year 8 science
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Cells
Provide structure, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialised functions.
Cells → Respiration
Cells need fresh oxygen to stay alive. They give off carbon dioxide as they do their job; this process is called respiration.
Nutrient
A substance that provides nourishment essential for the maintenance of life and for growth
Digestive system
made from the digestive tract, helps the body break down and absorb food
Why do living things require food?
Food has nutrients, which are used for energy, growth, and repair, the basic life processes.
Word Equation for Aerobic Respiration
💡 Glucose + Oxygen ➡(Adenosine Triphosphate)➡Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy
Aerobic Respiration
Requires Oxygen (O2). Glucose reacts with oxygen to form ATP that can be used by the cell. Byproducts include carbon dioxide, water and energy.
Process of Digestion
The breakdown of food into simple nutrients, like proteins, fats and carbs, that the body can absorb.
Identify the structures in the digestive system
Oesophagus, small intestine, large intestine, and anus. assistive organs include pancreas, gallbladder, and liver.
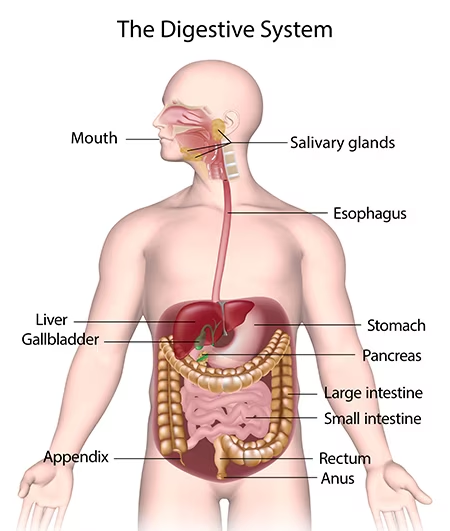
Function of Mouth
The entry point for food. Teeth help break down the food, and the tongue rolls it into a ball (bolus). Saliva helps with chemical digestion.
Function of Oesophagus
Tube that connects throat to stomach. Squeezed through by peristalsis (contraction and relaxation of muscles).
Function of Stomach
Churns and squeezes food into liquid (mechanical digestion). Gastric juices help with chemical digestion.
Function of Small intestine
Long and narrow, with a large surface area. Where the body absorbs most nutrients; peristalsis keeps the food moving.
Function of Large Intestine
Wide tube where water is absorbed. Good bacteria living here helps to break down fats and complex carbs.
Function of Anus
The end of the digestive tract, solid waste (stinky shit) expelled through anus.
Mechanical Digestion
Physically breaking down food into smaller pieces to aid in more efficient chemical digestion. Eg. churning, chewing and biting.
Chemical Digestion
Breaking down food into smaller molecules through the action of enzymes. Eg. saliva, stomach acid, and other digestive juices.
Absorption of nutrients in the intestines
Water and Nutrients move through tiny holes in the lining of the intestines, which go into the circulatory system to be passed around the body.
Nutrients are absorbed from the _____, lined with millions of finger-like projections called _____. Each _____ is connected to a mesh of _______.
Ileum, Villi, Villius, Capillaries
Energy can be measured in _____ and ________.
joules, Kilojoules
Excretory system
Removes excess and waste products from the body to maintain homeostasis.
Identify the structure of the Excretory system
Kidney, Ureter, Bladder, Urethra.
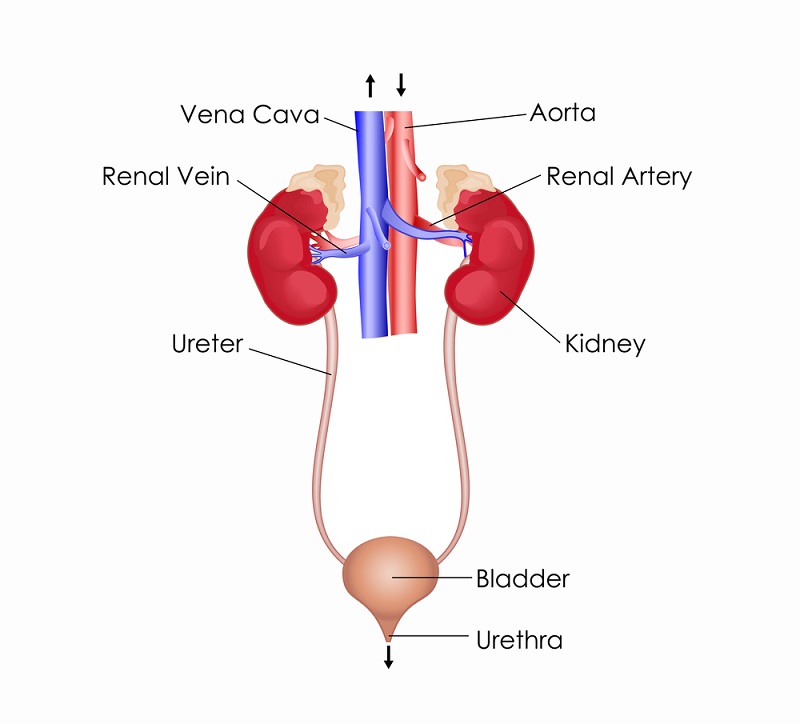
Function of Kidney
Filters impurities out of blood and removes excess water from body.
