Organisational Design and Management Structures
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
Organisational Design
The framework that provides a business with a structure to achieve its objectives.
Organisational Structure
The way in which the workforce within a firm is organised, including job roles and communication flows.
Organisational Charts
Visual representations of the organisational structure.
Authority
The power of an employee to instruct subordinates, make decisions and control the use of resources.
Centralised Authority
Authority maintained by a few at the centre of the organisation.
Decentralised Authority
Authority spread across the organisation.
Responsibility
When an employee has a duty to ensure a task is carried out to an acceptable standard.
Chain of Command
The way authority and power is passed down the levels of hierarchy.
Span of Control
The number of subordinates that a manager or supervisor is directly responsible for.
Wide Span of Control
When a manager has many subordinates.
Narrow Span of Control
When a manager has few subordinates.
Delegation
The passing of authority down the hierarchy.
Job Enrichment
A motivational strategy that provides workers with more responsibility and opportunities for personal growth.
Delayering
The process of removing levels of hierarchy within an organisation.

Empowerment
Giving employees the authority and responsibility to make decisions.
Control of Workforce
The process of managing and directing employees' actions and decisions.
Hierarchical Structure
An organisational structure where employees are grouped and assigned a supervisor.
Flat Structure
An organisational structure with few or no levels of middle management between staff and executives.
Tall Structure
An organisational structure with many levels of hierarchy.
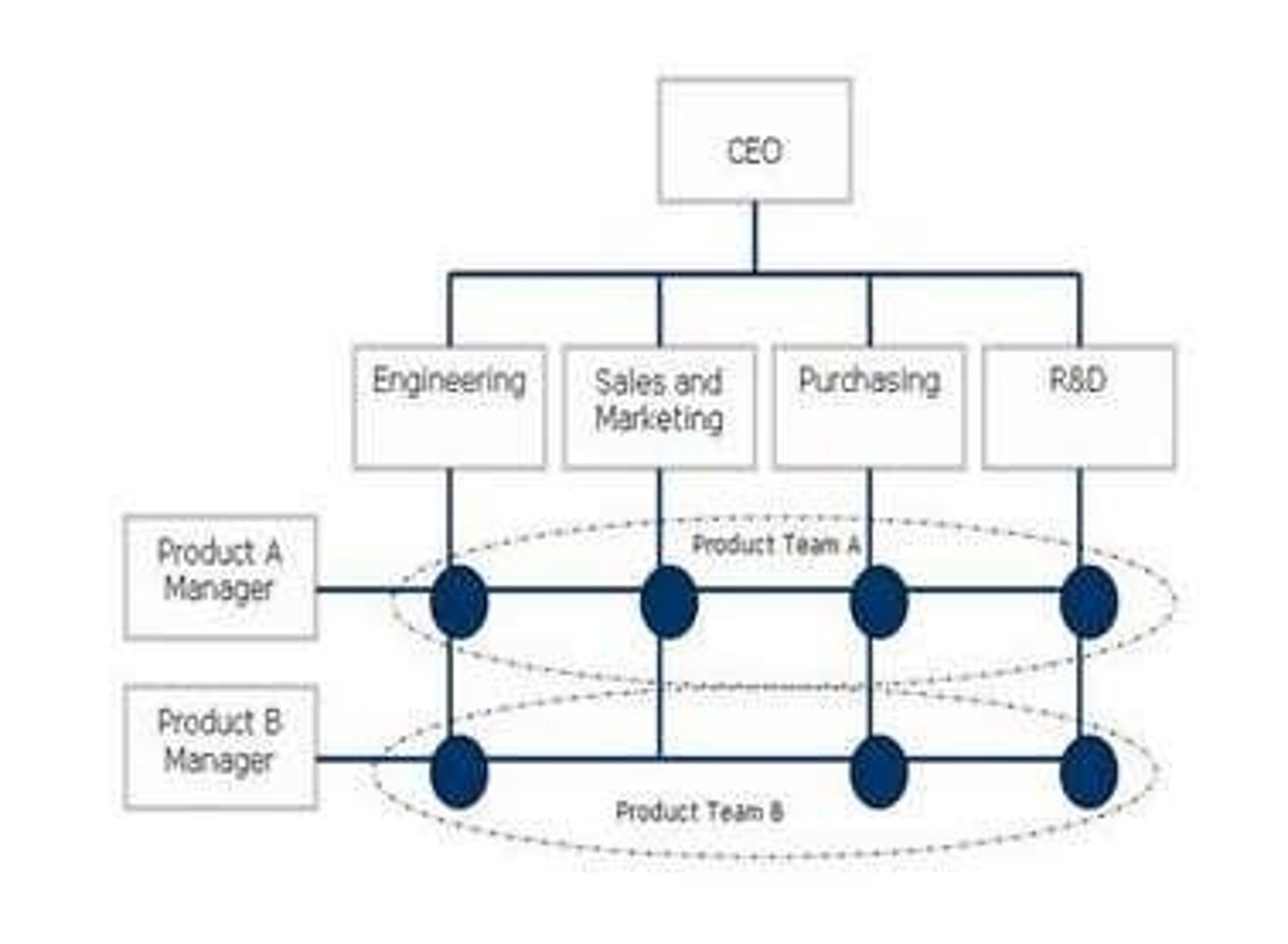
Matrix Structure
An organisational structure that groups employees by both function and product.
Communication Flow
The movement of information within an organisation.
Motivators
Factors that encourage employees to perform at their best.
Accountability
Being responsible for the outcomes of one's actions.
Hierarchy
The structure of the workforce within an organisation showing who is accountable to whom.
Tall Structure
Occurs where each superior is responsible for a few subordinates, allowing for closer supervision and communication between the two levels.
Wide and Flat Structure
Means that each superior is responsible for a large number of subordinates, requiring greater delegation but fewer levels allowing for quicker communication through the firm.
Centralisation
