geo term 2
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
what are earthquakes?
they are the sudden vibrations of the Earth’s surface due to the collision of the plates
the distribution of earthquakes are:
The Circum-Pacific belt –the Ring of Fire
The Mediterranean-North Indian Belt
The Mid-Atlantic belt
what are parts of an earthquake:
epicenter
plate movement
focus
seismic waves
whats the ‘epicenter’?
the point on the Earth’s surface which receives the strongest shock waves
whats the ‘focus’?
the point in the Earth’s crust where an earthquake originates
whats the ‘fault’?
its a break in the rocks that make up the Earth’s crust
whats the ‘seismic waves’?
the are vibrations that travel through the Earth carrying the energy released during earthquake
the primary impacts of earthquakes to people and the environment are:
building collapse
road cracks
furniture falls over
topped bridges
windows shattered
the secondary impacts of people and the environment are:
fires caused by the broken glass
diseases caused by dead bodies
contaminated water supplies
the long term effects are of earthquakes on people and the environment are:
loss of jobs for people
crops damaged
electricity lines were brought down
schools damaged
tress troppied
what can be the strategies to reduce the impacts of earthquakes?
install adequate warning system
construct earthquakes
educate the public
earthquake drills
emergency plans
river transport:
a river uses its energy to carry or transport eroded materials
what are the 4 river transport processes?
traction
saltation
suspension
solution
what are the 4 river erosion?
attrition
hydraulic action
solution
corrasion/abrasion
what is corrasion/abrasion?
the grinding at rock fragments carried by the river against the banks and bad at the channel
what is attrition?
its the knocking of the rock fragments in the water against each other
what is solution/corrosion?
its the process by which water in the river reacts chemically with soluble minerals in the rocks
when does river deposition occur?
deposition occurs when a river lacks enough energy to carry its lead and bumps the sediments
what are the necessary conditions for river deposition to deposit the sediments?
discharged from the river drop
floods subside
Inside a meander bends, and when rivers enter the sea, it slows the current
how do rivers reduce their speed?
rivers reduce their speed when they enter flat land
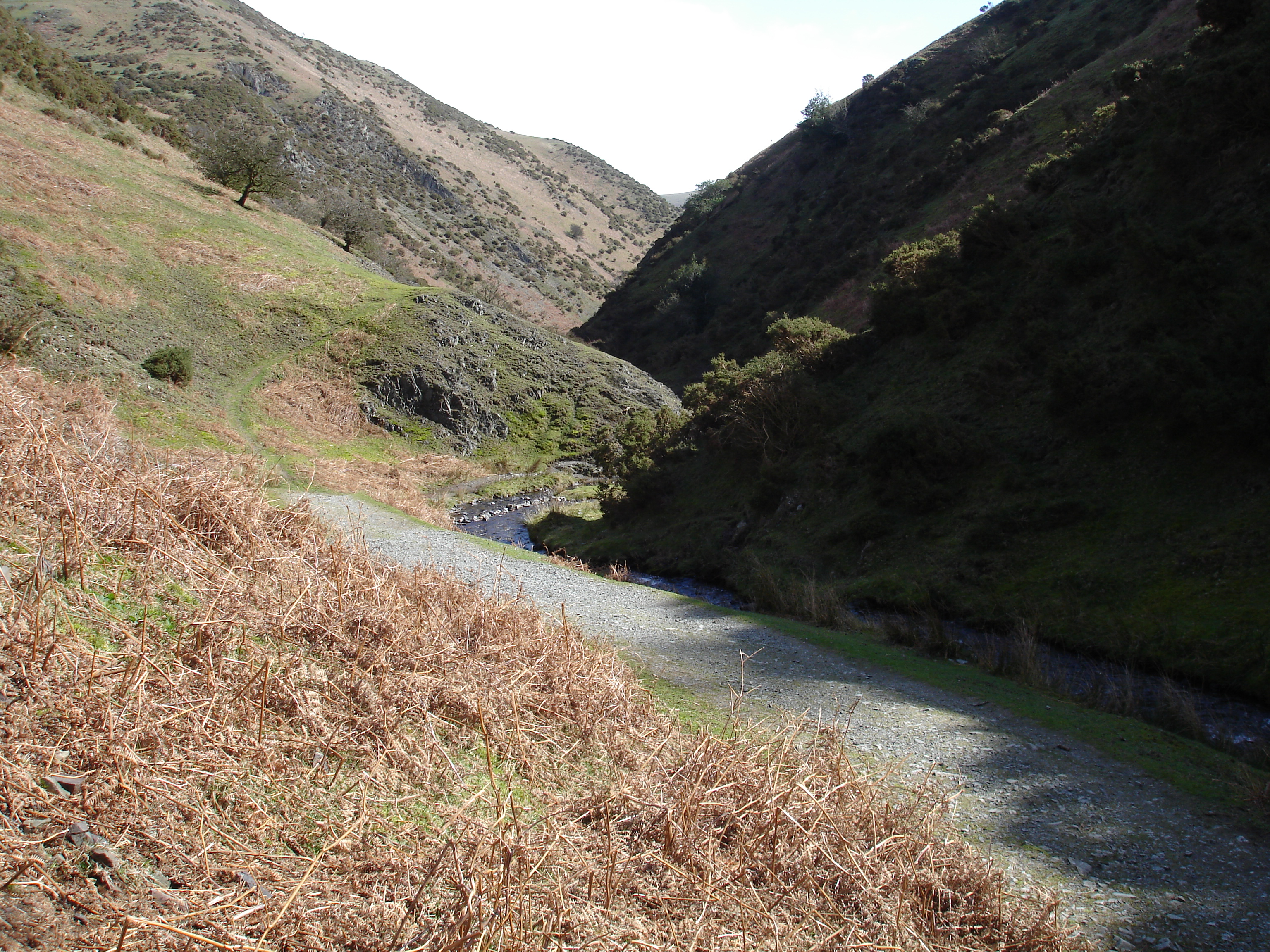

