor neuron and muscle fiber
Motor End Plate
the “pocket” formed around motor neuron by sarcolemma
Neuromuscular Cleft
the “short gap” between neuron and muscle fiber
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Storage sites for calcium
terminal cisternae: 2 enlarged portion of the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Transverse Tubules
extend from sarcolemma to sarcoplasmic reticulum
Satellite Cells
play role in muscle growth and repair
Muscle Shortening
occurs because of the movement of the actin filament over the myosin filament which forms cross bridges between actin and myosin filaments
Sarcomeres Shortening During Muscle Contraction
the heads of the myosin filaments latch on to myosin binding sites on the actin filament
as the heads cock to one side they pull the actin along contracting the muscle
E-C Coupling - Muscle Excitation
nerve signals arrive at the synaptic knob
Acetylcholine is released into synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on motor end plate, opening ion channels and allowing sodium to enter the muscle fiber
E-C Coupling - Contraction
depolarization of t-tubules causes release of Ca++ from sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ca++ binds to troponin, causing shift in tropomyosin to uncover myosin binding sites on actin
myosin binds to actin to form cross-bridge
Pi released from myosin and cross-bridge movement occurs
new ATP attaches to myosin, breaking the cross bridge; ATP is then broken down to ADP + Pi, which energizes myosin
E-C Coupling - Muscle Relaxation
motor neuron stimulation ends acetylcholine is no longer released and muscle fiber repolarizes
Ca++ is pumped back into SR and tropomyosin returns to original position covering myosin binding sites on actin, and muscle relaxation occurs
Biochemical Properties of Muscles
1) oxidative properties — how many capillaries, mitochondria, and how much myoglobin?
2) type of myosin ATPase activity — determines the speed of ATP utilization
3) abundance of contractile protein within the fiber — larger amounts of actin and myosin generate more force than fibers with low levels of contractile proteins
Contractile Properties of Muscles
1) maximal force production — force per unit of cross sectional area (specific tension)
2) speed of contraction — Vmax is determined by the rate of cross-bridge cycling, the key biochemical here is Myosin ATPase activity
3) maximal power output — power = force x shortening velocity
4) muscle fiber efficiency — more efficient fiber would require less energy to perform certain amount of work produced (amount of force production / ATP used)
Types of Skeletal Muscle
type I
slow twitch fibers
slow oxidative fibers
type IIa
intermediate fibers
fast-oxidative glycolytic fibers
type IIx
fast twitch fibers
fast-glycolytic fibers