Ureter
Tube that carries Urine from kidney to bladder
Bladder
Holds urine until it builds up and is released
Urethra
Deposits liquid wastes.
What does the excretory system do with salt and water in the Blood?
The kidneys help to regulate salt and water levels in the blood and body by filtering it out and excreting it through the urethra.
Define energy
The ability to ‘do work’, meaning it causes some kind of change.
How can energy be detected
Movement, sound, heat or light are all proofs energy is present and being used.
Kinetic Energy
Energy possessed by the virtue of being in motion, so basically movement.
Potential Energy
Energy stored in an object.
Gravitational Potential
Energy an object possesses because of its possession in a gravitational field.
Elastic Potential
energy stored as a result of applying a force to deform an elastic object
Chemical Potential
the energy stored in the chemical bonds of a substance
Thermal Energy
the energy contained within a system that is responsible for its temperature
Renewable Energy
Energy from renewable resources such as the sun or wind that naturally replenish on a human timescale.
Energy Transfer
The conversion of one form of energy into another remaining in the same form. When a bat hits a ball, some of the bat's kinetic energy moves to the ball. However, the energy stays in the same form
Energy Transformation
The changing of forms of energy from one to another. Gasoline (chemical) is put into our cars, and with the help of electrical energy from a battery, provides mechanical (kinetic) energy
Electrical energy
Electrical energy is the power an atom's charged particles have to cause an action or move an object. The movement of electrons from one atom to another is what results in electrical energy.
Conductors
Electrons in conductors (metals) are free to move, with little to no resistance. The electrons are loosely bound and can freely move. Eg. metal, water, metal alloys.
Insulators
Electrons in insulators are tightly packed, meaning they are not free to move. Eg. many objects made from non metals, plastic and rubber.
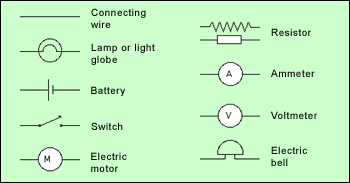
Electric Circuit diagram symbols
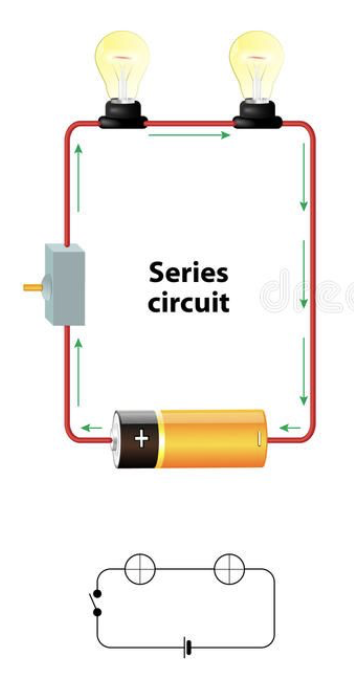
Series circuits
Connected “one after another”. There is a single path, and failure in one component breaks the whole thing. Different potential voltage exists across each component. Less commonly used.
Parallel circuits
Components are connected in a “head to head” manner. There are multiple paths, and if one component breaks, the others are still usable. The potential voltage is equal across each component. Commonly used.
Difference between heat and temperature
Heat is the transfer of energy between objects due to a temperature difference, while temperature measures the average kinetic energy of the particles in an object.
Heat Energy
Related to the kinetic energy of vibrating and colliding atoms in a substance
Conduction
Conduction is the transfer of heat or electricity through a material. Conduction works by some particles moving around, bumping into others to make them move around.
Conduction and insulation (heat)
Conductors of heat have atoms tightly packed, meaning they will all move around together, eg metal; insulators have spread out atoms, like glass and plastic.
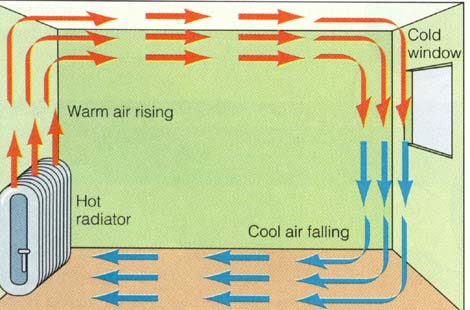
Convection
The spread of heat due to the movement of particles in liquids and gases; heat rises, cold sinks
Radiant heat can be:
________ = bounce off/sent back
________ = pass through/broadcast
________ = heat is taken in, and temperatures of the surface rise
Reflection, Transmitted, Absorbed
Convection Currents
When a liquid or gas is hot, the particles are less dense, and things less dense than what surrounds it rise. The flow of warm air up and cool air down creates these.
Voltage
the pressure from an electrical circuit’s power source that pushes the current through the loop. (more voltage = faster movement of electrons through current) measured in Volts.
Resistance
a measure of the opposition to current flow in an electrical circuit. Measured in Ohms.
Radiation
Radiation is the emission of energy in the form of waves or particles. Heat travelling by radiation Is called radiant heat
How is infrared radiation related to the Sun?
Infrared radiation, which has longer wavelengths than visible light, is one of the types of electromagnetic radiation the Sun emits. it is not visible to us, but we can feel it in the form of heat. that’s why we can see the heat of IR cameras and the sun heats the earth.
What is needed in electrical circuit
source, wire, component
Validity
Controlled variables, only 1 thing changes
Reliability
Multiple tests are conducted and results are consistent