CDI 8- INTRODUCTION TO CYBERCRIME AND ENVIRONMENTAL LAWS AND PROTECTION
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
Cybercrime
Any criminal action perpetrated primarily through the use of a computer
Cyber
refers to a computer or a computer network, the electronic medium in which online communication takes place
1834 first cyber attack in the world
a couple of robbers hack the French Telegraph System
Creeper virus
first computer virus
Ian Murphy (a.k.a. "Captain Zap")
first person convicted of a cybercrime
The Morris Worm
The first worm to infest the Internet; deployed in 1988 by Robert T. Morris
Melissa Virus
A virus infects Microsoft word records
Stuxnet Worm
the world's first software bomb
I Love You Virus
first computer virus in the Philippines created by Onel De Guzman
Basic Functions of a Computer
1. Input Function
2. Central Processing Unit
3. Data Storage
4. Output Function
Input Function
The process of entering any type of data and instructions into a computer system. Uses the input devices such as a keyboard, mouse, scanner, microphone, etc, in order to receive user signals to the computer.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Brain of the computer that performs instructions defined by software
Data storage
records and preserves digital information
Primary Storage of Computer Data
1. Random Access Memory (RAM)
2. Read Only Memory (ROM)
Random Access Memory (RAM)
This is volatile memory, meaning it loses its data when the power is turned off. It's used to store data that the computer is currently working on, such as open programs and documents.

Read Only Memory (ROM)
This is non-volatile memory, meaning it retains its data even when the power is turned off.

Secondary Storage of Computer Data
1. Hard Disk Drives (HDDs)
2. Solid-State Drives (SSDs)
3. USB Flash Drives/Pen Drives
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs)
These are magnetic storage devices that store data on spinning platters. HDDs are relatively slow but offer large storage capacities at a low cost.

Solid State Drive (SSDs)
These are non-volatile storage devices that use flash memory to store data. SSDs are much faster than HDDs but are more expensive

USB Flash Drive/Pen Drives
These are small, portable storage devices that use flash memory to store data. USB flash drives are fast, reliable, and inexpensive.

Output Function
means the results generated by the computer once the processing of CPU is completed, based on the instruction given by the user. Results are displayed on your computer screen.
Nota Bene
1. Computer use 2 binary numbers, 0 and 1
2. Hash values
3. The word "bit" is an abbreviation for binary digit
Binary numbers
Represents values using 0 and 1
Hash values
Can be thought of as fingerprint for files. The contents of a file are processed through a cryptographic algorithm, and a unique numerical value is produced that identifies the contents of the file.
Binary digits
The means by which computers represent data; also called bits. A binary digit is either a zero or a one.
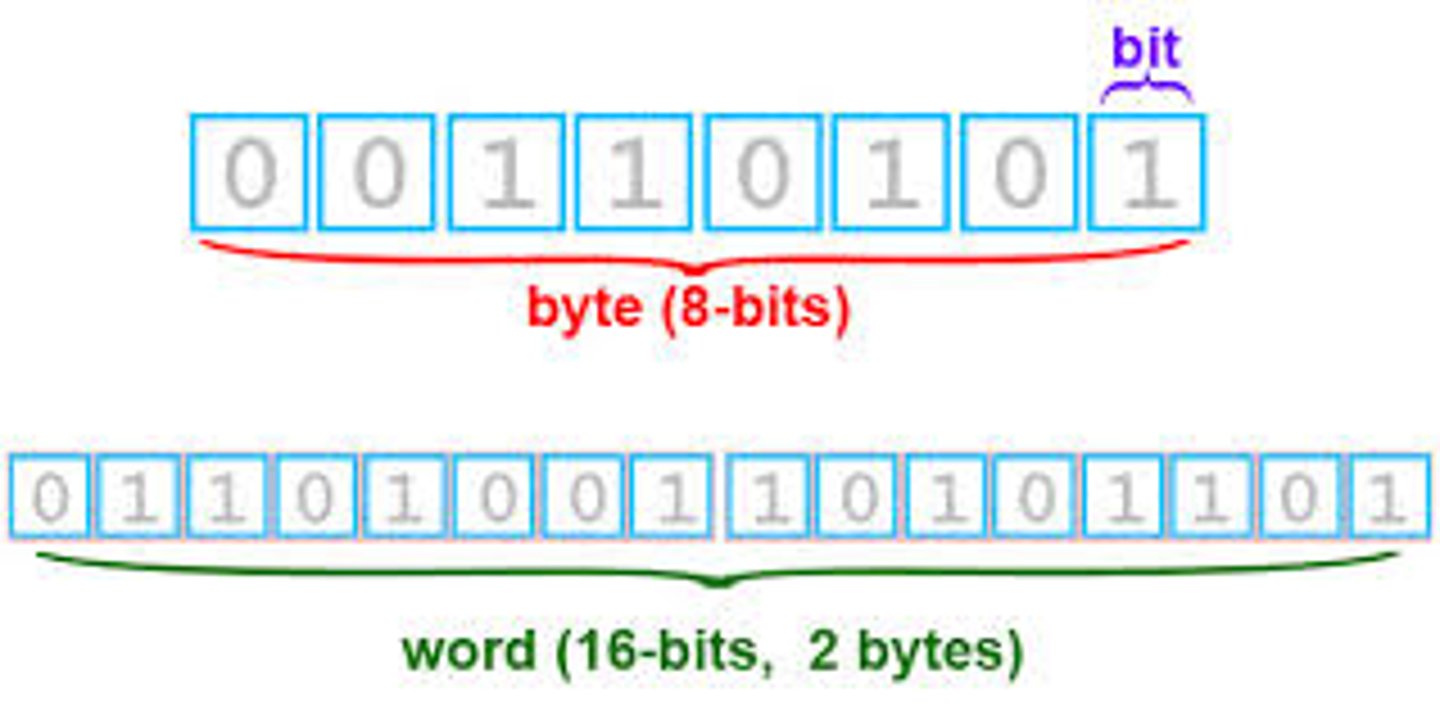
1 Byte
8 bits
1 Kilo Byte
1024 bytes
1 Mega Byte
1024 kilobytes
1 Gigabyte
1024 megabytes
1 Terrabyte
1024 gigabytes
1 Petabyte
1024 terabytes
Other Components of Computer System
1. Computer Case
2. Motherboard
3. Graphics card
4. Power supply unit
5. Monitor
6. Keyboard
7. Mouse
RA 10175
Cybercrime Prevention Act of 2012
Computer
refers to an electronic, magnetic, optical, electrochemical, or other data processing or communications device, or grouping of such devices, capable of performing logical, arithmetic, routing, or storage functions and which includes any storage facility or equipment or communications facility or equipment directly related to or operating in conjunction with such device. It covers any type of computer device including devices with data processing capabilities like mobile phones, smart phones, computer networks and other devices connected to the internet.