what river feature is this
v-shaped valley and interlocking spurs (upper course)
how does the v-shaped valley form?
the river forms a winding course as the river cuts downwards forming a v-shapes valley
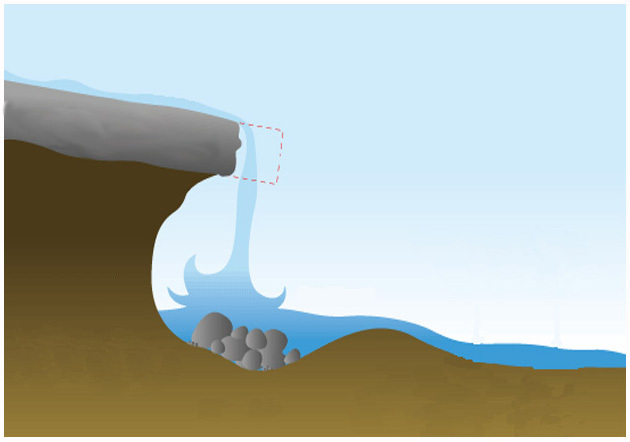
what river feature is this
waterfall (upper course)
how are waterfalls formed?
it forms when a river flows across rocks or different resistance

what river feature is this
plunge pool (upper course)
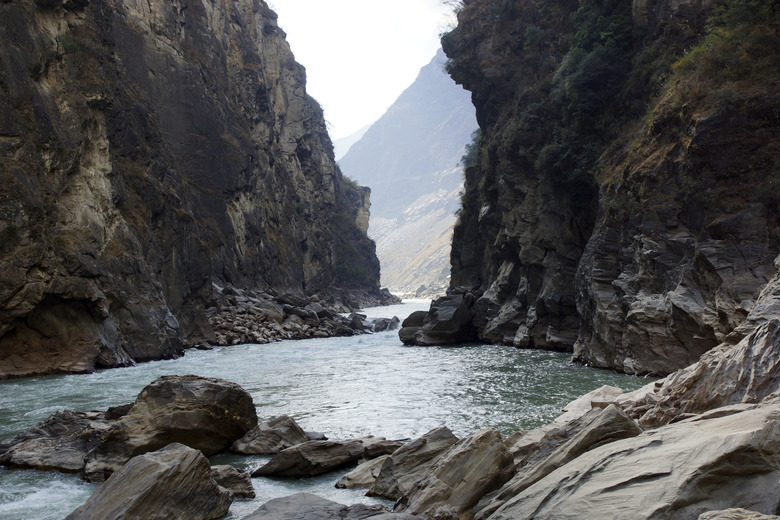

what river feature is this
gorge (upper course)
how do gorges form?
the river forms faster than the sides can be worn away.verticle erosion continuous to produce a narrow. steep-sided valley