When the responsibility for decision making is maintained by a limited number of senior managers at the top of the hierarchy.
Decentralisation
When the responsibility for decision making is delegated to a number of middle managers throughout the hierarchy.
Empowerment
Involves delegating responsibility to employees, allowing them to use their abilities and to have a greater say in the decision-making process of the company.
Delayering
Involves reducing the levels in the hierarchy, and hence chain of command, by removing levels of management.
Matrix Structure
A structure where teams are put together from different functional areas to work on specific projects.
Span of Control
The number of subordinates that a manager is responsible for.
Chain of Command
The line of authority within an organization, outlining who reports to whom.
Bureaucratic
A system characterized by strict rules and regulations, often associated with centralisation.
Advantages of Tall Structure
Allows for closer supervision and more levels of management.
Disadvantages of Tall Structure
Can lead to slower decision making and communication.
Advantages of Flat Structure
Enables quicker decision making and communication due to fewer levels.
Disadvantages of Flat Structure
May lead to overburdening managers with too many subordinates.
Impact on Efficiency
Affected by the speed of decision making, flow of communication, and degree of supervision.
Employee Motivation
Can be influenced by opportunities for promotion, clarity of roles, and cross-functional relationships.
Legal Form
Refers to the legal structure of a business, which can influence centralisation and decentralisation.
Business Objectives
Goals that a business aims to achieve, influencing its structure and decision-making processes.
Response to Changes in Technology
How an organization adapts its structure and processes in reaction to technological advancements.
Degree of Confidence and Stability
Refers to the economic environment's influence on an organization's decision-making structure.
Organisational Design
The arrangement of a business to carry out its activities.
Authority
The power or right to give orders, make decisions, and enforce obedience.
Responsibility
The obligation to perform assigned tasks and duties.
Chain of Command
The paths that communication takes place along, indicating who reports to whom.
Span of Control
The number of subordinates directly answerable to a manager.
Delegation
The process of passing work and responsibilities to others, generally lower in the hierarchy.
Hierarchy
A system of organization in which people or groups are ranked one above the other according to status or authority.