Computer data
refers to any representation of facts, information, or concepts in a form suitable for processing in a computer system including a program suitable to cause a computer system to perform a function and includes electronic documents and/or electronic data messages whether stored in local computer systems or online.
Critical infrastructure
refers to the computer systems, and/or networks, whether physical or virtual, and/or the computer programs, computer data and/or traffic data so vital to this country that the incapacity or destruction of or interference with such system and assets would have a debilitating impact on security, national or economic security, national public health and safety, or any combination of those matters.
Cybersecurity
refers to the collection of tools, policies, risk management approaches, actions, training, best practices, assurance and technologies that can be used to protect the cyber environment and organization and user's assets.
Interception
refers to listening to, recording, monitoring or surveillance of the content of communications, including procuring of the content of data, either directly, through access and use of a computer system or indirectly, through the use of electronic eavesdropping or tapping devices, at the same time that the communication is occurring.
Traffic data
refer only to the communication's origin, destination, route, time, date, size, duration, or type of underlying service, but not content, nor identities.
Cybercrime Offenses
(a) Offenses against the confidentiality, integrity and availability of computer data and systems:
1. Illegal Access
2. Illegal Interception
3. Data Interference
4. System Interference
5. Misuse of devices
6. Cyber-squatting
(b) Computer-related Offenses:
1. Computer-related Forgery
2. Computer-related Fraud
3. Computer-related Identity Theft
(c) Content-related Offenses:
1. Cybersex
2. Child Pornography
3. Unsolicited Commercial Communications
4. Libel
Other Cybercrime Offenses
1. Aiding or Abetting in the Commission of Cybercrime
2. Attempt in the Commission of Cybercrime
Illegal Access
The access to the whole or any part of a computer system without right.
Illegal Interception
The interception made by technical means without right of any non-public transmission of computer data to, from, or within a computer system including electromagnetic emissions from a computer system carrying such computer data
Data Interference
The intentional or reckless alteration, damaging, deletion or deterioration of computer data, electronic document, or electronic data message, without right, including the introduction or transmission of viruses.
System Interference
The intentional alteration or reckless hindering or interference with the functioning of a computer or computer network by inputting, transmitting, damaging, deleting, deteriorating, altering or suppressing computer data or program, electronic document, or electronic data message, without right or authority, including the introduction or transmission of viruses.
Misuse of Devices
The use, production, sale, procurement, importation, distribution, or otherwise making available, without right, a device, including a computer program, designed or adapted primarily for the purpose of committing any of the offenses under this Act; or a computer password, access code, or similar data by which the whole or any part of a computer system is capable of being accessed with intent that it be used for the purpose of committing any of the offenses under this Act.