what river feature is this?
meander (middle course)
how do meanders form?
theyre formed when the moving water in a river erodes the outer banks and widens the valley
what is a meander gets cut off from the main stream?
it forms and oxbow lake
what are some 3 characteristics of river in the middle course?
a greater discharge
erosion
deposition
what are some 3 characteristics of river in the lower course?
flat and wide floor plain
an even greater gradient
very wide and deep shallow
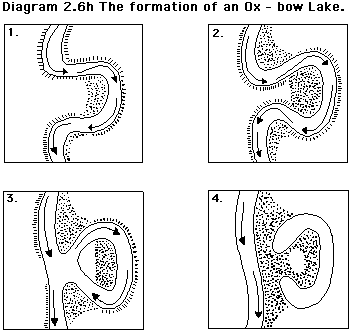
how does number 1 form?
with constant erosion of the concave banks and deposition on the convex banks, a meander gets separated by a narrow of land
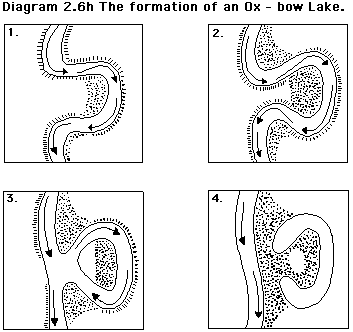
how does number 2 form?
when the neck becomes more narrow with continued erosion and deposition
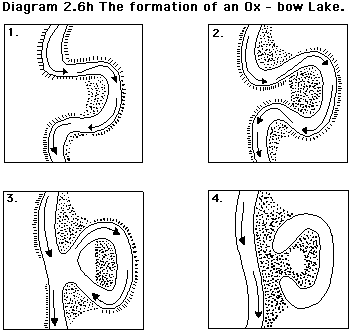
how does number 3 form?
when the river breaks through the narrow neck and flows straight through the channel
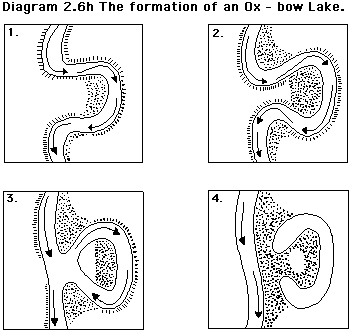
how does number 4 form?
the meander that is cut off forms an oxbow lake
what are floodplains?
its the flat piece of land in the lower section of the river
what are levees?
levees are raised edges along riverbanks.
how are levees formed?
they are formed when flooding happens repeatedly and heavier soil build up on the sides of the river
what is a ‘delta’
its a low-lying area of landformed at the mouth of a river where the stream loses velocity and drops part of its sediment load
how are deltas formed?
theyre formed when its deposited more quickly than the sea’s currents and tides remove it
what is a river system?
it refers to many inter-connected streams if different sizes and lengths
whats the drainage basin?
its the area drained by the river system
whats a watershed?
its a stretched of land that forms the boundary around a drainage basin
whats drainage density?
its the total length of a river per unit area in a drainage basin
formula: total length of river distribution
area of the surface of the drainage basin
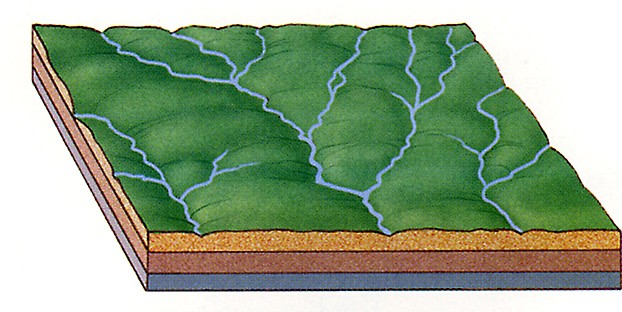
what pattern is this
dendritic pattern
how is a dendritic formed?
its formed by the river network of the main river and it often resembles a tree

what pattern is this?
trellis pattern
how are trellis patterns formed?
theyre formed by bricks in a wall
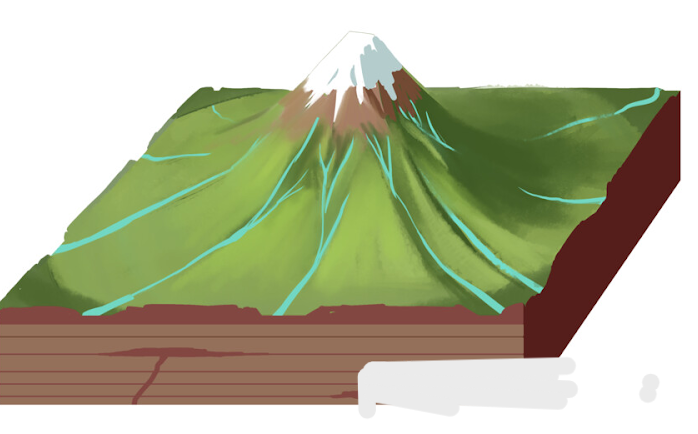
what pattern is this?
radial pattern
how are radial patterns formed?
radial patterns radiates from the top of a hill or volcanic cone
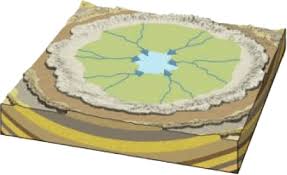
what pattern is this?
centripetal pattern