Centralisation
The concentration of decision-making authority at the top levels of the organization.
Decentralisation
The distribution of decision-making governance closer to the point of service or action.
Empowerment
The process of enabling employees to take initiative and make decisions.
Delayering
The process of removing levels of hierarchy in an organization.
Hierarchical Structure
An organizational structure characterized by a multi-layered hierarchy of authority.
Flat Structure
An organizational structure with few or no levels of middle management between staff and executives.
Tall Structure
An organizational structure with many levels of hierarchy.
Matrix Structure
An organizational structure that creates a grid of reporting relationships, often across different departments.
Levels of Hierarchy
The different layers within an organization, each with its own level of responsibility.
Subordinate
A person who is immediately below another in the hierarchy.
Line Manager
The person who is immediately above the worker, to whom they answer.
Communication Routes
The paths through which information is shared within the organization.
Bureaucratic
A system characterized by excessive red tape and rigid procedures.
Responsibility Levels
The degree of accountability assigned to different layers of the hierarchy.
Promotion/Career Path
The progression of roles and responsibilities within an organization.
Control
The authority over decisions and actions within the organization.
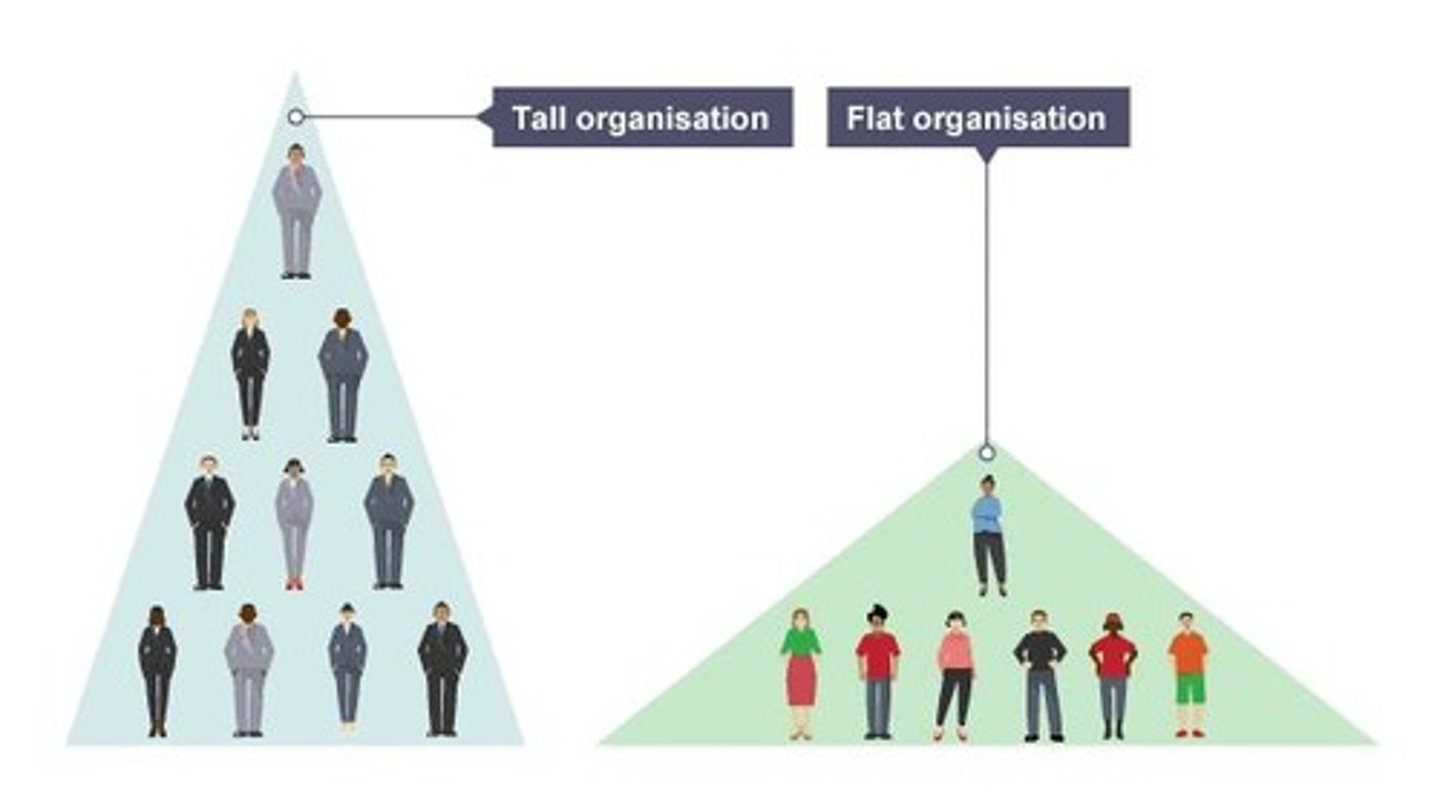
Tall organisation
Has a long chain of command, many levels of hierarchy and narrow spans of control leading to close control over employees.