Cyber-squatting
The acquisition of a domain name over the internet in bad faith to profit, mislead, destroy reputation, and deprive others from registering the same, if such a domain name is similar, identical, or confusingly similar to an existing trademark registered with the appropriate government agency.
Computer-related Forgery
The input, alteration, or deletion of any computer data without right resulting in inauthentic data with the intent that it be considered or acted upon for legal purposes as if it were authentic, regardless whether or not the data is directly readable and intelligible; or the act of knowingly using computer data which is the product of computer-related forgery as defined herein, for the purpose of perpetuating a fraudulent or dishonest design.
Computer-related Fraud
The unauthorized input, alteration, or deletion of computer data or program or interference in the functioning of a computer system, causing damage thereby with fraudulent intent.
Computer-related Identity Theft
The intentional acquisition, use, misuse, transfer, possession, alteration or deletion of identifying information belonging to another, whether natural or juridical, without right.
Cybersex
The willful engagement, maintenance, control, or operation, directly or indirectly, of any lascivious exhibition of sexual organs or sexual activity, with the aid of a computer system, for favor or consideration.
Child Pornography
The unlawful or prohibited acts defined and punishable by Republic Act No. 9775 or the Anti-Child Pornography Act of 2009, committed through a computer system.
Unsolicited Commercial Communications
The transmission of commercial electronic communication with the use of computer system which seek to advertise, sell, or offer for sale products and services are prohibited. Also known as spam.
Libel
The unlawful or prohibited acts of libel as defined in Article 355 of the Revised Penal Code, as amended, committed through a computer system.
Law Enforcement Authorities
The National Bureau of Investigation (NBI) and the Philippine National Police (PNP) shall be responsible for the efficient and effective law enforcement of the provisions of this Act. The NBI and the PNP shall organize a cybercrime unit or center manned by special investigators to exclusively handle cases involving violations of this Act.
Preservation of Computer Data
The integrity of traffic data and subscriber information relating to communication services provided by a service provider shall be preserved for a minimum period of six (6) months from the date of the transaction. Content data shall be similarly preserved for six (6) months from the date of receipt of the order from law enforcement authorities requiring its preservation.
Disclosure of Computer Data
Law enforcement authorities, upon securing a court warrant, shall issue an order requiring any person or service provider to disclose or submit subscriber's information, traffic data or relevant data in his/its possession or control within seventy-two (72) hours from receipt of the order in relation to a valid complaint officially docketed and assigned for investigation and the disclosure is necessary and relevant for the purpose of investigation.
Custody of Computer Data
All computer data, including content and traffic data, examined under a proper warrant shall, within forty-eight (48) hours after the expiration of the period fixed therein, be deposited with the court in a sealed package, and shall be accompanied by an affidavit of the law enforcement authority executing it stating the dates and times covered by the examination, and the law enforcement authority who may access the deposit, among other relevant data.
Common Types of Internet Frauds
1. Boiler Room
2. Romance Scam/Catphishing
3. Lottery Scam
4. Card skimming
5. Phishing
6. Email Spoofing
7. Nigerian Scam
8. Check over payment Scam
9. Inheritance Scam
10. Emergency Scam
Boiler Room
refers to an outbound call center selling questionable investments by telephone.
Card skimming
An illegal practice where a device is used to capture information from a debit card's magnetic stripe without the cardholder's knowledge.
Phishing (Brand Spoofing)
An attack that sends an email or displays a Web announcement that falsely claims to be from a legitimate enterprise in an attempt to trick the user into surrendering private information
Nigerian Scam
one of the most common cybercrimes. a nigerian sends an e-mail asking prospective victims to assist him or her to transfer millions of recently acquired dollars out of Nigeria in exchange for a substantial part of the money.
Incident Response, Preservation and Collection
1. When the computer is off- do not turn it on
2. If the computer is on- do not turn it off
3. Label the evidence "Fragile Cargo"
4. Keep away computer evidence from hostile environment
5. Observe Body Worn Camera
6. Do not use Aluminum powders
7. Photograph front and back of the monitor, CPU, etc.
8. Image the RAM
Stages of Digital Forensic Investigation
Stage 1: Identification
Stage 2: Acquisition
Stage 3: Examination/Analysis
Stage 4: Reporting
Stage 5: Court Presentation
Cybercrime Warrants
1. Warrant to Disclose Computer Data (WDCD)
2. Warrant to Intercept Computer Data (WICD)
3. Warrant to Search, Seize, and Examine Computer Data (WSSECD)
4. Warrant to Examine Computer Data (WECD)
Warrant to Disclose Computer Data (WDCD)
authorizes law enforcers to disclose or submit subscriber's information, traffic data, or relevant data in the possession or control of a person or service provider.
Duty of the authorized law enforcement officer
Within 48 hours from implementation or after the expiration of the effectivity of the cybercrime warrants, the law enforcement officer shall submit a return to the court and simultaneously turn over the custody
Warrant to Intercept Computer Data (WICD)
authorizes law enforcers to listen, record, monitor, or surveil the content of the communications through electronic eavesdropping or tapping devices, while the communication is occurring.
Warrant to Search, Seize and Examine Computer Data (WSSECD)
authorizes law enforcers to search a particular place for items to be seized and/or examined.
What must first be done by law enforcement authorities on site?
1. Make a forensic image (copy of the computer data)
2. Limit search specified in the warrant
3. Try not to seize computer items is search can be done on site
Warrant to Examine Computer Data (WECD)
authorizes law enforcers to search a computer device or computer seized during a lawful warrantless arrest.
Cybercrime Warrant effecitivity
10 days
Failure of law enforcement to make a return to the court
shall be subjected to contempt of court
Failure to comply with the orders of the law enforcement authorities
certain individual shall be punished for Obstruction of Justice
Natural Environment
encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally, meaning in this case not artificial
Ecosystem
is the basic functional unit of nature.
Basic Rights in Relation to Environmental Justice
1. Sovereignty Over Natural Resources and the Obligation Not to Cause Harm
2. Principle of Prevention
3. Precautionary Principle
4. Sustainable Development
5. Intergenerational Equity
6. Rights-based Approach
Sovereignty Over Natural Resources and the Obligation not to cause harm
gives the state the right to the utilization and benefits over the resources within its territory
Principle of Prevention
aims to stop environmental damage even before it occurs or when it is critical and potential damage may already be irreversible
Precautionary Principle
this principle advocates that the potential harm should be addressed even with minimal predictability at hand.
Sustainable Development
Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Intergenerational Equity
Each generation's responsibility to leave an inheritance of wealth no less than what they themselves have inherited.
Rights-based approach
the right of persons to environmental protection has the same level as basic human right
The Seven Environmental Principles
1. Everything is connected to everything else
2. All forms of life are important
3. Everything must go somewhere
4. Ours is a finite earth
5. Nature knows best
6. Nature is beautiful and we are stewards of God's creation
7. Everything changes
International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)
This is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use natural resources.. It is involved in data gathering and analysis, research, field projects, advocacy, and education.
Classification of Environmental Laws
1. Green laws- forest and other land-based natural resources, and wildlife
2. Blue laws- body of water
3. Brown laws- pollution control
Green Laws
1. PD 705- Revised Forestry Code
2. RA 9175- Chain saw act of 2002
3. RA 9147- Wildlife Resources Conservation and Protection Act
4. RA 7586- National Integrated Protected Areas System (NIPAS)
5. RA 7942- Mining Act of 1995
6. RA 7076- People's Small-scale Mining Act
PD 705
Revised Forestry Code of the Philippines
Alienable and disposable lands
refer to those lands of the public domain which have been the subject of the present system of classification and declared as not needed for forest purposes
Forest lands
include the public forest, the permanent forest or forest reserves, and forest reservations.
Grazing land
refers to that portion of the public domain which has been set aside, in view of the suitability of its topography and vegetation, for the raising of livestock.
Kaingin
is a portion of the forest land, whether occupied or not, which is subjected to shifting and/or permanent slash-and-burn cultivation having little or no provision to prevent soil erosion.

Dipterocarp forest
is a forest dominated by trees of the dipterocarp species, such as red lauan, tengile, tiaong, white lauan, almon, bagtikan and mayapis of the Philippine mahogany group, apitong and the yakals.
Illegal logging
This is the cutting, gathering, or collecting timber or other forest products without the necessary permit from the government. Transporting illegally cut timber and forest products are also covered here.
Unlawful occupation or destruction of forest and grazing lands
This is done when a person unlawfully or illegally enters, stays, and occupies forest or grazing lands, or destroys the same.
Can you cut a tree in your own private land?
Yes, there is no cutting permit required for ordinary species.
How many trees can you cut in a private property?
Up to 10 trees may be cut within a private property without a permit. DENR permit is required if more than 10 trees will be cut.
Civil Code, Article 680
If the branches of any tree should extend over a neighboring estate, tenement, garden or yard, the owner of the latter shall have the right to demand that they be cut off insofar as they may spread over his property, and, if it be the roots of a neighboring tree which should penetrate into the land of another, the latter may cut them off himself within his property.
Civil Code, Article 681
Fruits naturally falling upon adjacent land belong to the owner of said land.