Delayering
Removing levels of hierarchy, thus flattening the organisation structure.
Entrepreneurial structure
Exists when a few key workers at the core of the business (frequently the owner) make all major decisions.
Independent structure
Exists where the organisation does not have an obvious structure, common in professional practices like lawyers, doctors, and accountants.
Flat organisation
Has a short chain of command, few levels of hierarchy and wide spans of control, leading to employees operating with more independence.
Matrix structure
Often used when cross-functional teams are created to run a project, emphasizing coordination and support of specialist teams.
Project teams
Composed of team members from different disciplines, run by project managers who call upon specific skills in the organisation.
Increased motivation
Result of the delegation of authority in a flatter organisational structure.
Quick decision making
Decisions are made more quickly by those nearest the 'ground' in a flatter organisational structure.
Communication barriers
Flatter structures break down barriers to communication and ensure better project coordination.
Empowerment of workers
A benefit of a flatter organisational structure that helps spread ideas and innovation throughout the business.
Loss of central control
A disadvantage of matrix structures where central control of the workforce may be diminished.
Coordination problems
May occur in matrix structures as people are drawn from different departments, potentially slowing down decision making.
Divided loyalties
Can occur in matrix structures where employees may face conflicts between project and department managers.
Factors determining internal structure
Include views and philosophy of management, communication systems, industry, traditions of the business, and skills of the workforce.
Democratic leadership style
Encourages workers to take responsibility and impacts the internal structure of the business.
Autocratic leadership style
Prefers a recognisable hierarchical structure and impacts the internal structure of the business.
Layers of hierarchy
This is the management structure of an organisation and indicates who is responsible to whom.
Chains of command
These are the paths along which communication takes place and instructions or orders are passed down.
Levels of responsibility
Each layer of the hierarchy will have its own level of responsibility.
Span of control
The span of control tells us how many workers are directly responsible to a manager or supervisor.
Traditional hierarchical structure
The hierarchy is an example of the traditional pyramid-shaped hierarchy.
Narrow span of control
A narrower span of control operates in strictly hierarchical organisations where control is tight and centralised.
Wide span of control
When there has been a high level of delegation the span of control is often wide.
Retailing industry structure
Retailing encourages a hierarchical structure, with clear-cut responsibilities and chains of command.
Software development structure
In software development, the boundaries of responsibility are less clear and the chains of command tend to be much shorter.
Government-owned businesses
Businesses that have been owned by the government for many years often have a traditional structure.
New economy businesses
Businesses in the 'new economy' work towards achieving a less rigid organisational structure.
Highly skilled workforce
The more highly skilled the workforce, the more likely they are to need less supervision.
Flatter organisational structure
A flatter, more open structure where involvement in the decision-making process is encouraged at all levels.
Chief Constable
In the police force, the Chief Constable is at the top of the chain of command.
Constable
The Constable is at the bottom of the hierarchy in the police force.
Assistant Chief Constable
This position is one of the layers in the police force hierarchy, above the Constable.